¶ Introduction
Business systems were initially created to meet the general requirements of a variety of organizations spanning diverse business sectors. Over time, support for new business processes was continuously added, resulting in an extensive range of functionalities within the business system. As a result, during project implementation, many enterprises are now inundated with the sheer volume of available functionalities. The configuration of a business system encompasses a multitude of "usage controls," which can be toggled on or off to align its functionalities with the requirements of users. The initial step involves the installation of necessary modules and configuring them based on the project scope. Numerous configuration rules, amounting to thousands, exist to dictate the operation of the system.
¶ Microsoft D365 F&O setups
¶ Users
In order to gain access to the finance and operations applications, it is necessary to be added to the Users page (System administration > Users > Users). This category encompasses internal employees of the organization, as well as external customers and vendors, who may be added either manually or via importation. It is imperative that all users possess the requisite licenses to ensure compliant use.
- Go to System administration > Users > Users.
- On the Action Pane, select New.
- In the User ID field, enter a unique identifier for the user.
- In the User name field, enter the user's name.
- In the Provider field:
- For internal users, use the defaulted value. For example, your Azure AD tenant prefixed with https://sts.windows.net/.
- For non-Azure AD users, such as Service-2-Service accounts, enter a basic text value. For example, NA. This value will help avoid incorrect authentication calls that might result in errors if a valid identity provider value is used.
- For external or guest users, add their Azure AD tenant name after https://sts.windows.net/.
- In the Email field, enter the user's full Email/User Principle Name.
- In the Company field, select the default startup company for the user.
- Select Save.
¶ Workers
The Worker list is a fundamental component of HRM master data within Microsoft Dynamics 365 Human Resources and serves as a cornerstone for all personnel-related actions. Organizations can capture a wealth of information pertaining to their workers. It is imperative that an organization conducts a comprehensive analysis of its requirements prior to initiating the creation of HR master data setups to avoid managing extraneous data that does not offer direct benefits to the company.
Accurate records of the various worker categories are crucial to the effective functioning of both the human resources and payroll systems. The data entered can be leveraged to monitor workers, track personal information, generate correspondences, and produce reports. It is essential to maintain up-to-date information that reflects the current activities of workers, companies, legal entities, and organizations. There are two primary worker classifications: Employees and Contractors.
It is imperative for workers to be linked to users via the Maintain user relation versions from the users detail form.
¶ Legal entities
A legal entity is an organization that is identified through registration with a legal authority. Legal entities can enter into contracts and are required to prepare statements that report on their performance. The following procedure explains how to create a legal entity. The demo data company used to create this procedure is USMF.
- Go to Navigation pane > Modules > Organization administration > Organizations > Legal entities.
- Click New.
- In the Name field, type a value.
- In the Company field, type a value.
- In the Country/region field, enter or select a value.
- Click OK. In the General section, provide the following general information about the legal entity: Enter a search name, if a search name is required. A search name is an alternate name that can be used to search for this legal entity. Select whether this legal entity is being used as a consolidation company. Select whether this legal entity is being used as an elimination company.
¶ Numbering sequences
Number sequences are used to generate readable, unique identifiers for master data records and transaction records that require identifiers. A master data record or transaction record that requires an identifier is referred to as a reference.
Before you can create new records for a reference, you must set up a number sequence and associate it with the reference. We recommend that you use the pages in Organization administration to set up number sequences. If module-specific settings are required, you can use the parameters page in a module to specify number sequences for the references in that module. For example, in Accounts receivable and Accounts payable, you can set up number sequence groups to allocate specific number sequences to specific customers or vendors.
When you set up a number sequence, you must specify a scope, which defines which organization uses the number sequence. The scope can be Shared, Company, Legal entity, or Operating unit. Legal entity and Company scopes can be combined with Fiscal calendar period to create even more specific number sequences.
Number sequence formats consist of segments. Number sequences with a scope other than Shared can contain segments that correspond to the scope. For example, a number sequence with a scope of Legal entity can contain a legal entity segment. By including a scope segment in the number sequence format, you can identify the scope of a particular record by looking at its number.
In addition to segments that correspond to scopes, number sequence formats can contain Constant and Alphanumeric segments. A Constant segment contains a set of letters, numbers, or symbols that does not change. An Alphanumeric segment contains a set of letters or numbers that increment every time that a number is used. Use a number sign (#) to represent incrementing numbers and an ampersand (&) to represent incrementing letters. For example, the format #####_2017 creates the sequence 00001_2017, 00002_2017, and so on.
¶ Number sequences for completeness:
Using the Generate button; users are guided and D365 will propose/create numbering sequence records for all transactions and some master data objects.
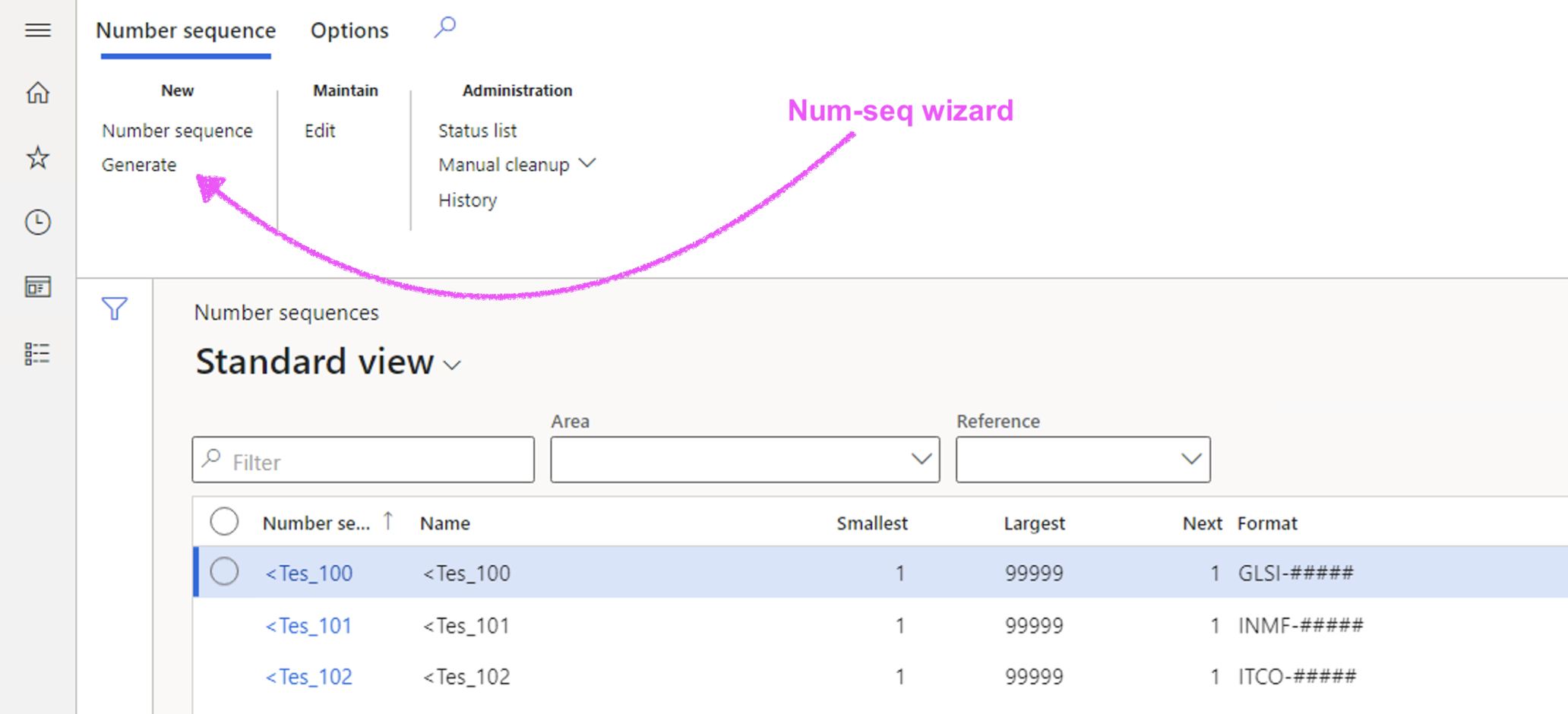
¶ Number sequences for relevance:
Then using the Numbering wizard button; D365 will change the numbering sequence records format to the relevant area (reference) being used. For example; Inspection journals; the wizard will change the generic scope text change to "Ins".
¶ Sites (inventory storage)
Inventory dimensions are assigned to products (items). Before you can assign inventory dimensions, you must set up inventory dimension groups.
The inventory dimensions can be assigned to inventory dimension groups:
|
Product dimension group:
|
Storage dimension group:
|
Tracking dimension group:
|
¶ Departments
Departments are operating units that represent a functional area of a business, such as sales or accounting. Many companies have organizational hierarchies that display the various departments within a business. This procedure walks through the process of creating departments, and adding those departments to an organizations departmental hierarchy.
¶ Items (Products)
In Microsoft Dynamics 365 items and products are referred to interchangeably. A product name is always associated with an item ID. The main concepts that are associated with items are product, product master and product variant.
- Product – A fixed product definition that does not include any variations
- Product master – A product definition that forms the basis of product variants
- Product variant – Products that are based on a product master. Product variants are made distinct through the product dimension setup and through configurations
Products are used throughout Microsoft Dynamics 365. This includes procurement, sales, and projects. You can use the On-hand inventory page to view which products are on hand.
¶ Resources
“Operations” resources are the machines, tools, workers, facilities, physical areas or vendors that perform the activities of a project or a production process. They can be of different types and can have different capabilities.
- Vendor – An external resource that performs project activities or production operations. An example is a subcontractor. By linking vendor resources to a vendor account, you can generate purchases for subcontractors, based on the bill of materials (BOM) lines or production lines.
- Human resources – A project or production worker that perform an activity, either alone or as an operator of a tool or a machine. If you're using the Human resources functionality, you can link human resources to a worker. The scheduling engine can then allocate the resources, based on the competencies that are defined for the corresponding worker.
- Machine – A machine or other production equipment that is required in production.
- Tool – An instrument or device that is typically used together with another resource to perform an activity in a project or in production.
- Location – A physical location of a specific size that is required in order to perform an activity. An example is an assembly area.
- Facility – A building or fixed structure that is required in order to perform an activity.
¶ Setup Batch groups
Batch groups are used to group and run selected tasks on a specific batch server. When the batch process is started, the jobs and reports in the batch group are run according to the start date, start time, and recurrence parameters that are specified on the individual jobs.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>System Administration>Setup>Batch group
- The following batch groups must be created:
- Job that will create payment journals
- Job that will create interest journals
- Job that will create allocation journals (term allocation still needs to be added)
- Job that will create loan capital journals for bulk-imported loans
¶ Treasury (TMS) setups
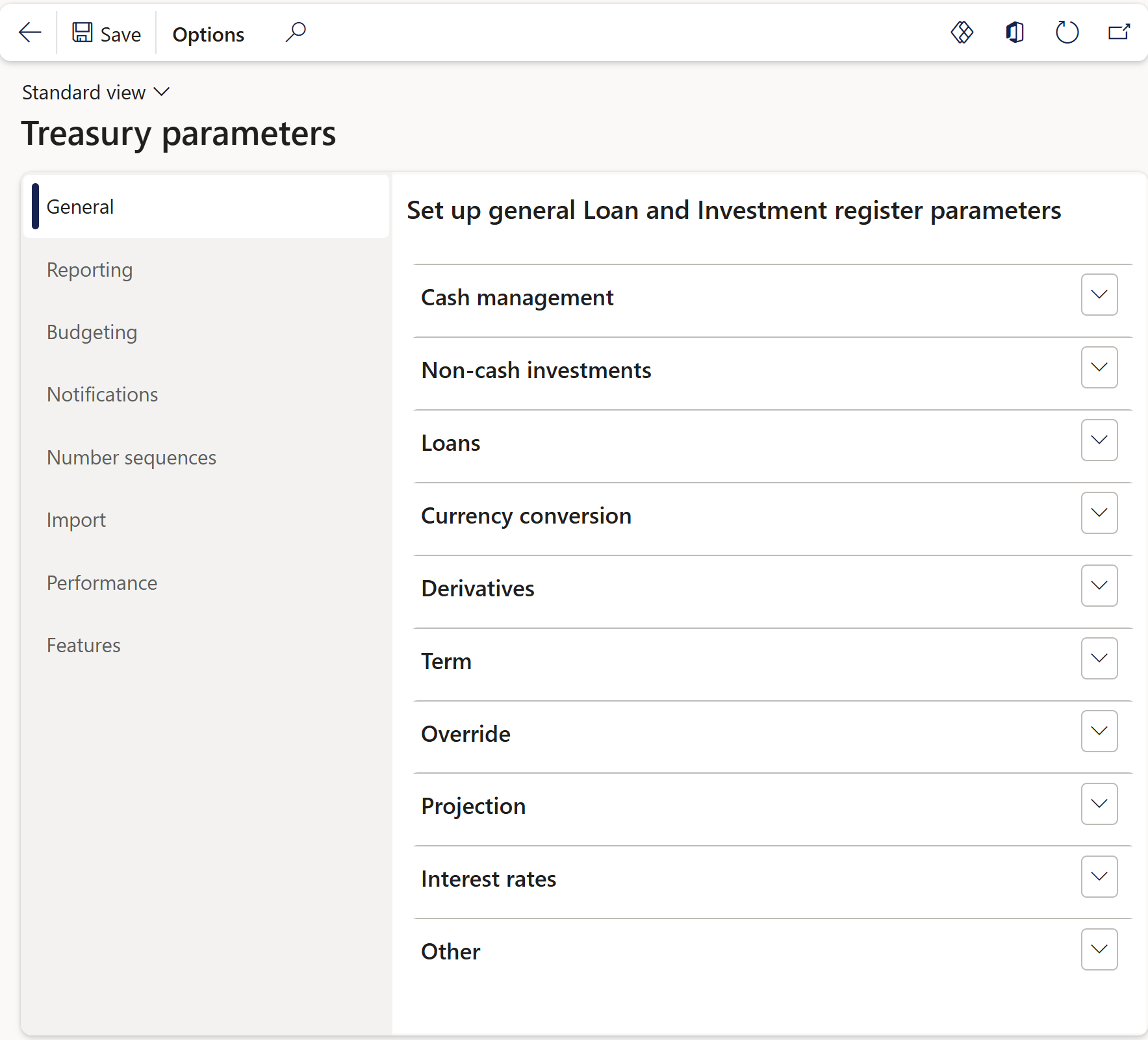
¶ Treasury Parameters
Treasury parameters is the place where General loan register parameters are set up, as well as Reporting, Alerts & notifications, and Number sequences for Treasury.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury parameters
- The following tabs are available:
- General
- Reporting
- Budgeting
- Insurance contracts
- Notifications
- Number sequences
- Import
- Performance
- Features
¶ Treasury Number sequences
Number sequences forms part of the basic setups. Basic number sequences are done under the Organization administration module.
Specific setup for TMS:
- To set up number sequences for TMS, go to Treasury > Setup > Treasury Parameters
- Click on the Generate number sequence button
A blue line with a confirmation message that the Number sequence has been successfully generated, will appear
¶ Set up Number seqeunces for Loans
The number sequence will be a unique identifier for the loan. When this setup is done, the system will perform automatic numbering of all loans going forward.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury parameters
- This is where the setup is done for the numbering of all your loans.
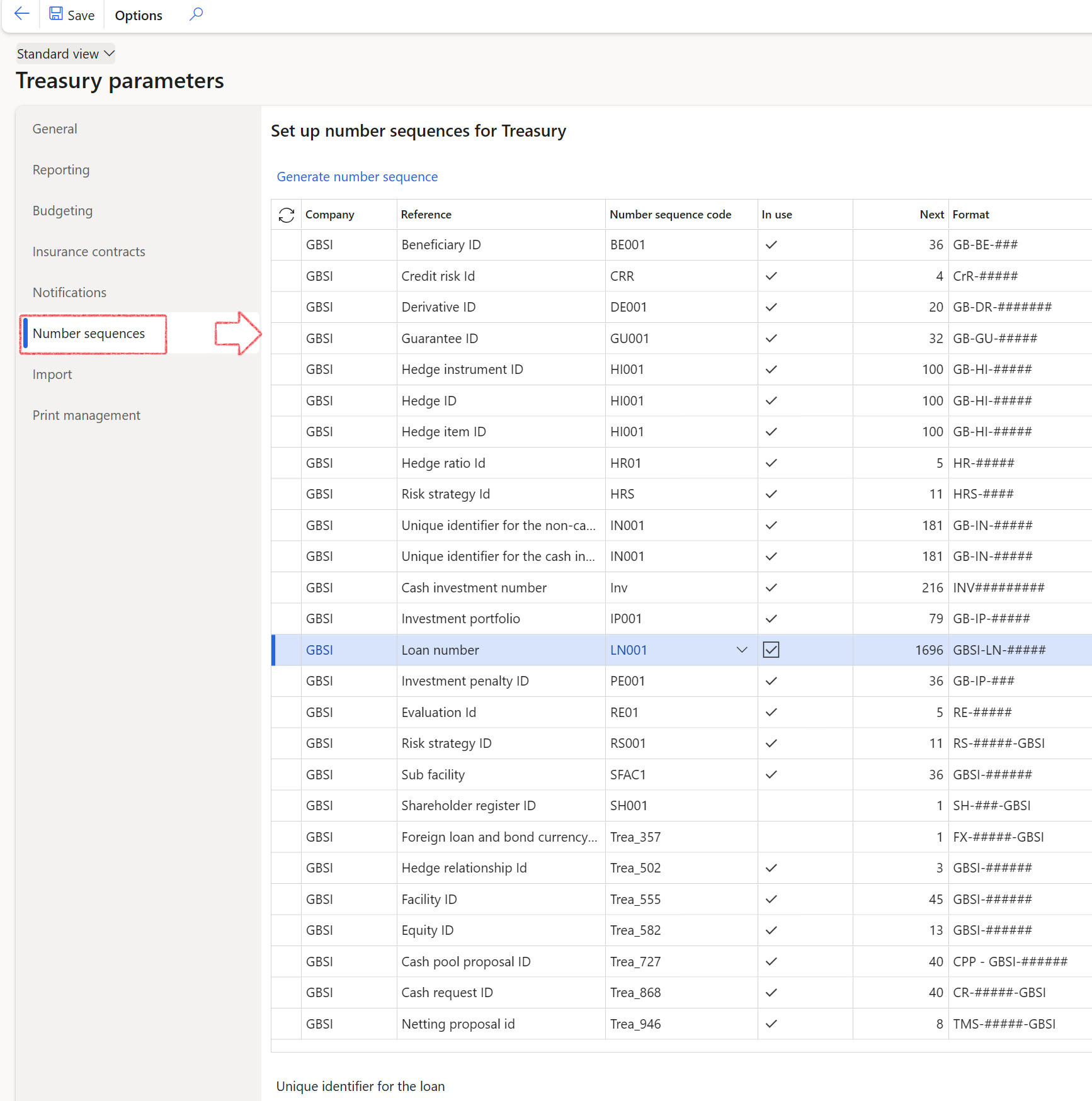
- Click on a specific Number sequence code to edit the Number sequences
- A new page will open, with FastTabs that should be configured. See screenshots below:
- The identification FastTab contains the Number sequence code and Name
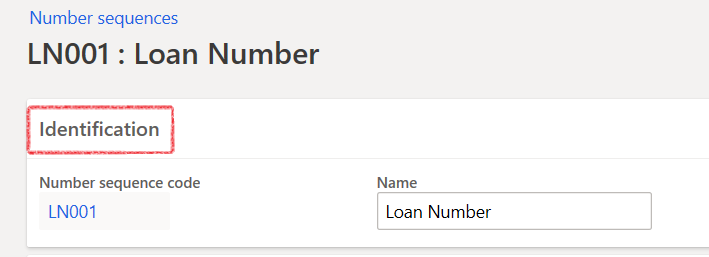
- Select the company under the Scope parameters FastTab
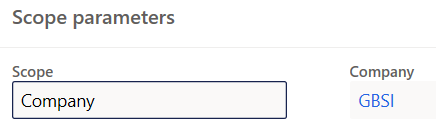
- Add segments for the numbering format: company, a constant, and an alphanumeric number length.
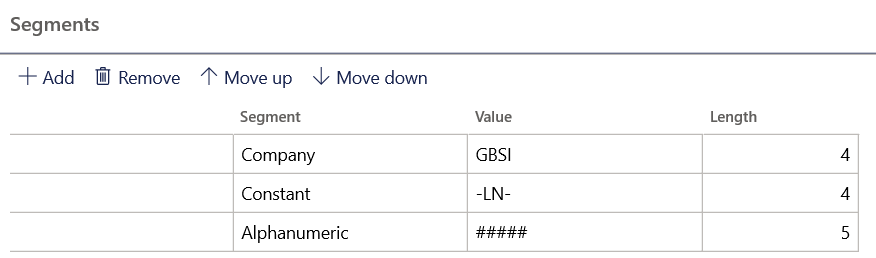
- Complete the area and reference for the References FastTab

- The General FastTab can be set up as follows:
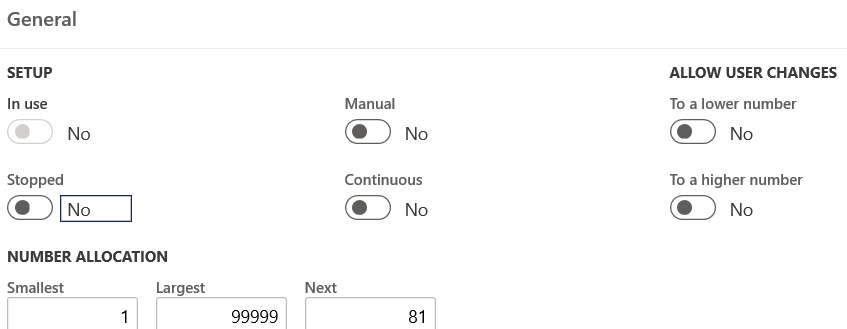
The Generate number sequence button will take the generic numbering format created by D365 (Organization admin) and apply numbering rules in line with the attached reference. For example: for Loan number Format, the Format will change from USMF-###### to LN-####-USMF
¶
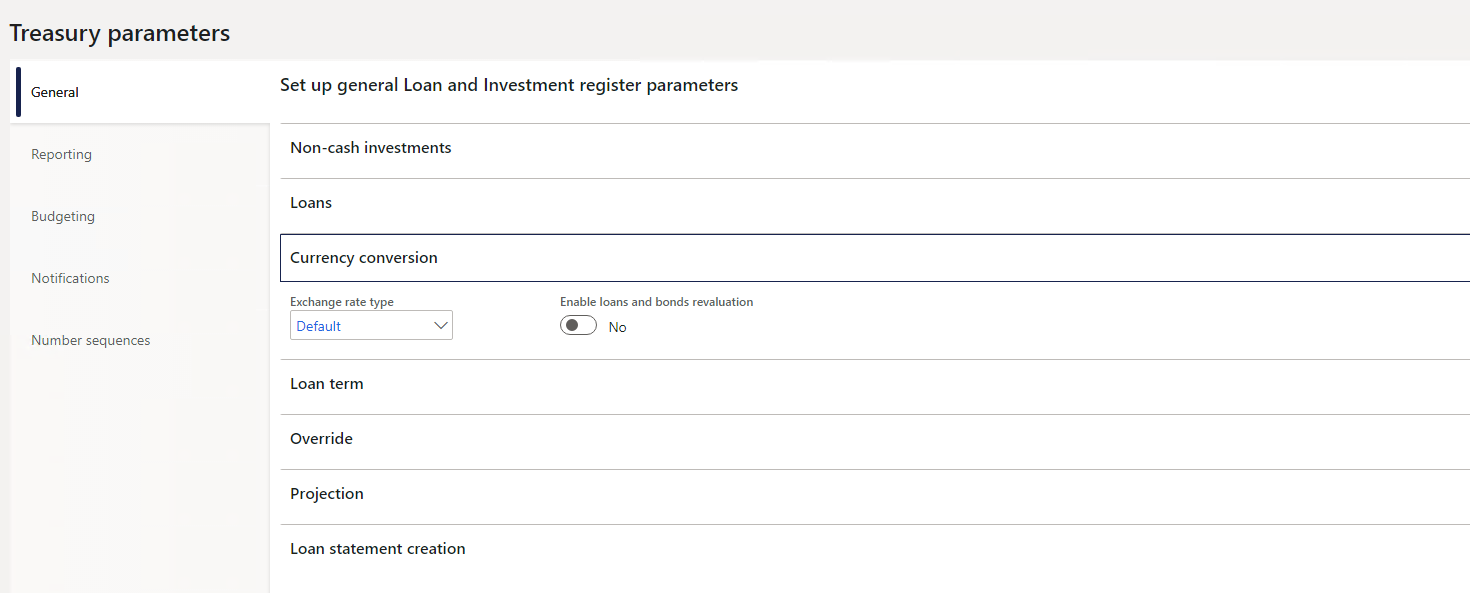
Set up Currency conversion
Select the default Exchange rate type for Currency conversion.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury parameters
- On the General tab, expand the Currency conversion FastTab
- Select the default Exchange rate type
¶ Set up Reporting
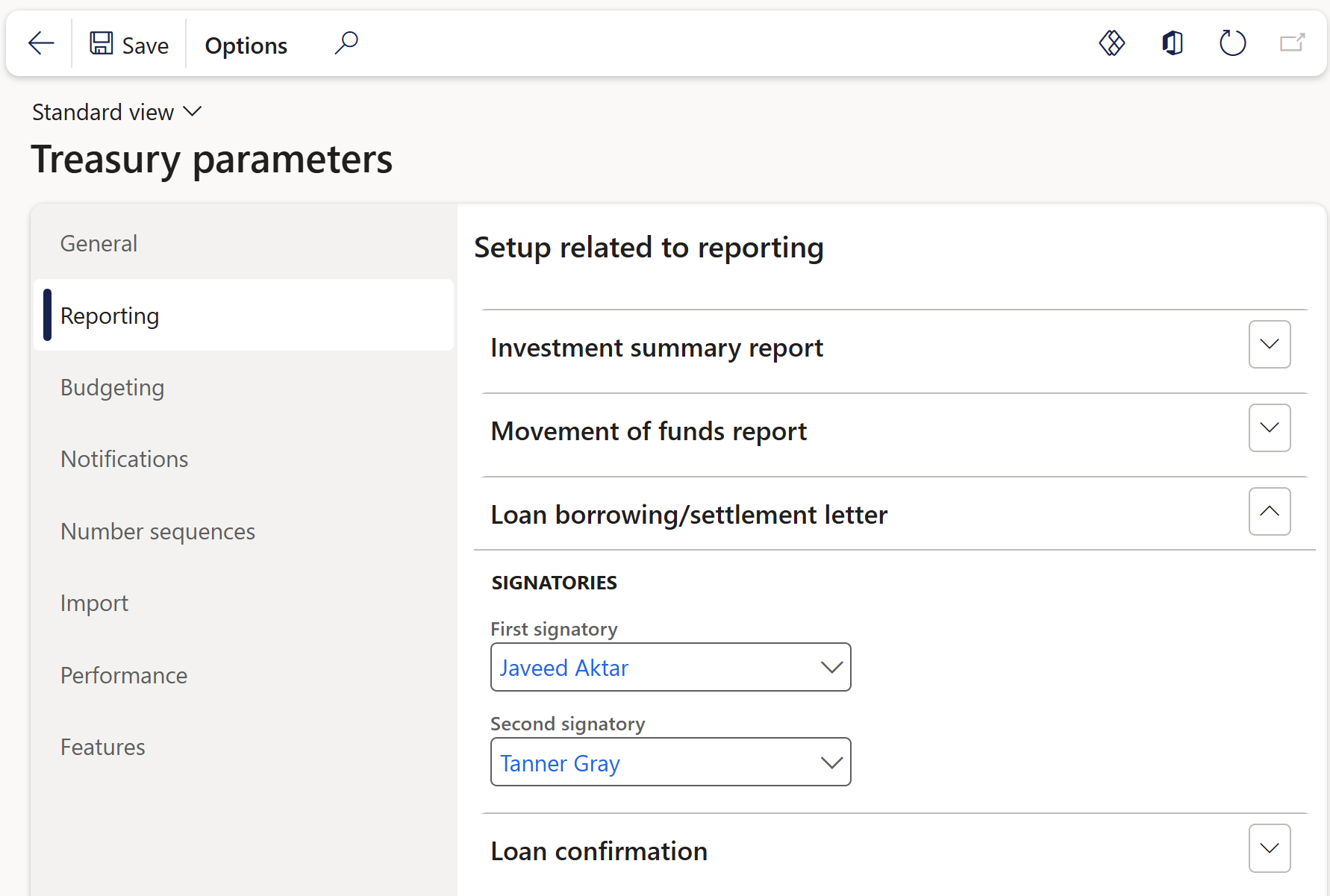
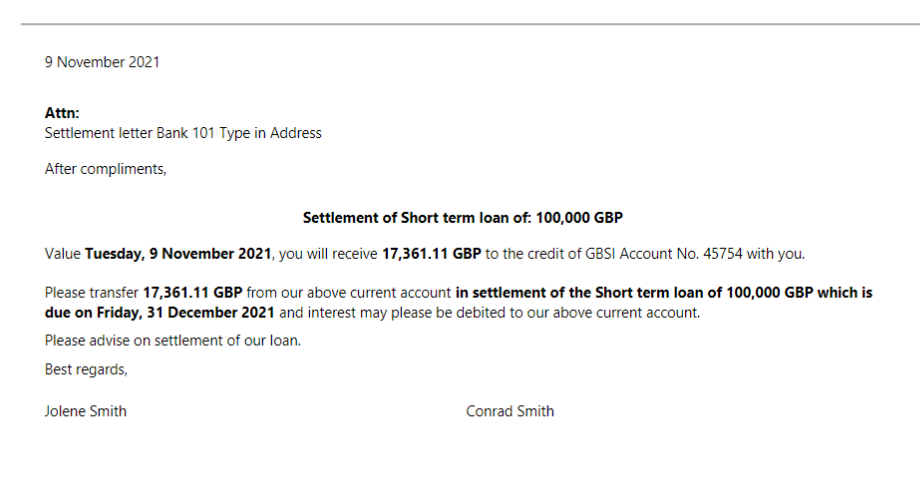
Loan borrowing and Settlement letters setup:
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury parameters
- On the Reporting tab, expand the Loan borrowing/Settlement letter FastTab
- Select a person for each report
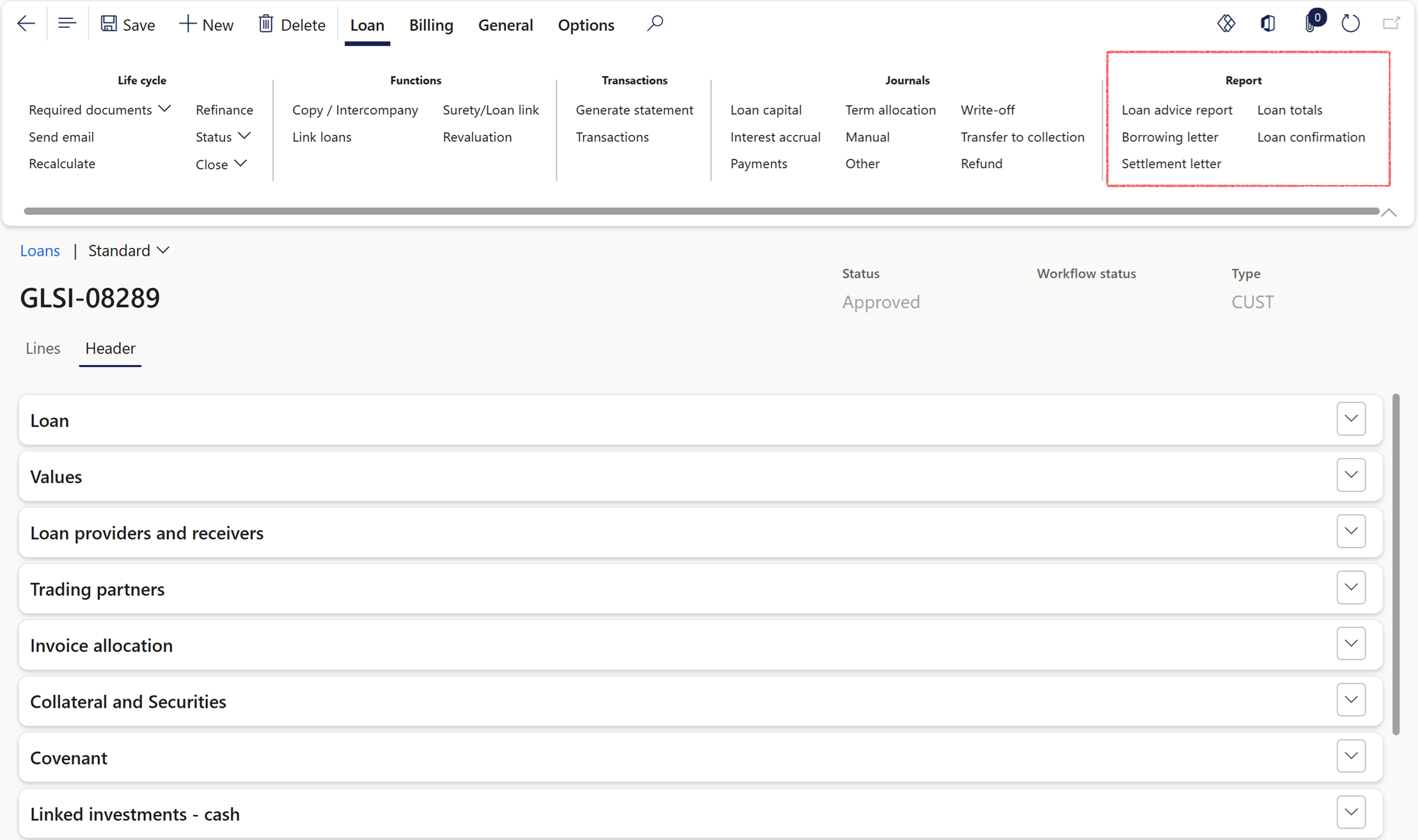
- To access this report, go to Treasury>Loans>Loans and select the loan
- In the action pane, click on Reports, choose Borrowing letter or Settlement letter
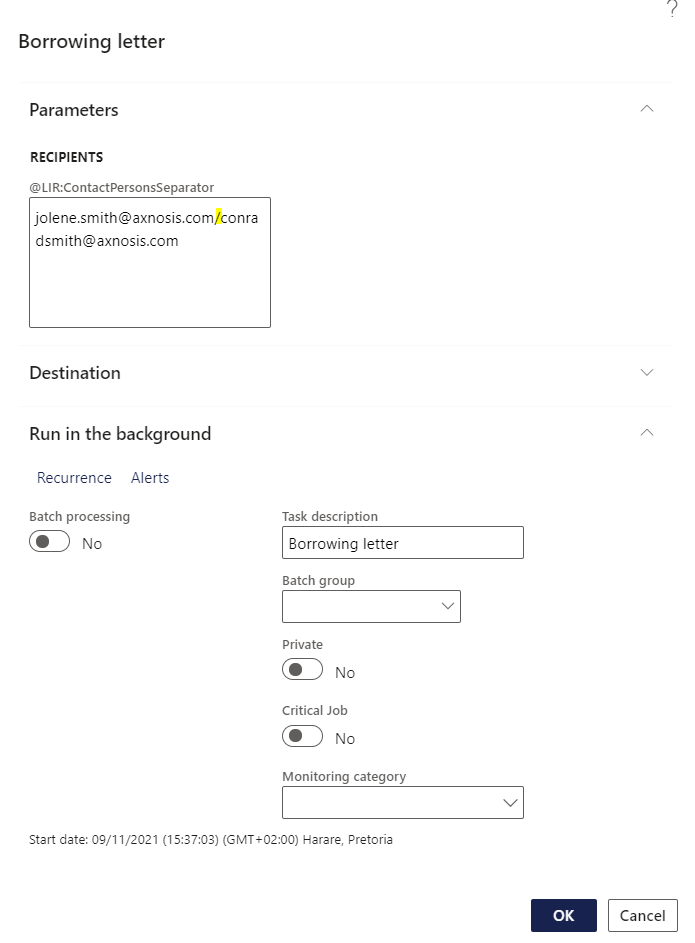
- In the Recipients block on the Letter Parameters, separate the names with a forward slash to display in a separate line.

¶ Set up Notifications
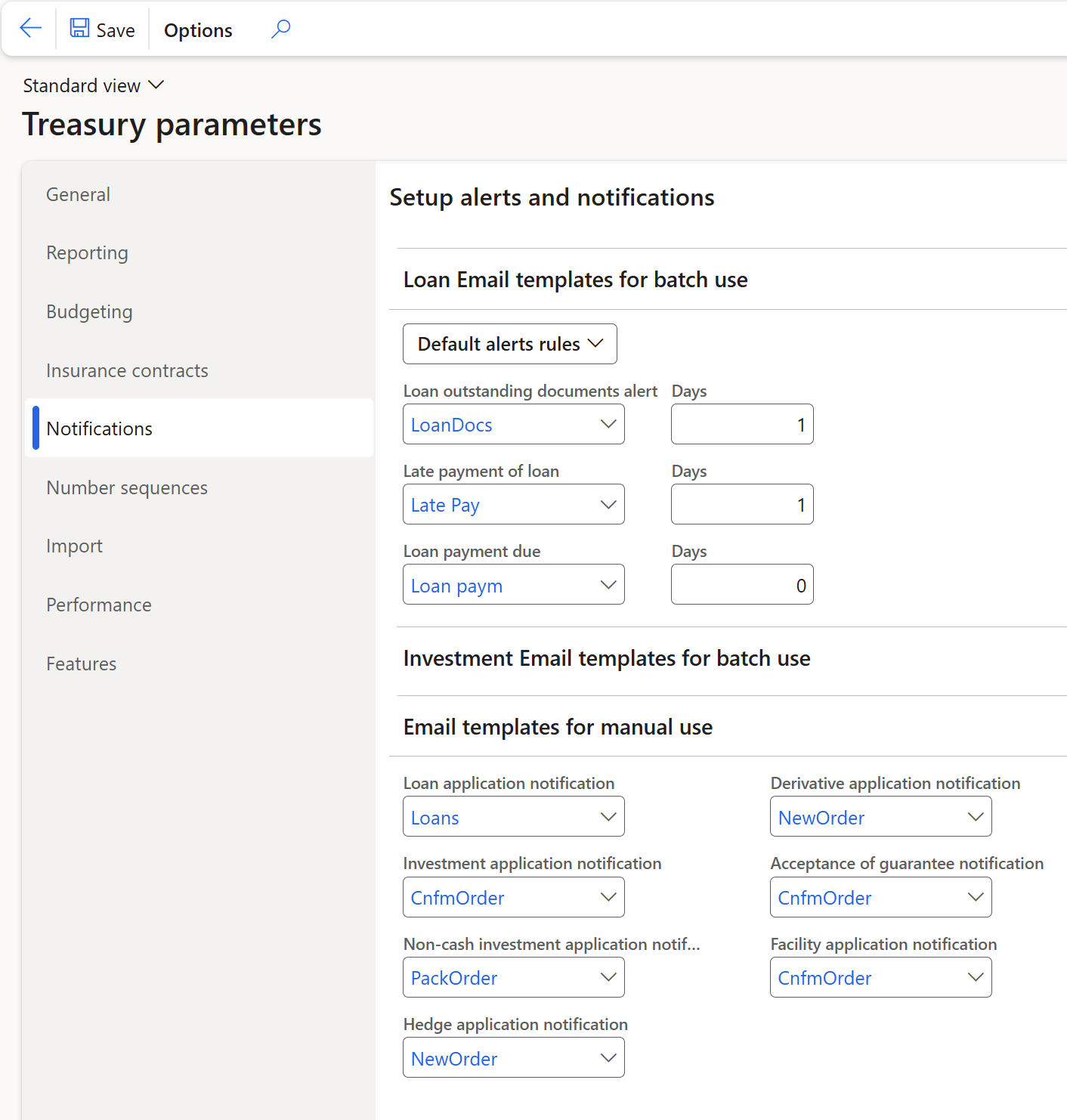
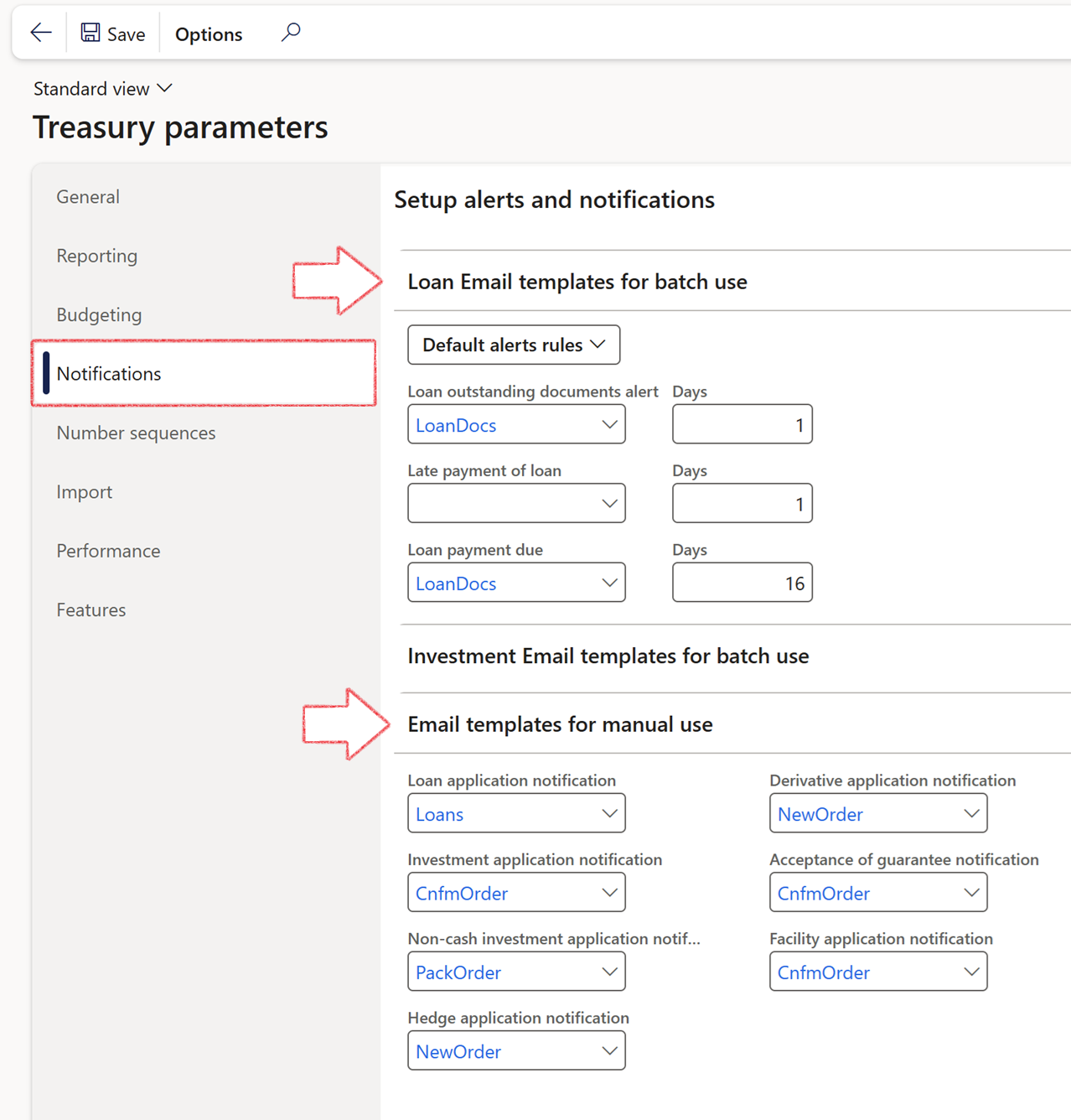
To setup Alerts and Notifications for outstanding loan documents, late payments of loans and loan payments due, go to:
- Treasury> Setup> Treasury parameters
- On the Notifications tab, expand the Loan E-mail templates for batch use FastTab
- multiple Loan E-mail templates can be selected from here, for example the Loan payment due notification.
- This can be setup for a specific template, with days to indicate the number of days, from today, where the due date that falls within that time window, must be included in the batch.
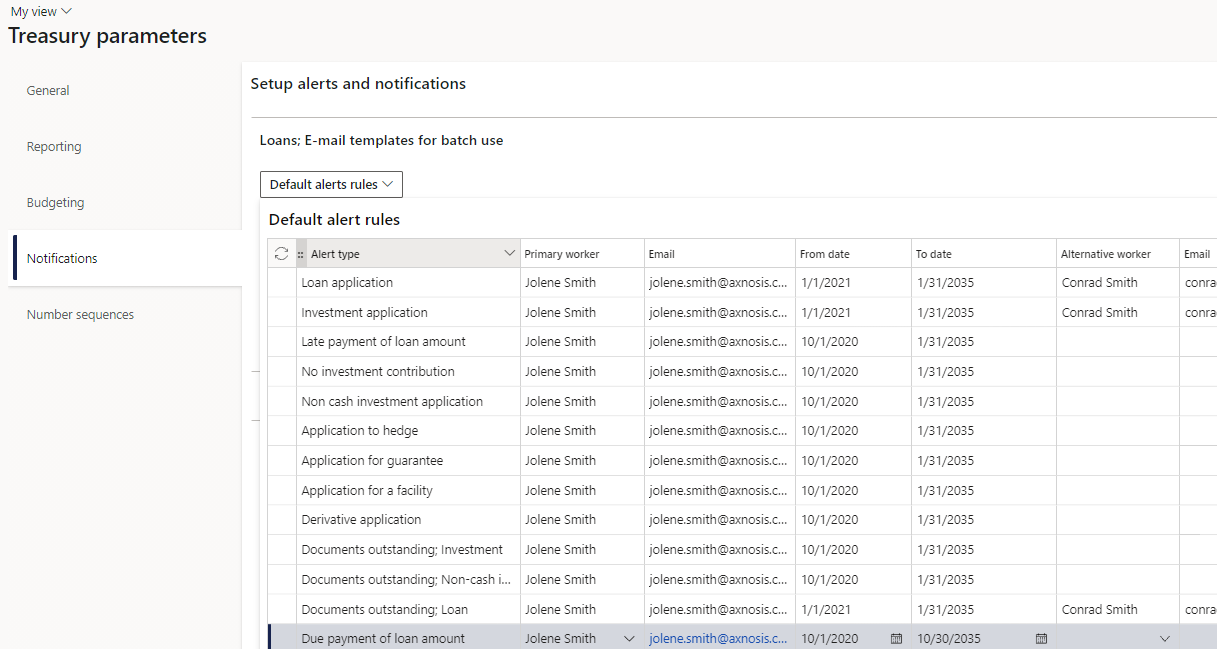
- An alert rule is created for Loan payments due.
Organizational e-mail templates for alerts and notifications are set up in the Organization administration module in D365.
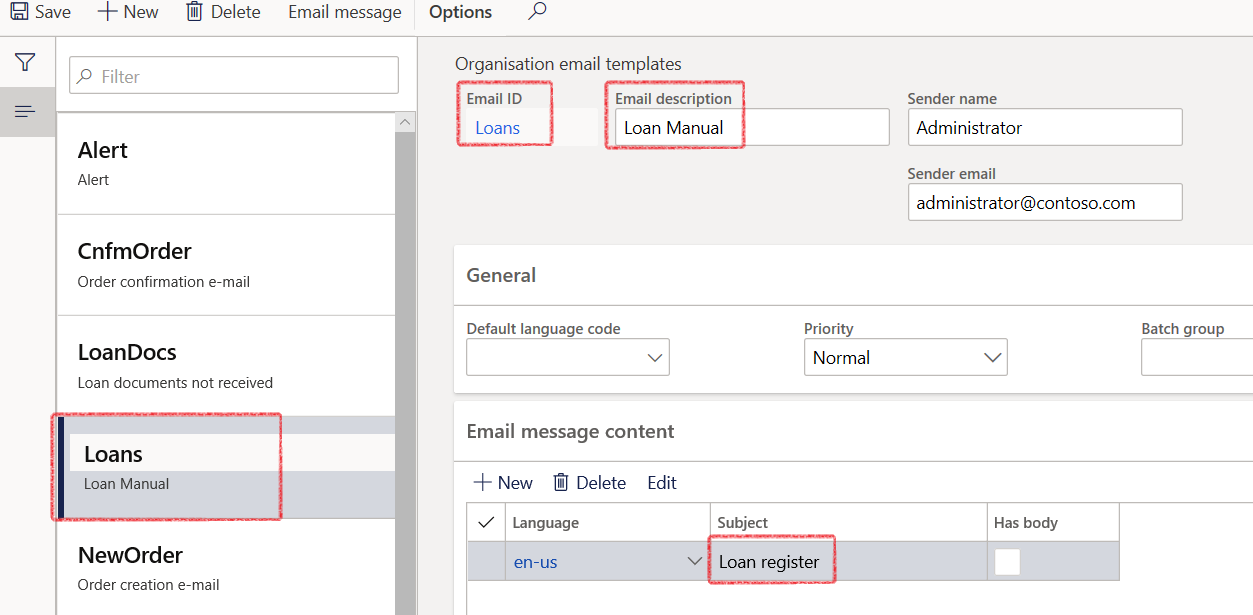
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules > Organization administration > Setup > Organization e-mail templates
- Create a template for Loan Documents not received, and Loan manual for the Loan register.
- Enter the e-mail id (name for e-mail template), e-mail Description and the Senders e-mail id
- In E-mail message content FastTab, create new, select language, and enter subject and click E-mail message (on top, in grey / blue ribbon bar)
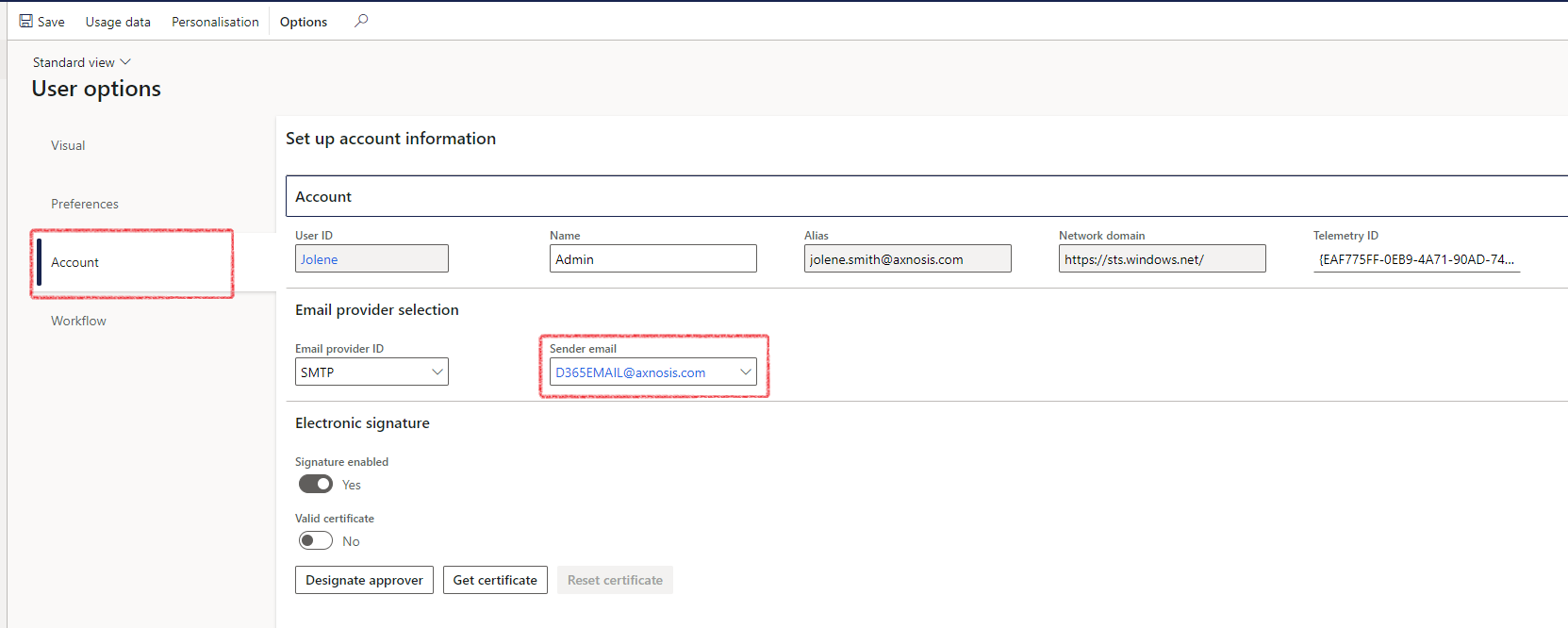
- Ensure that the sender’s e-mail is setup under User Options as well.
Generally, this would be the generic e-mail address that will be used within the company.
- Click on the Account tab under user options to enter the Sender email.
- The same should be setup under System administration e-mail parameters
- A side bar will appear on the right. Click browse and select the file, then click upload and once the bar fills, click OK
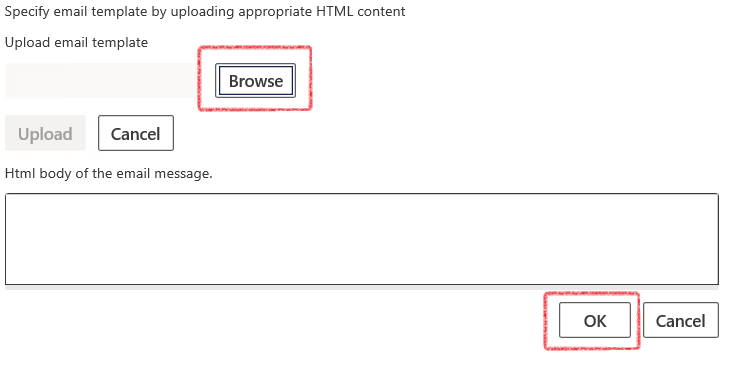
- Notifications are set up for Loans and e-mail templates for batch use or manual use
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury Parameters>Notifications
- Select the relevant Loan Email templates for batch use and Email templates for manual use
¶ Treasury Workflows
Treasury workflows will be used in the stages of a Loan or Investment
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury workflows
- Click on New
- A screen will open to Create workflow. Select the Workflow type and click Close
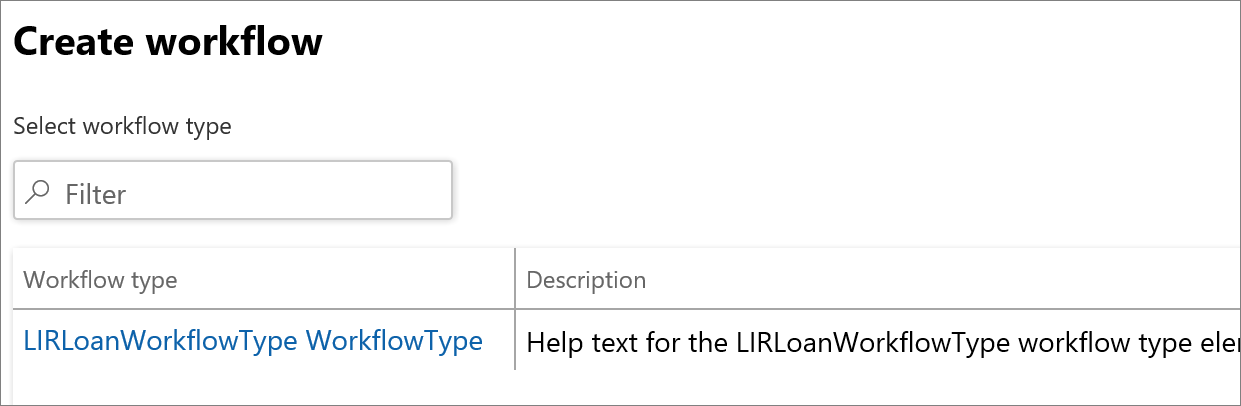
- When selecting the Workflow type, the following screen will appear:
- To submit a loan to workflow, click on the Workflow button in the Action pane, and select “Submit to workflow”.
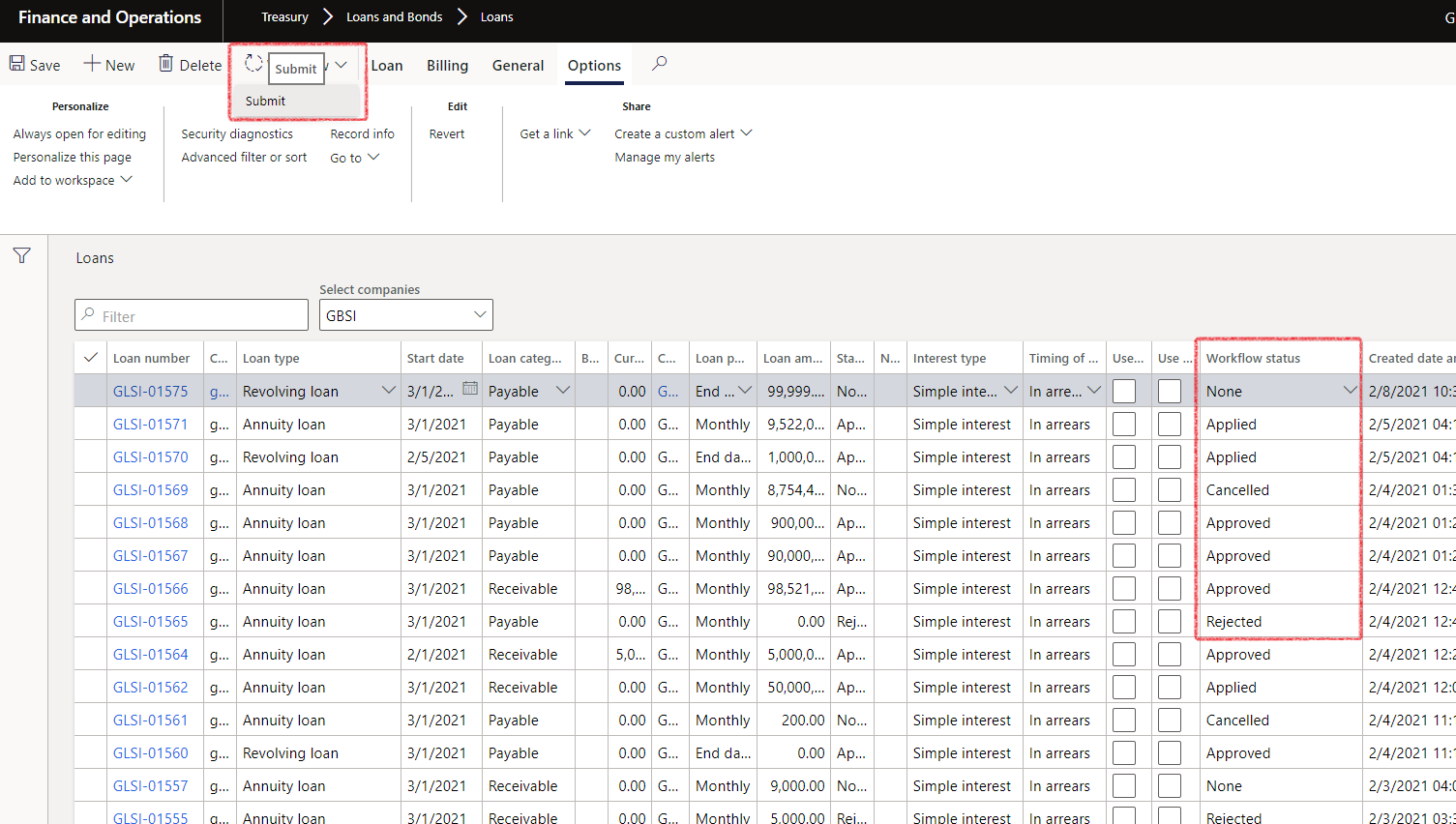
- The loan will move to the approvers list of workflow items to approve.
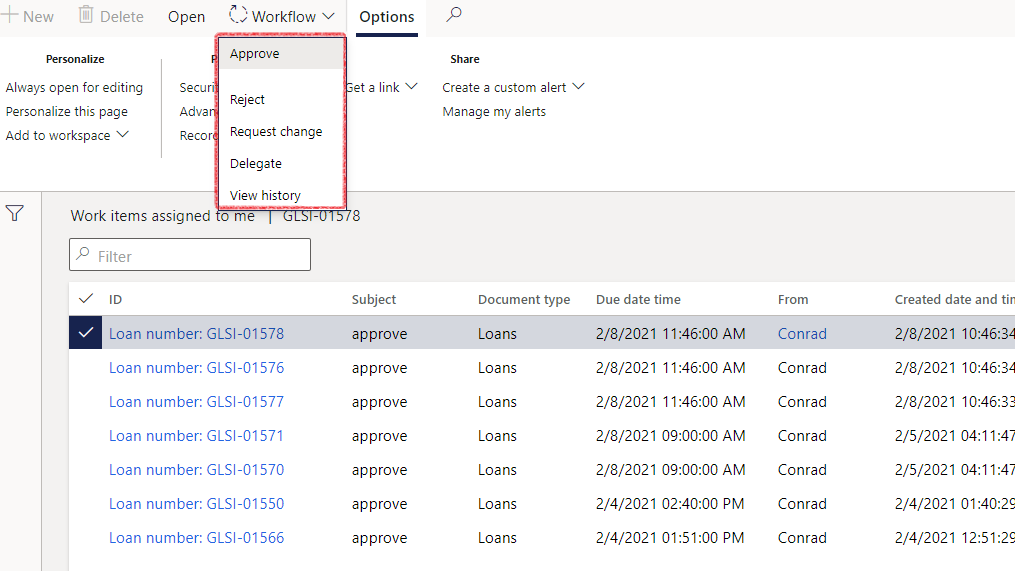
- The approver can view workflow history by navigating to Organization administration>Workflow>Workflow history
- Alternatively, the approver can also go to Common>Work items>work items assigned to me
- The following actions can be taken:
- Approve
- Reject
- Request change
- Delegate
- View history
- The user can also view all work items assigned when opening the Home page:
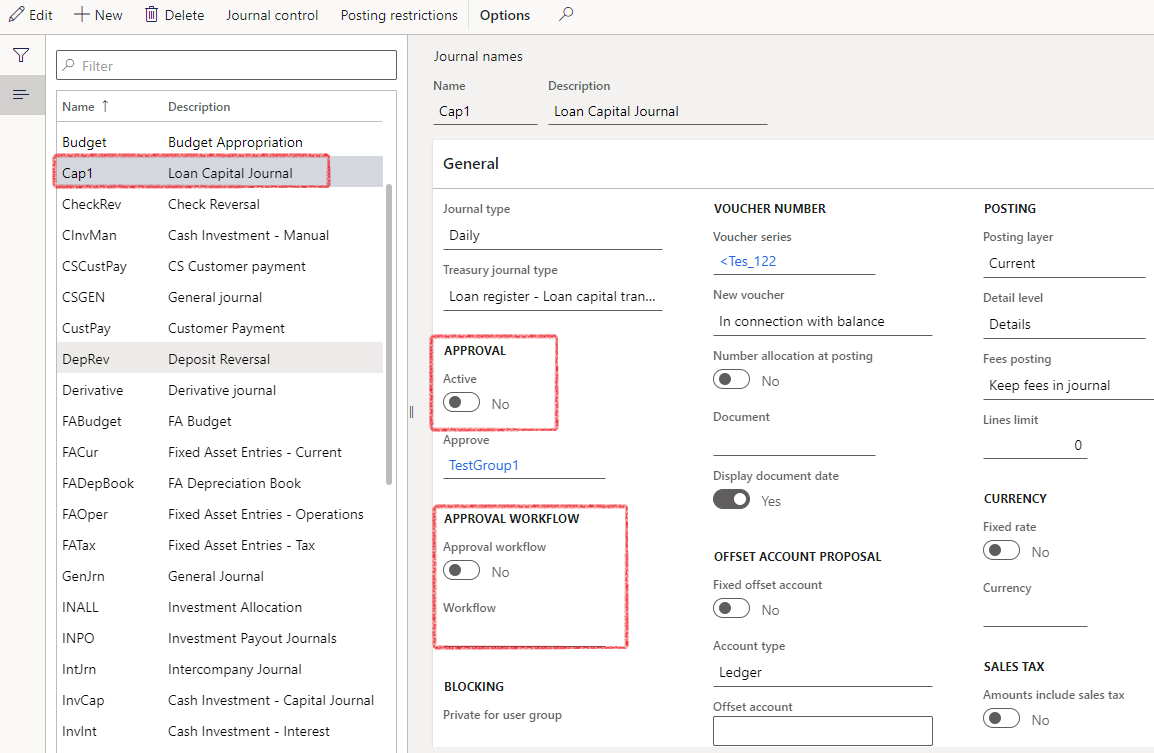
- Treasury>Setup>Journal names
- Select the journal name on the left-hand side
- Then slide the “Active” to Yes on the Approval workflow section
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Common>Broker
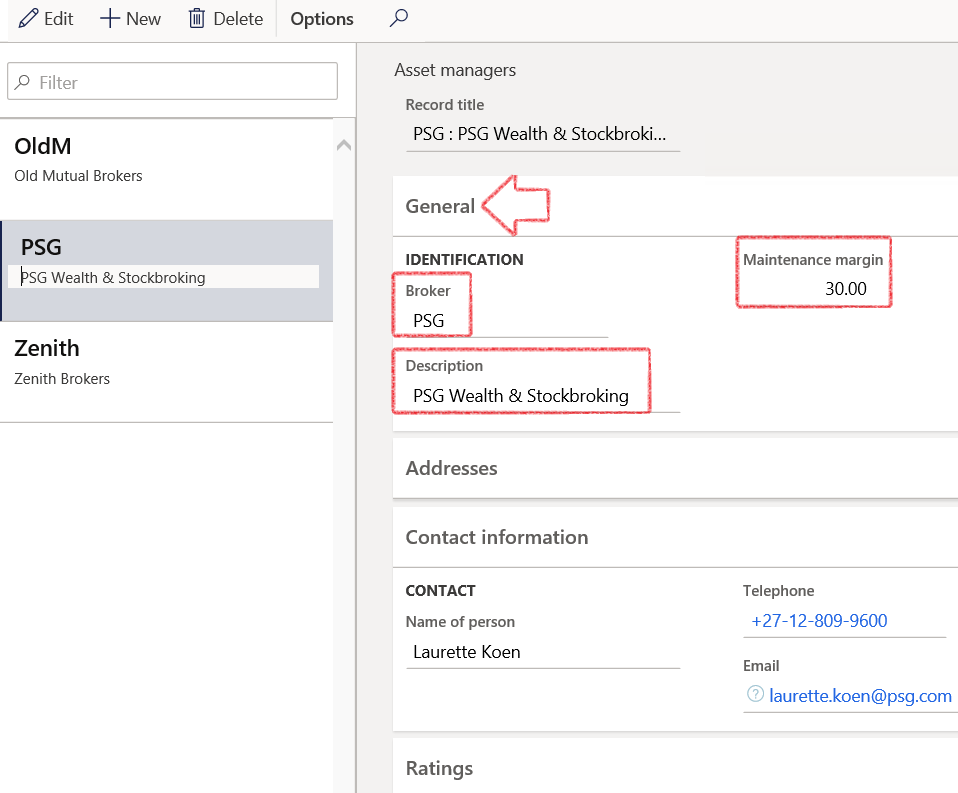
- Click on New
- On the General FastTab, enter the following information
- Broker name
- Description
- Maintenance margin
- Address, contact information and ratings are optional
- Remember to link the newly created broker, to the broker’s bank account
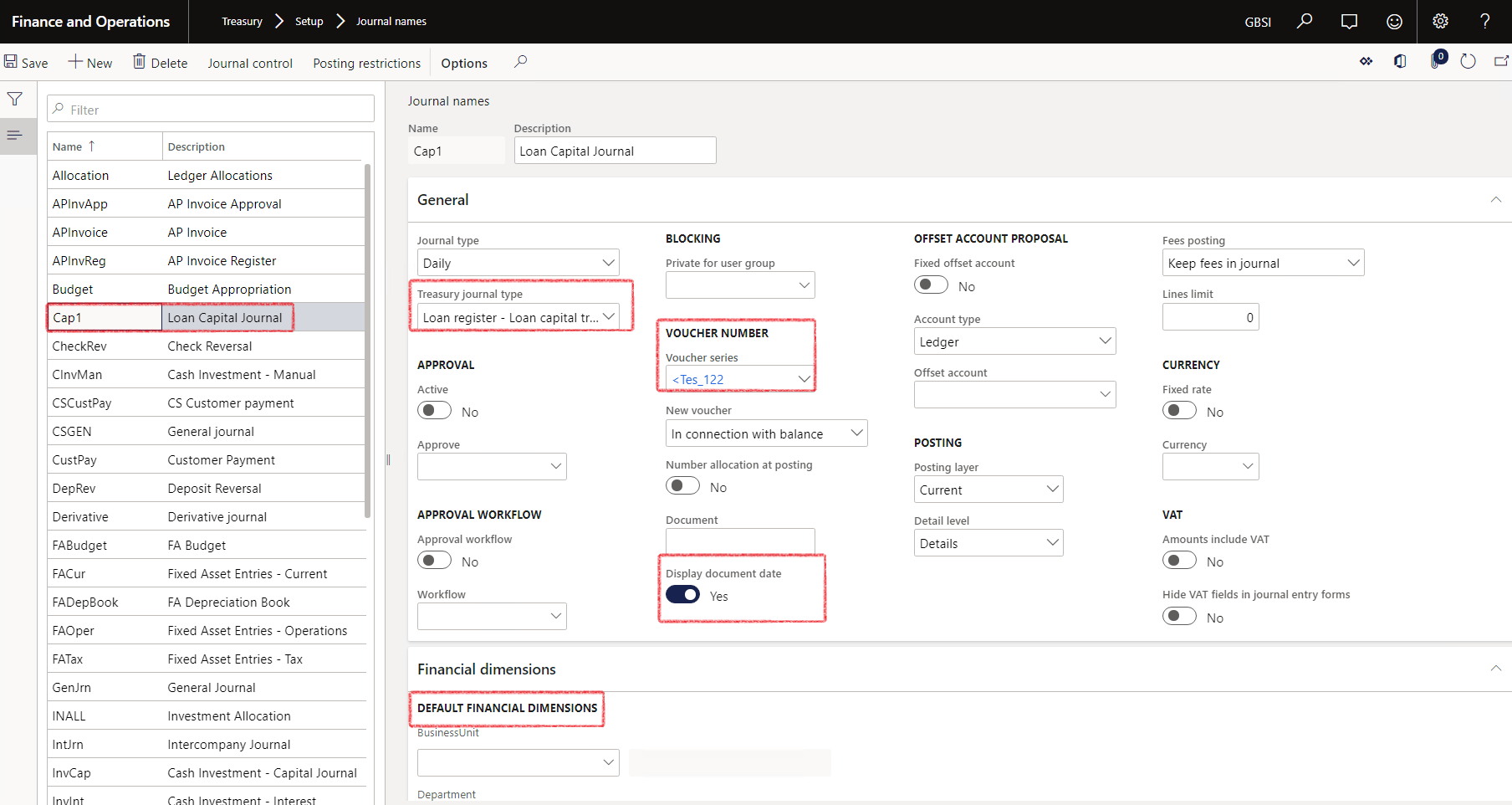
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Journal names
- For Loans, the following journal names are used most often:
- To display the Document date on the journal, the slider should be enabled to Yes. This setting should be on every journal name where you want the document date to display
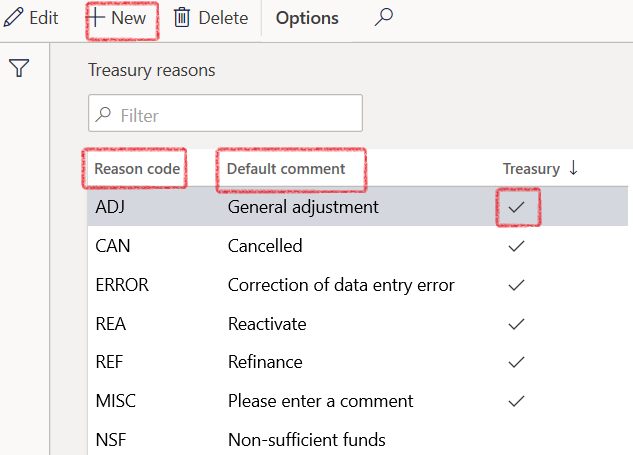
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury reasons
- For loan invoices, ensure the Treasury slide is Yes
- Note on Invoice lines, there is an option to “Use statement”. This will use the amount due on the loan statement, without the user having to manually insert an invoice amount.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Lists
- Click the New button
- Enter ID
- Type a Description
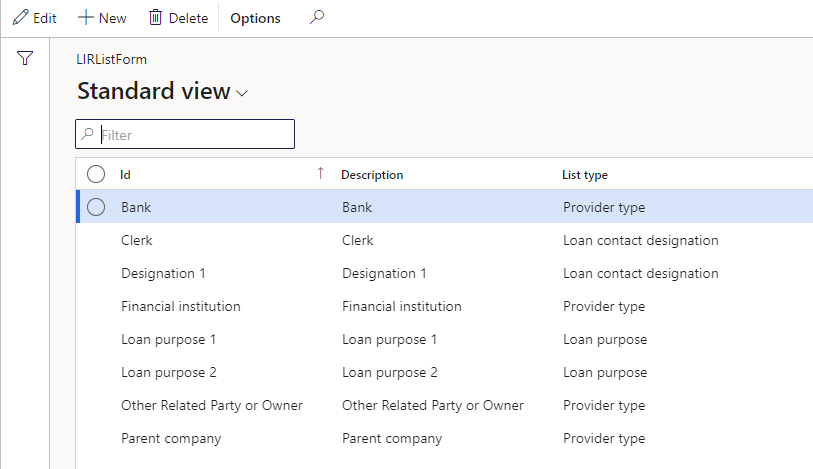
- Select List type
- For Designation on loans, select Loan contact designation
- For the Purpose field on Loans, select List type Loan purpose
- For Provider type on Loan providers and receivers, select List type Provider type
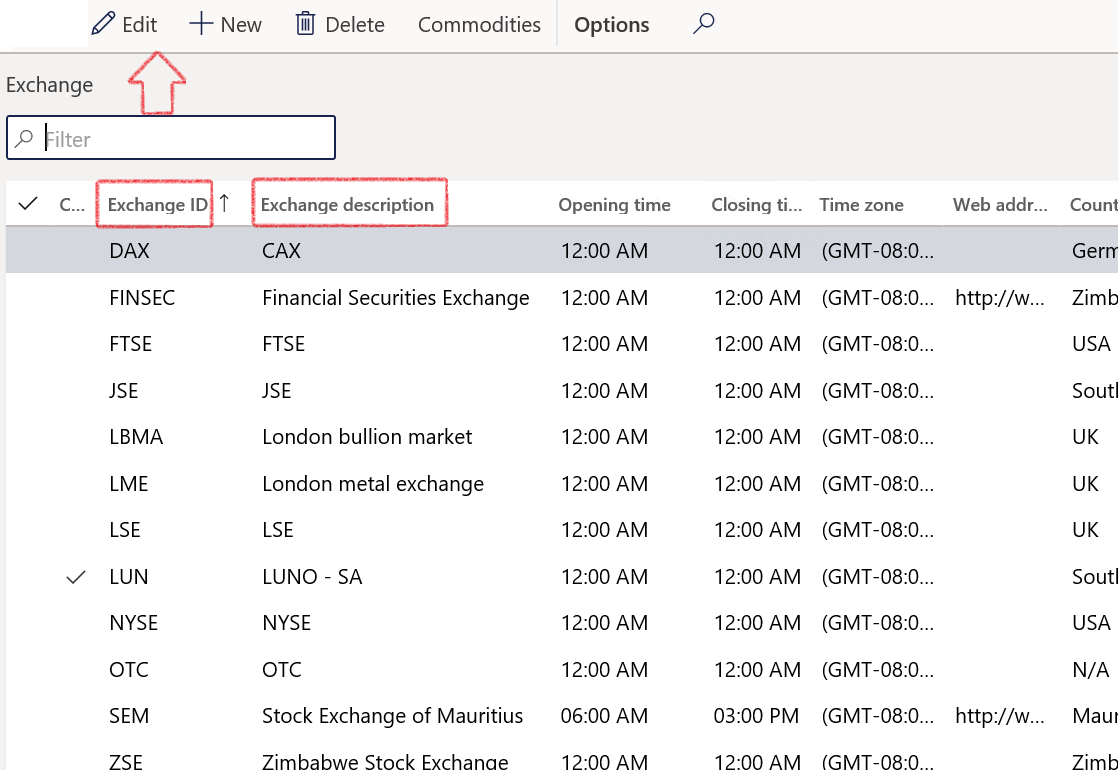
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Common>Exchange
- Click the New button
- Enter the Exchange ID and Description
- Also complete the Web address
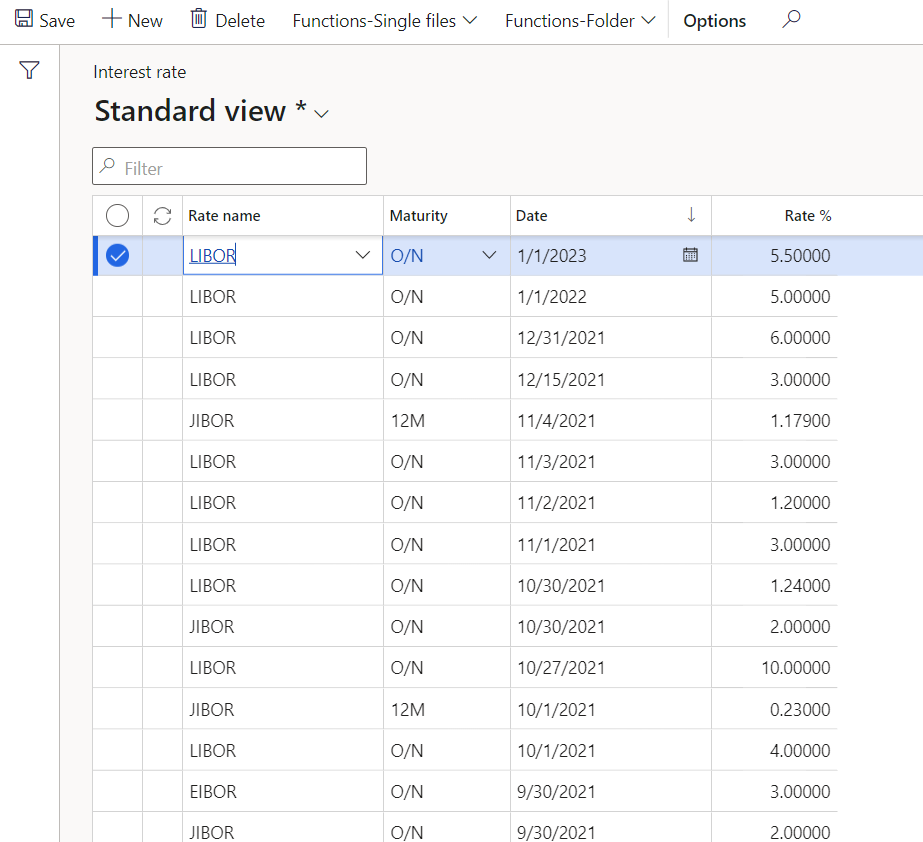
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Common>Interest rate
- Then click New
- In the Rate name field, select a Rate name
- Select a Maturity period
- Enter a Date
- Enter a Rate %
- Save
- Treasury>Common>Periodic> Batch trade agreements creation – new interest rates
- Click OK to run the batch job
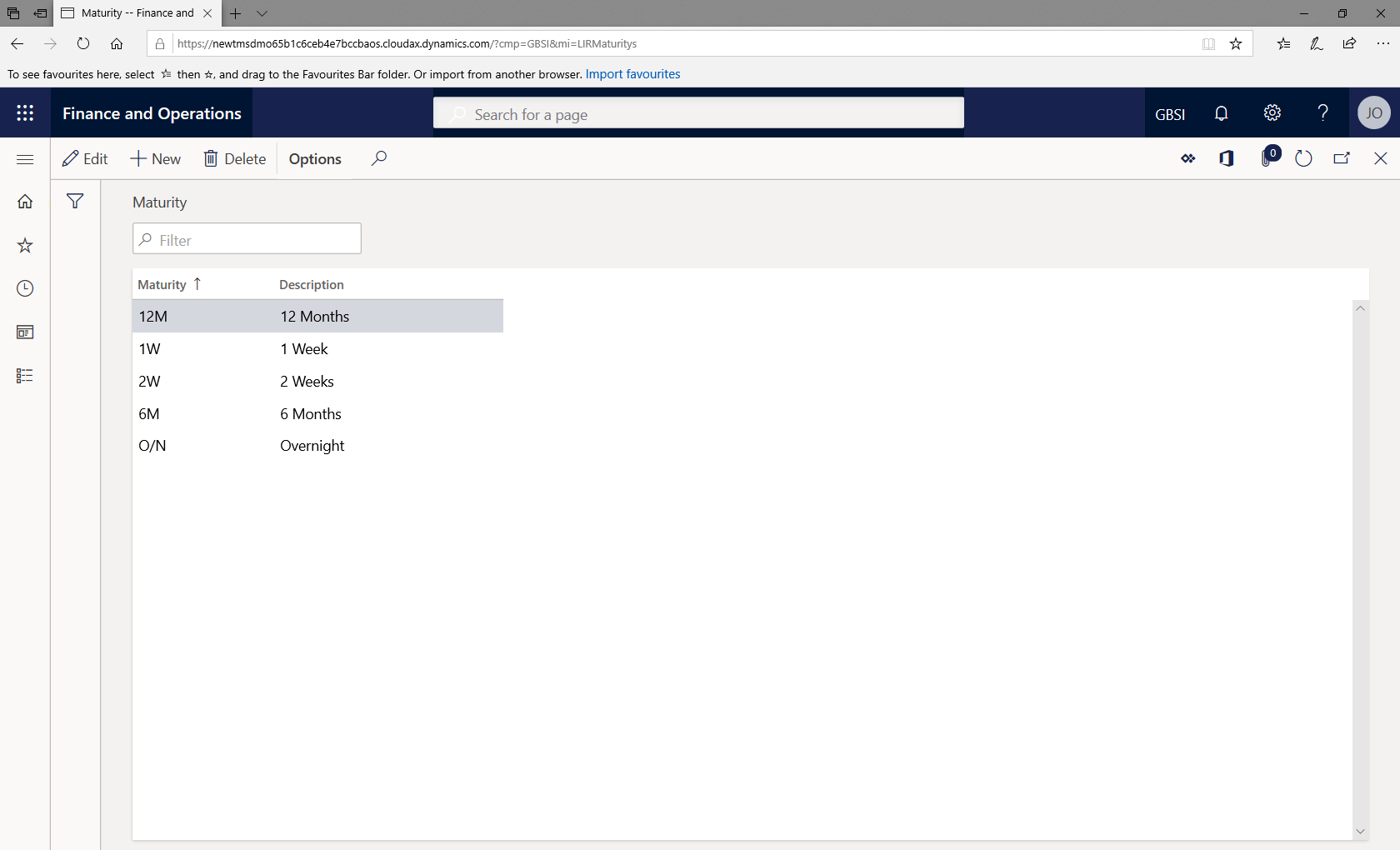
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Interest rate>Maturity
- Click on New
- Complete fields for Maturity and Description and save
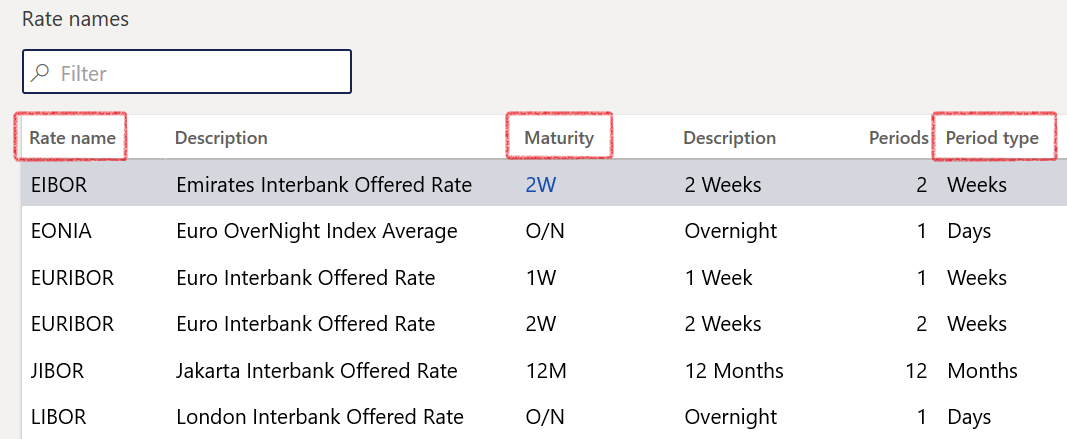
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Interest rate>Rate names
- Click on New to create a new Rate name
- Complete the Description
- Select Maturity from a dropdown list and
- Select the relevant Period type
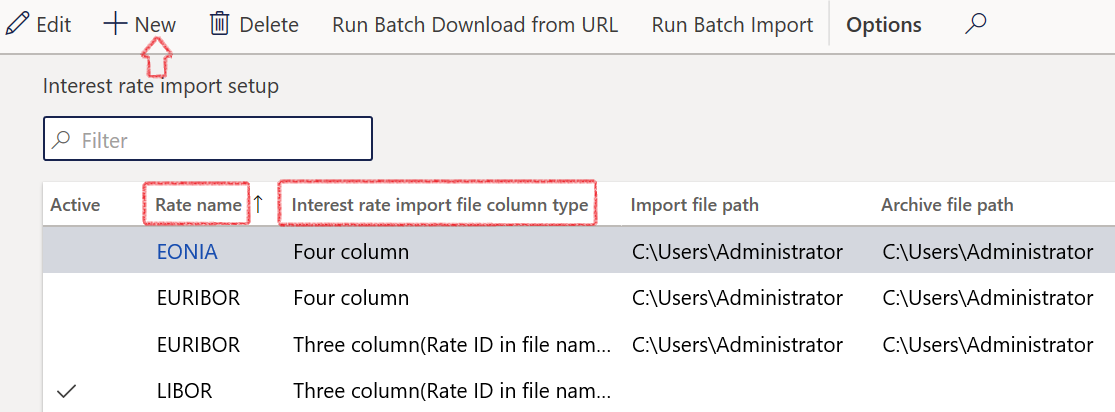
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Interest rate>Interest rate import setup
- Click on New to create a new link for interest rates
- Select the Rate name and select the Interest rate import file column type
- Enter the Import file path
- Enter the Archive file path
- Enter the Interest rate URL path
- Save the record
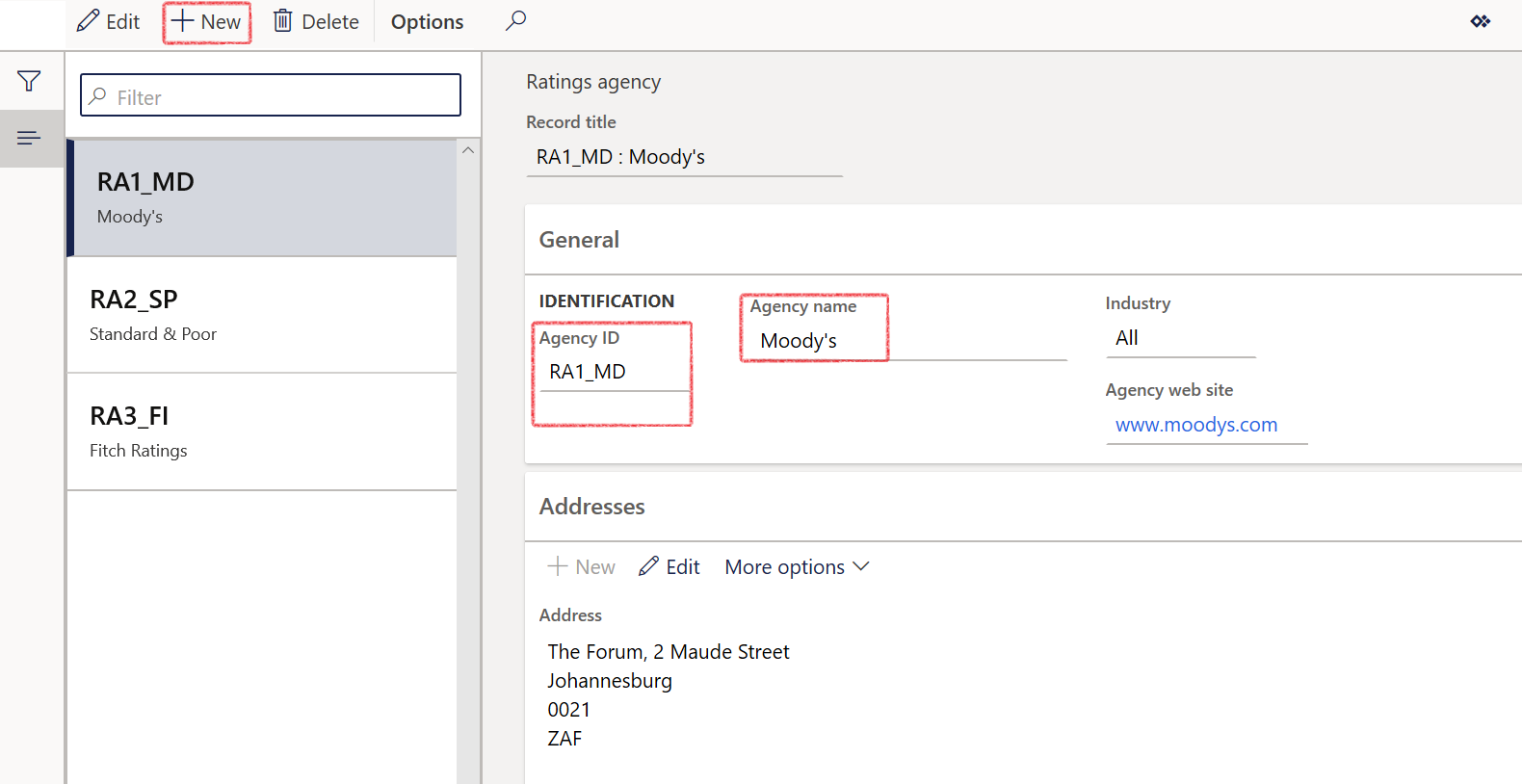
- To set up various Ratings agencies, go to: Treasury>Setup>Credit ratings>Ratings agency
- Click on New
- Enter an Agency ID and name
- Complete all other relevant fields and save the record.
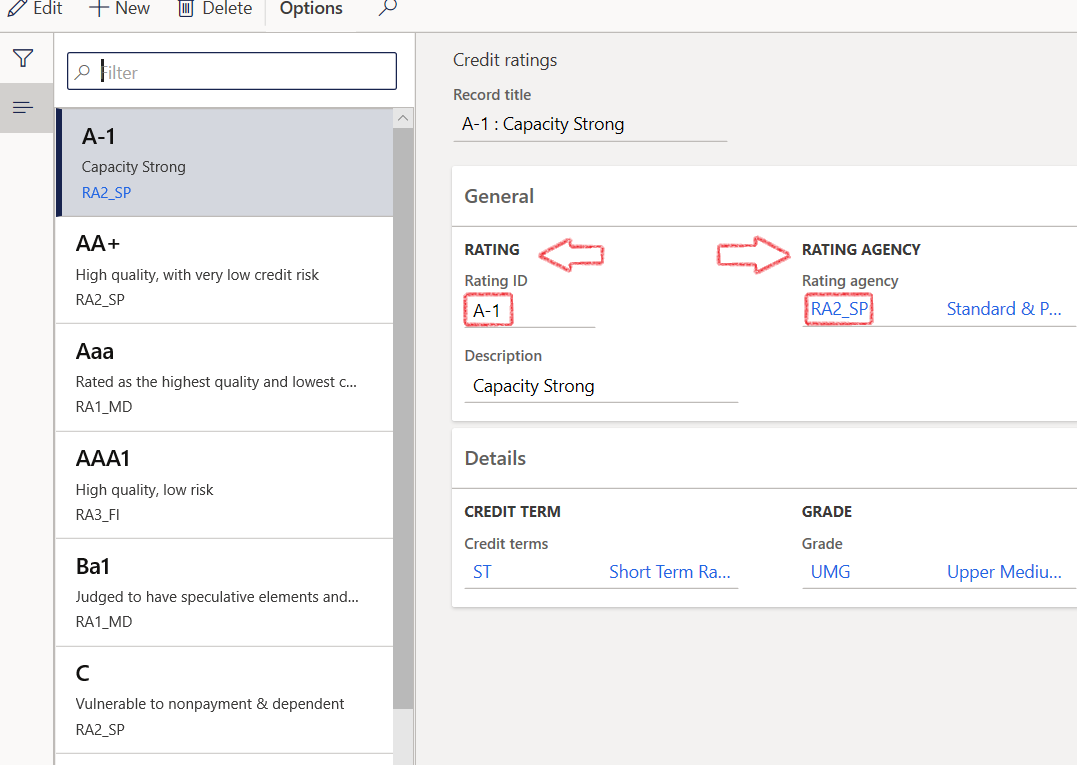
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Credit ratings>Credit ratings
- Create a Rating ID and Select a Rating agency form the dropdown list
- Save the record.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Credit ratings>Credit terms
- Create a Rating ID and Select a Rating agency form the dropdown list
- Save the record.
- In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Credit ratings>Grades
- Click on New and type a Grade and a Description
- Save the record
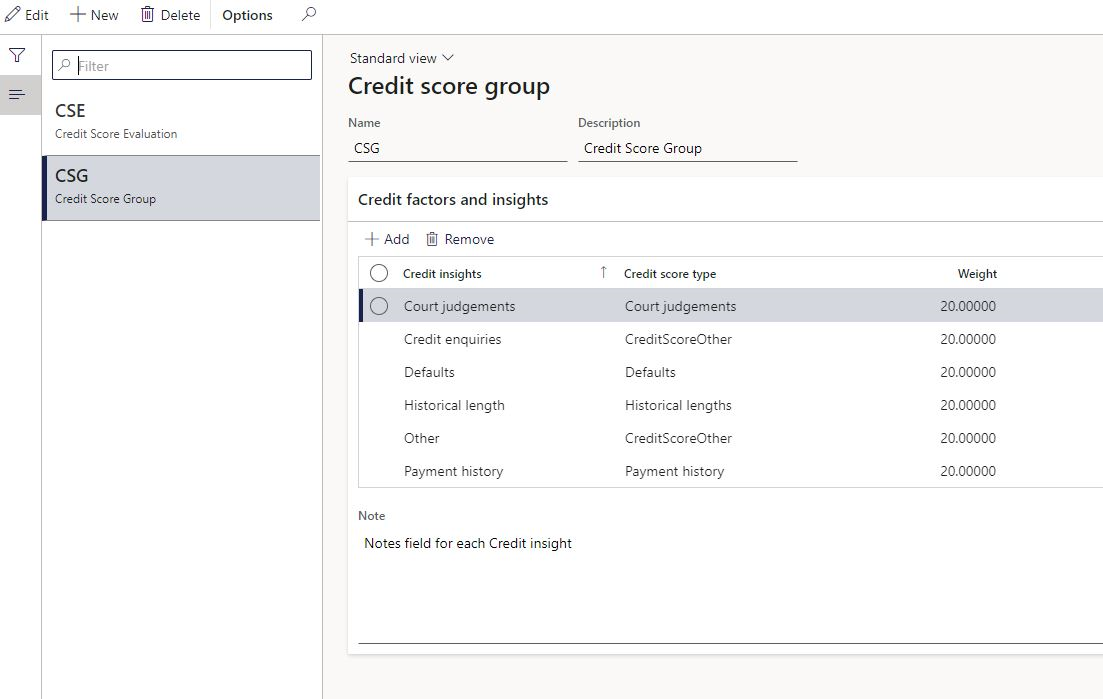
- Navigate to Treasury > Setup > Credit ratings > Credit score group
- Click on New
- Enter a Name
- Enter a Description
- Expand the Credit factors and insights FastTab
- Click on Add
- Enter a Credit insights name
- Select a Credit score type. Choose between:
- Payment history
- Defaults
- Court judgements
- Credit enquiries
- Historical length
- Other
- Enter a Weight percentage
- For each Credit insight, a Note can be added
To activate workflow on a specific journal, go to:
Note, if the Approval slide is “yes”, the Post button on the specific journal will be greyed out
¶ Broker
¶ Create a Broker for Margin trading
A broker loan is a loan that the lender (usually a bank) can obligate the borrower (a brokerage house) to repay at any time. A broker loan is granted to a brokerage house in need of short-term capital for financing clients' margin portfolios. The lending bank can call a loan at any time. Likewise, the brokerage house may repay a broker loan in full without prepayment penalties. Broker loans are collateralized using securities with interest accruing daily at an unsecured adjustable rate.
¶ Treasury Journal names
When creating a journal, the first selection to be done is a journal name. In Treasury, each journal name setup is done by linking the journal name to a Treasury journal type, as well as an Account type. Part of standard Journal name setup is selecting a Journal type.
Proper selection of the Treasury journal type is of paramount significance as it determines the corresponding journal generation in the Posting profiles. Failure to associate the relevant Treasury journal type with the posting profile will result in the non-creation of specific journals.
|
Journal name |
Description (journal) |
Linked to Journal Type |
Appear under |
| LNCap | Loan Capital journal | Loan register-Loan capital transaction | Loan Capital |
| LNAll | Loan Allocation journal | Loan register-allocation | Allocation |
| LRBC | Loans – Bank Charges | Loan register - transactions | Manual |
| LNBP | Loan Penalties Journal | Loan register - transactions | Manual |
| LNIcc | Loan Interest Accrual jnl | Loan register- monthly interest accrual | Interest Accrual |
| LNMan | Loan Manual Adjustment | Loan register- transactions | Manual |
| LNPay | Loan Payment journal | Loan register- payment | Payment |
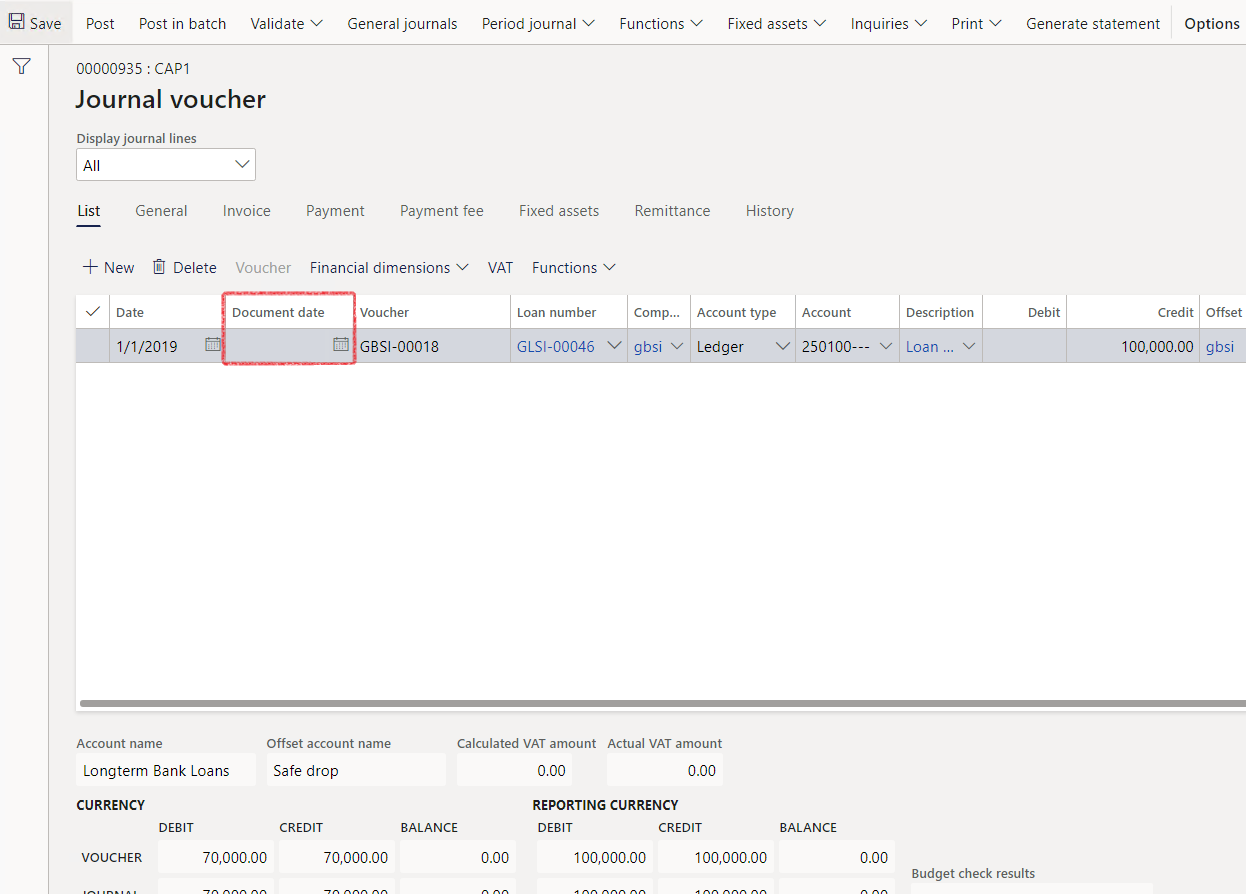
Remember to also enable “Use document date” on Treasury Parameters by navigating to Treasury>Setup>Treasury Parameters and changing the slide to “Yes” under General>Loans FastTab
¶ Treasury reasons
A reason code is a code that users can select to record the reason for a change or transaction, such as a write-down adjustment or payment reversal. You can use the financial reasons form in Organization administration to create reason codes for a variety of financial modules, or alternatively open the Treasury reasons form from a specific module to set up reason codes for only that module. In this case, the reason codes will be for Treasury reasons.
¶ Treasury Invoice templates
Treasury invoice templates are intended for the user responsible for managing and processing Accounts Receivable invoices.
In the navigation pane, go to: Modules>Treasury>Setup>Treasury invoice templates
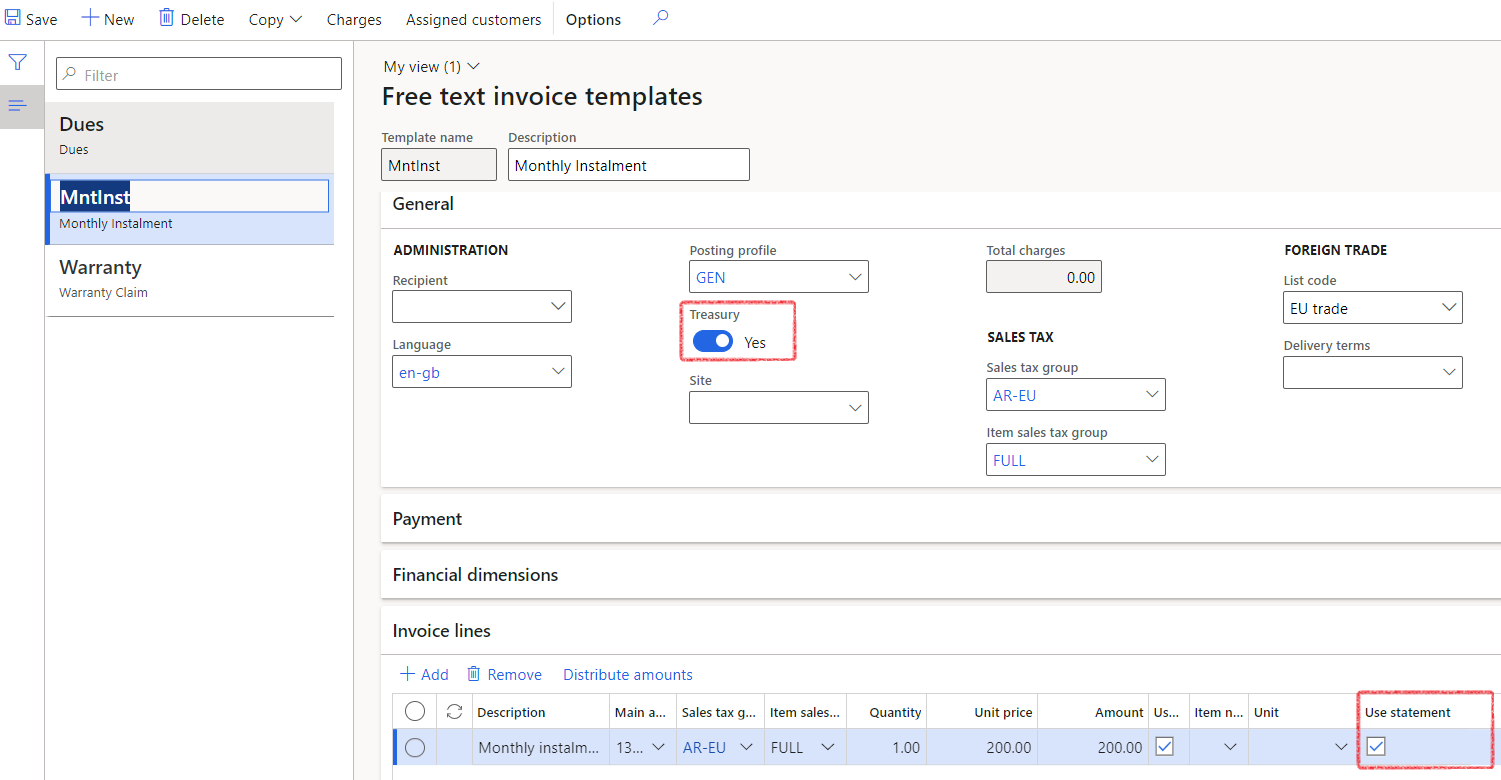
You can also save an existing free text invoice as a template. When you select Save to template from the Invoice tab, provide a name and a description for the template. If a template with the name already exists, you will see a notification that a template with that name already exists. You can still click on Ok to replace it.
¶ Treasury invoice templates on Loan groups
To be able to invoice customers from Loans, a Treasury Invoice templates should be selected on the Loan group
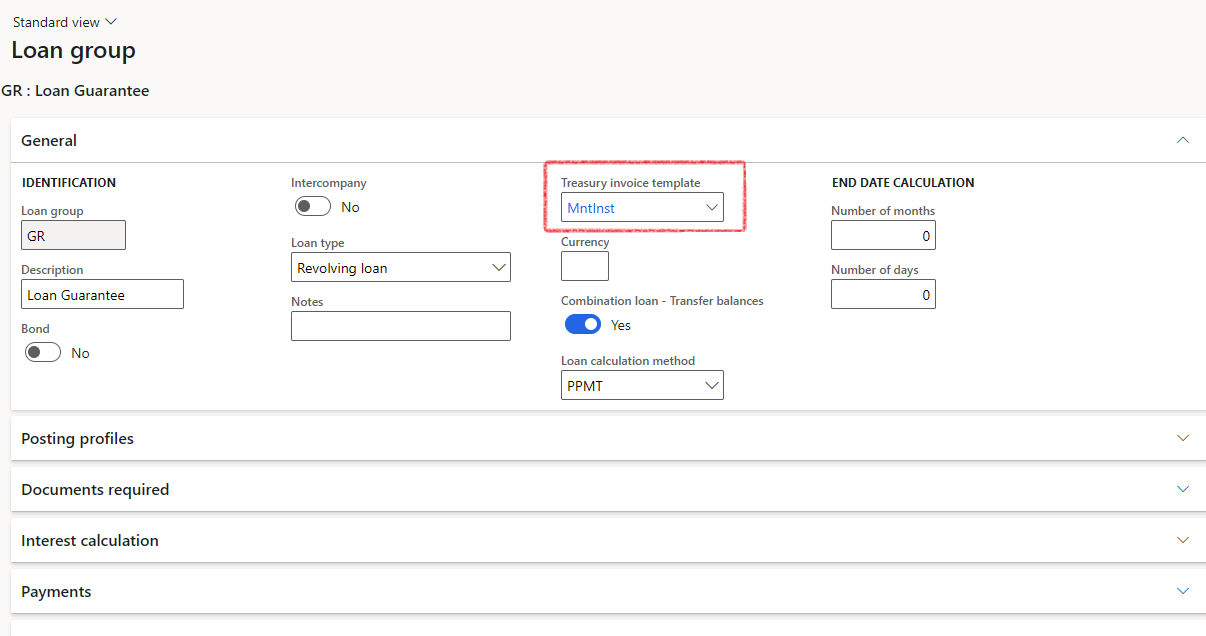
¶ Lists
Setup lists for the contact person Designation on loans
¶ Exchanges
Exchange refers to the market for Interest rate indexes. Typical market rate indexes include LIBOR, Bloomberg Foreign Exchange, and Reuter’s Foreign exchange. An index categorizes the various market rates that you track.
¶ Interest rates, Maturity, Rate names and Interest rate import setup
On Interest rate form, create lines for each interest rate relevant for Loans and Investments. One needs to capture the exchange (market for rate obtained), date, maturity period, and the actual rate quoted. These rates indicate the rate at which banks are prepared to lend one another money with a specific maturity date.
¶ Setup Interest rates
Interest rates can setup to be used to automatically update all interest rate agreements.
To run a batch job to automatically update the Interest rate agreements on Loans and Credit facilities, go to
¶ Maturity
¶ Rate names
¶ Setup Interest rate import
Interest rates can be imported and does not have to be captured manually.
¶ Ratings agency
A credit rating agency (CRA, also called a ratings service) is a company that assigns credit ratings, which rate a debtor's ability to pay back debt by making timely principal and interest payments and the likelihood of default. An agency may rate the creditworthiness of issuers of debt obligations, of debt instruments and in some cases, of the servicers of the underlying debt, but not of individual consumers.
¶ Credit ratings
Credit ratings can address a corporation's financial instruments i.e. debt security such as a bond, but also the corporations itself. Ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies, they use letter designations such as A, B, C, etc. Higher grades are intended to represent a lower probability of default.
A credit rating is an evaluation of the credit risk of a prospective debtor (an individual, a business, company or a government), predicting their ability to pay back the debt, and an implicit forecast of the likelihood of the debtor defaulting. The credit rating represents an evaluation of a credit rating agency of the qualitative and quantitative information for the prospective debtor, including information provided by the prospective debtor and other non-public information obtained by the credit rating agency's analysts.
The setup for Ratings agency should be done before this step
¶ Credit terms
Long-term credit ratings are orientated on the US-American grade system. Ratings from AAA to BBB- are being considered investment grade, lower ratings are being referred to as non-investment grade.
A positive or negative outlook respectively signals that the credit rating in the medium- to long-term might be raised or lowered, while a stable outlook indicates that the rating most probably will stay at the same level. To set up Credit terms:
¶ Grades
Ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies, they use letter designations such as A, B, C; Higher grades are intended to represent a lower probability of default.
¶ Credit score group
This credit score ratings engine will provide more depth for credit ratings that is done in the Treasury module. This setup forms the basis for the Last credit score that can be done on Customers, Vendors, Loan applicants and Loan providers and receivers.