¶ Introduction
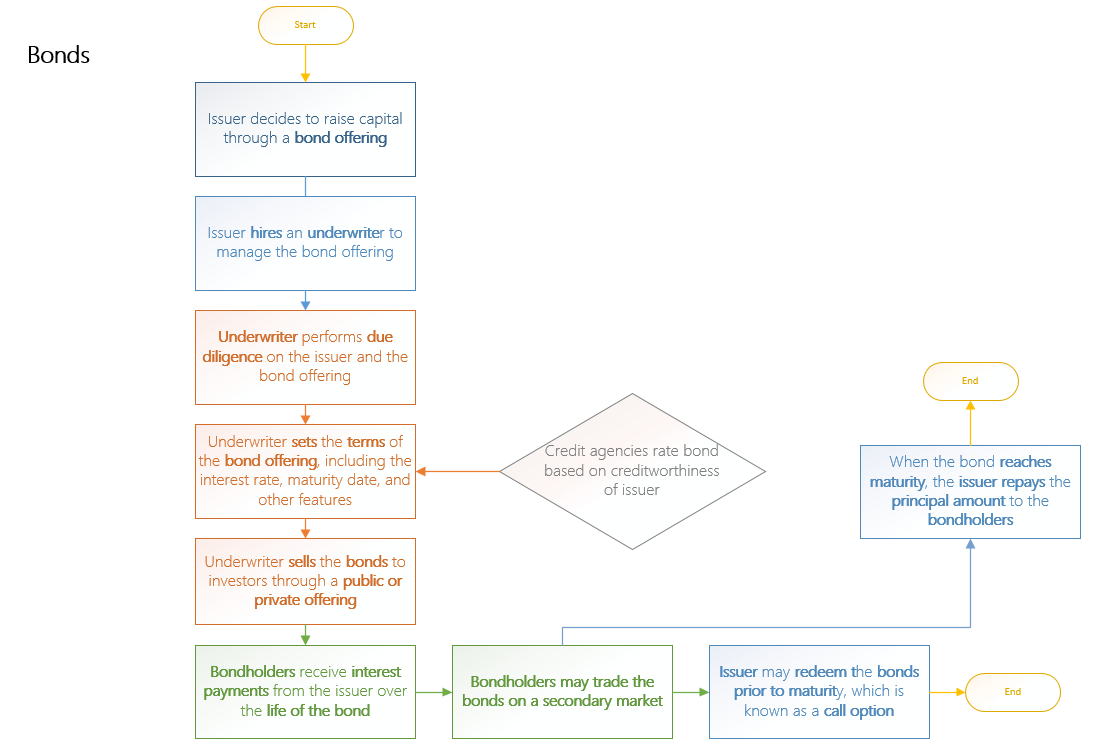
A bond is a financial instrument that allows governments, corporations, and other organizations to raise capital by borrowing from investors. When an investor buys a bond, they are effectively lending money to the issuer. In exchange, the issuer commits to paying regular interest over a set period and returning the principal amount at maturity.
Bonds are generally seen as relatively low-risk investments since they offer fixed returns and carry a legal obligation for repayment. Credit rating agencies evaluate the issuer’s credit strength, helping investors gauge the likelihood that payments will be made as promised.
Different categories of bonds exist, such as government, municipal, corporate, and convertible bonds. Each type has distinct features, including maturity terms, interest rates, and varying levels of risk.
Investors often use bonds to diversify their portfolios and to generate consistent income through interest payments. Bond values are affected by changes in interest rates and economic conditions, which also makes them a potential safeguard against inflation and other financial uncertainties.
This is a general overview of how bonds work, though the exact structure and process can differ depending on the specific bond issue and market environment.
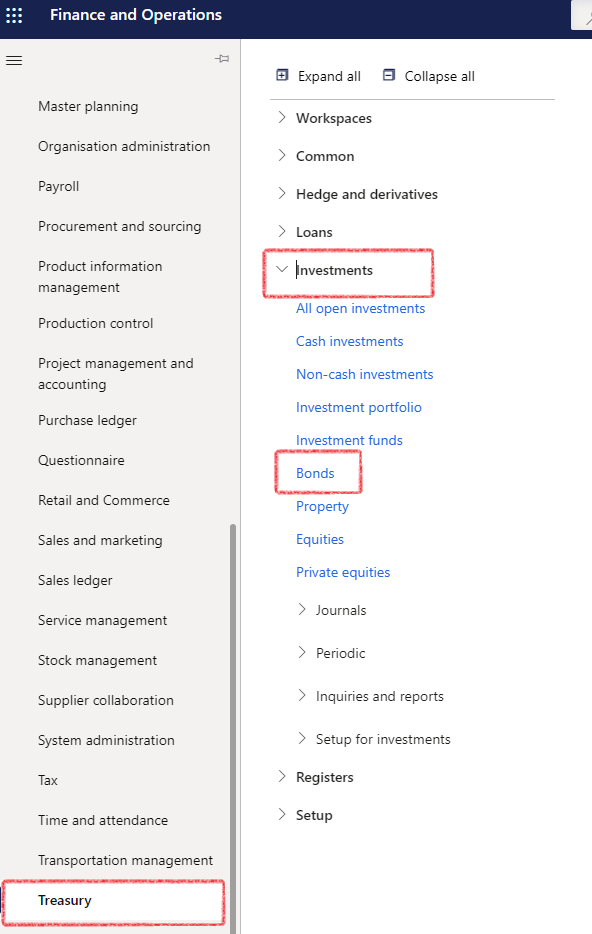
¶ Navigation
¶ Daily use
¶ Bonds list page
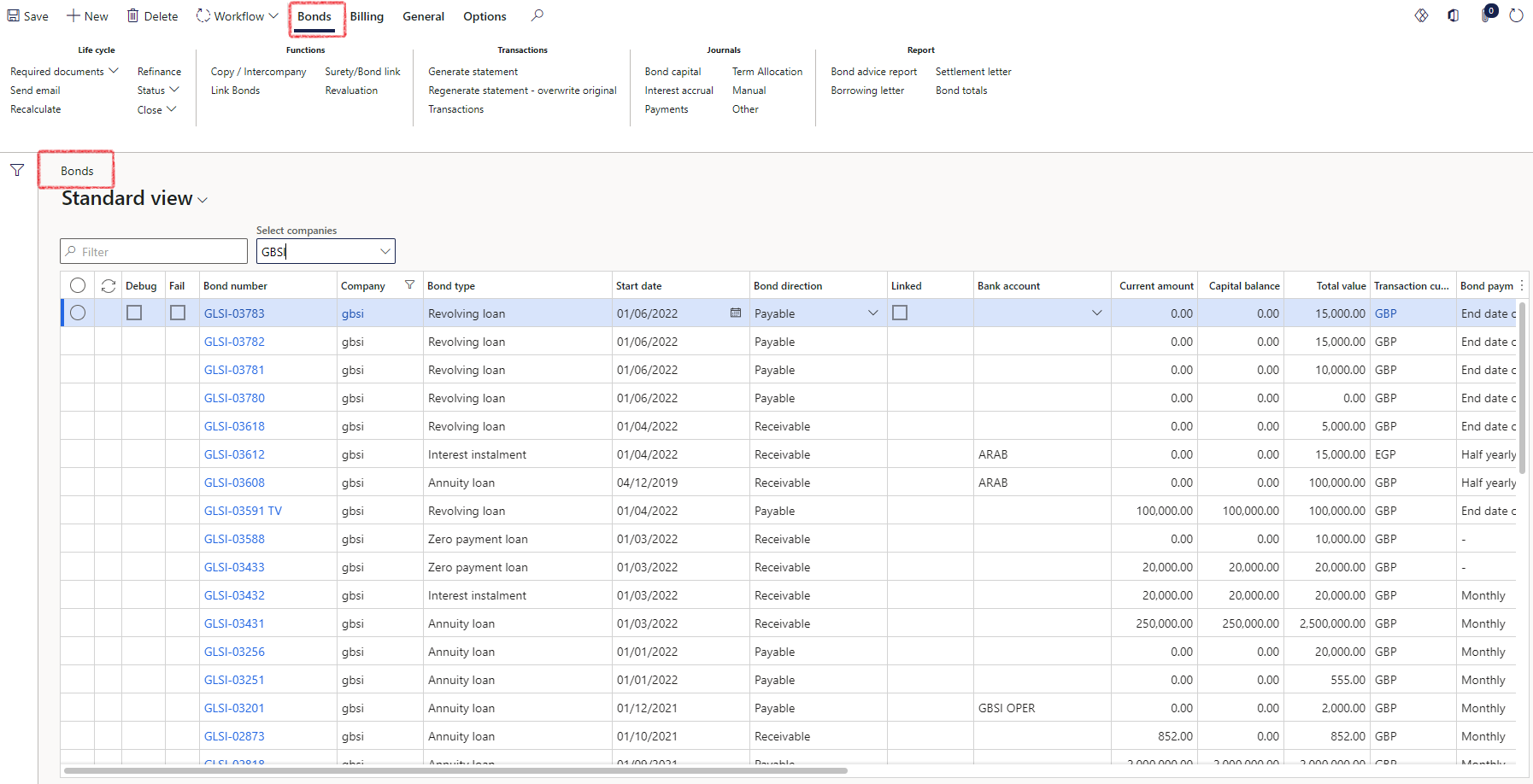
The development of TMS Bonds functionality is currently in progress.
