¶ Introduction
Business systems were developed based on generic requirements of various types of organizations; from diverse business segments it evolved through continuous adding support for new business processes. Consequently business system now offers numerous functionalities, which overwhelm most of the enterprises, during project implementation.
Configuration of a business system deals with numerous "usage controls", which can be switched off or on, so as to balance its functionalities to user needs. First thing to happen is to install specific modules needed and configuring these modules, as per the scope of the project. Thousands of configuration rules are present, which define how the system should work etc.
¶ Microsoft D365 F&O setups
¶ Users
Before you can access finance and operations apps, you must first be added to the Users page (System administration > Users > Users). Users include internal employees of your organization, or external customers and vendors. Users can be imported or added manually. All users must be correctly licensed for compliant use.
To manually add a user:
- Go to System administration > Users > Users.
- On the Action Pane, select New.
- In the User ID field, enter a unique identifier for the user.
- In the User name field, enter the user's name.
- In the Provider field:
- For internal users, use the defaulted value. For example, your Azure AD tenant prefixed with https://sts.windows.net/.
- For non-Azure AD users, such as Service-2-Service accounts, enter a basic text value. For example, NA. This value will help avoid incorrect authentication calls that might result in errors if a valid identity provider value is used.
- For external or guest users, add their Azure AD tenant name after https://sts.windows.net/.
- In the Email field, enter the user's full Email/User Principle Name.
- In the Company field, select the default startup company for the user.
- Select Save.
¶ Workers
The Worker list is HRM master data and is the key to every personnel related action in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Human Resources. Businesses can register lots of information about their workers. An organisation must thoroughly analyze its needs before it starts to create HR master data setups. This avoids managing data that does not directly benefit the company.
Records for your various types of workers are important to your human resources and payroll systems. The information that you enter can be used to track workers and personal information, to write letters, and to print reports. It is important to keep up-to-date information to reflect the current activities of your workers and of your companies, legal entities, and organizations.There are two worker types: Employee and Contractor.
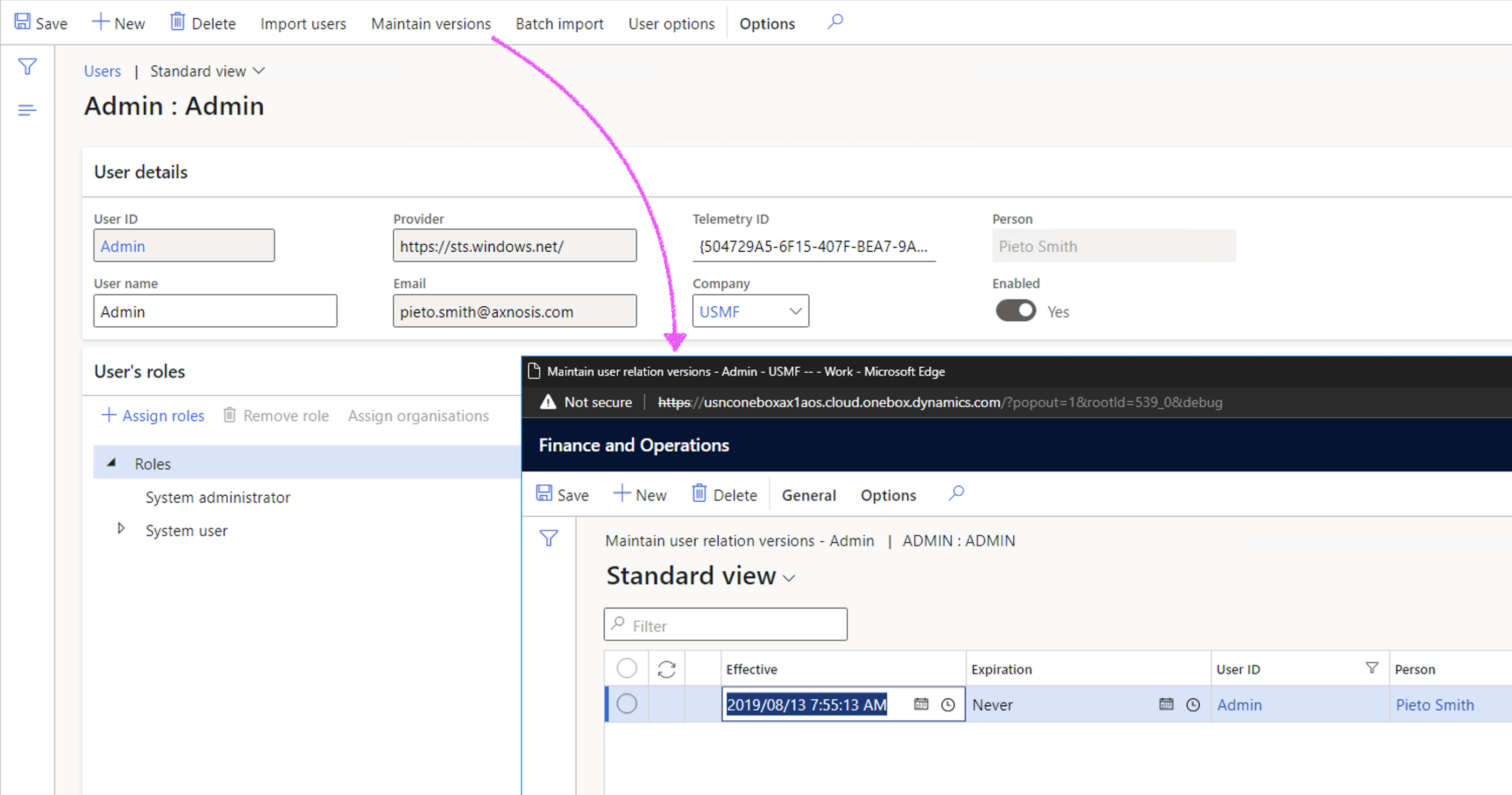
It is imperative for workers to be linked to users via the Maintain user relation versions from the users detail form.
¶ Legal entities
A legal entity is an organization that is identified through registration with a legal authority. Legal entities can enter into contracts and are required to prepare statements that report on their performance. The following procedure explains how to create a legal entity. The demo data company used to create this procedure is USMF.
- Go to Navigation pane > Modules > Organization administration > Organizations > Legal entities.
- Click New.
- In the Name field, type a value.
- In the Company field, type a value.
- In the Country/region field, enter or select a value.
- Click OK. In the General section, provide the following general information about the legal entity: Enter a search name, if a search name is required. A search name is an alternate name that can be used to search for this legal entity. Select whether this legal entity is being used as a consolidation company. Select whether this legal entity is being used as an elimination company.
¶ Numbering sequences
Number sequences are used to generate readable, unique identifiers for master data records and transaction records that require identifiers. A master data record or transaction record that requires an identifier is referred to as a reference.
Before you can create new records for a reference, you must set up a number sequence and associate it with the reference. We recommend that you use the pages in Organization administration to set up number sequences. If module-specific settings are required, you can use the parameters page in a module to specify number sequences for the references in that module. For example, in Accounts receivable and Accounts payable, you can set up number sequence groups to allocate specific number sequences to specific customers or vendors.
When you set up a number sequence, you must specify a scope, which defines which organization uses the number sequence. The scope can be Shared, Company, Legal entity, or Operating unit. Legal entity and Company scopes can be combined with Fiscal calendar period to create even more specific number sequences.
Number sequence formats consist of segments. Number sequences with a scope other than Shared can contain segments that correspond to the scope. For example, a number sequence with a scope of Legal entity can contain a legal entity segment. By including a scope segment in the number sequence format, you can identify the scope of a particular record by looking at its number.
In addition to segments that correspond to scopes, number sequence formats can contain Constant and Alphanumeric segments. A Constant segment contains a set of letters, numbers, or symbols that does not change. An Alphanumeric segment contains a set of letters or numbers that increment every time that a number is used. Use a number sign (#) to represent incrementing numbers and an ampersand (&) to represent incrementing letters. For example, the format #####_2017 creates the sequence 00001_2017, 00002_2017, and so on.
¶ Number sequences for completeness
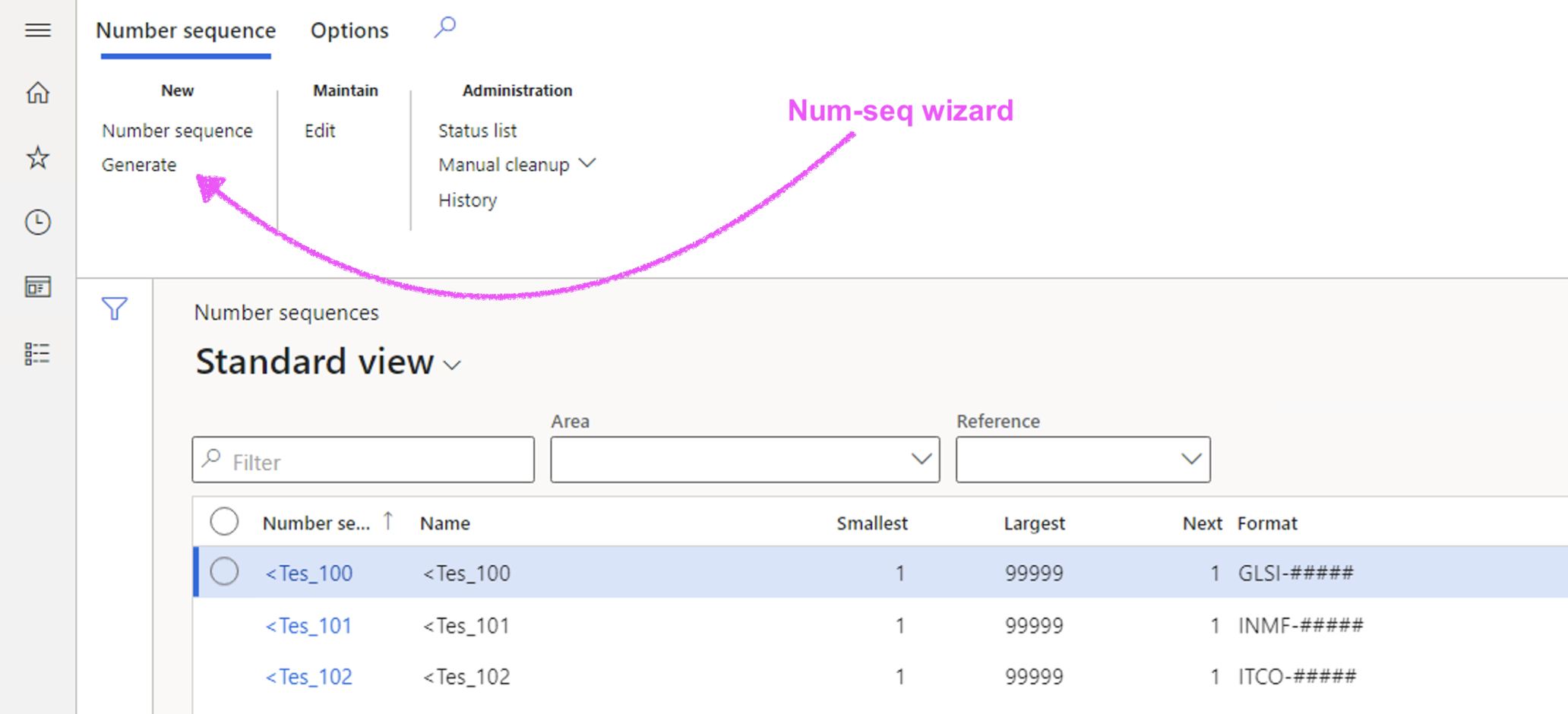
Using the Generate button; users are guided and D365 will propose/create numbering sequence records for all transactions and some master data objects.
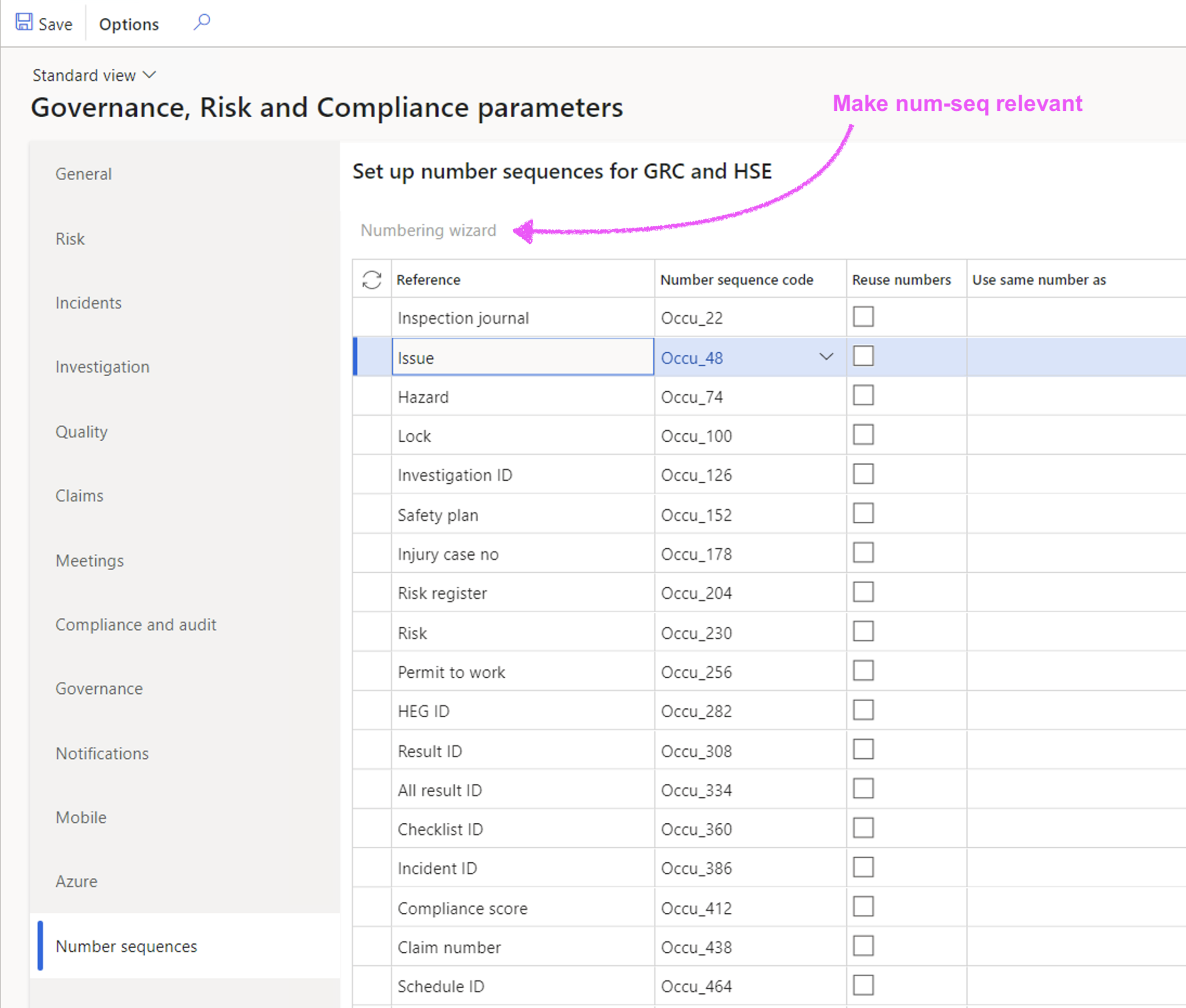
¶ Number sequences for relevance
Then using the Numbering wizard button; D365 will change the numbering sequence records format to the relevant area (reference) being used. For example; Inspection journals; the wizard will change the generic scope text change to "Ins".
¶ Sites (inventory storage)
Inventory dimensions are assigned to products (items). Before you can assign inventory dimensions, you must set up inventory dimension groups.
The inventory dimensions can be assigned to inventory dimension groups:
|
Product dimension group:
|
Storage dimension group:
|
Tracking dimension group:
|
¶ Departments
Departments are operating units that represent a functional area of a business, such as sales or accounting. Many companies have organizational hierarchies that display the various departments within a business. This procedure walks through the process of creating departments, and adding those departments to an organizations departmental hierarchy.
¶ Items (Products)
In Microsoft Dynamics 365 items and products are referred to interchangeably. A product name is always associated with an item ID. The main concepts that are associated with items are product, product master and product variant.
- Product – A fixed product definition that does not include any variations
- Product master – A product definition that forms the basis of product variants
- Product variant – Products that are based on a product master. Product variants are made distinct through the product dimension setup and through configurations
Products are used throughout Microsoft Dynamics 365. This includes procurement, sales, and projects. You can use the On-hand inventory page to view which products are on hand.
¶ Resources
“Operations” resources are the machines, tools, workers, facilities, physical areas or vendors that perform the activities of a project or a production process. They can be of different types and can have different capabilities.
- Vendor – An external resource that performs project activities or production operations. An example is a subcontractor. By linking vendor resources to a vendor account, you can generate purchases for subcontractors, based on the bill of materials (BOM) lines or production lines.
- Human resources – A project or production worker that perform an activity, either alone or as an operator of a tool or a machine. If you're using the Human resources functionality, you can link human resources to a worker. The scheduling engine can then allocate the resources, based on the competencies that are defined for the corresponding worker.
- Machine – A machine or other production equipment that is required in production.
- Tool – An instrument or device that is typically used together with another resource to perform an activity in a project or in production.
- Location – A physical location of a specific size that is required in order to perform an activity. An example is an assembly area.
- Facility – A building or fixed structure that is required in order to perform an activity.
