¶ Introduction
Definition
Utilities are goods and services provided by a utility company.
In D365FO this is typically but not limited to, electricity, gas and water.
Utility management means understanding how various energy, and water usage metrics impact your business. Measuring your use of energy and being able to identify waste or problems quickly can minimize costs. Finally, using quality, trackable, historic data to make changes can save time, energy, and money.
Energy can be procured in different forms and unit of measures, for example:
- Coal purchased in tons
- Diesel purchased in liters
- Petrol purchased in liters
- Natural Gas purchased in cubic meters
- Liquid petroleum gas purchased in GJ
- Electricity purchased in MWh
- Electricity generated in kWh
- Etc.
To calculate the company’s energy usage, all these must be converted into the same unit of measure. In short, it all comes down to the joule.
What is a joule?
A joule is a measurement of energy.
The definition of a joule can be slightly different depending on whether you are measuring electricity, fuel, or natural gas usage, but it is all energy.
For example, you can use joules to measure the energy needed to power a lightbulb or the energy needed to heat a litre of water.
Joule definition for electricity
As far as your electricity bill goes, the definition of a joule is the energy needed to emit one watt of power for one second (watt-second).
The equation for a joule is as follows: 1 joule = 1-watt X 1 second
Which means: 1 watt = 1 joule/second (one joule per second)
The equation for converting kWh to GJ is simple:
1 GJ = 0.0036 X kWh
Joule definition for natural gas
When it comes to natural gas, the definition of a joule applies to thermal (heat) energy. In other words, how much energy it takes to raise the temperature.
For context, it takes 4200 joules to increase the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius. When a water heater, for example, burns natural gas, it transfers joules of energy from the natural gas to the water in the form of heat.
What is a gigajoule?
The prefix “giga” means “billion,” so a gigajoule (GJ) equals one billion joules. This may seem like an astronomical figure, but a single joule is actually a very small amount of energy.
One GJ of natural gas has the same amount of energy as:
- 39 liters of propane
- 27 liters of fuel oil
- 26 liters of gasoline
- 277 kilowatt-hours of electricity
Water
When it comes to water usage, it may be measured in Liters, Kiloliters, or Cubic meters.
To calculate the company’s water usage, all these must be converted into the same unit of measure.
What is a liter?
Liter is a basic metric unit which is used to measure the capacity of liquids and is equal to one cubic decimeter (1 liter = 1 dm³). A liter is denoted with the letter 'l' or L.
Important notes
- Unit conversion is an important part of measurement and units are converted using the correct conversion factor of the quantity.
- 1 liter is equal to:
- 1000 milliliters
- 0.264 gallon
- 1.0566 quarts
- 2.1133 pint
- 1 kilogram
¶ Navigation
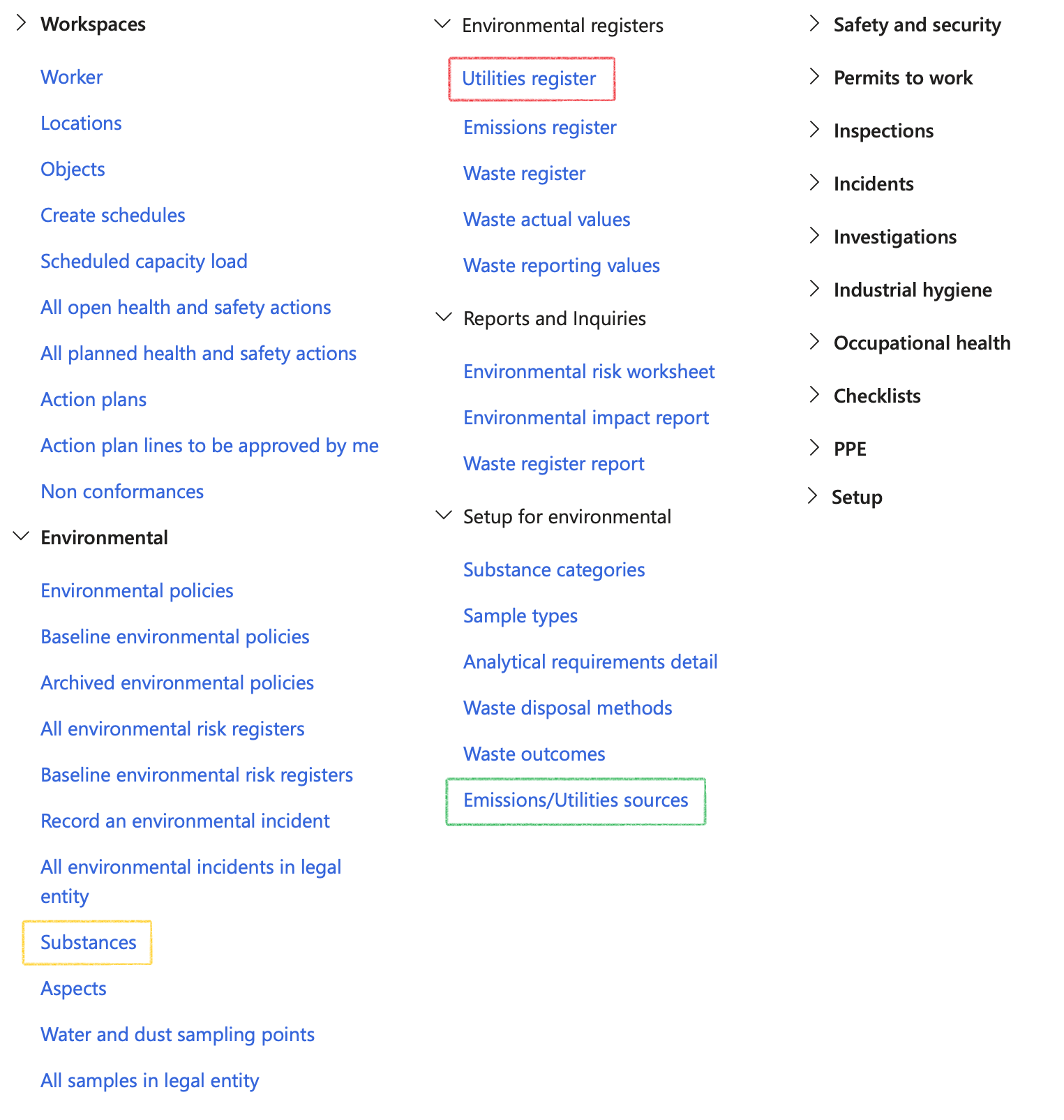
¶ Specific setups
¶ Step 1: Setup Emissions/Utilities sources
Go to: HSE > Environmental > Setup for environmental > Emissions/Utilities sources
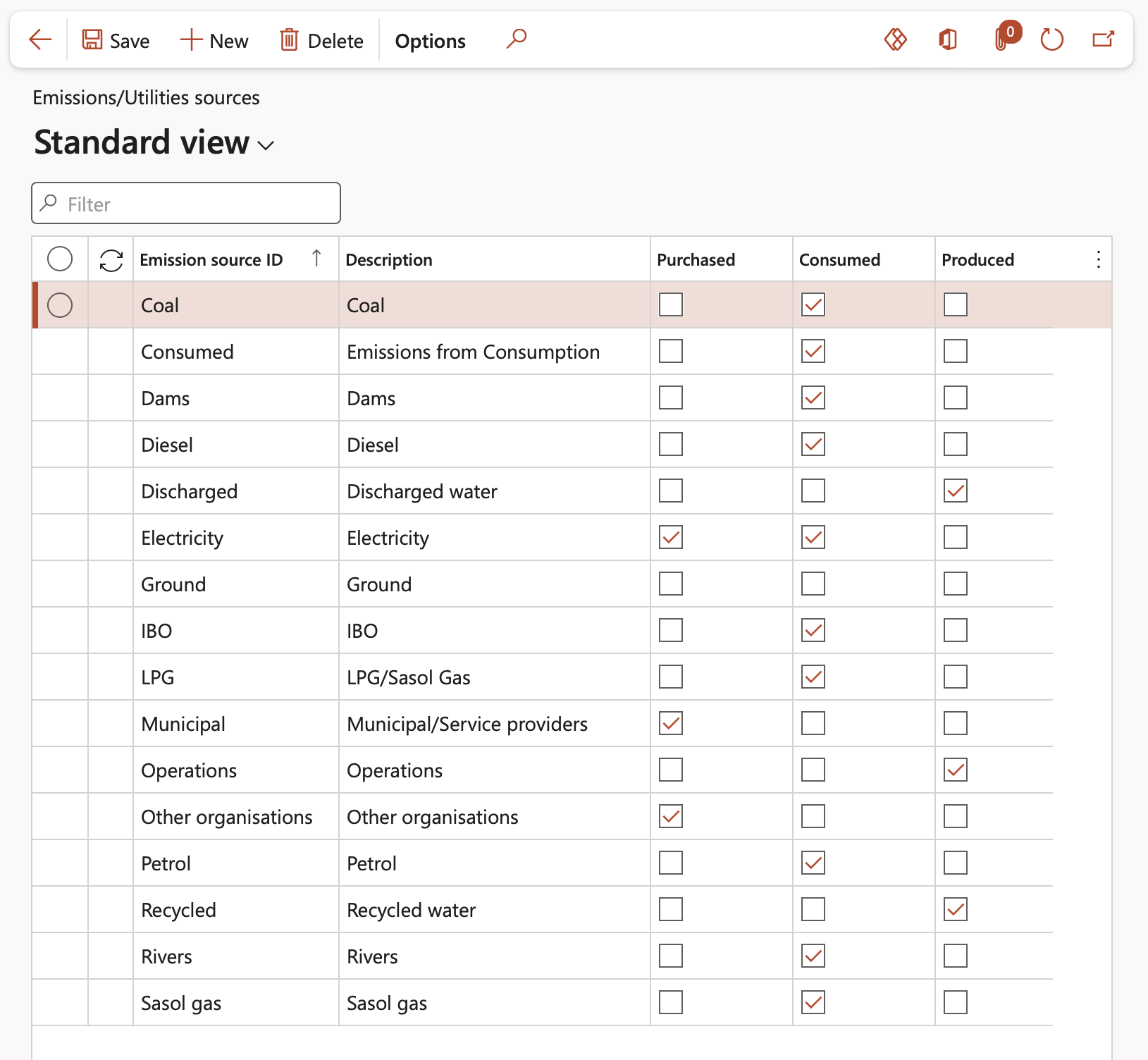
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter an Emission source ID (A unique short, but descriptive name or ID)
- Enter a brief Description of the emission source
- Indicate whether the emission is Purchased, Consumed or Produced
¶ Step 2: Create Utilities register
The Utilities register is the heart of the Utilities management system.
This form is used for the creation and maintenance of the Utilities register.
We will first concentrate on the header part of the form for now.
Go to: HSE > Environmental > Environmental registers > Utilities register
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Under the Utilities (Header) section, enter a Utilities register ID
(A unique short, but descriptive name or ID)
- Enter a brief Description of the utilities register
- Select an Item number from the dropdown list
- Select an asset Counter from the dropdown list
- Select a Site (This is very handy in a multi-site environment)
- Select a Department (This is used were actuals and targets are tracked by department, but can be left blank)
- Select the relevant Project from the dropdown list (If required)
- Select a Trading partner from the dropdown list.
- Select the Source of the emission from the dropdown list
- Enter the Planned quantity
- Select the relevant Unit from the dropdown list
- Enter the Conversion factor that will be used to calculate the Utilities substance quantity
- Select the relevant Energy unit from the dropdown list
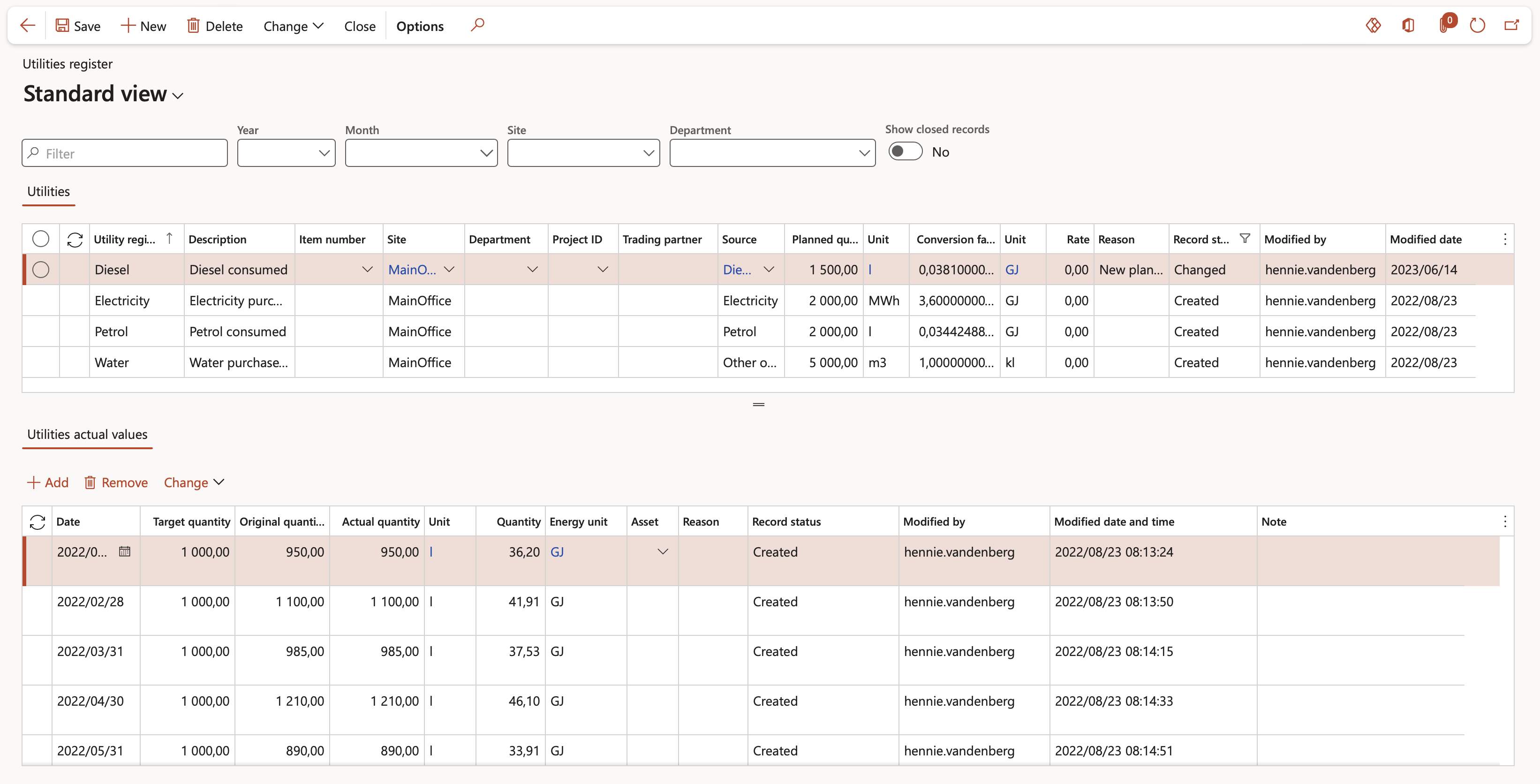
- Click on the Close button on the Action pane to close the selected record
- The user has the option to Show closed records as well
- Utilities registers can also be created from the Project
¶ Periodic tasks
¶ Step 3: Maintain targets
The target for every Utilities stream can be updated at any point.
- On the Utilities register, select the relevant record
- On the Action pane, click on the Change button
- The Change dialog will open
- Note that the Date will be recorded as today’s date
- Enter a new Planned quantity (This will become the new planned quantity for the selected record)
- Enter a Reason for changing the Planned value (For example, “New planned quantity for 2022”)
- Click on the OK button
- The Planned quantity and the Modified date, as well as the Reason will be updated
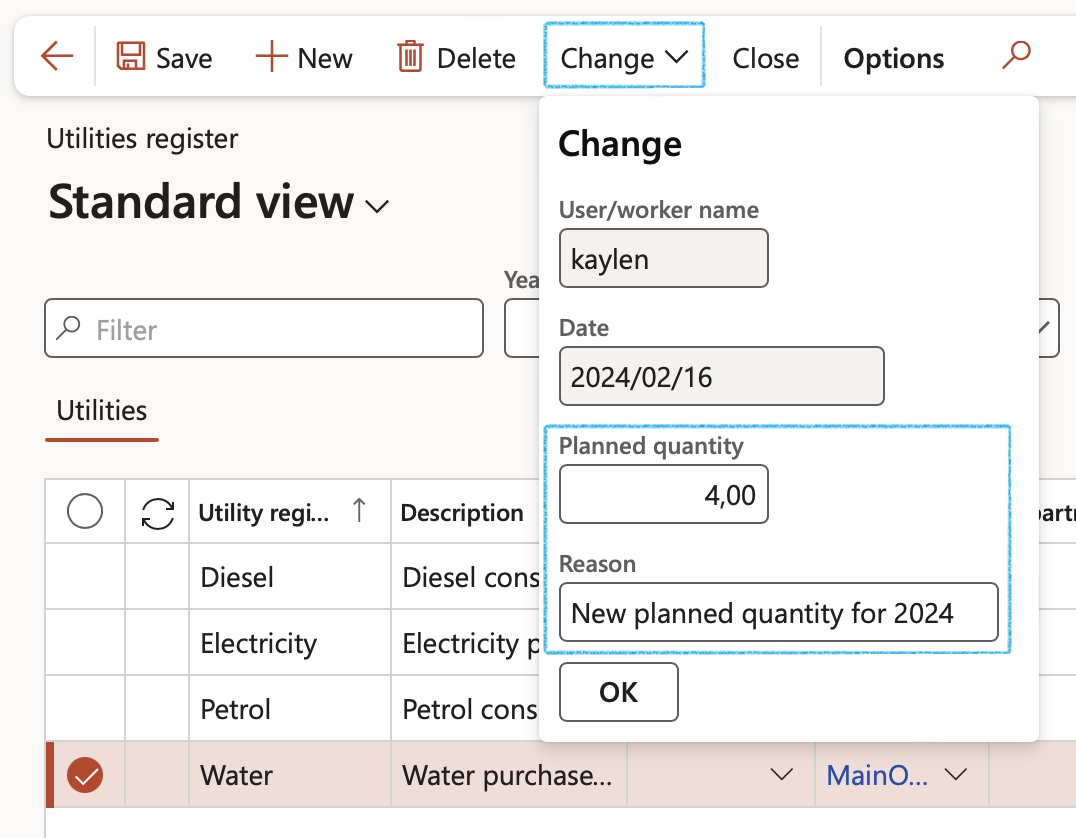
From this point forward, any new lines that are created for the actuals, will inherit the new planned quantity
¶ Step 4: Update Asset counter issue history
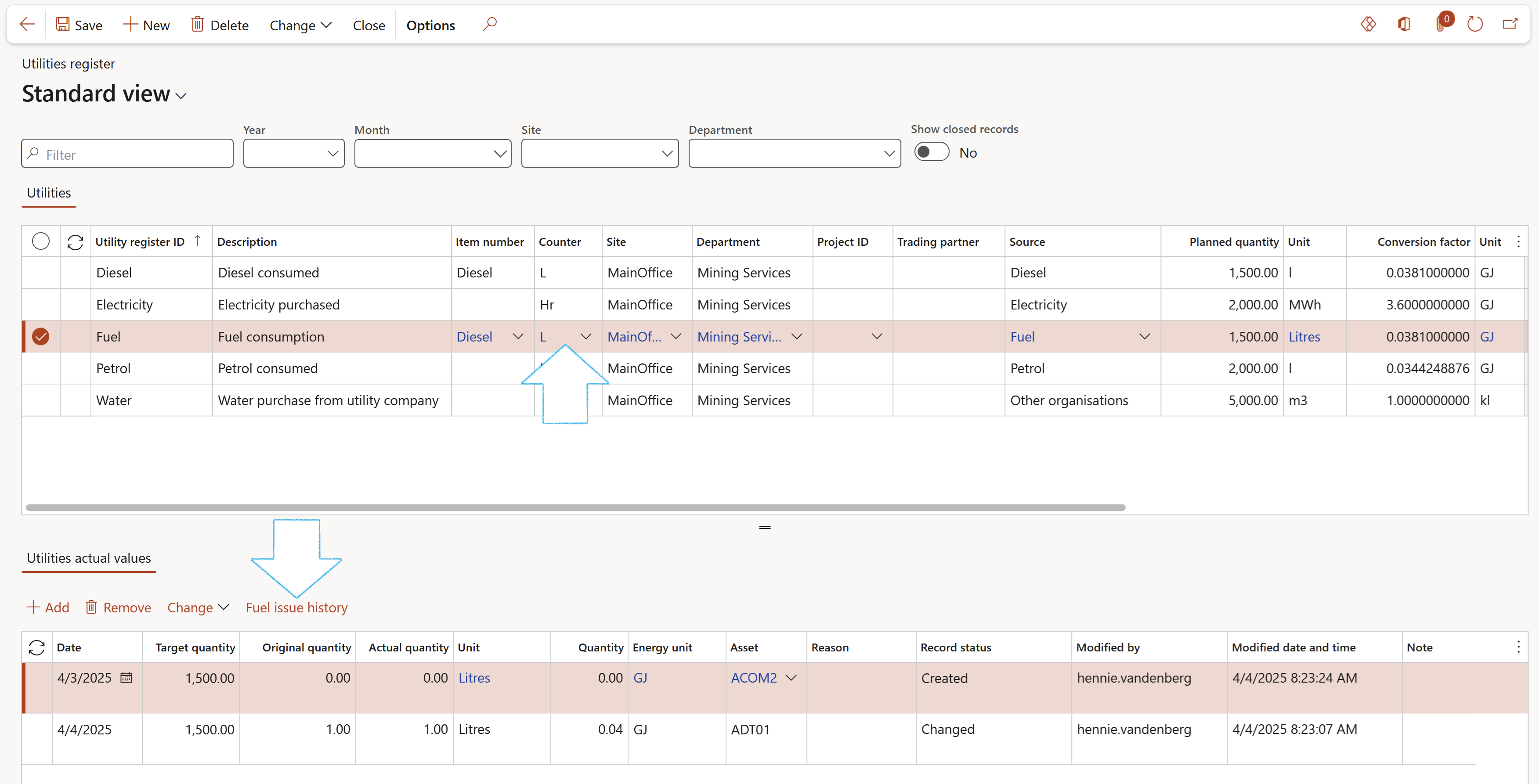
- On the Utilities register, select the relevant record in the Utilities grid
- Under the Utilities actual values grid, click on the Fuel issue history button
- The Utilities register will be updated with any missing records under the Utilities grid
The data comes from the Asset counters where the item on the asset counter is the same as the item number on the Utilities register
¶ Daily use
¶ Step 5: Add Utilities actual values
The Lines section of the Utilities register is where the actual values are recorded.
Go to: HSE > Environmental > Environmental registers > Utilities register
- Select the relevant record under the Utilities section
- Under the lines, Utilities actual values section, click on the Add button
- The Date will default to today’s date but can be edited
- Enter the Actual quantity
- The following fields in the grid will default from the header and cannot be changed on the line:
- Target quantity
- Unit
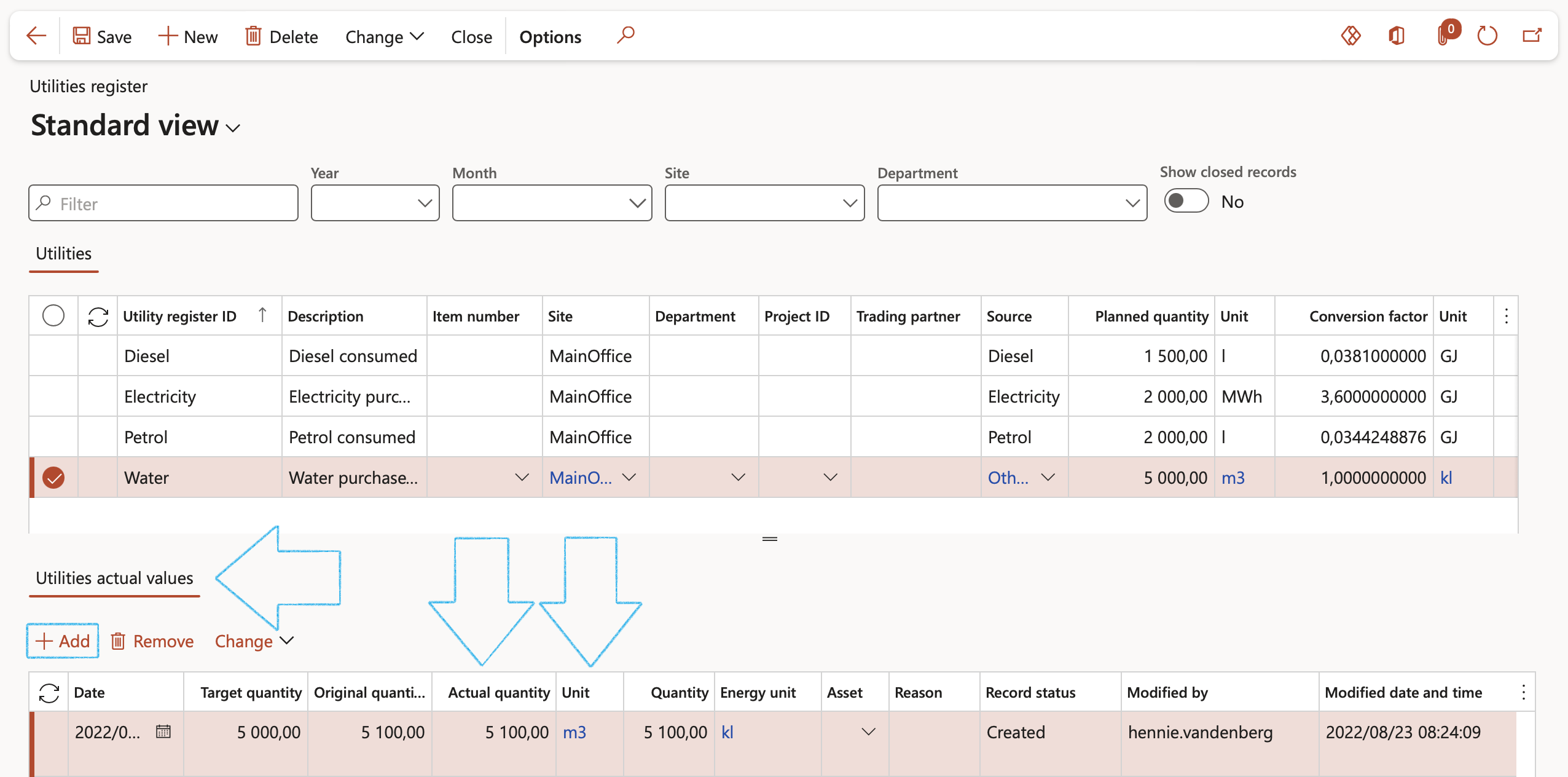
- The rest of the fields are updated by the system and will be discussed later
- There is no fixed schedule that is prescribed by the system when an actual value needs to be recorded. The client can decide when an actual value will be recorded. This can be daily, monthly, quarterly, annually, etc.
Example: The user enters the quantity of liters of diesel consumed; the system will calculate the Energy quantity by using the conversion factor on the header.
¶ Periodic tasks
¶ Step 6: Changing or correcting values
Any recorded actual value can be changed or corrected at any time
- On the Utilities register, select the record to be updated in the lines under the Utilities section
- Under the Utilities actual values section, in the Button strip, click on the Change button
- The Change dialog will open
- Note that the Date is read only and cannot be changed. This is the date when the change is made
- Enter the corrected Actual quantity
- Enter the Reason for changing the Target value (For example, “Fixed incorrect quantity”)
- Click on the OK button
- The Target quantity and the Reason will be updated. The Record status will be Changed
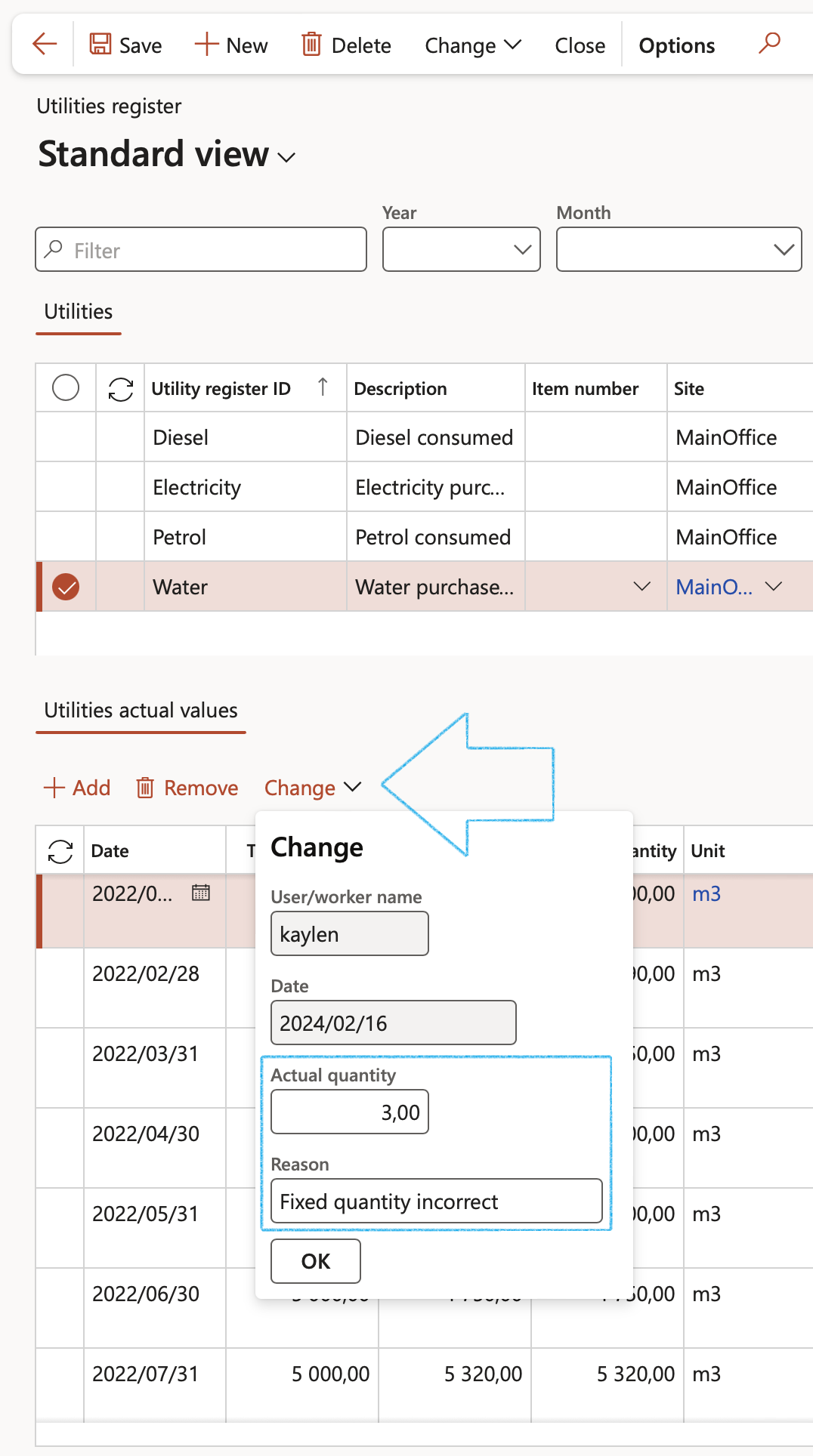
- Please note that the Actual quantity is updated with the new actual value, and will reflect the last change/correction done
- The Original quantity field is where the system stores the originally captured quantity This is updated by the system and cannot be changed by the user
- The Reason field only shows the last change to this record
- The Record status will be set to Changed
- The Modified by and Modified date and time are also updated by the system
¶ Reporting
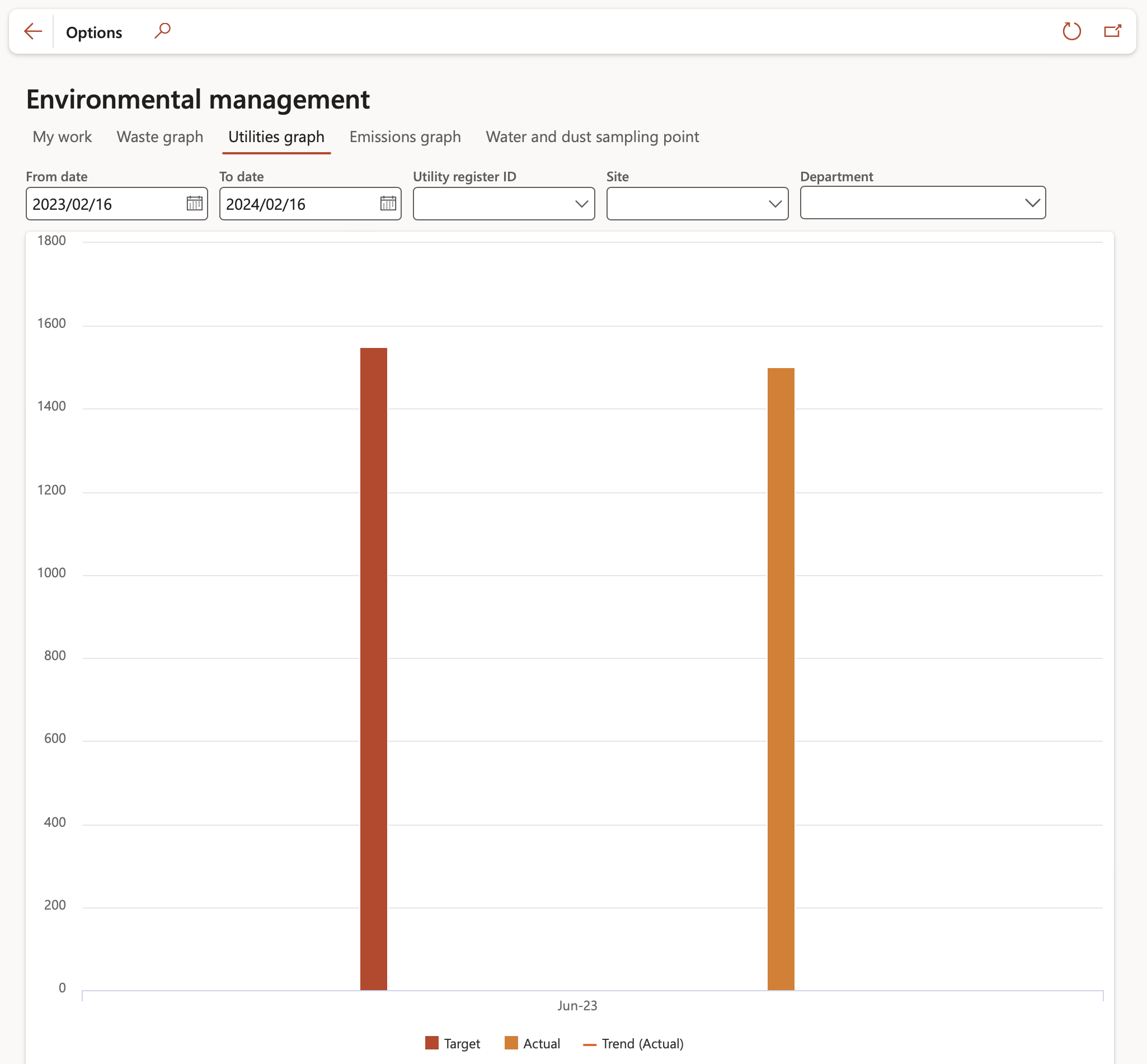
¶ Step 7: Utilities trend graph
Displays the trend of actual values per emission type per department over a period
Go to: HSE > Worksapces > Environmental management > Utilities graph
- Use the filters to refine your search