¶ Introduction
The role of internal audit is to provide independent assurance that an organisation's risk management, governance and internal control processes are adequate and operating effectively.
Normally Internal audit is risk based. Therefore, it is imperative for an audit to have visibility and access to the risk registers and related functions.
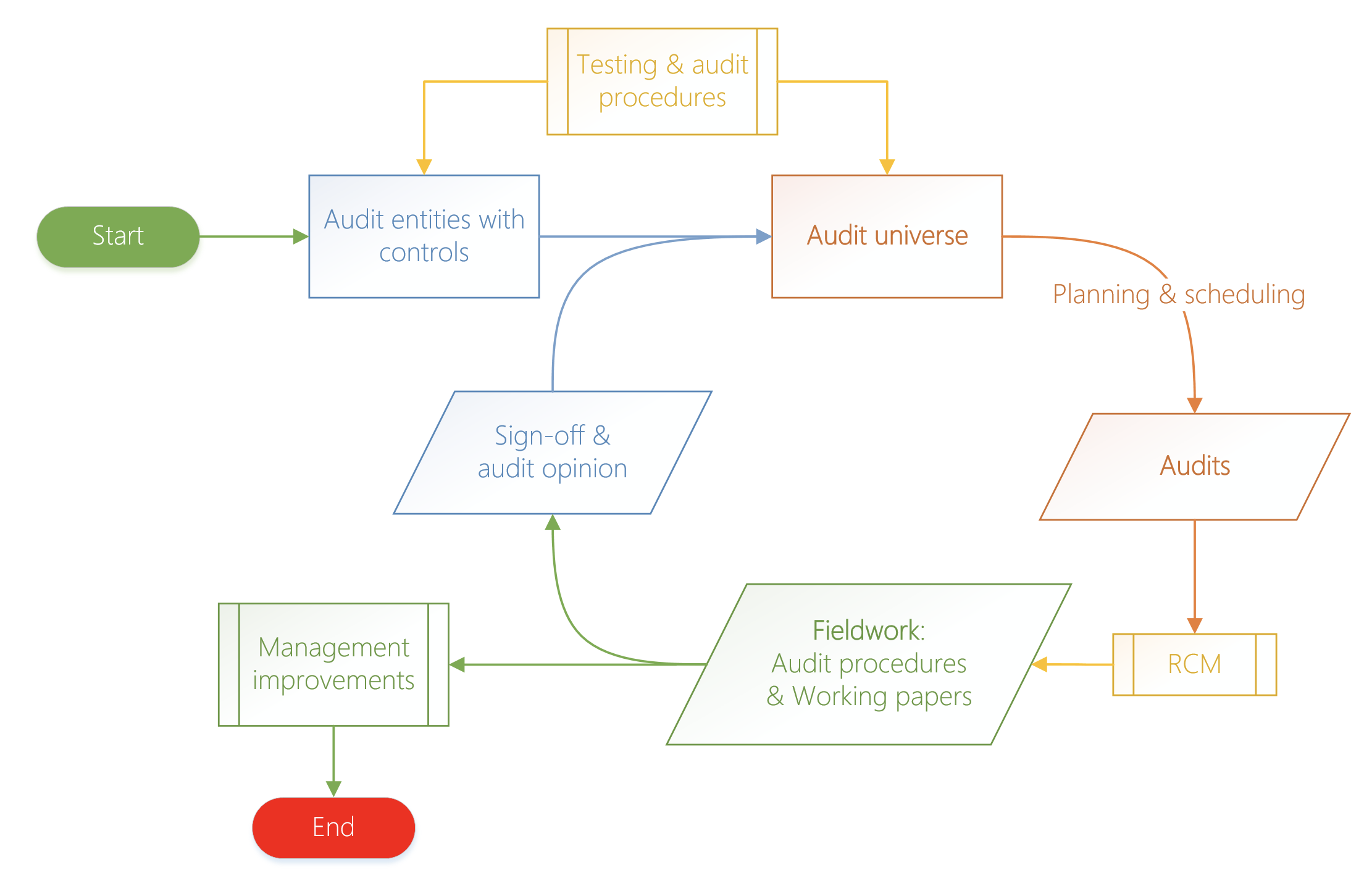
In practice the internal audit function can be summed up (see diagram below) with these items:
- List of entitites to be audited inclusive of controls and its effectiveness
- List of controls explaining types, frequency and
- List of testing procedures with time frames to complete them
- An Audit "universe" which collects entitites that will be audited
- Based on above, the creation of a formal Audit and supporting Audit file(s)
- A list of the audit Risk & Control Matix ('RCM') with sampling rules
- Finaly Fieldwork where auditors raise findings, complete audit procedures and generate Working papers
¶ Navigation

¶ Specific setups
¶ Step 1: Parameters
This form is used for system wide control of functions. The important and relevant ones are dealt with below.
¶ Step 1.1: Compliance and audit Bullet
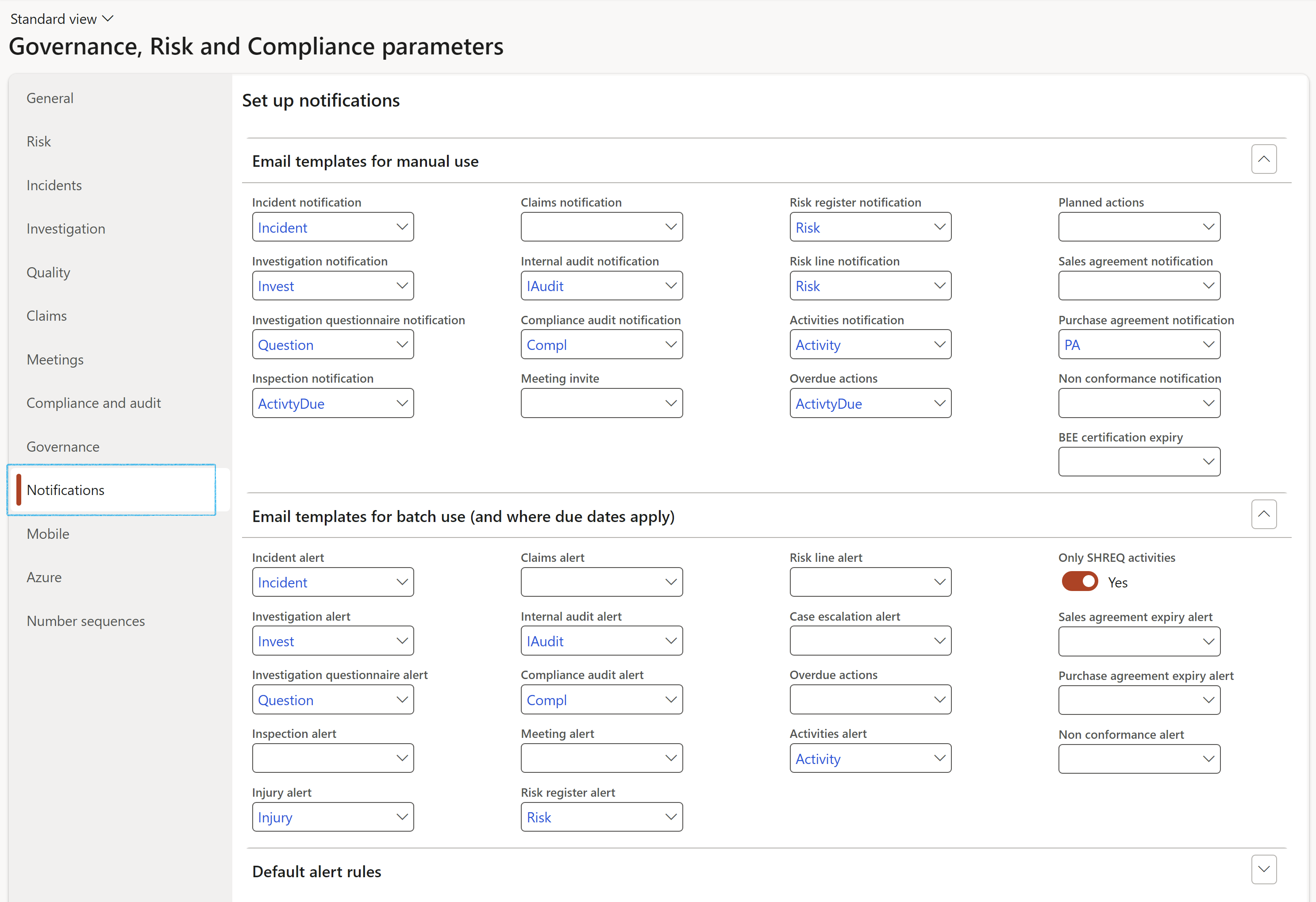
Go to: GRC > Setup > Governance, Risk and Compliance parameters
Users can select rules to be used when controls are scored for effectiveness.
Dynamics 365 GRC supports ISO Audits and Internal Audits.
Select the group of users that will work with Internal Audits.
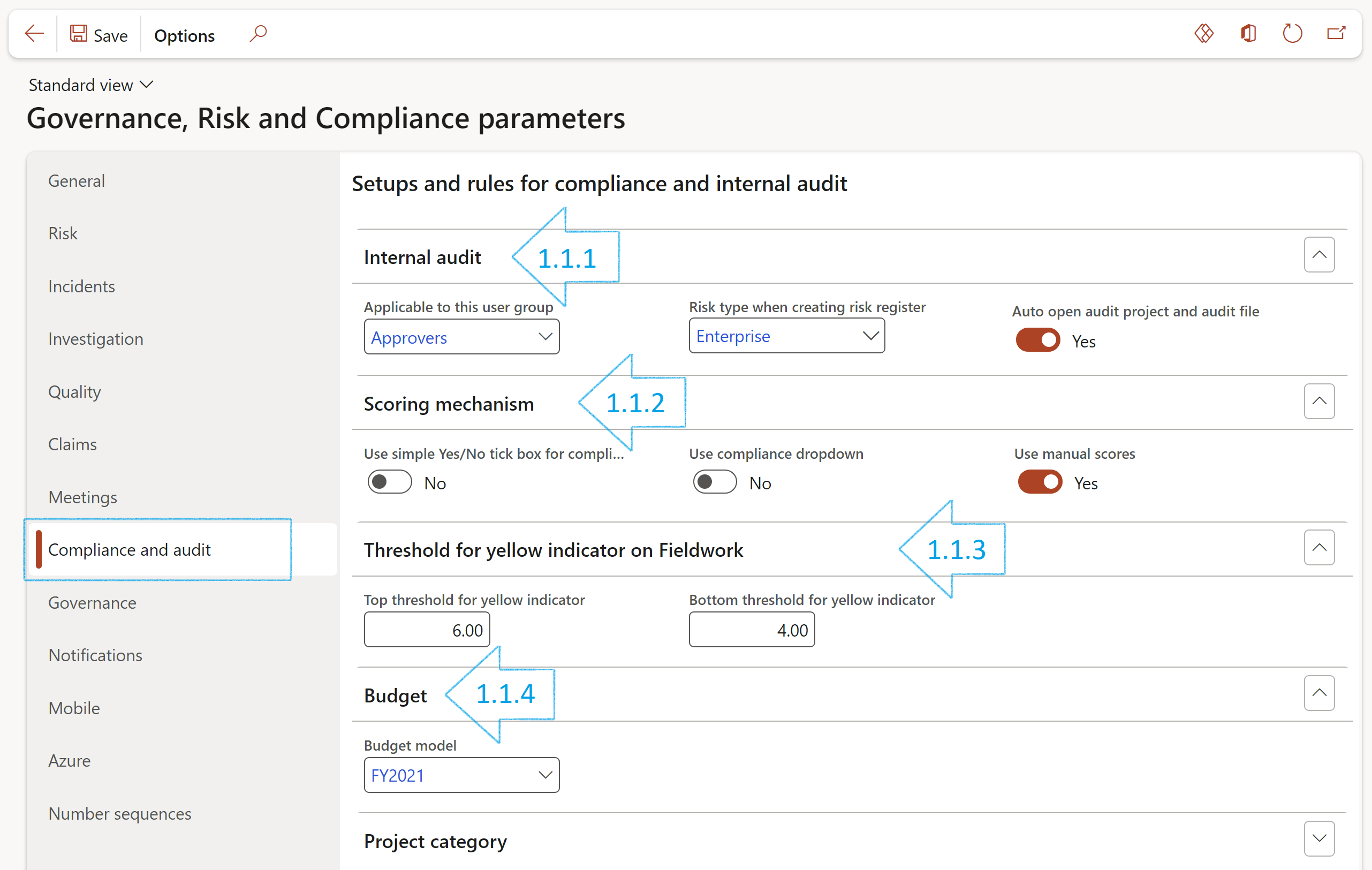
¶ Step 1.1.1: Internal audit Fast tab
- In the Applicable to this user group field, select the relevant group from the dropdown list
- In the Risk type when creating risk register field, select the relevant type for when a risk assessment is done from the risk & control matrix (RCM).
- If the Auto open audit file slider is set to Yes, the audit file will be started and the declaration done
The Internal audit user group is critical. Only users in this group can interact with the forms, functions and reports of Internal audit. Reasons are obvious. Audit data is sensitive and certain data must be "ring fenced".
¶ Step 1.1.2: Scoring mechanism Fast tab
The user can do the following:
- Choose to use a simple Yes/No tick box for fieldwork
- Choose to use values from a dropdown list
- Enter % values to use as upper and lower limits to determine the compliance indicator
These rules are default for all types of audits, but D365 allows different scoring rules for every Audit type. Refer to Step 7 below.
¶ Step 1.1.3: Threshold for yellow indicator on Fieldwork Fast tab
- Select the top threshold for the yellow indicator
- Select the bottom threshold for the yellow indicator
In the example below, the top threshold for yellow indicator is set on 6 because the Expected score is 10.
Because the Expected score is 10, the bottom threshold for yellow indicator is set on 4.
¶ Step 1.1.4: Budget Fast tab
Select a default Budget model for audit purposes. Thus, when planning for an audit, users will choose from the budgets in Dynamics 365, but filtered on the model selected here on the Parameters form.
¶ Step 1.2: Notifications bullet
Users choose which email templates to use for sending email notifications for audits to be done. This is applicable when auditors engage in an audit from the Area of compliance.
¶ Step 2: Case setups
Auditors can record audit findings while performing Audit procedures and completing the Fieldwork. Two types of audit findings are support. Audit issues (less critical) and non conformances (critical). Audit issues result in cases being created. For Audit issues (cases) the following setups are needed:
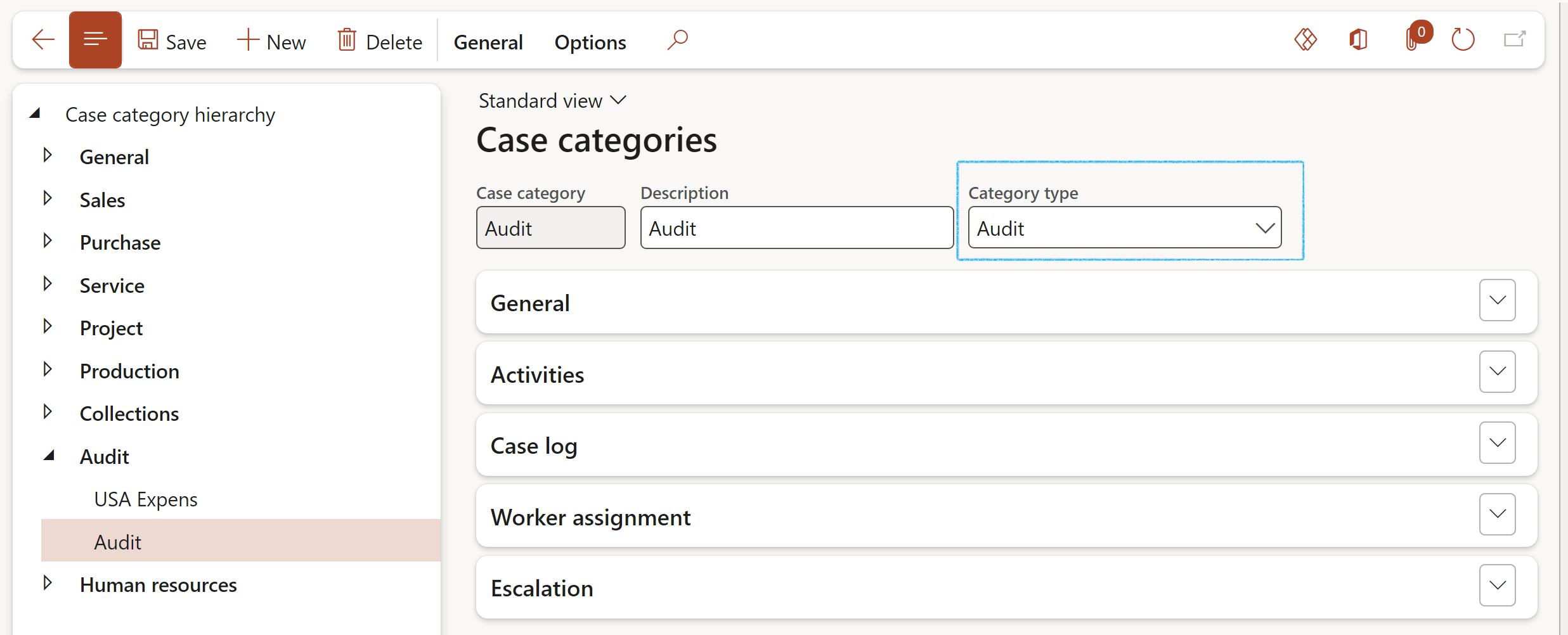
¶ Step 2.1: Setup Case categories
Remember to setup a Case category of type Audit to use when recording an audit issue.
Go to: GRC > Governance > Setup for governance > Case categories
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter the Case category and a brief Description
- Select the relevant Category type from the dropdown list
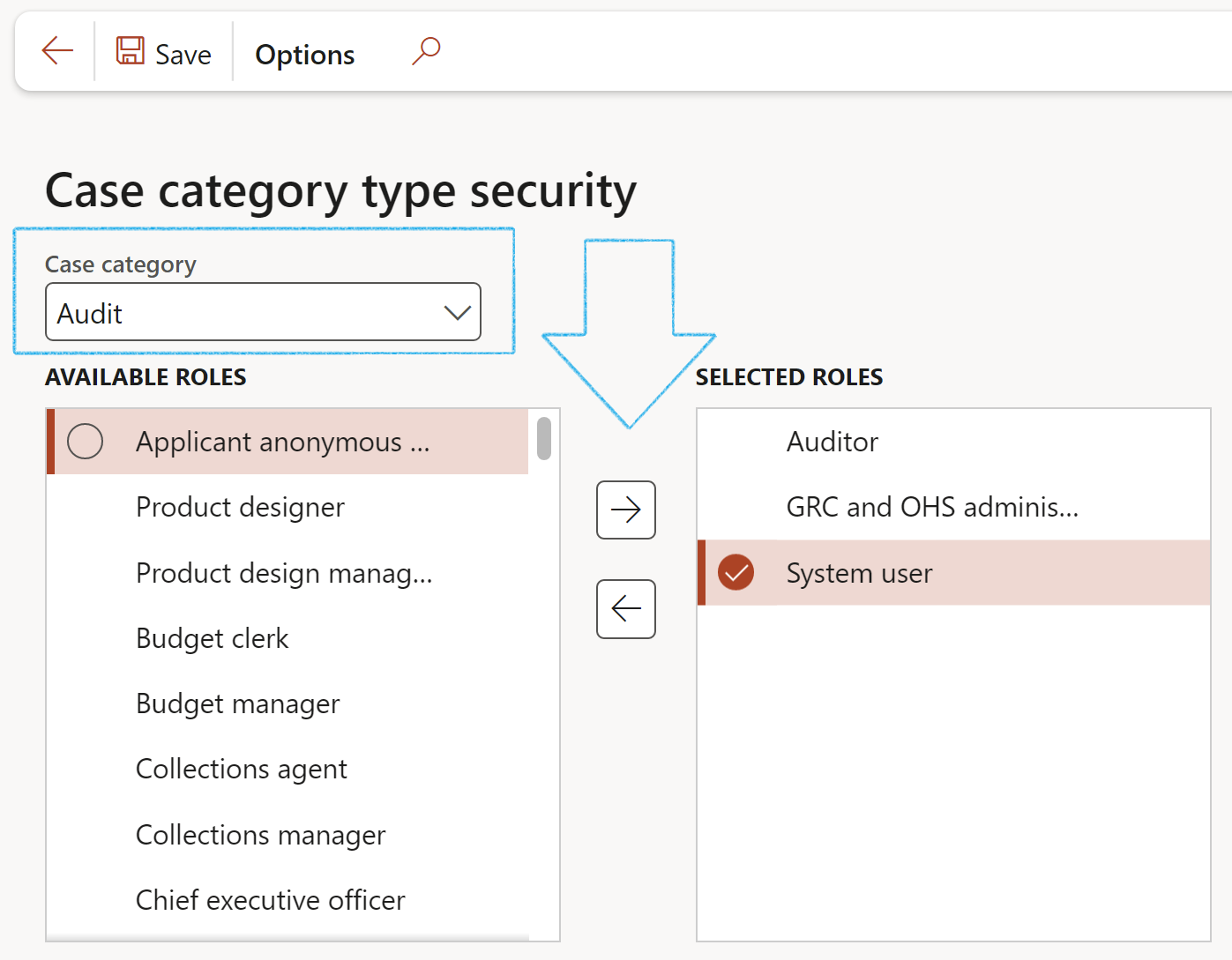
¶ Step 2.2: Setup Case category type security
By selecting roles for the Case category type security, only users with these roles assigned to them, will have the privilege to create a New contract request/Request for contract review.
Go to: Organization administration > Setup > Cases > Case category type security
- Select the Case category from the dropdown list
- Select the required role/s from the Available roles list
- Click on the right pointing arrow button to move the selected role/s to the Selected roles list
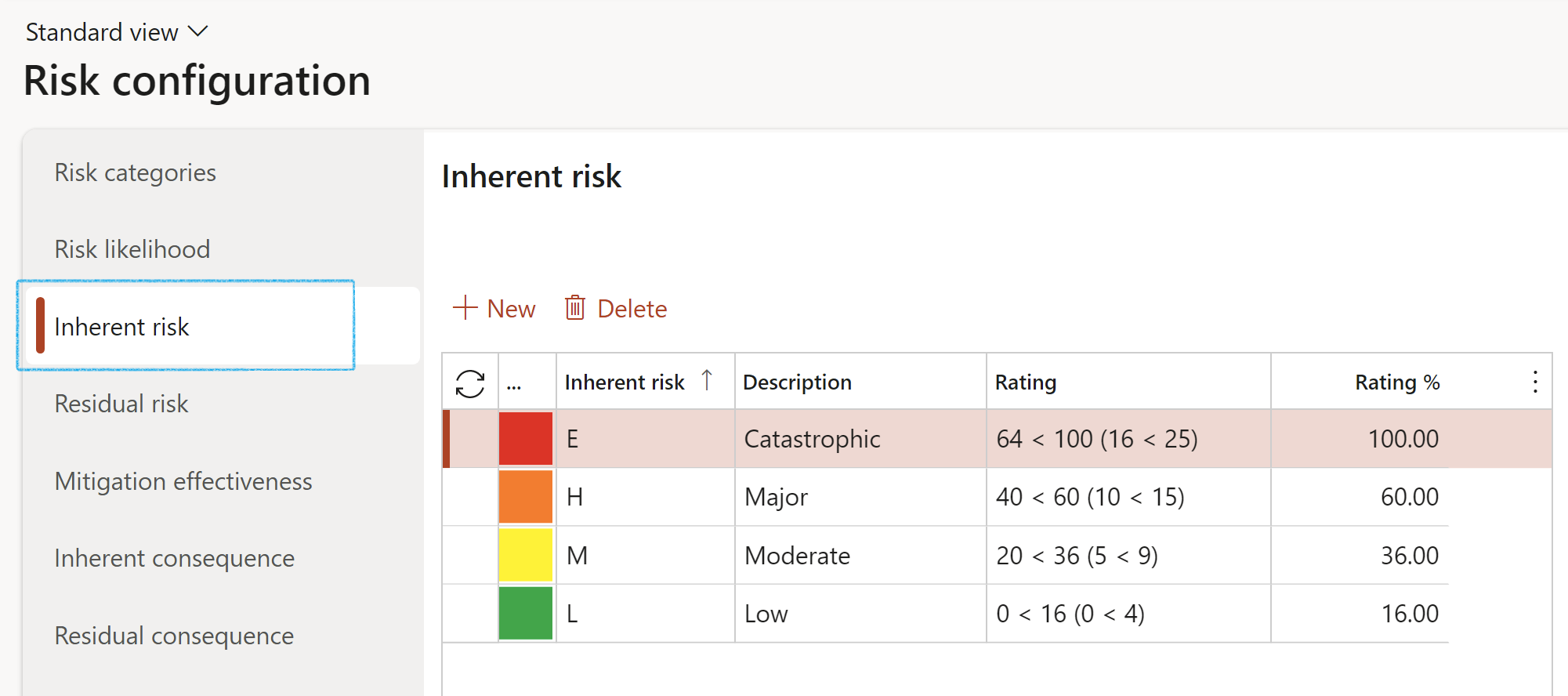
¶ Step 3: Setup Risk configuration
Dynamics 365 GRC aids auditing by supporting a risk-based approach. For this, users must define Risk categories, and in particular, Inherent risk values. these are used on auditable entitites; audit universe and in particular on the RCM. See Step 19.
Go to: GRC > Risk > Setup for risks > Risk configuration
- Click on the Inherent risk tab
- Click New
- Select the Inherent risk from the dropdown list and enter a brief Description
- Enter the Rating as well as the Rating percentage
- Click on the Save button
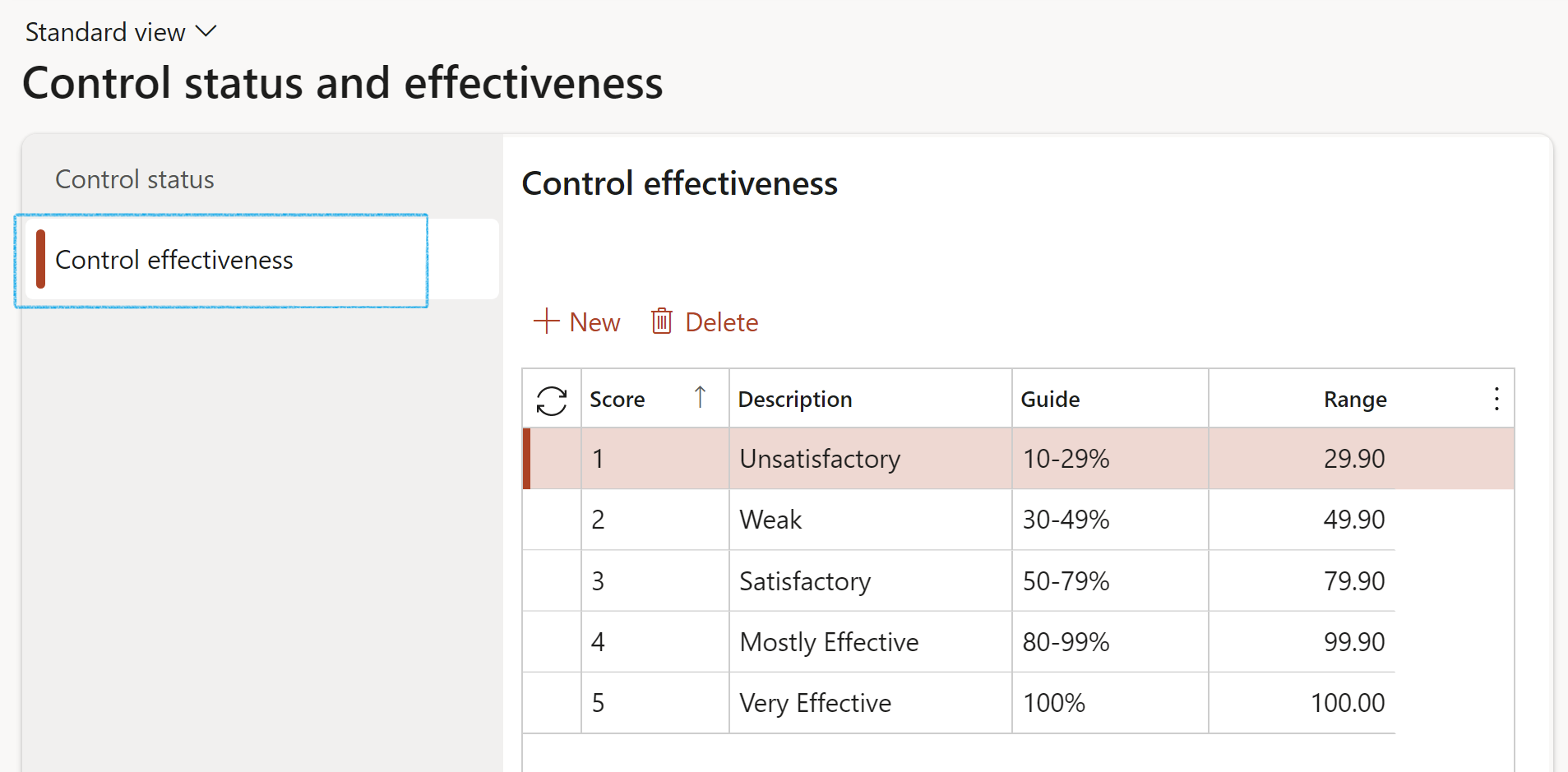
¶ Step 4: Control status and effectiveness
This form contains the Control effectiveness. These values are used as lookups on the Auditable entities.
Go to: GRC > Risk > Setup for risks > Control status and effectiveness
- Click on the Control effectiveness bullet
- Click New
- Select the Risk score level from the dropdown list and enter a brief Description
- In the Guide field, enter description details
- Enter the upper percentage value of the score range
- Click Save
¶ Step 5: Create Goals
When planning an audit, auditors might want to achieve a specific goal. A lookup to the Goals form exist on the header section of the Audit universe. the records being used is from the Goals base table.
Go to: HR > Performance > Goals
¶ Step 5.1: Setup Goal category
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Goal category
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- In the Goal category field, enter an identification for the goal category
- In the Description field, enter a brief description of the goal category
- The Active tick box indicates whether new goals can be related to the goal category
A Goal category is selectable when the Audit scope, goal and rationale (SGR) are specified - on the Audit
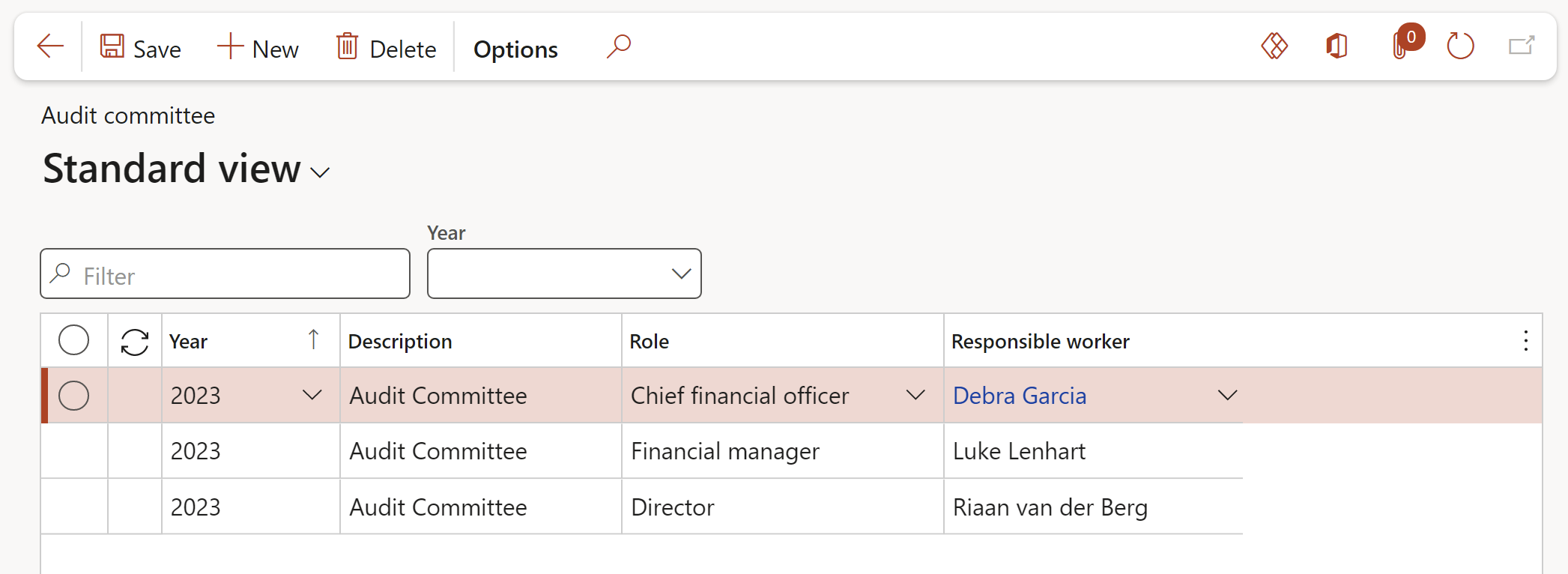
¶ Step 6: Audit committee
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Setup for internal audits > Audit committee
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Select the Year that the committee was selected for
- Enter a Description for the committee
- Select the relevant Role of the worker from the dropdown list
- Select the Responsible worker from the dropdown list
¶ Step 7: Audit type
Users must define types of audits. This is imperative as the type of audit will guide D365 GRC to add or remove functionality. In specific internal audit functions differ from compliance type (ISO etc.) audits.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Setup for internal audit > Audit type
- Click on the New button
- Enter a unique Audit type ID
- Enter a brief Description of the Audit type
- If the box is ticked in the Manual audit field, an audit will be created with the following limitations:
- Schedule will not be auto-approved
- Audit file will not be created
- In the Team field, select the team that will be responsible for the selected audit type
- Select the relevant Job plan from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Budget from the dropdown list
- Indicate which scoring method should be used
- Select the relevant Email template from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Declaration rules from the dropdown list
- Click on the Save button
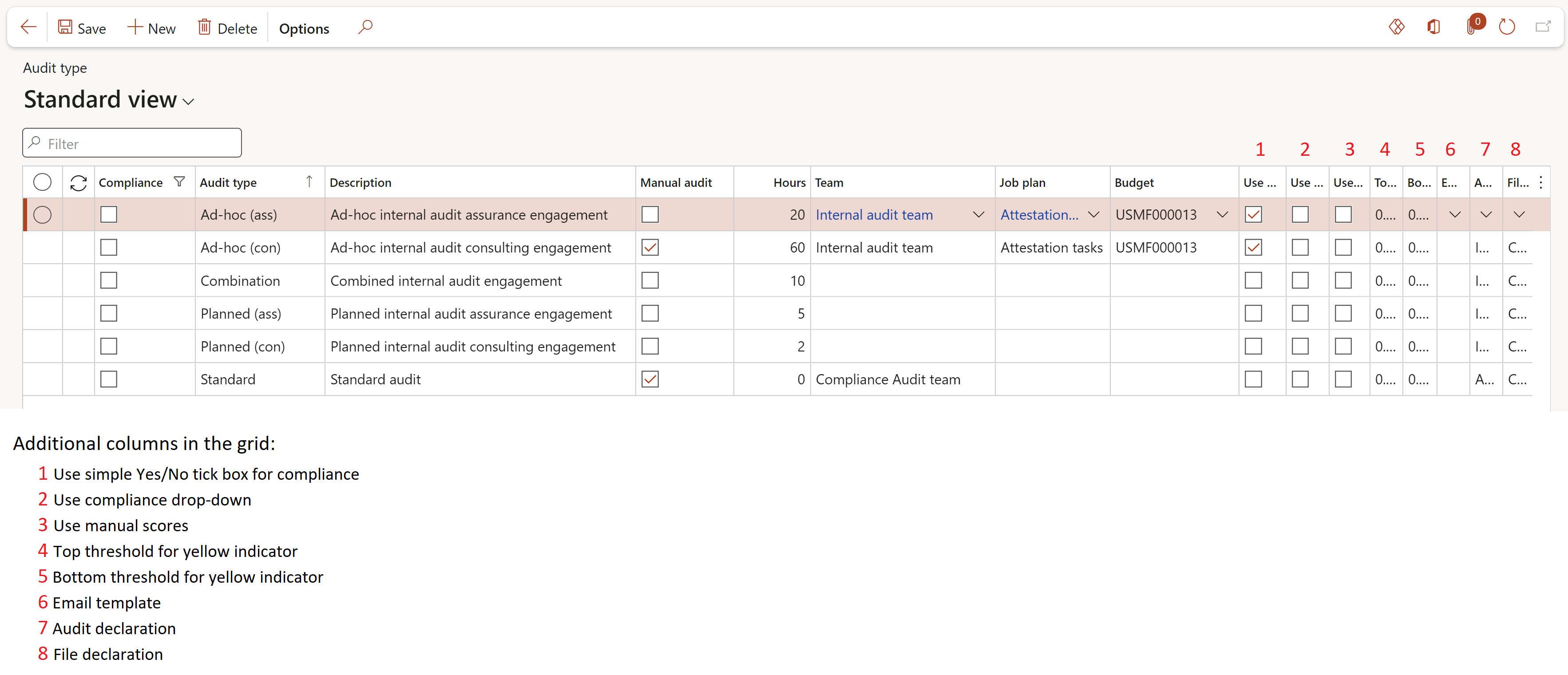
- If a team is not selected here, individual Auditable entity clause lines cannot be assigned to a Planned user to audit
- If no scoring method is specified on the Audit type, the scoring method specified on the Parameters will be used
- These values default to the scope of the Audit universe
¶ Step 8: Audit procedures
Audit procedures are the techniques, processes, and methods that auditors use to obtain reliable audit evidence. We use checklists created form a Job plan of type Audit. Audit procedures are performed in order to test financial statement assertions. Therefore, the first step in explaining an audit procedure is to identify the assertion that needs to be tested.
A brief explanation of the various assertions is as follows:
Completeness - This means that all transactions have been recorded in the financial statements, i.e. all assets, liabilities, equity interests (capital and reserves) and other disclosures, have been included in the financial statements.
Occurrence - This assertion means that transactions and events and other matters that have been recorded, actually took place, and relate to this organisation.
Valuation and allocation - This means that all items have been included in the financial statements at appropriate amounts according to company policy and the relevant financial reporting framework. Furthermore, any allocations or valuation adjustments required (like impairment) have been made and financial and other information is disclosed fairly and at appropriate amounts.
Classification and understandability - Financial information is appropriately presented and disclosed, and disclosures are clearly expressed so as to make them understandable to the users. For this, the disclosures should use simple language and state matters clearly and concisely.
Accuracy - Accuracy means that amounts and other data relating to transactions and events have been recorded at the correct amounts, i.e. at the amounts appearing in the source documents.
Rights and obligations - This means that the entity has a right to its assets, i.e. it is free to use or dispose of the assets as it sees fit. Furthermore, the entity is obliged to pay off the liabilities that are shown in the statement of financial position.
Existence - This means that assets, liabilities and equity interests (capital and reserves) are physically present/belong to the entity on the reporting date.
Cut-off - This means that transactions and events have been recorded in the correct accounting period. For example, if goods are delivered prior to year end, they are included in the cost of goods sold, not inventory.
Go to: GRC > Setup > Job plan
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Under the Checklist Fast tab, add the checklist lines
- Under the General Fast tab, move the Audit slider to Yes
- Click on the Save button
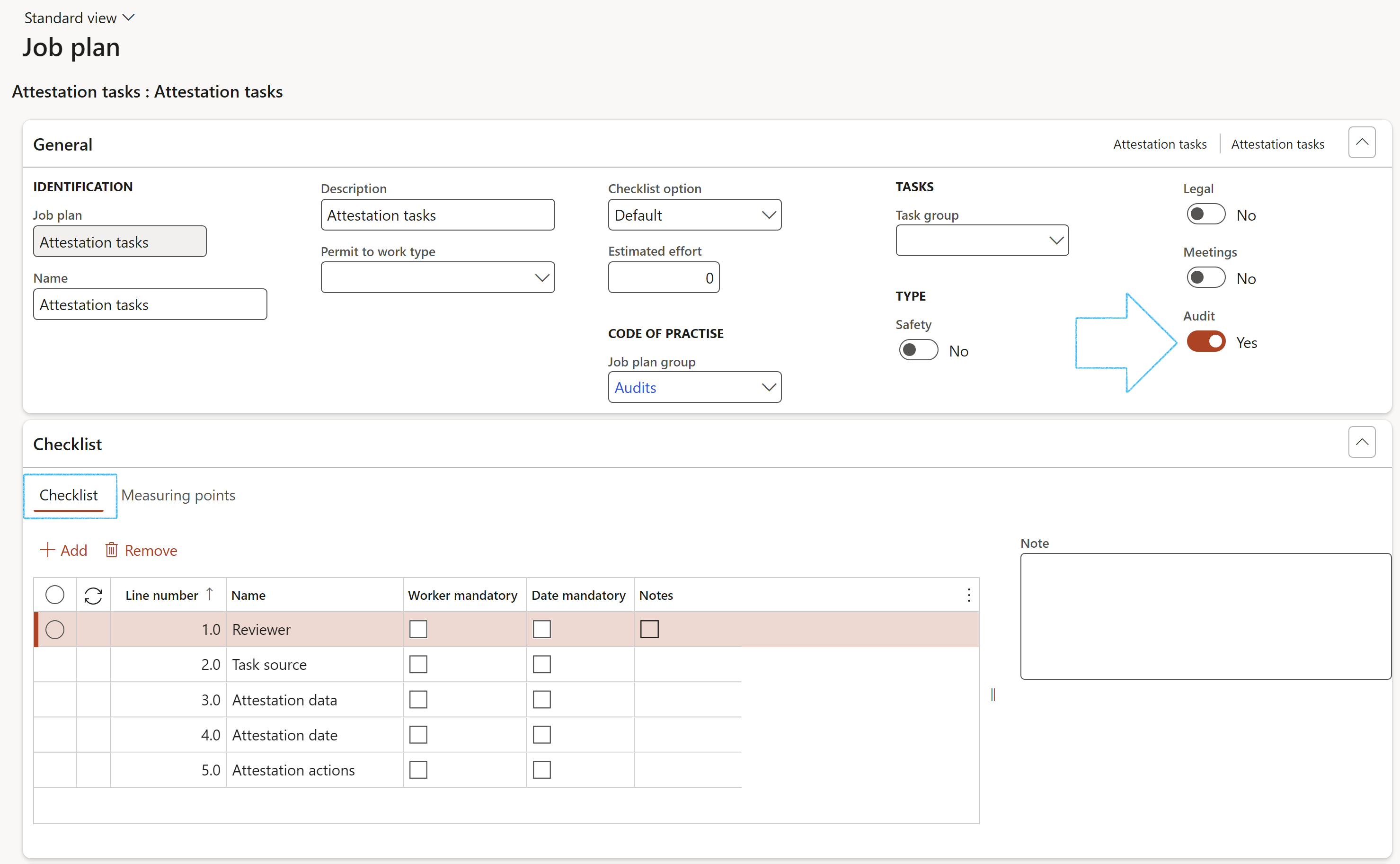
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Periodic > Audit procedures. These will be covered below in Step 21.
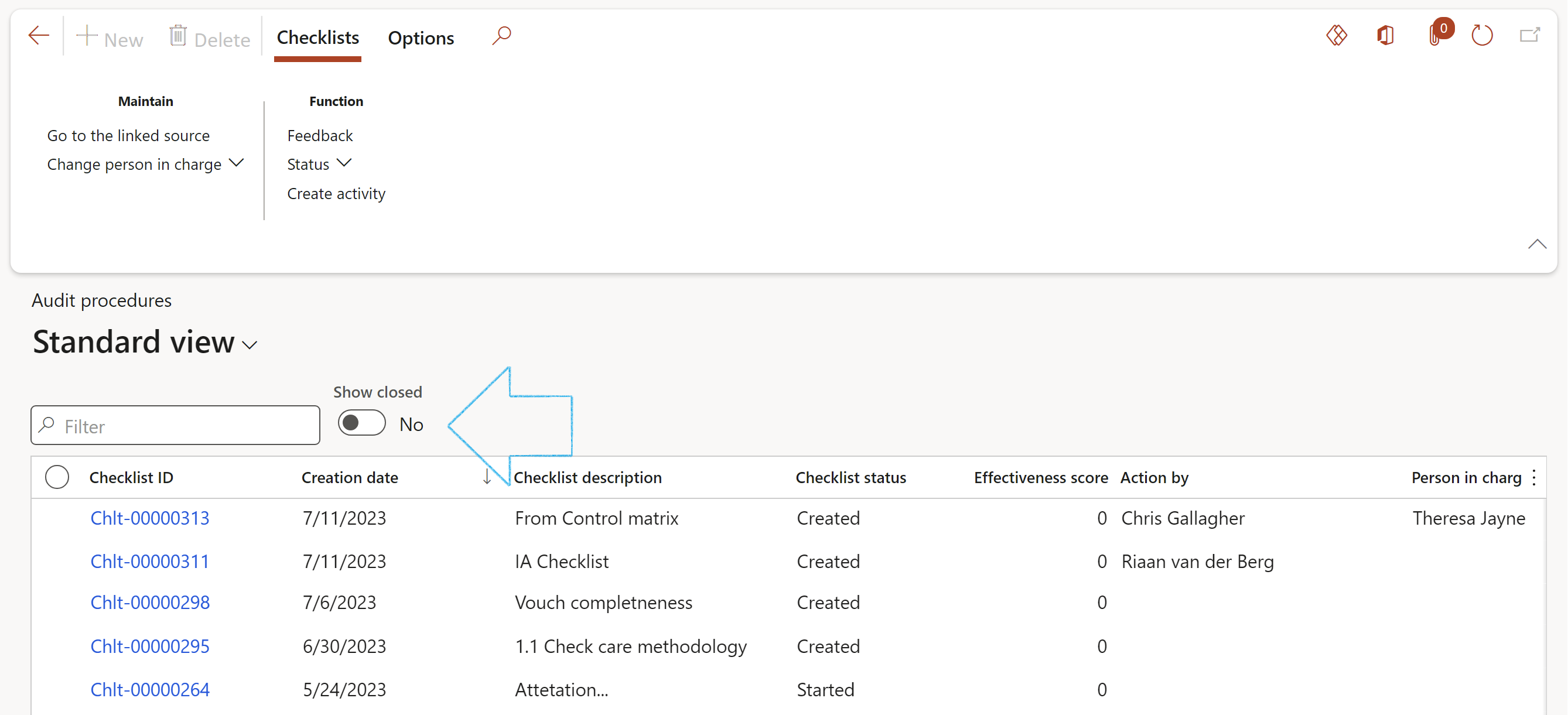
On the Audit procedute list page, move the Show closed slider to Yes if you want to see all the checklists including the closed records
The Audit procedure statusses are:
- Started
- Closed
- Void
When the status of a Working paper is set to Void, the Audit procedure status will also be changed to Void
¶ Step 9: Auditable entity
Auditable entities are in essence the business functions to be audited. They contain multiple controls to be checked for effectiveness and adequacy.
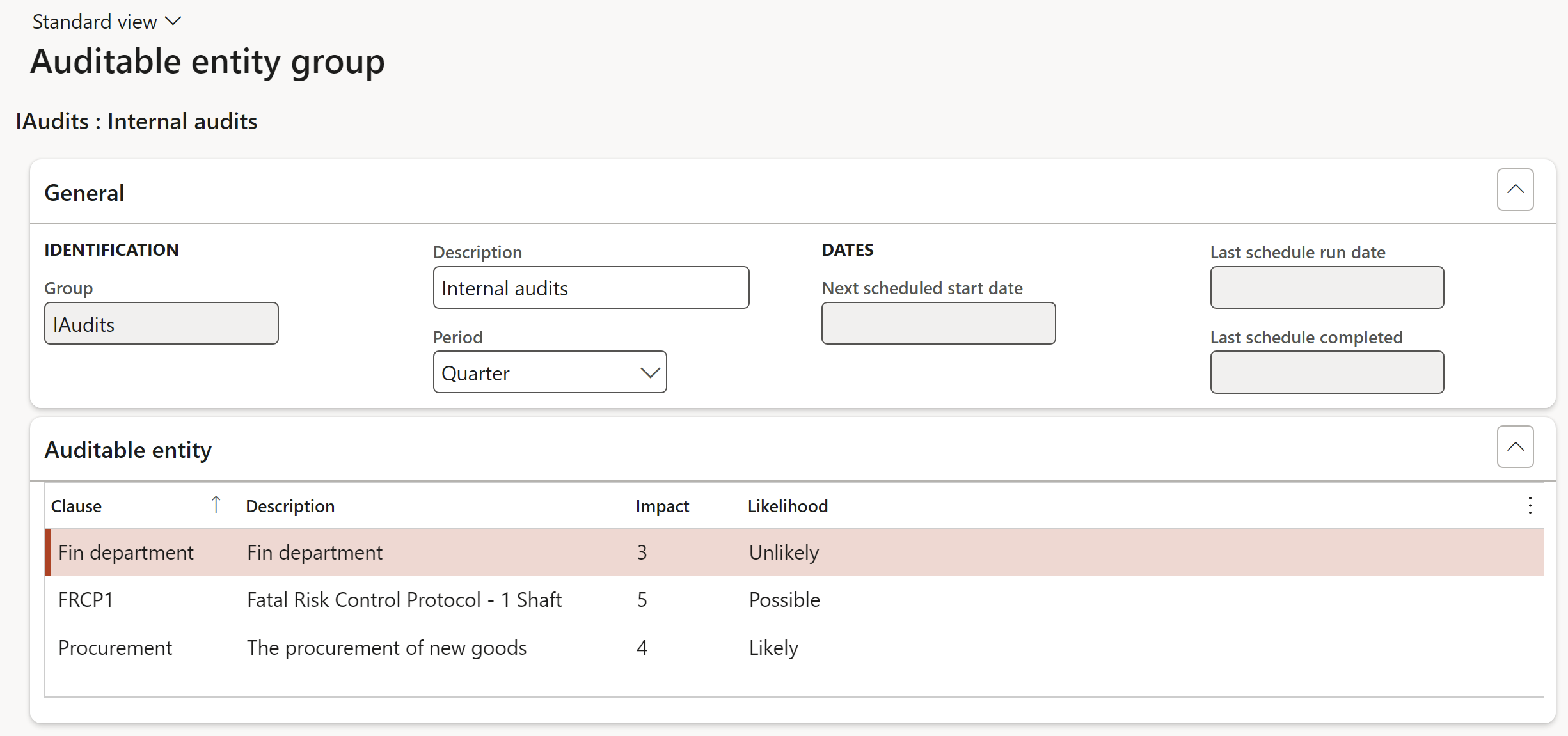
¶ Step 9.1: Create Auditable entity group
Auditable entity groups, group individual Auditable entities together and carry rules for time-based audits, i.e., scheduling of future audits.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Setup for internal audit > Auditable entity group
- Click on the New button
- In the Group field, enter the Auditable entity group name
- In the Description field, enter a brief description of the Auditable entity group
- In the Period field, select the frequency value for scheduling purposes
- The Next scheduled start date, Last schedule run date and Last schedule completed fields are displayed, indicating dates of the last applicable schedule.
¶ Step 9.2: Define Auditable entity
General fast tab: Some general information is contained in this section of the form. Accounting area and related business process is of particular importance.
To create a new Auditable entity:
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Auditable entity
- Click on the New button
- Enter a name for the Auditable entity
- Select the relevant Accounting area from the dropdown list
- Enter a brief Description for the Auditable entity
- Select the relevant Compliance group from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Business process name from the dropdown list
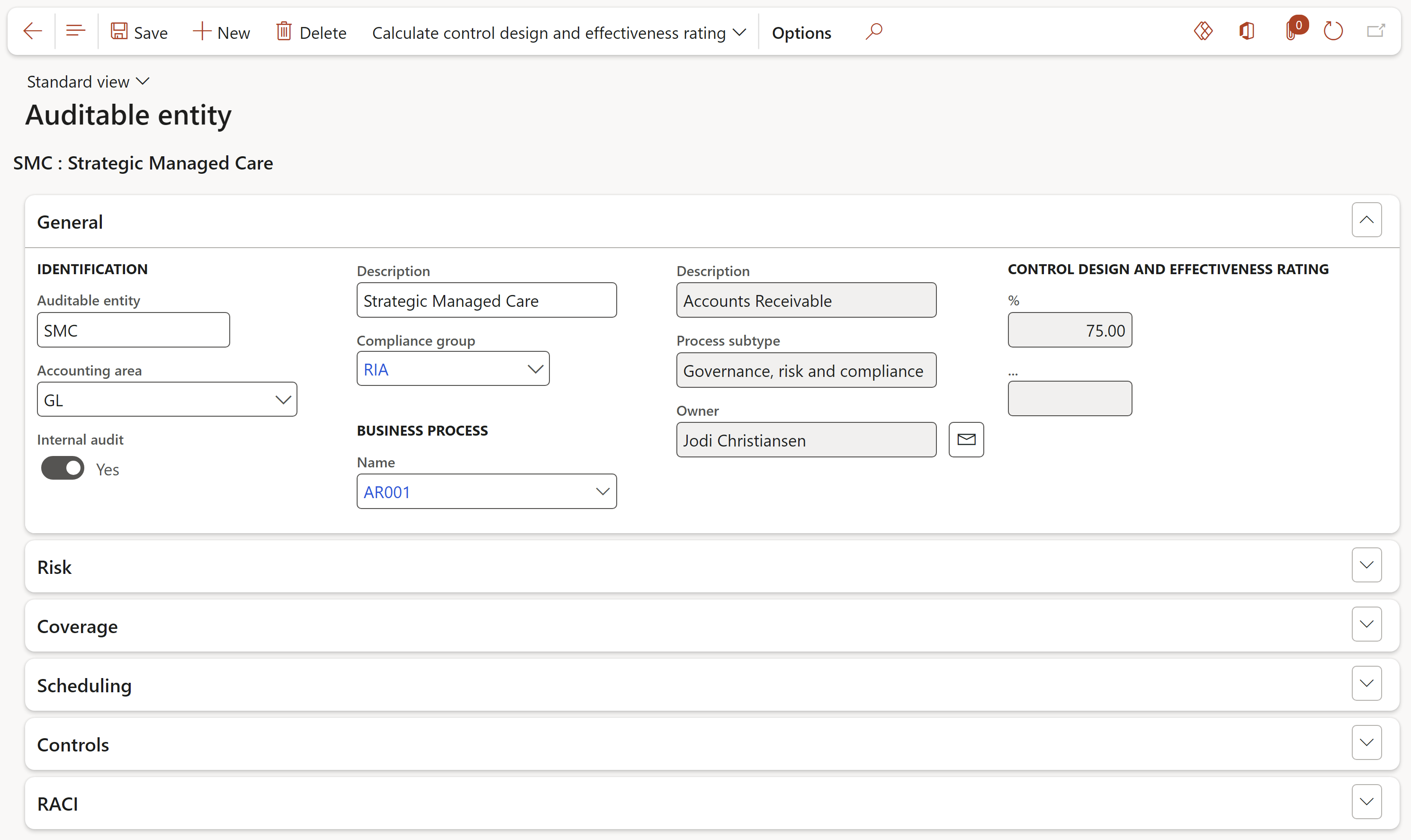
Expand the Risk Fast tab
- Select the relevant Risk register from the dropdown list
- Under the Manual risk field group, select the relevant risk Impact level from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant risk Likelihood level from the dropdown list
- In the Control effectiveness field, select the relvant control score level
- In the Manual residual risk field, select the relvant residual risk level
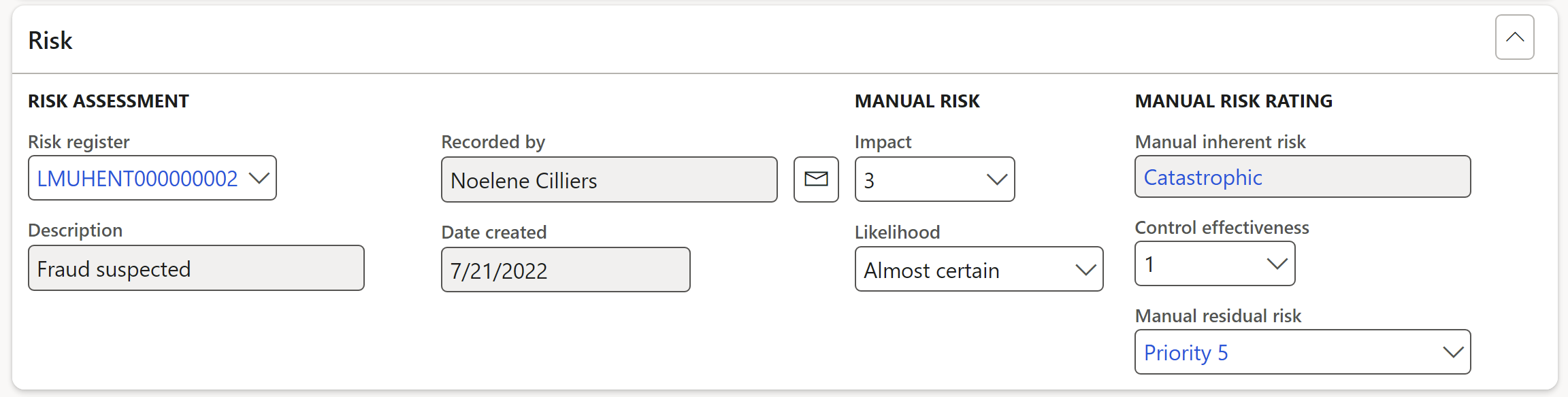
Expand the Coverage Fast tab
- Under the Current year field group, select the current Year form the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Coverage value for the different periods, from the dropdown lists
- Select the relevant name from the Done by dropdown lists, for the different periods
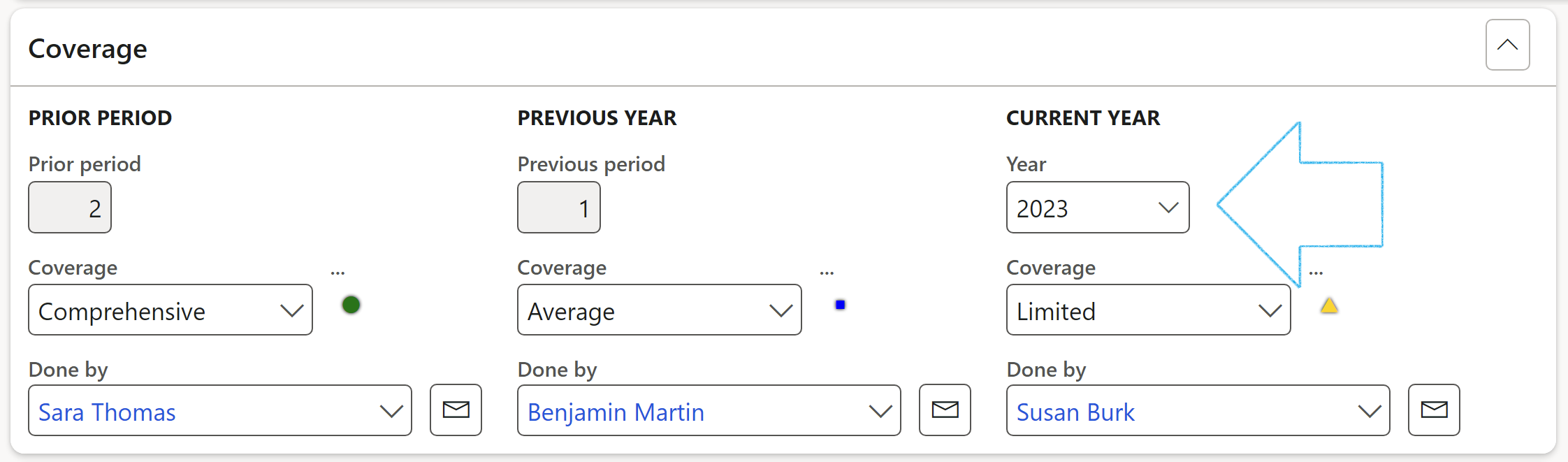
Expand the Scheduling Fast tab
- Select the relevant frequency Period from the dropdown list
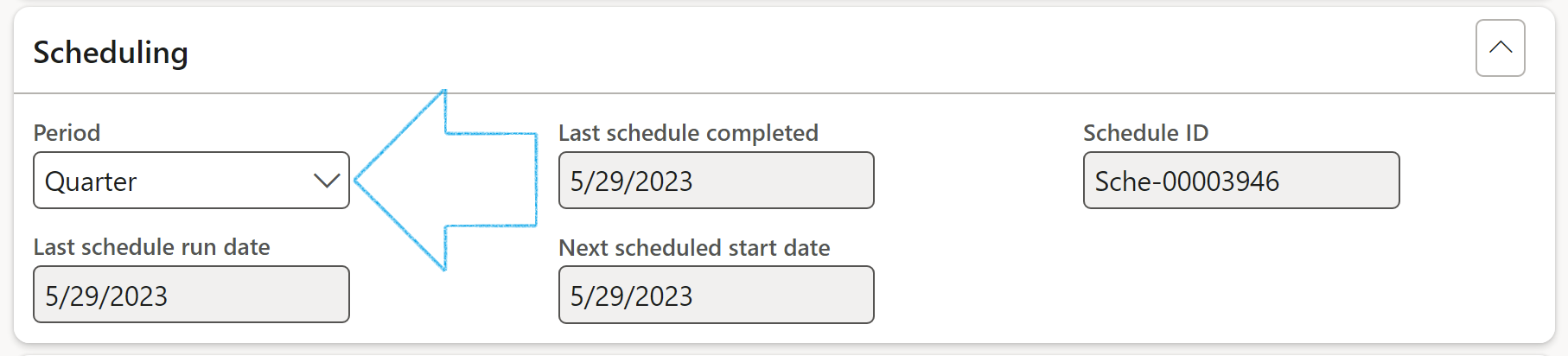
Expand the Controls Fast tab
- Click on the Add button
- Enter the Section number/identifier
- Enter the Control number
- Enter a brief Description
- Select the relevant Control type from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Audit procedure from the dropdown list
- Enter the inherent Risk %
- Line group is used in reporting. So if controls are going to be “compared” they must have the same line group number
- Enter Notes where applicable
OR
- Click on the Add from control galaxy button to add Accounting controls
For the controls to be on the dropdown list, make sure of the following:
- The Accounting area on the Control galaxy and on the Auditable entity under the Generel Fast tab, has to be the same
- The Effective date on the Control galaxy cannot be earlier than today's date
- The Active slider on the Control galaxy has to be set to Yes
OR
- Click on the Add from risk register button to add the risks from the selected risk register
- Select the relevant Audit procedure from the dropdown list
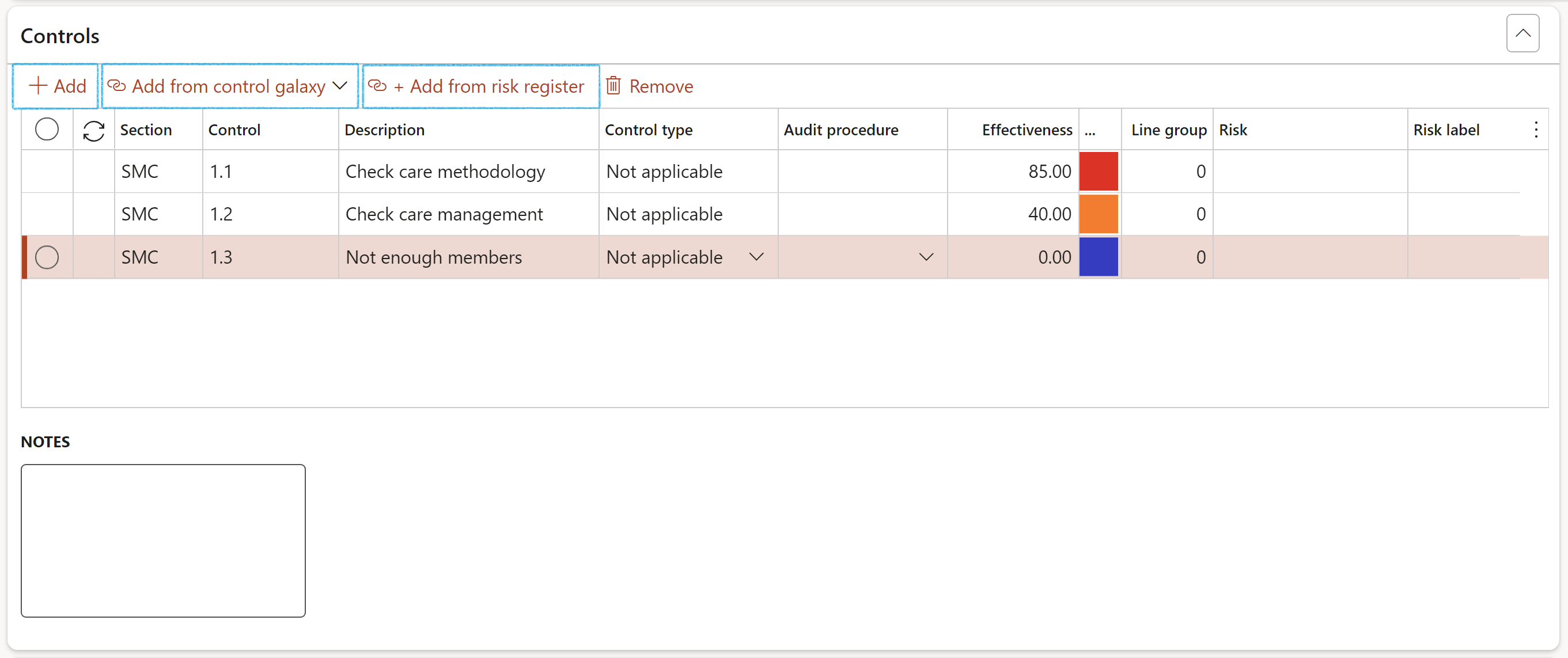
Users can calculate the control design and effectiveness for the Auditable entity by clicking on the button on the Action pane. This will take the individual control lines and aggregate the Effectiveness.
Expand the RACI Fast tab
- Select the relevant workers in the 4 RACI fields
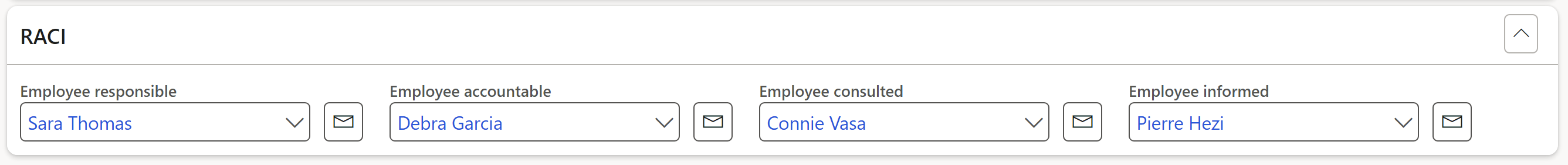
- To send an email to workers selected under the RACI field group, click on the email icon next to the relevant name
- The selected worker must have a primary email address
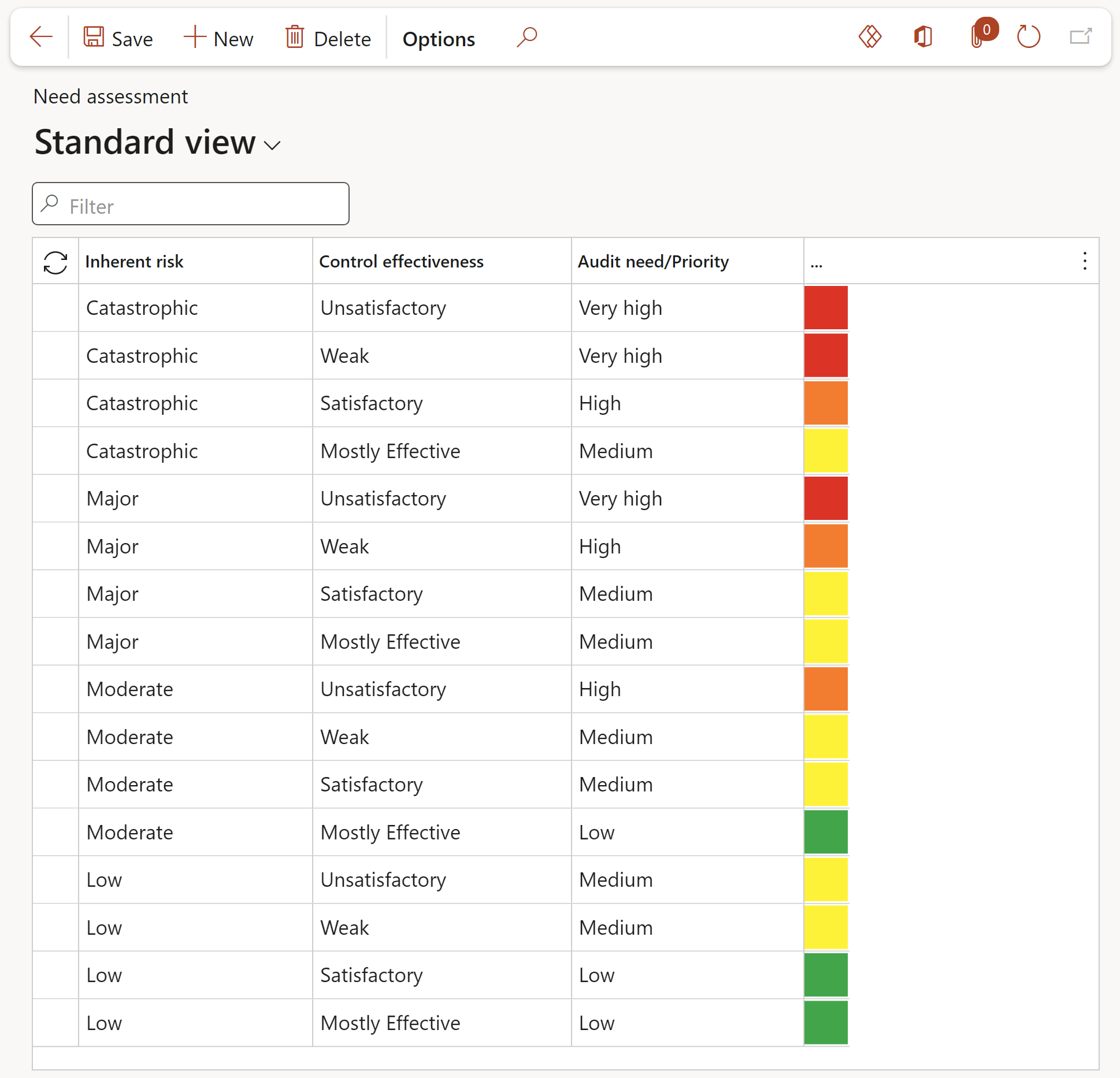
¶ Step 10: Audit need assessment
Once the inherent risk and control environment ratings are calculated (on the Auditable Entity) an Audit Needs Assessment ('ANA') can be determined. The ANA outcomes will be used to determine the areas of focus for internal audit and provide the basis for the risk-based audit plan. The setup form below contains ANA ratings.
The ANA is executed on the lines (Auditbale entity) section of the Audit univers.
Go to:GRC > Internal audit > Setup for internal audit > Audit need assessment
- In the Button strip, click on the New button
- In the Inherent risk field, select one of the following:
- Extreme
- High
- Moderate
- Low
- Insignificant
- In the Control effectiveness field, select one of the following:
- Excellent
- Marginal
- Effective
- Poor
- Non-Existent (None)
- In the Audit need field, select one of the following:
- Low
- Medium
- High
- Very high
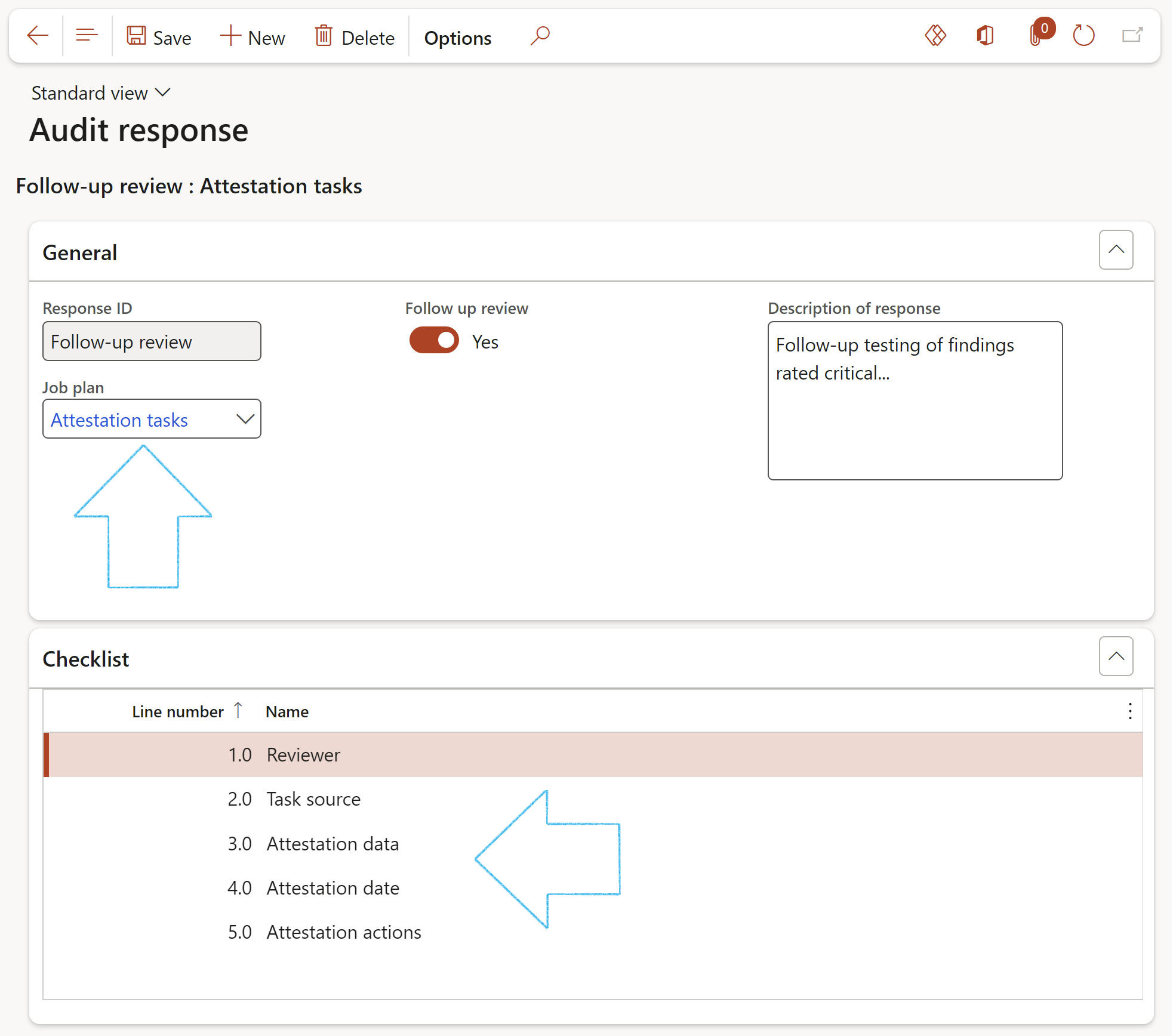
¶ Step 11: Audit response
"Audit clients” normally require a written report with related audit findings. Management of "Audit clients” reply to the Audit report for correcting or improving the finding situation. The auditor can then respond to management’s improvement plan. All collaborations are included in the final audit report that is distributed to the Board of Directors and the external auditors.
The records in this form will be used in creating an Audit response checklist. See Step 18 below for a typical flow of the audit process.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Setup for internal audits > Audit response
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a Response ID
- Select a Job plan from the dropdown list.
- Under the Follow up review section, select the Yes option if the job plan is going to be used as a follow up review job plan for the selected audit response
- Enter a Description of the response
- The selected job plan’s lines will be displayed under the Activities Fast tab
¶ Step 12: Creating an Audit report template
As was noted in the above step, audit reports must be generated. To help auditors in the generation of a report, Dynamics 365 GRC requires a baseline or template. Follow the steps below to create a template.
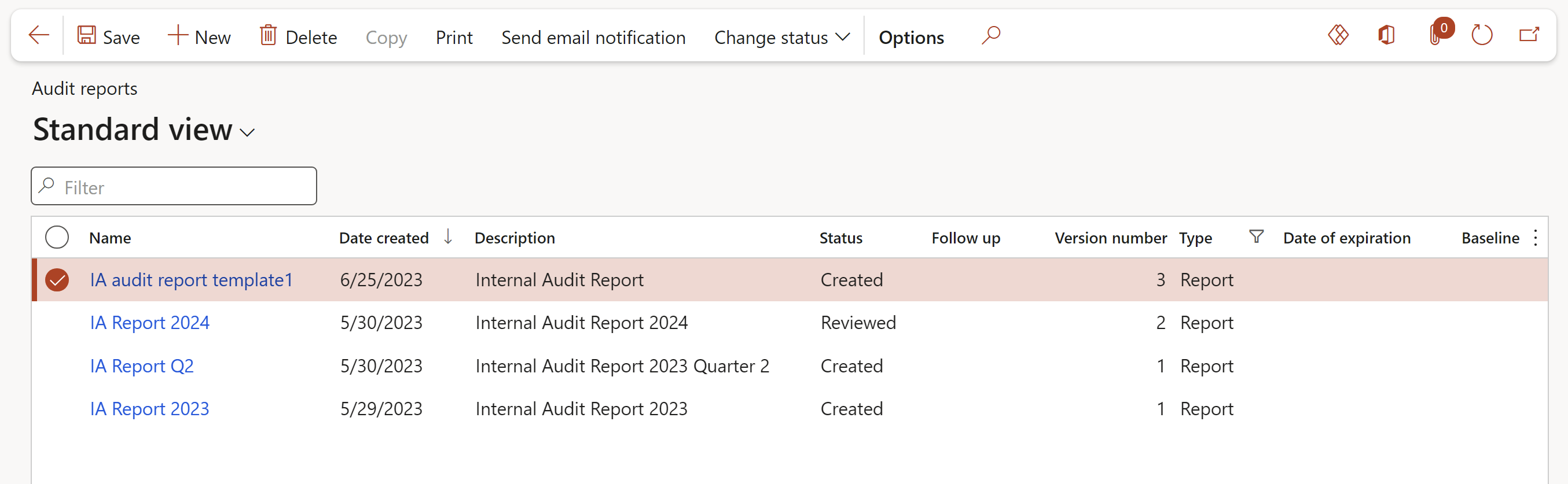
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Audit reports
- On the Action pane, click on the New button and select Document
- Complete the New audit report dialog
- Click on the OK button
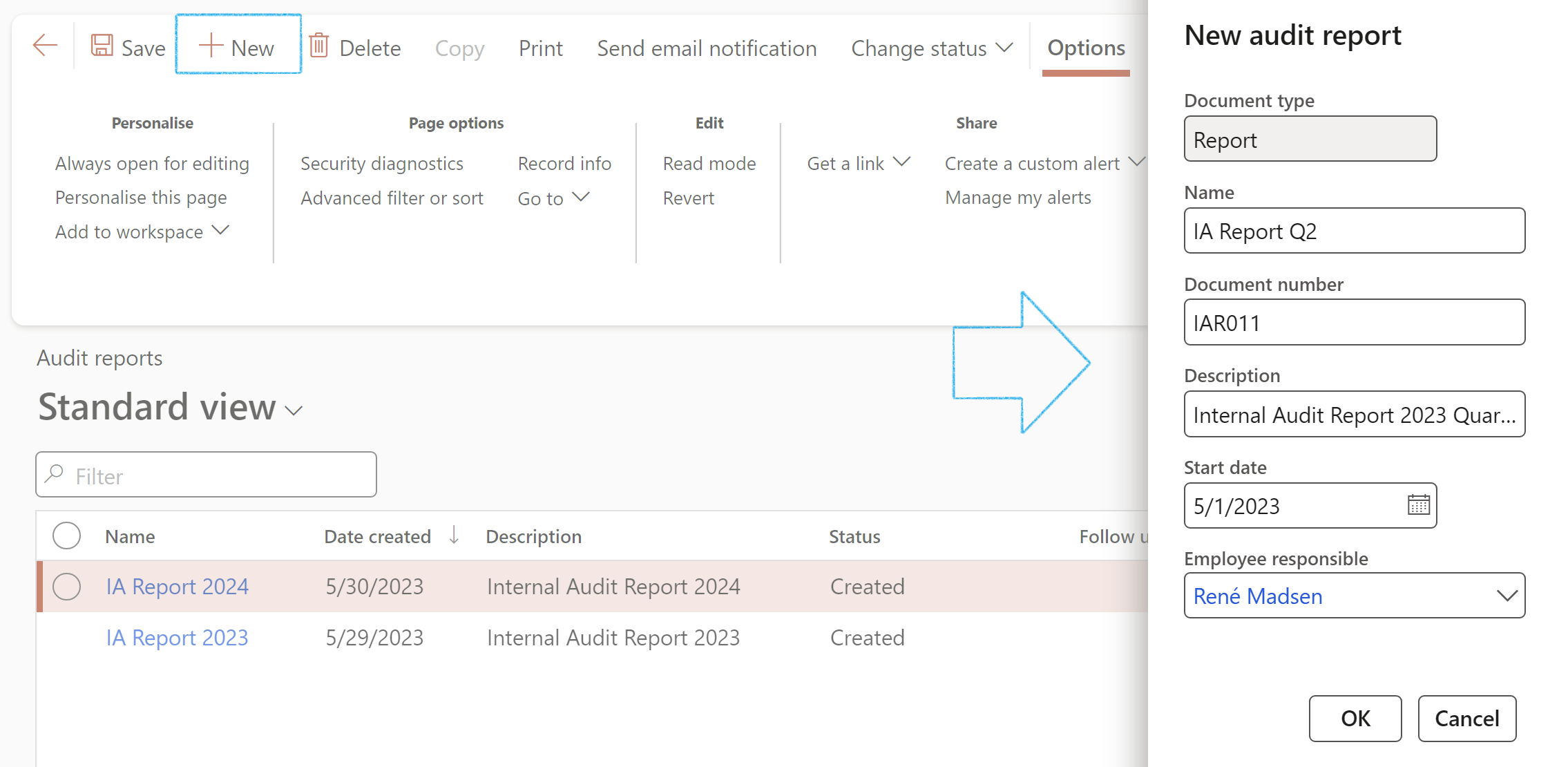
- Expand the Content Fast tab
- Under the Cover page Index tab:
- The Document type field will be populated with Report
- Enter values in the fields as required
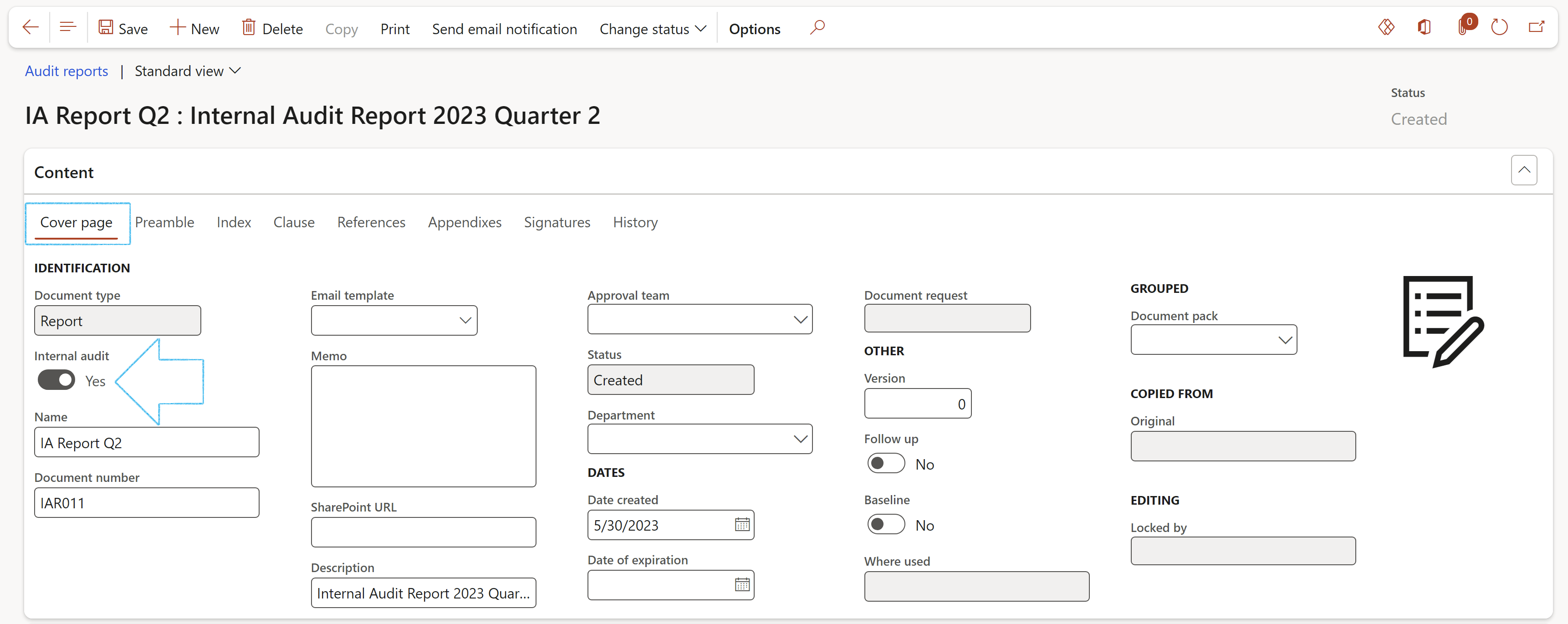
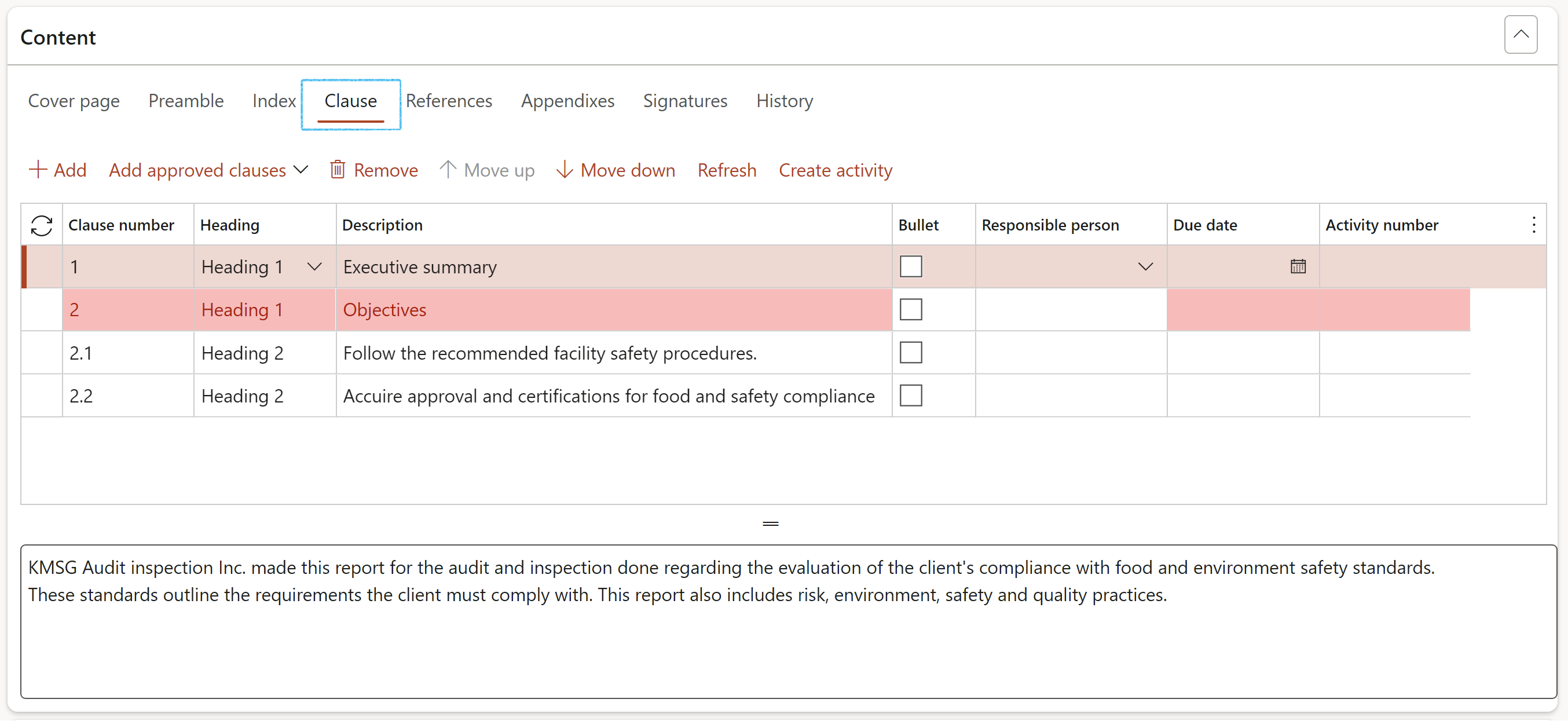
- Open the Clause Index tab
- In the Button strip, click on the Add button
- The Clause number will be generated by the system
- Select the Heading (Heading 1 for a primary heading, Heading 2 for a secondary heading)
- Enter a Description
- Use the box provided to type the Clause definition
- There is a list of field names that are on the Internal audit (Project) form on the dropdown list in the Audit mapping field. Select the field which values should be printed under the selected heading and description.
- If no values from fields from the Internal audit (Project) form should be printed on the report, and you want to enter your own text, for example under an Introduction heading, enter the text in the memo box provided under the grid
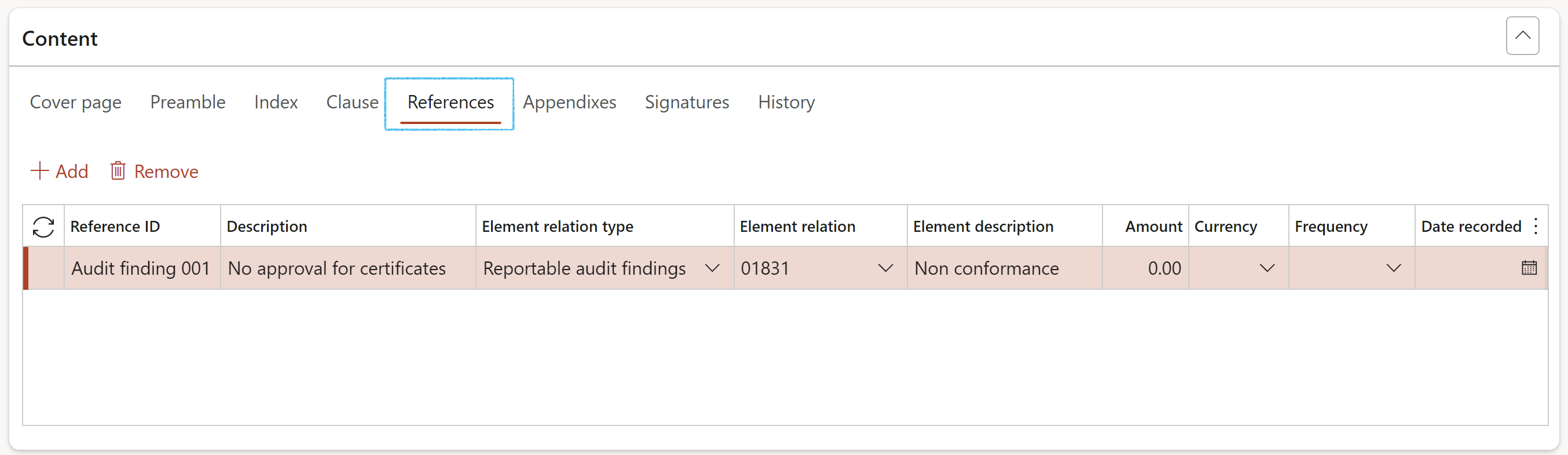
When the report is generated from an Internal audit, the audit as well as the list of audit files linked to the audit, will be displayed under the References Index tab
¶ Step 13: GRC actions and questions
In short these are used to create user spesific text for Audit and Audit file declarations.
Go to: GRC > Setup > GRC actions and questions
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- In the Question ID field, enter the unique question ID
- In the Source field, select IAF for Audit file/IAU for Internal audit
- In the Action field, select Declaration
- In the Answer type field, select Yes/No declaration from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Negative outcome from the dropdown list
- In the Question text note box, enter the wording of the declaration
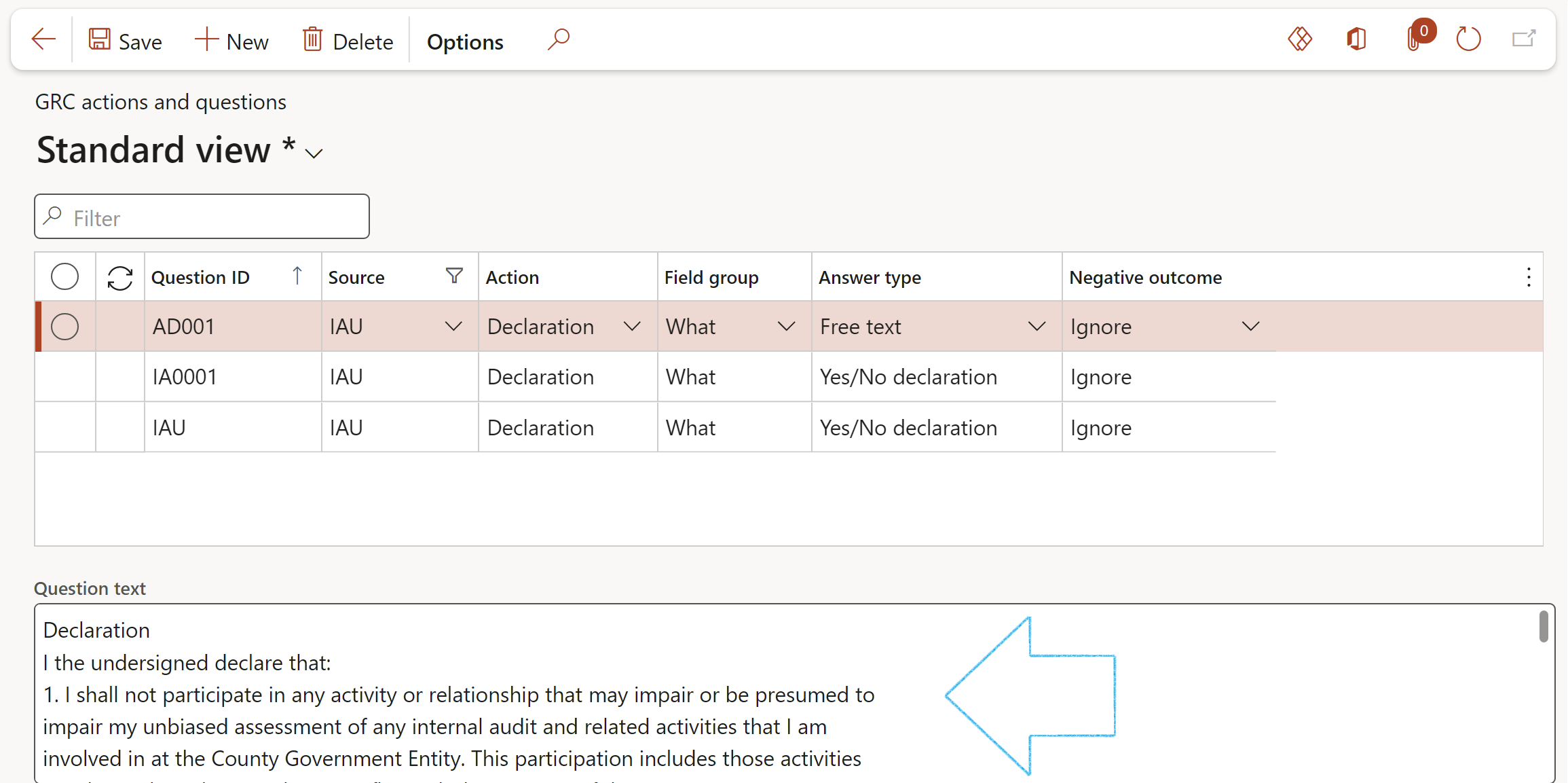
The Question text is the text that is displayed on the Declaration of interest dialogue on the Audit file.
A question must have an Answer type:
- Yes/No declaration – this will display the Question text with a tick box on the Declaration of interest dialogue
The response to the question is set by the Negative outcome setting:
- Force entry – The Declaration of interest dialog will not be able to be closed if this field is not completed i.e. a Tick is required in the tick box
- Warning – this will give a warning if there is no input against the question, but will allow the action to continue
- Ignore – the action can continue if there is no response to the question
¶ Daily use
Dynamics 365 GRC supports Audit, Risk Management and Compliance processes without forcing users into a particular methodology or workflow. The Internal audit module is explained using the illustration below.
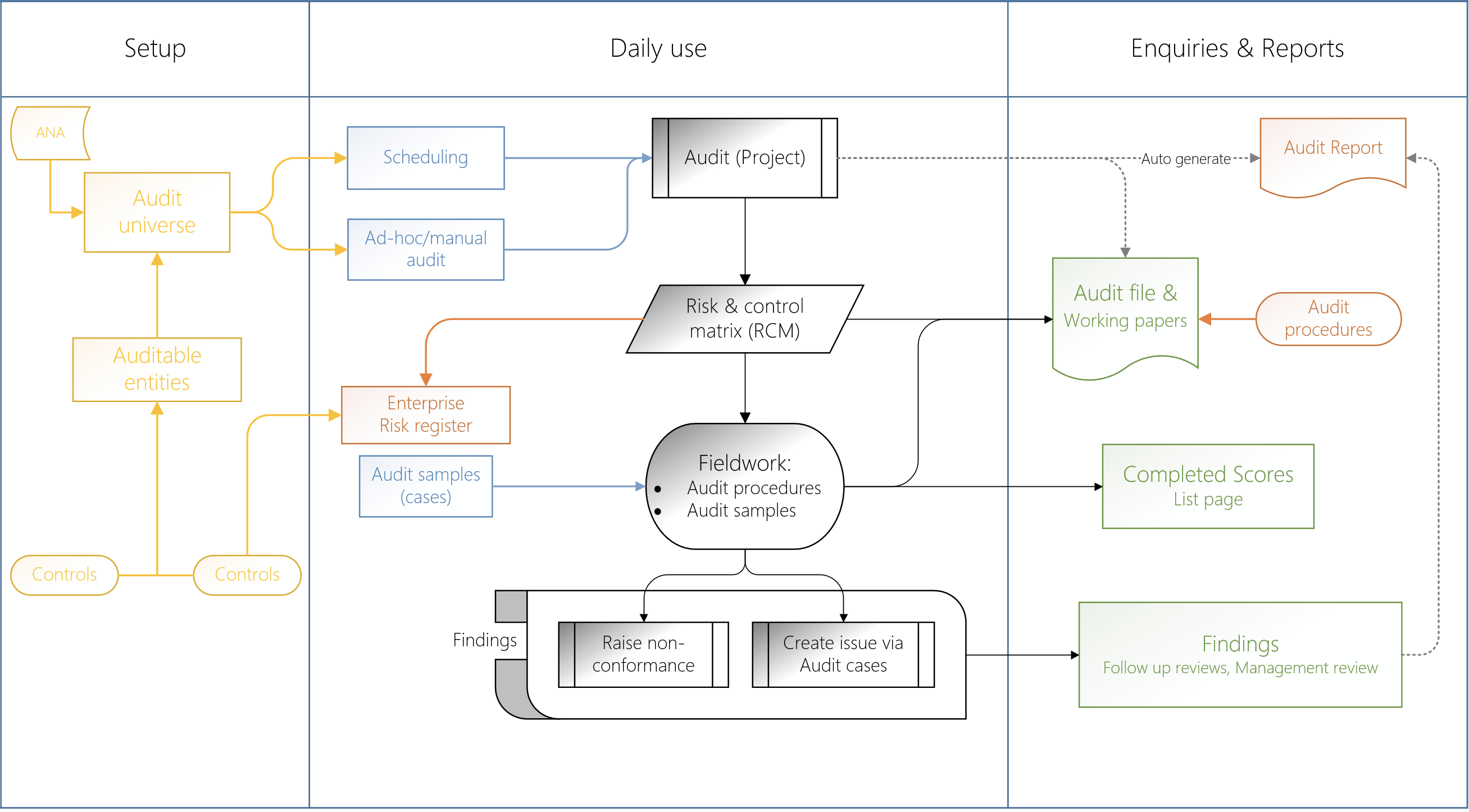
For the purpose of this document, it will start with controls and then move to associated risks. Then taking into account auditable entitites, the audit universe will be explored.
¶ Step 14: Control galaxy
What is a "Control galaxy"? It is a list of internal controls which are basically processes used in an enterprise to ensure the integrity of reporting.
Controls help enterprises to comply with laws and regulations, and prevent fraud. They also can help to improve operational efficiency by ensuring that budgets are adhered to, policies are followed, and risks are mitigated.
The records in this form will be used on the Auditable entity, under the Controls Fast tab.
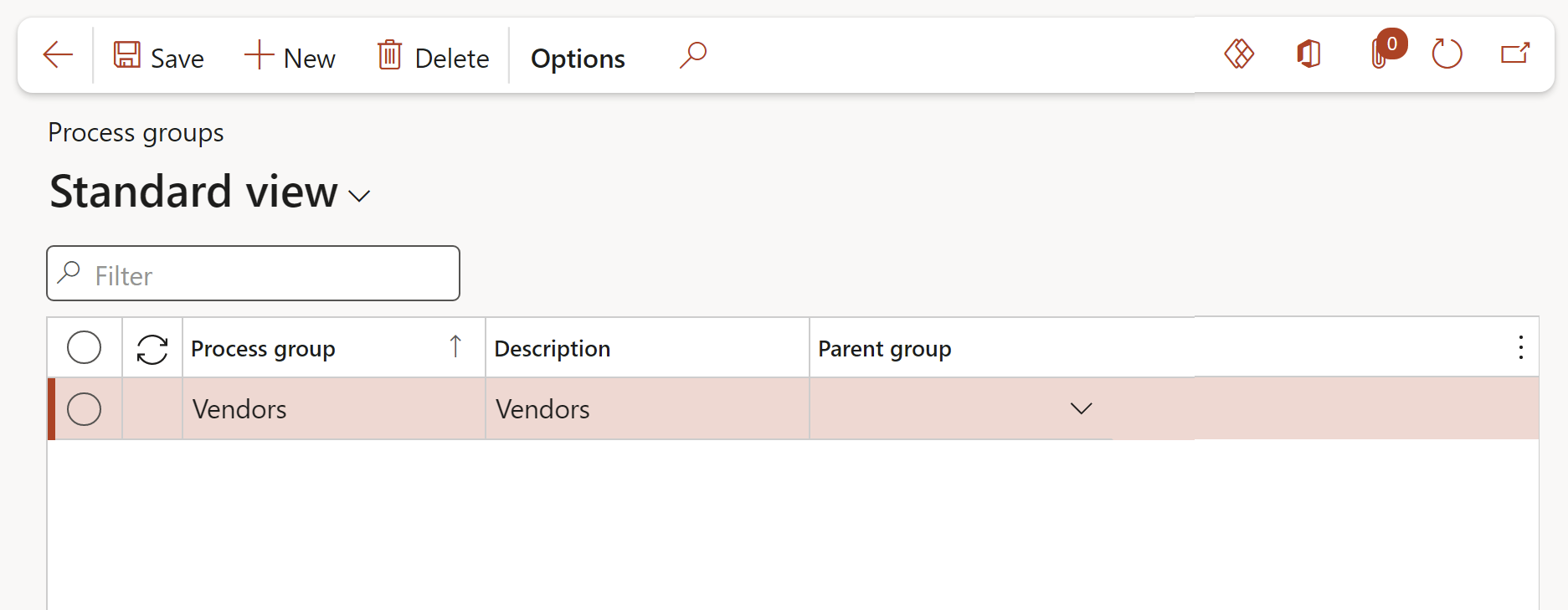
¶ Step 14.1: Process groups
Go to: GRC > Risk > Setup for risks > Process groups
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a name for the Process group
- Enter a brief Description for the Process group
- Select a Parent group from the dropdown list (if applicable)
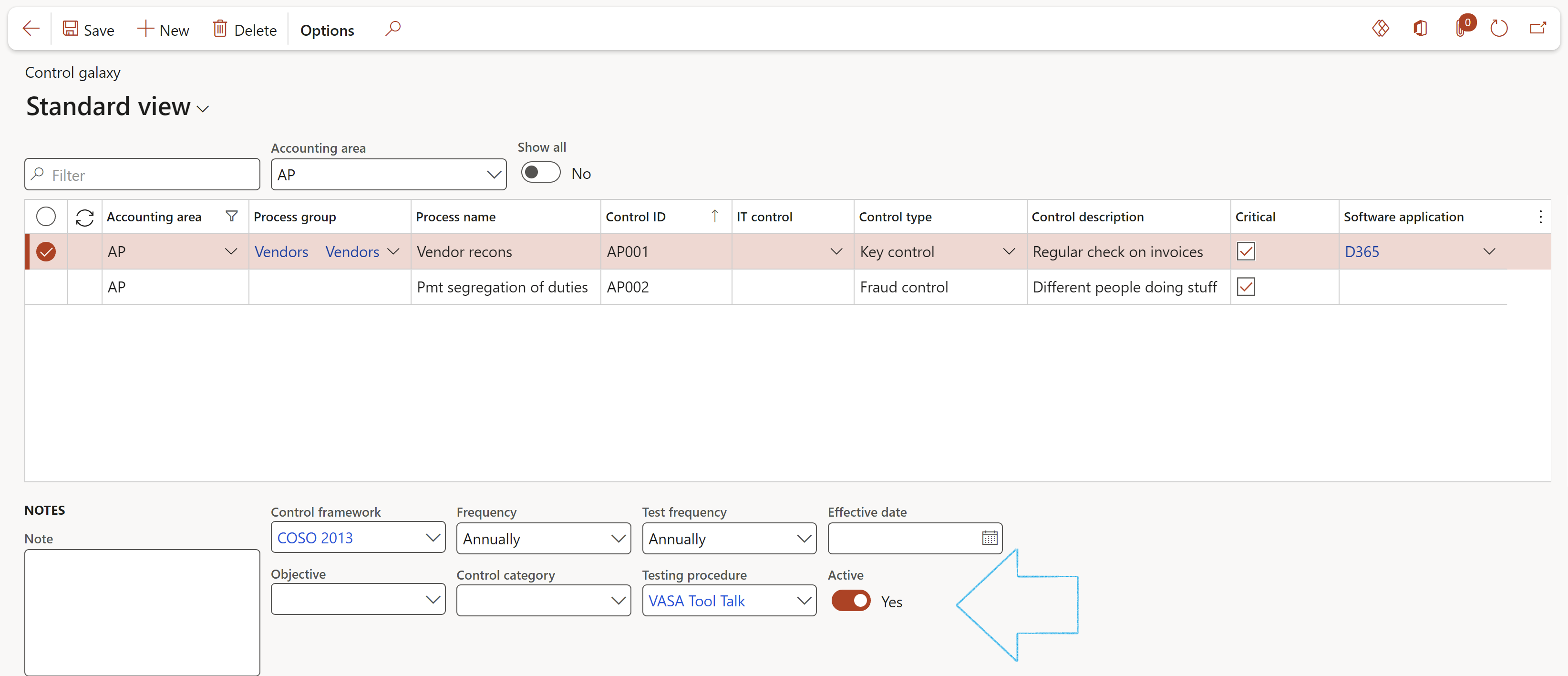
¶ Step 14.2: Control galaxy
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Control galaxy
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Select the relevant Accounting area from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Process group from the dropdown list
- Enter a Process name for the control
- Enter a Control ID
- Select the relevant Control type from the dropdown list
- Enter a brief Control description
- Enter notes in the Note box provided
- Select the relevant Control framework from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Objective from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Frequency from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Control category from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Test frequency from the dropdown list
- Enter the Effective date
- Indicate whether the Accounting area is Active
¶ Step 15: Identify business risks and use controls
Risks are things that threaten the integrity of a subprocess. For example, unauthorized changes to vendors, and bank accounts that do not reconcile. There are several fields that categorize risks to help with this.
Risks identified by users should be recorded in the Dynamics 365 GRC risk register.
Controls exist to mitigate these identified business risks. These controls can be created manually on the risk register, or by adding controls from the Control galaxy. On the control galaxy, controls can be flagged as of control type Manual process, Key control, Fraud detecting, or Computerized.
Go to: GRC > Risk > Registers > All enterprise risk registers
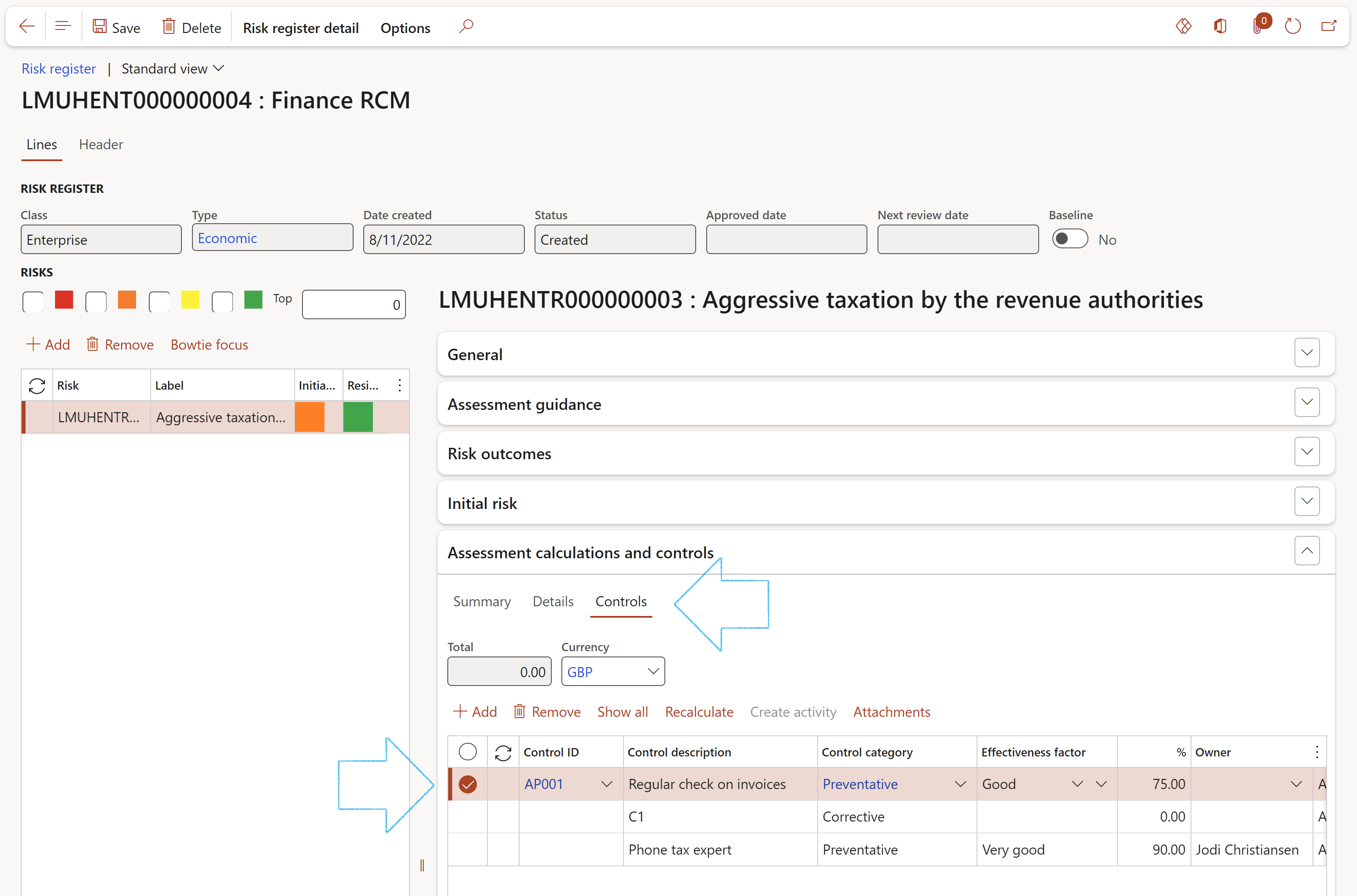
By using the “risk register type” (in this example it is "Economic") users can group risks together. It is also useful to use the risk registers on the Control matrix (RCM). Users can:
- Add additional risks “back” into the risk registers.
- Create new risk registers (a default “risk register type” value exists on the parameters form for when users do this).
¶ Step 16: Audit universe
The Audit universe represents a range of potential audit activities to be carried out by internal auditors. It consists of several auditable entities (refer back to Step 9 above), controls, processes, procedures and systems.
Its starts with a basic definition (on the header) and other identification fields. The definition is expanded with RACI details, risk rating, scope, scheduling rules and documents (to be used in Audit files).
The detail follows as “lines” and “sub-lines”. The lines inside the Auditable universe list the Auditable entities, and are followed by the "sub-lines" which are the Controls per Auditable entity to be audited.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Audit universe
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
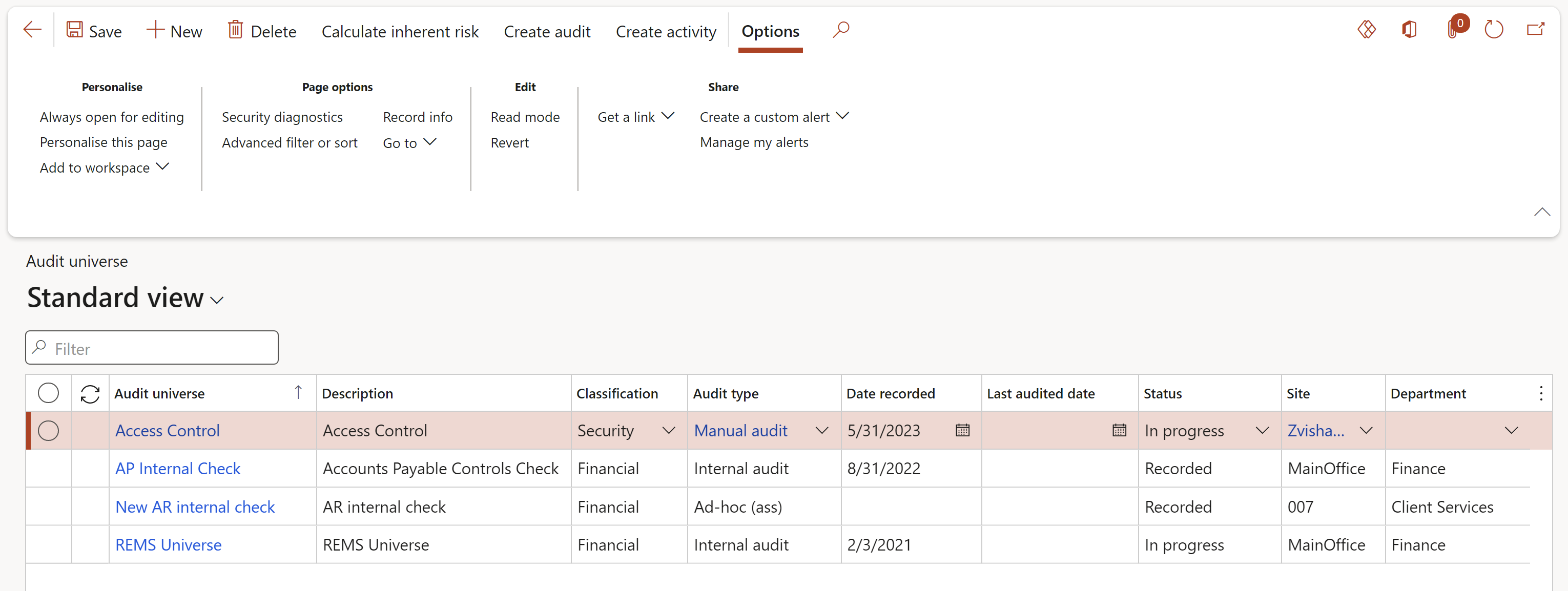
¶ Step 16.1: Create the Audit universe header
¶ Step 16.1.1: Header - General Fast tab
- Complete the applicable fields under the General Fast tab:
- Under the Identification field group:
- In the Audit universe field, type a unique Audit universe ID
- Enter a brief Description for the Audit universe
- Select the compliance Status of the Audit universe from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Classification from the dropdown list
- Select the Audit type from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Compliance agency from the dropdown list
- Using the External slider, indicate whether this compliance is required for external reasons
- Under the Dates field group:
- Select the relevant Dates
- Under the RACI field group:
- Employee responsible: Those who do the work to achieve the task. There is at least one role with a participation type of responsible, although others can be delegated to assist in the work required.
- Employee accountable: The one ultimately answerable for the correct and thorough completion of the deliverable or task, and the one who delegates the work to those responsible. In other words, an accountable employee must sign off (approve) work that the responsible employee provides.
- Employee consulted: Those whose opinions are sought, typically subject matter experts, and with whom there is two-way communication.
- Employee informed: Those who are kept up to date on progress, often only on completion of the task or deliverable, and with whom there is only one-way communication.
- To send an email to workers selected under the RACI field group, click on the email icon next to the relevant name
- The selected worker must have a primary email address
- Relevant characteristics of the audit engagement, such as the reporting framework used in order to set the scope of the engagement.
- Key dates for reporting and other communications
- Setting of materiality
- Preliminary risk assessment and whether internal controls are to be tested
- Consideration of resources available and how they are to be used
- Using all risks (per control found inside every Auditable entity), Dynamics 365 will calculate an average inherent risk for the current universe and display it as Inherent risk %
- Residual risk % is captured manually
- The Strategic objective can be selected from the dropdown list (refer to Step 5 above)
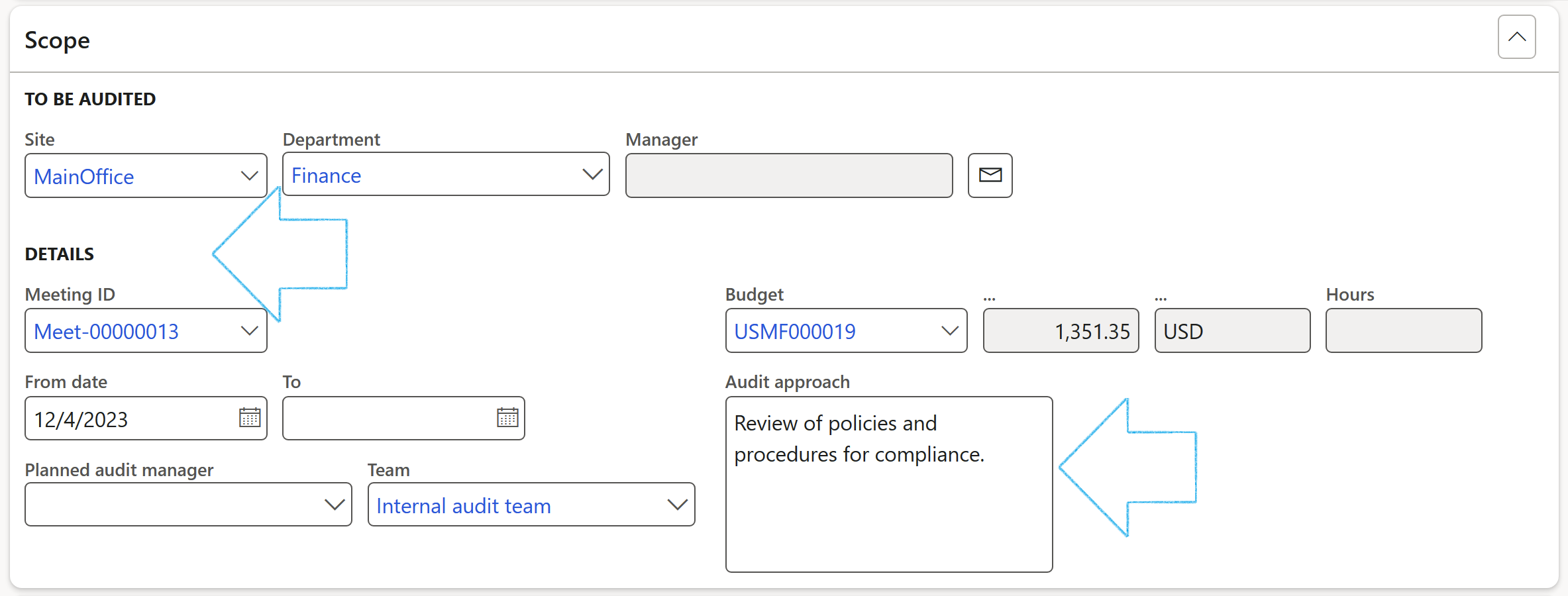
- Under the Details Field group, select the relevant Meeting ID from the dropdown list
- Enter the period under review From date and To date
- Select the Planned audit manager from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Team from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Budget from the dropdown list
- Enter additional Audit approach detail in the box provided
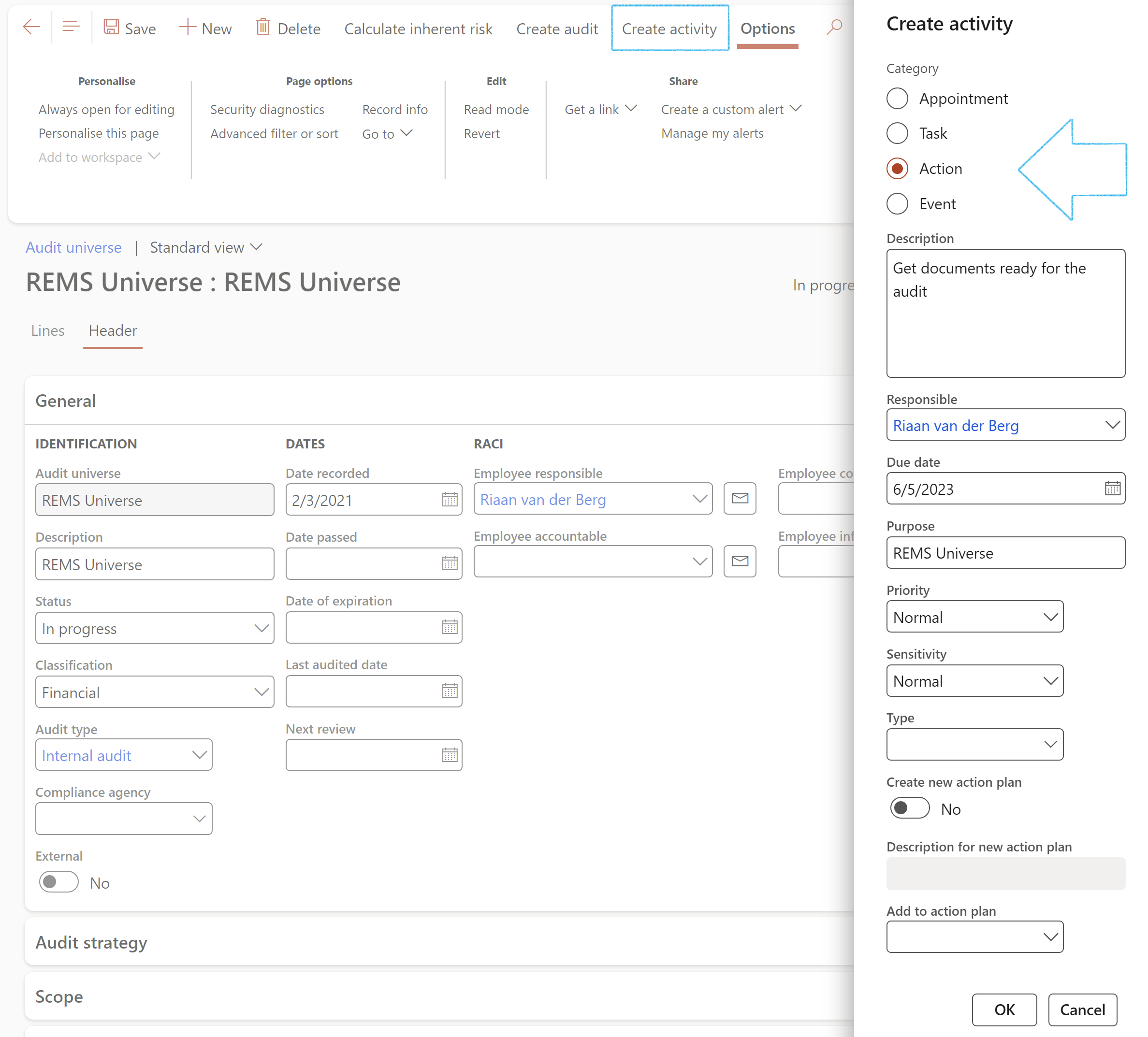
- On the Action pane, click on the Create activity button
- On the Create activity dialog:
- Select the relevant Category
- Enter a Description for the activity
- Select the Responsible person for the activity
- Enter the Due date for the activity
- Enter the Purpose of the activity
- Indicate the Priority and Sensitivity of the activity
- Choose to create a new Action plan for the activity, or to add it to an existing Action plan
- Click on the OK button
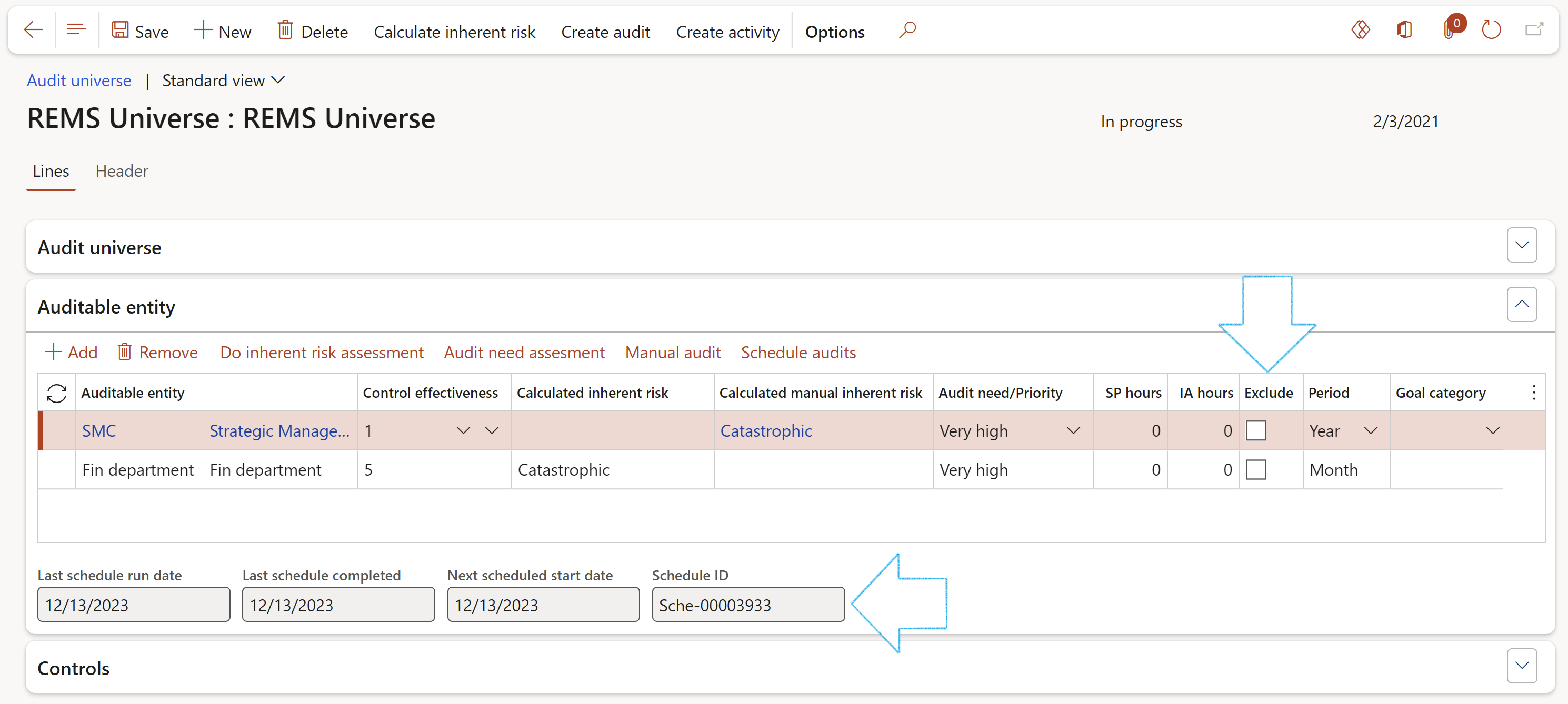
- In the Button strip, click on the Add button
- Select the relevant Auditable entity from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Control effectiveness (score level) from the dropdown list
- Select the degree of Audit need/priority for an audit from the dropdown list
- Enter the number of service provider hours required to assist with audit in the SP hours field
- Enter the number of internal audit team hours required to execute the audit in the IA hours field
- If an Auditable entity should be excluded from an audit, tick the Exclude tick box
- In the Period field, select the frequency value for scheduling purposes
- Select the relevant Goal category from the dropdown list
- The date fields, as well as the Schedule ID field, will be populated when audit schedules have been run for the audit universe
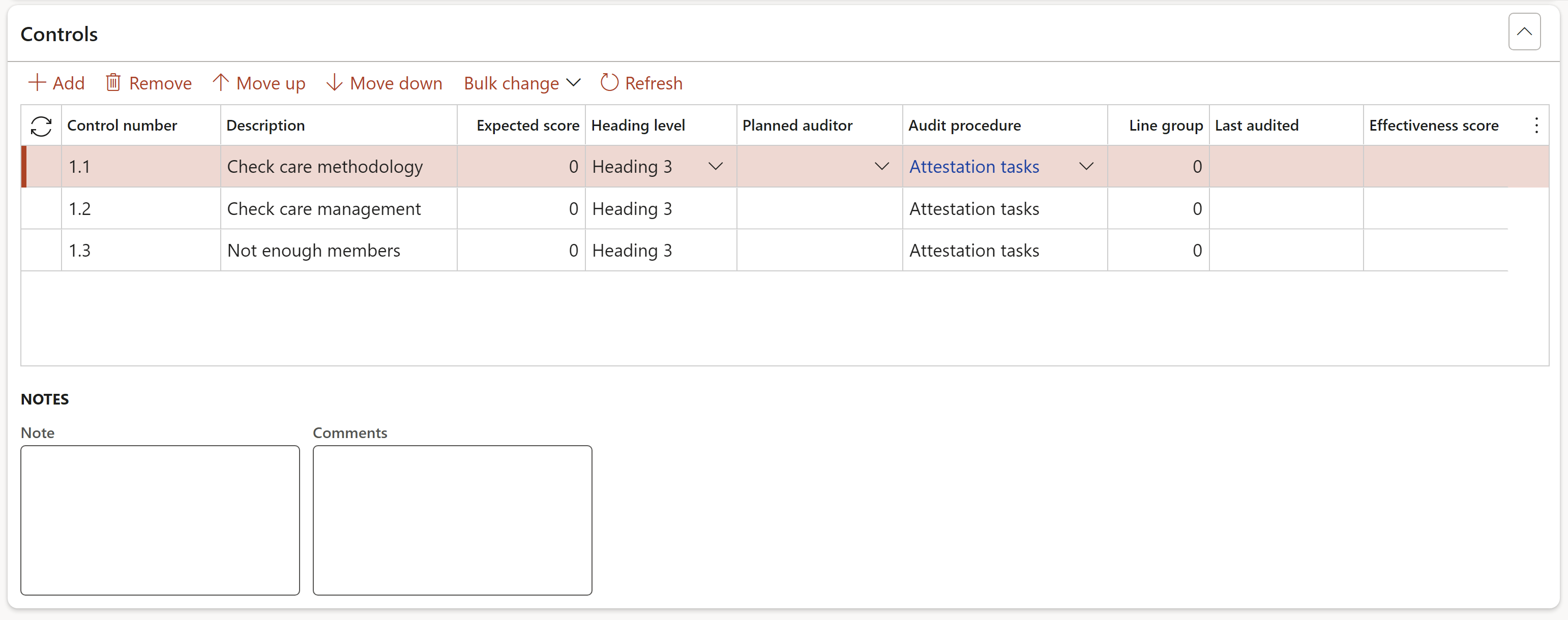
- In the Button strip, click the Add button
- Enter a Control number
- Enter a brief Description of the control
- Enter the Expected score for the control (The maximum score that can be given to the line when posting the scores).
- Select the Heading level
- Select the Planned auditor to perform scoring on the control line
- The Audit procedure field is populated with the value selected on the Auditable entity. If an Audit procedure was not selected on the Auditable entity, one can be selected here.
- Only users that belong to the Audit team that was selected on the Audit universe, will be on the Planned auditor dropdown list. If no Team was selected on the Audit universe, the system will take the Team that is linked to the Audit type
- A Bulk change can be made to all the lines by clicking on the button in the button strip and entering the required Score and Heading values on the dialog form
- The Expected score has to be entered before an audit is created otherwise scoring cannot be done on the Fieldwork form
- Enter a Line group number. This Line group number is used to group clauses beloning to the same ISO reference
- Notes and Comments can be entered per line
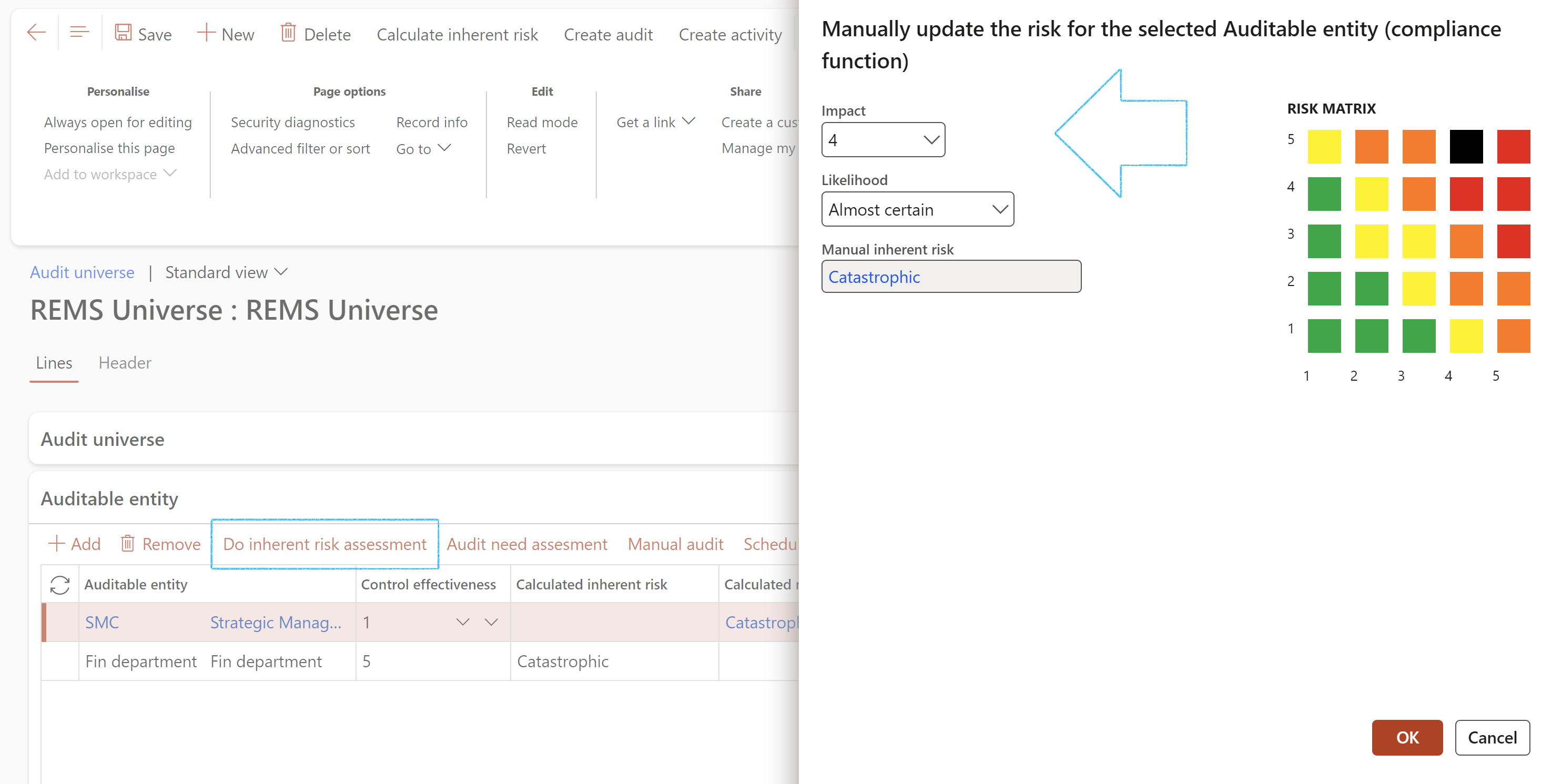
- Under the Auditable entity Fast tab, in the Button strip, click on the Do inherent risk assessment button
- On the Manual update risk dialog:
- Enter the Impact rating
- Enter the Likelihood rating
- Click on the OK button
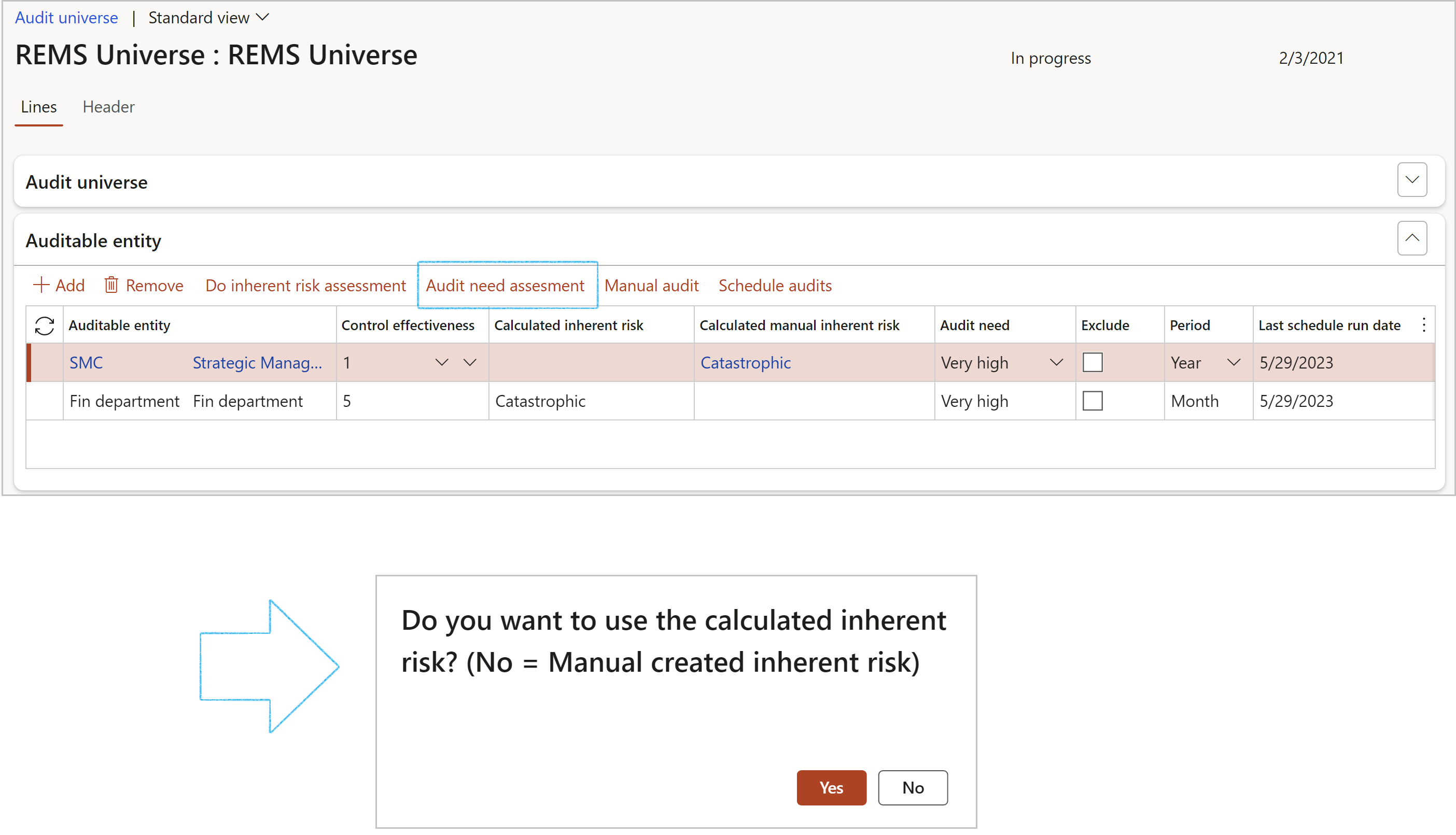
- Under the Auditable entity Fast tab, in the Button strip, click on the Audit need assessment button
- On the pop-up, the user has the option to use the calculated inherent risk or the manually created inherent risk
- Under the Auditable entity Fast tab, in the Button strip, click on the Manual audit button
- It is preferable to use Internal as the Project type (Ensure that the working times exist as per: Organization administration > Setup > Calendars > Calendars)
- Complete the Create a new audit and audit file dialog
- Click on ther OK button
- On engagement, Dynamics 365 will create a new audit file following the numbering sequence rules (found on the parameters form) ensuring a complete set with a unique identifier.
- This audit file will include a reference to the “manually created schedule”, links to the document pack from the Audit universe, and will automatically add applicable internal audit working papers from the field work.
- Also note that users can add any type of additional documents to the selected audit file via the attachment button.
- Finally, Dynamics 365 will propose a name (which is editable) based on the Audit universe and the Auditable entities. This proposal includes a semi colon after the Audit universe, and commas after each auditable entity.
- Complete the Create a new audit (project) and audit file dialog
- It is preferable to use Internal as the Project type (Ensure that the working times exist as per: Organization administration > Setup > Calendars > Calendars)
- Indicate which Auditable entities should be Excluded from the audit
- Click OK button
- Under the Auditable entity Fast tab, in the Button strip, click on the Schedule audits button
- Complete the Create schedules dialog
- Click on the OK button
- Select the budget register entry that contains the budget values for the audit
- Move the Audit slider to Yes
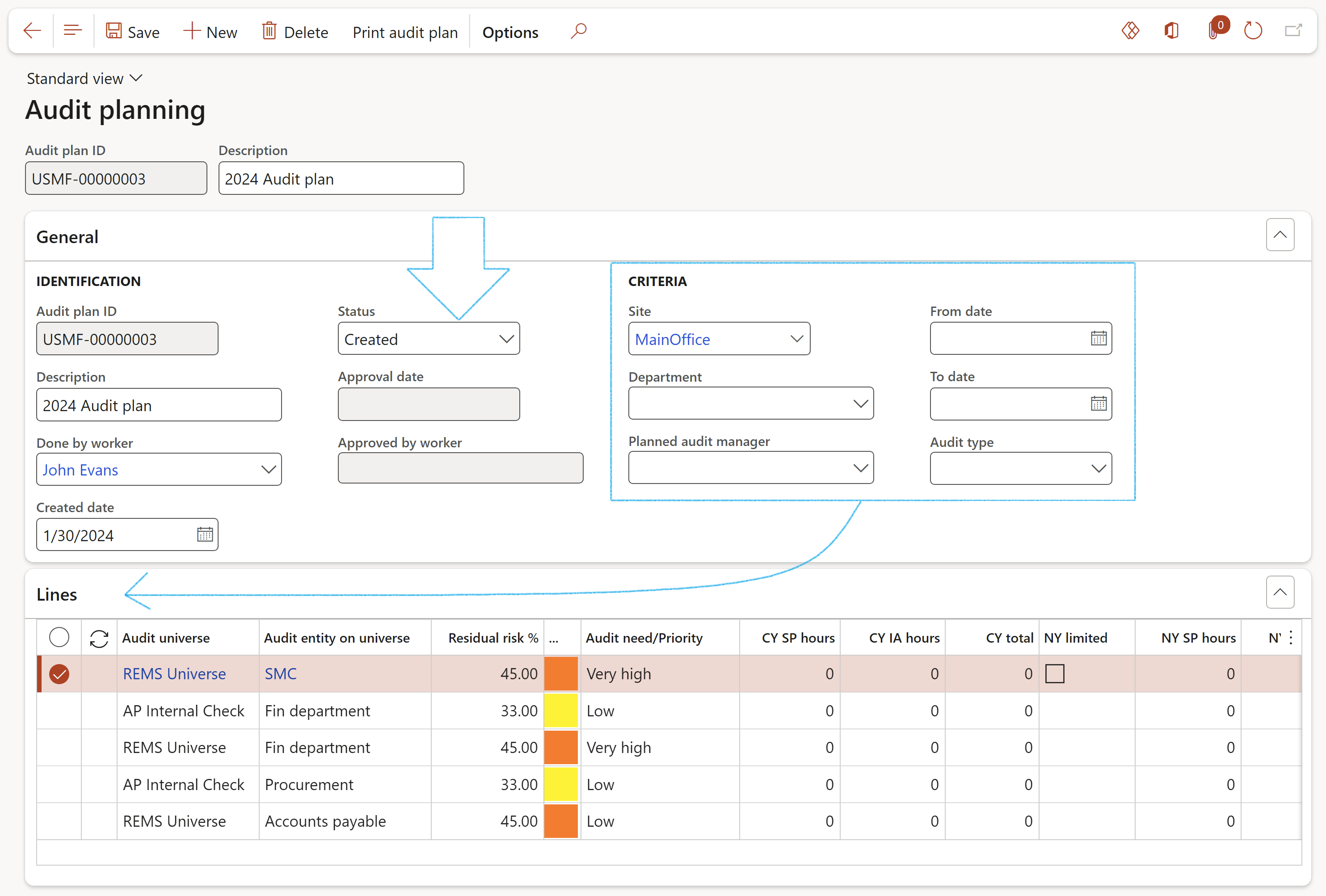
- In the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a Description for the Audit plan
- Expand the General Fast tab
- In the Done by worker field, select the worker who will be doing the audit, from the dropdown list
- The Created date field will by default be "today's" date. This can be changed
- The Status of the plan will by default be Created. When the status is Approved, the plan cannot be deleted.
- The records displayed under the Lines Fast tab are determined by the selection made under the Criteria field group
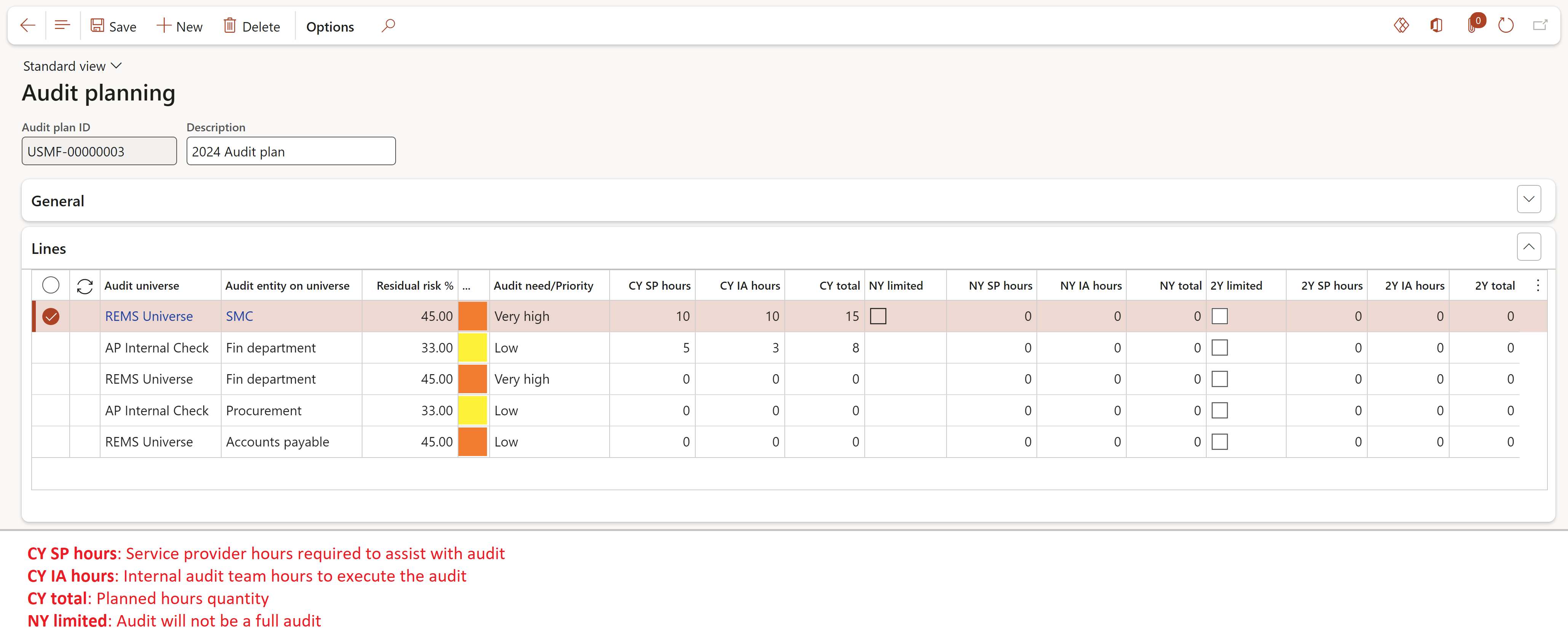
- Expand the Lines Fast tab
- The following can be entered for each line:
- Service provider hours required to assist with the audit (Current year, Next year, in 2 years)
- Internal audit team hours required to execute the audit (Current year, Next year, in 2 years)
- Indication whether it will be a full audit (Current year, Next year, in 2 years)
- Select the relevant parameters on the print dialog
- Click on OK
- Select the relevant Audit universe
- Expand the Auditable entity Fast tab
- The Scheduling period frequency for each Auditable entity will be displayed (it can be changed)
- The last date when a schedule for this Auditable entity was run is displayed, as well as the next scheduled start date.
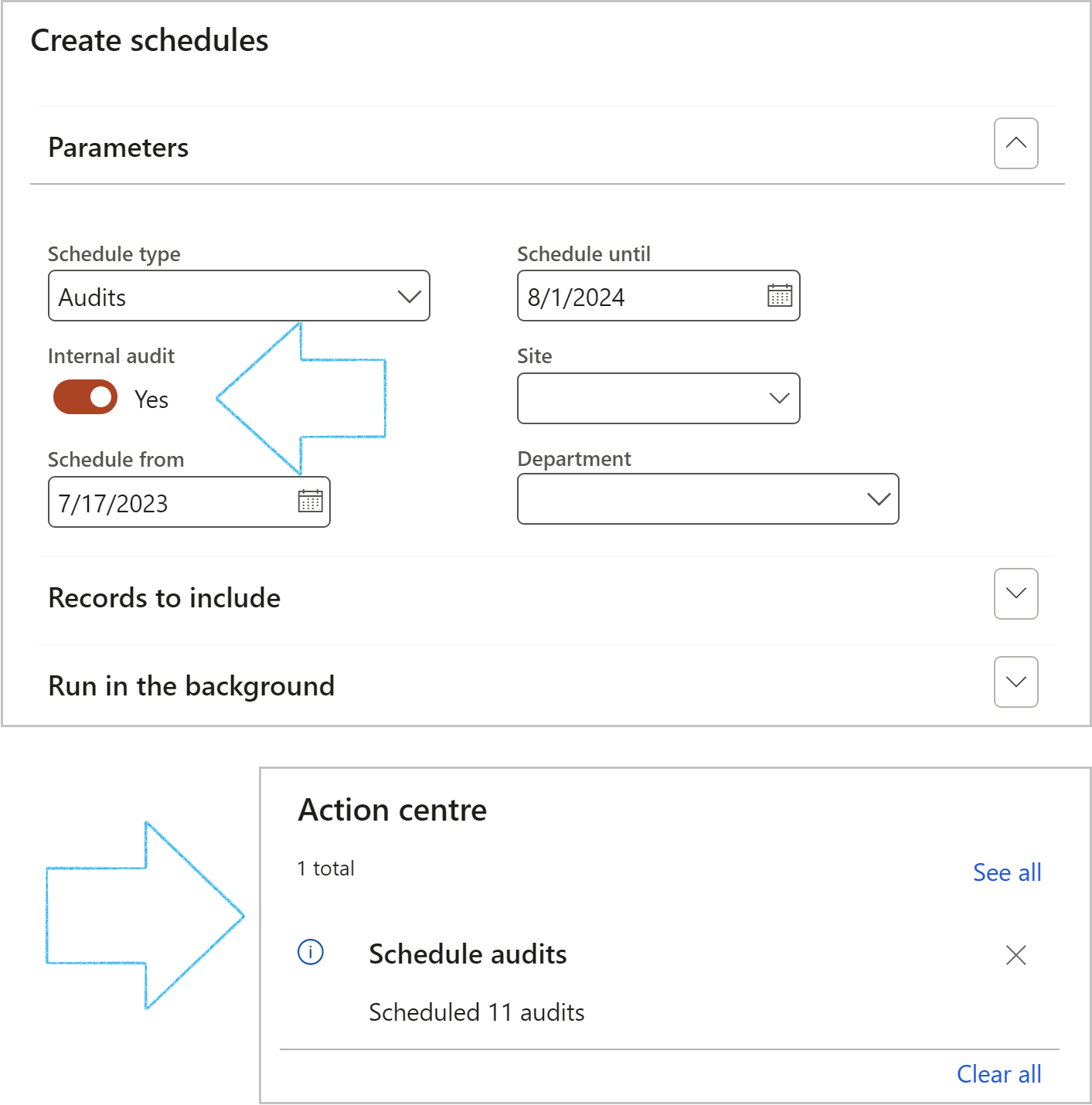
- In the Schedule type field, select Audits
- Select the From and Until dates
- Move the Internal audit slider to Yes
- Choose filters such as:
- Site
- Department
- Click on the OK button
- Only Approved records can be used and will allow users to enter field work. When the status is Approved, the Created, Scheduled and Approved buttons will be unavailable to the user.
- When the status is Created, the Created and Scheduled buttons will be unavailable to the user, and the record cannot be maintained in the Audit file.
- Capacity: Calculates the capacity load of the selected audit according to the budgeted hours
- Select the fields to be displayed
- Select the periods according to date, interval type and interval
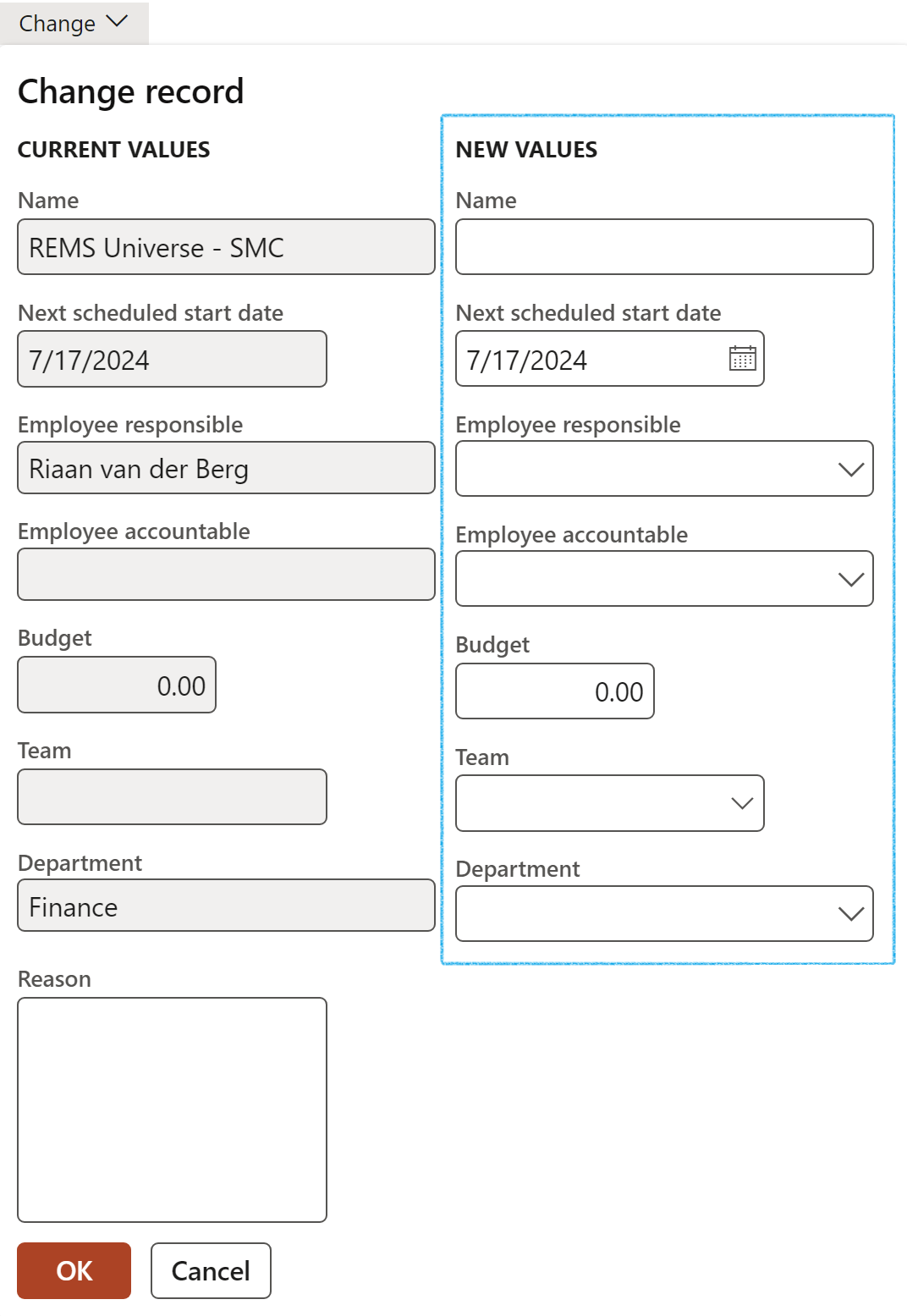
- Change: This function is only available when the status of the audit schedule is Created. The user can change the name of the audit, as well as the next scheduled start date.
- Audits: Opens the audit project list page for the selected Approved audit schedules
- Audit file: Opens the Audit file linked to the selected Approved audit schedule
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- On the Create a new audit (project) dialog, make sure to select Internal in the Project type field
- Enter a Project name (Internal audit name)
- Select the relevant Project group from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Audit universe from the dropdown list
- Edit the Audit file name (If required)
- Enter a Description for the audit file
- Click on the OK button
- Manually: From the Area of compliance (Audit universe) by clicking the Functions button and selecting the Engage option from the dropdown list
- Automatically: When an audit schedule has a status of created, it can be approved in order to create an audit
- Select the Audit (project) that needs to be edited/maintained
- On the Action pane, in the Maintain group, click on the Edit button
- Under the General Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the relevant Audit type from the dropdown list
- Select the Site and Department that the audit is for, from the dropdown lists
- Enter the From and To dates for the period under review
- Select the Team responsible for the auditing
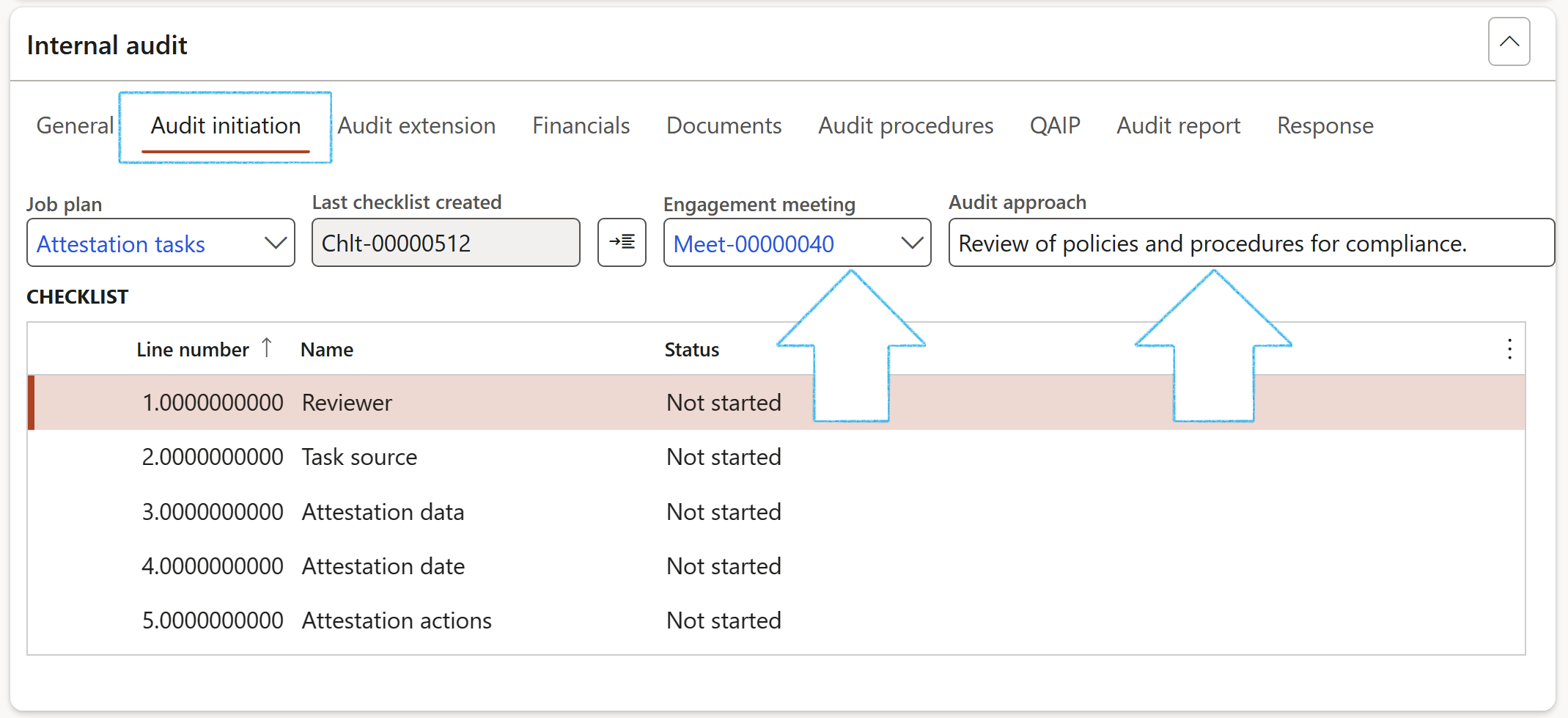
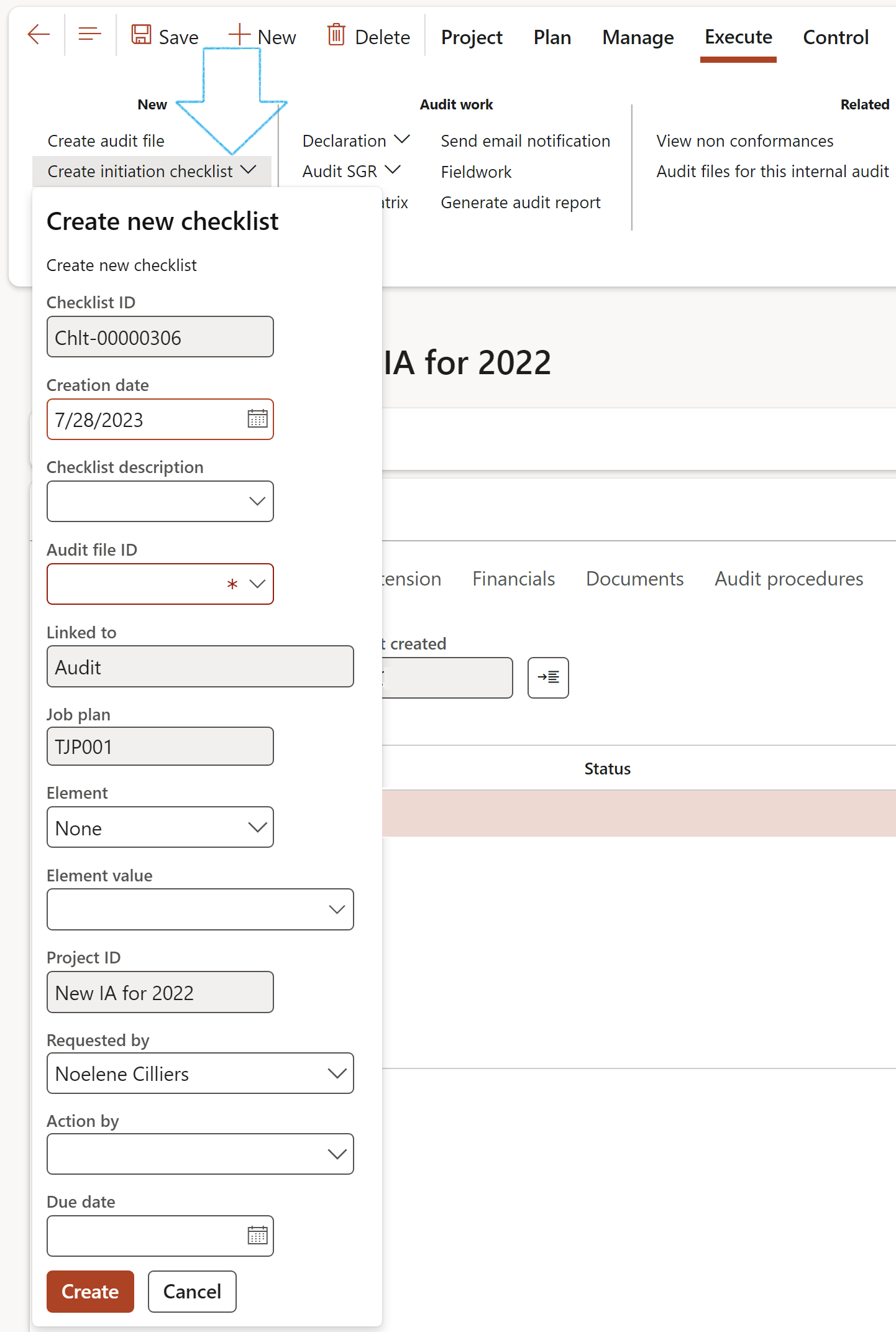
- Under the Audit initiation Index tab:
- Select the relevant Job plan from the dropdown list
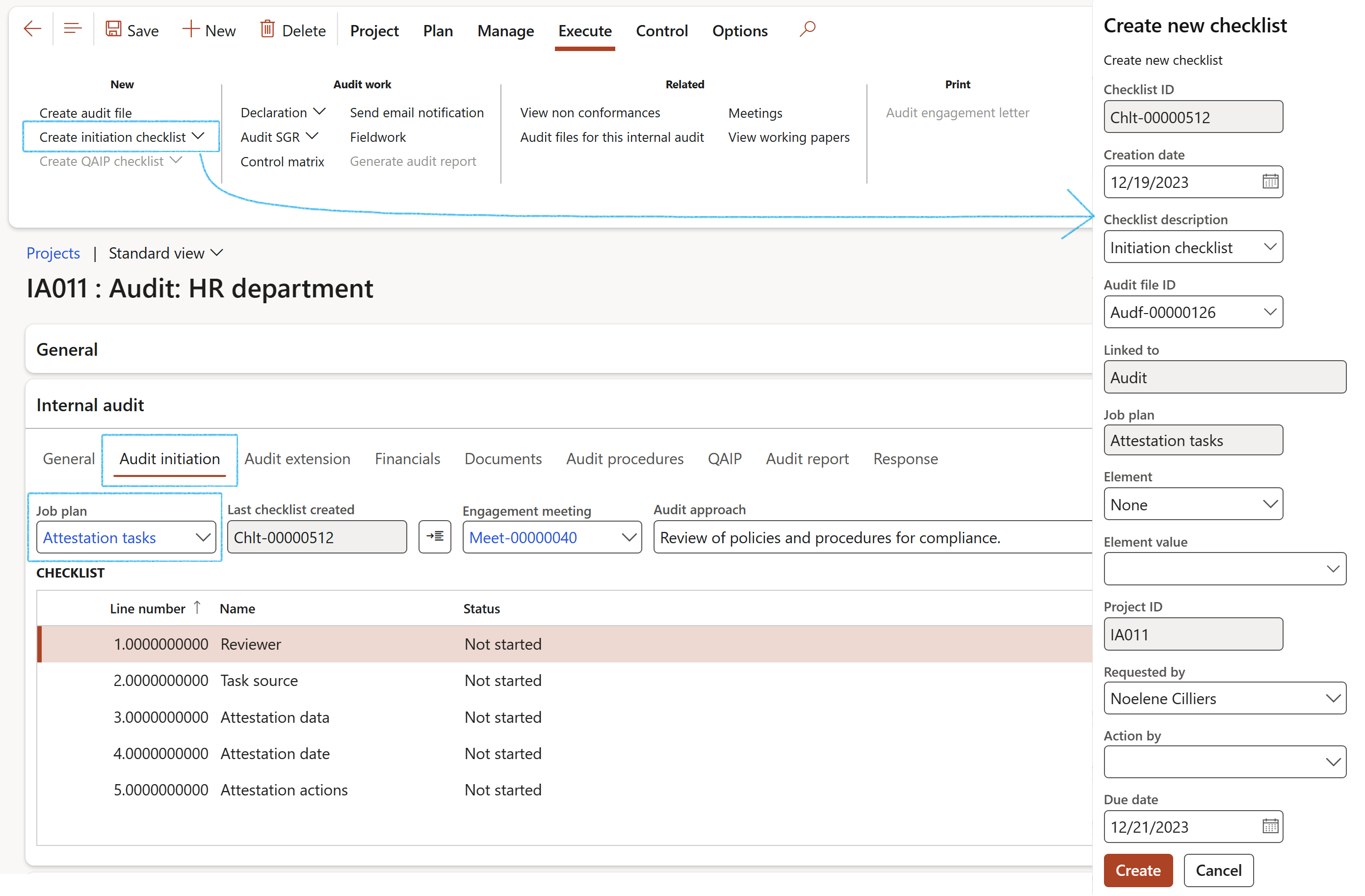
- On the Action pane, click on the Create initiation checklist button
- On the Create new checklist drop dialog, enter a Checklist description
- Select the relevant Audit file ID from the dropdown list
- Click Create
- If an Engagement meeting was held, it can be selected from the dropdown list
- Enter the Audit approach. If the Audit approach was entered on the Audit universe when the audit was created, it will be passed to the Audit.
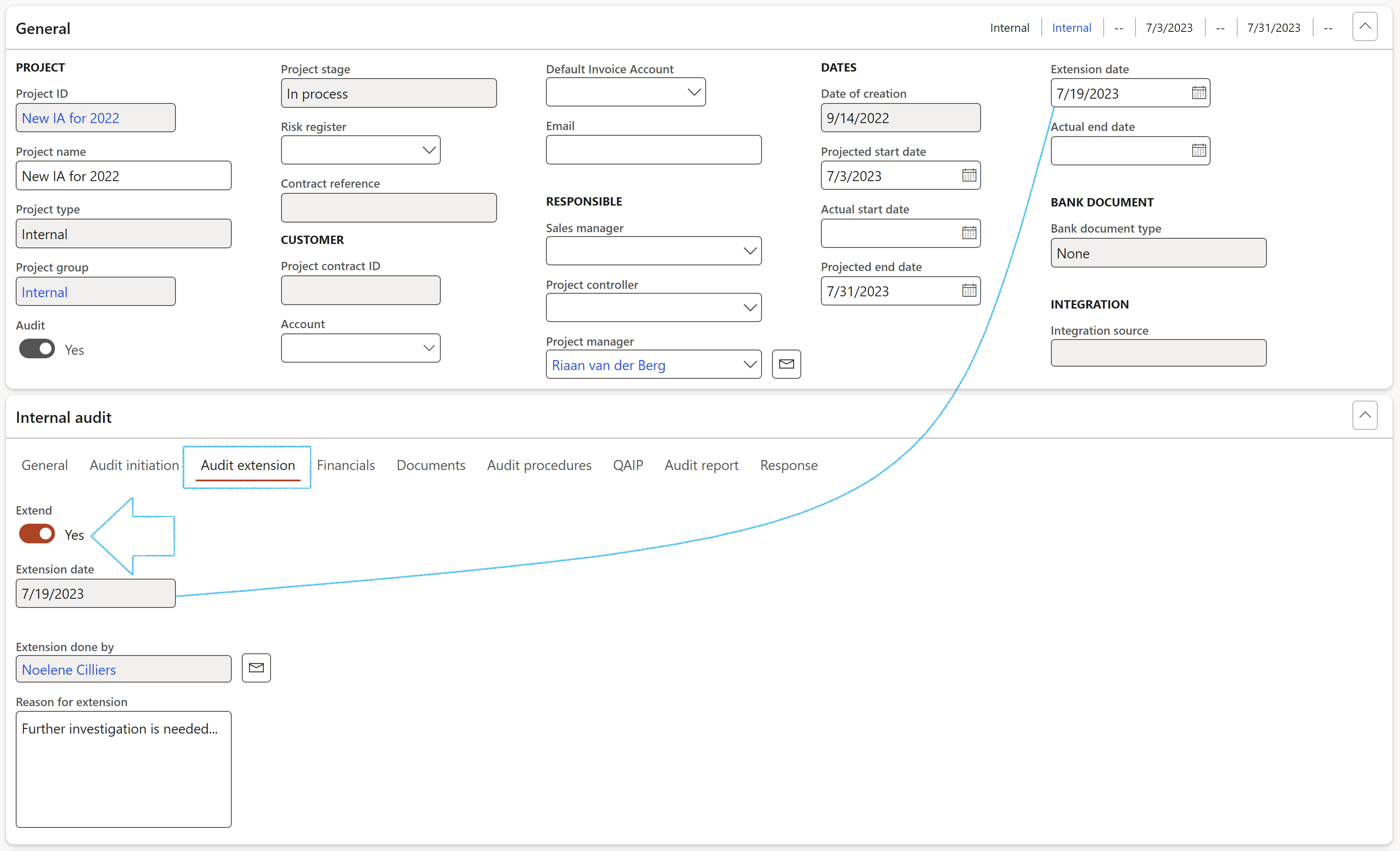
- Under the Audit extension Index tab:
- The date selected in the Extension date field under the General Fast tab will populate the Extension date field
- The logged in user's name will populate the Extension done by field
- A Reason for the extension can be entered
- Move the Extend slider to Yes as indication that the Audit project has been extended
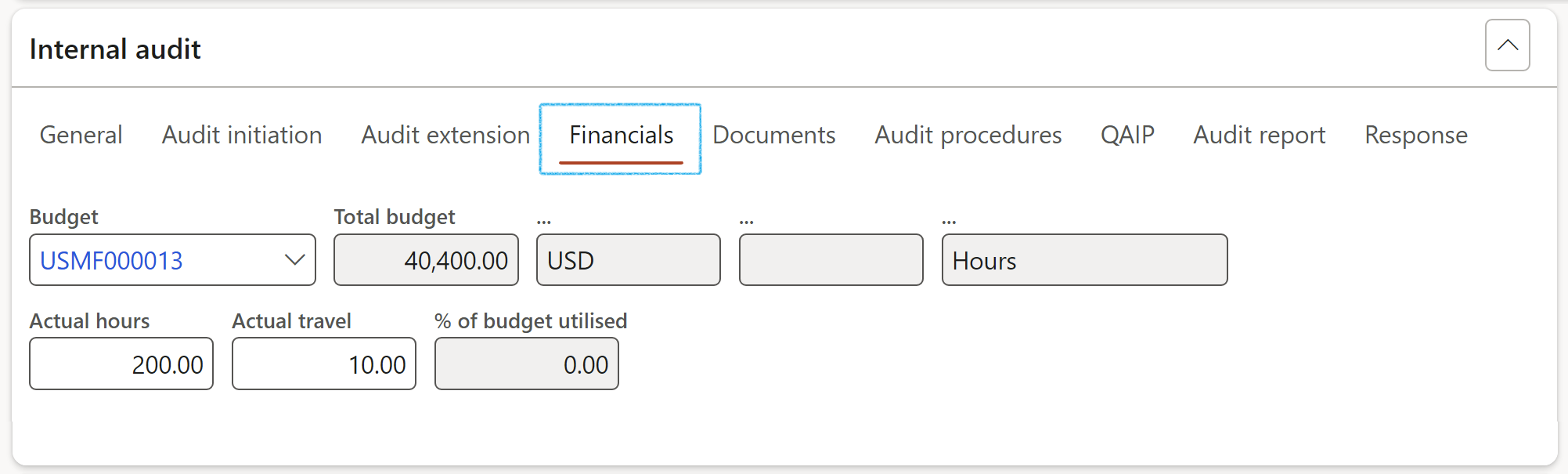
- Under the Financials Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the relevant Budget from the dropdown list
- Enter the Actual hours
- Under the Documents Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the relevant Audit pack from the dropdown list
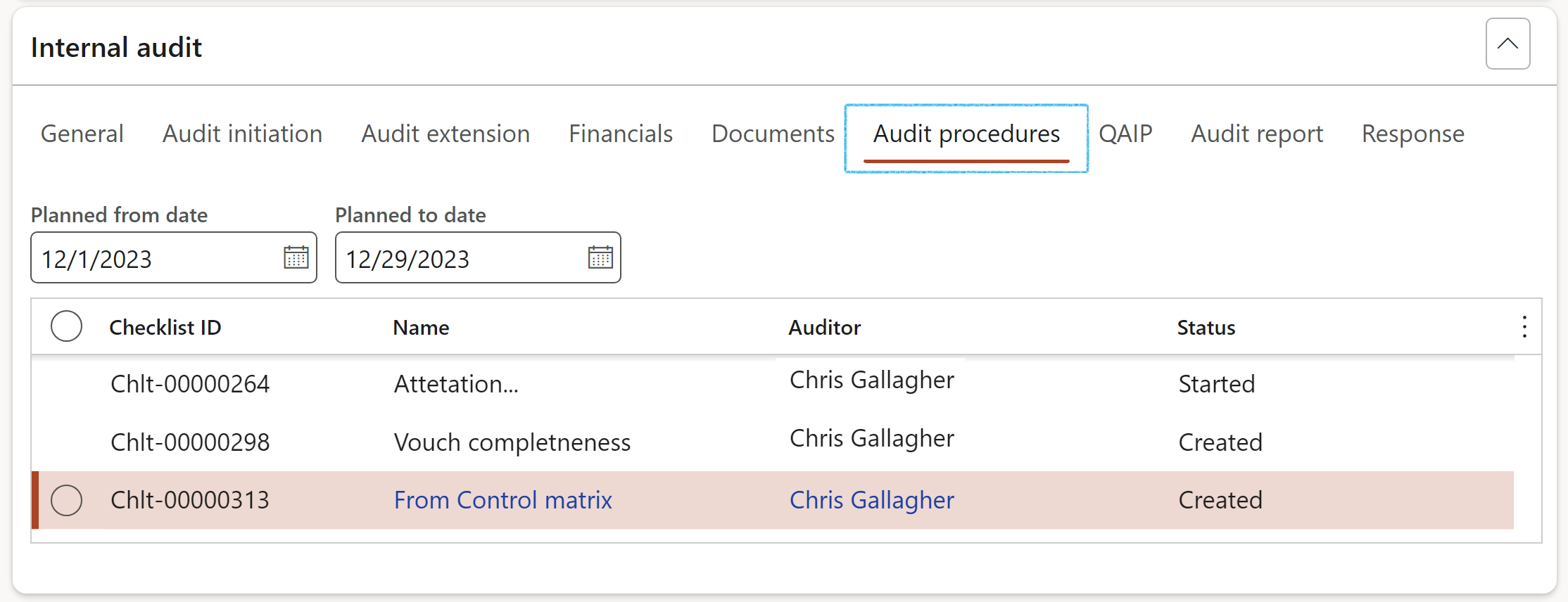
- Open the Audit procedures Index tab
- The Audit procedure checklists that were created from the RCM, are displayed here
- Select the Planned dates for the audit tests/procedures
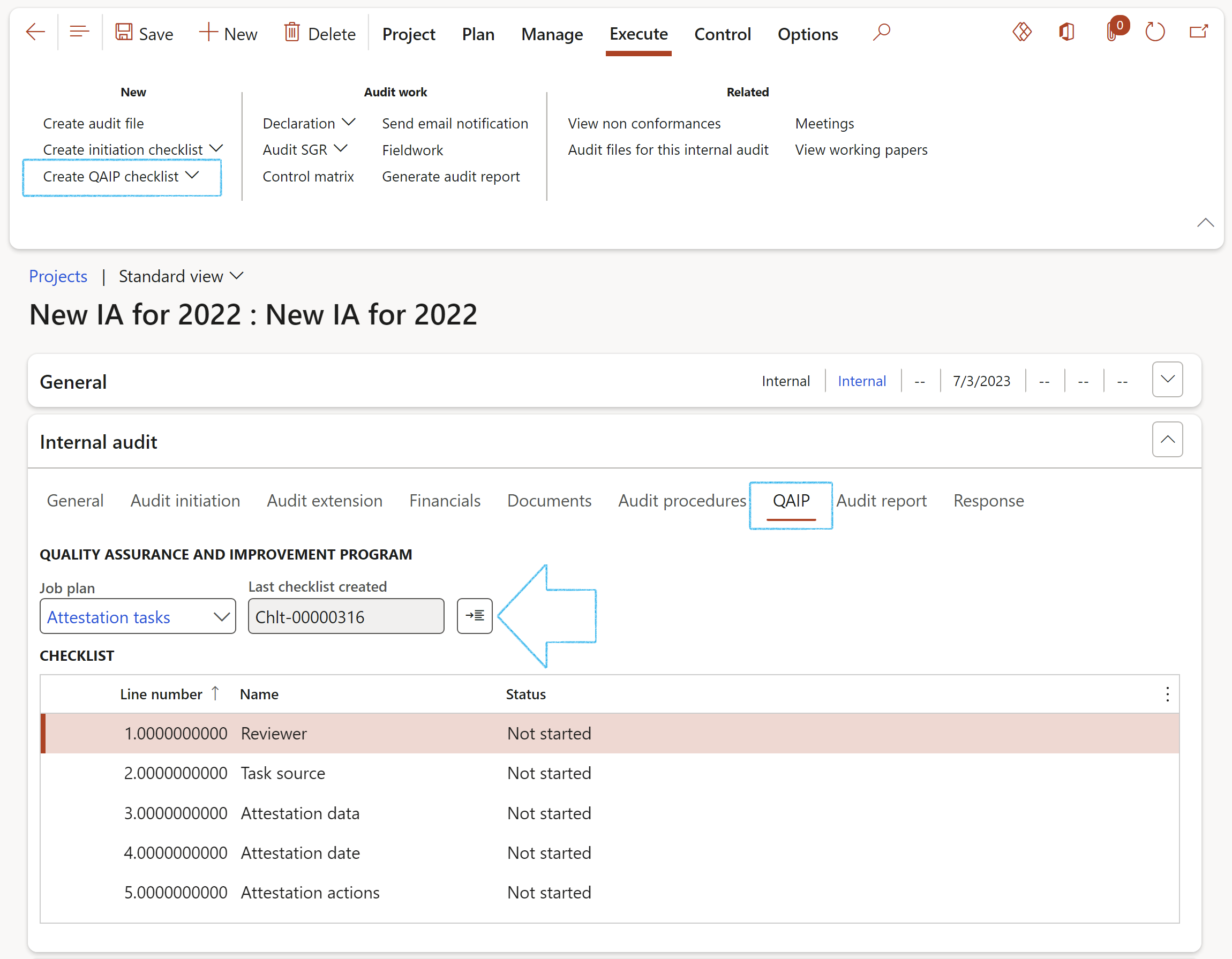
- Under the QAIP Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the relevant Job plan (Quality Assurance Improvement Plan) from the dropdown list
- In the Action pane, click on the Create QAIP checklist button
- Click on the Feedback button to do feedback on the checklist
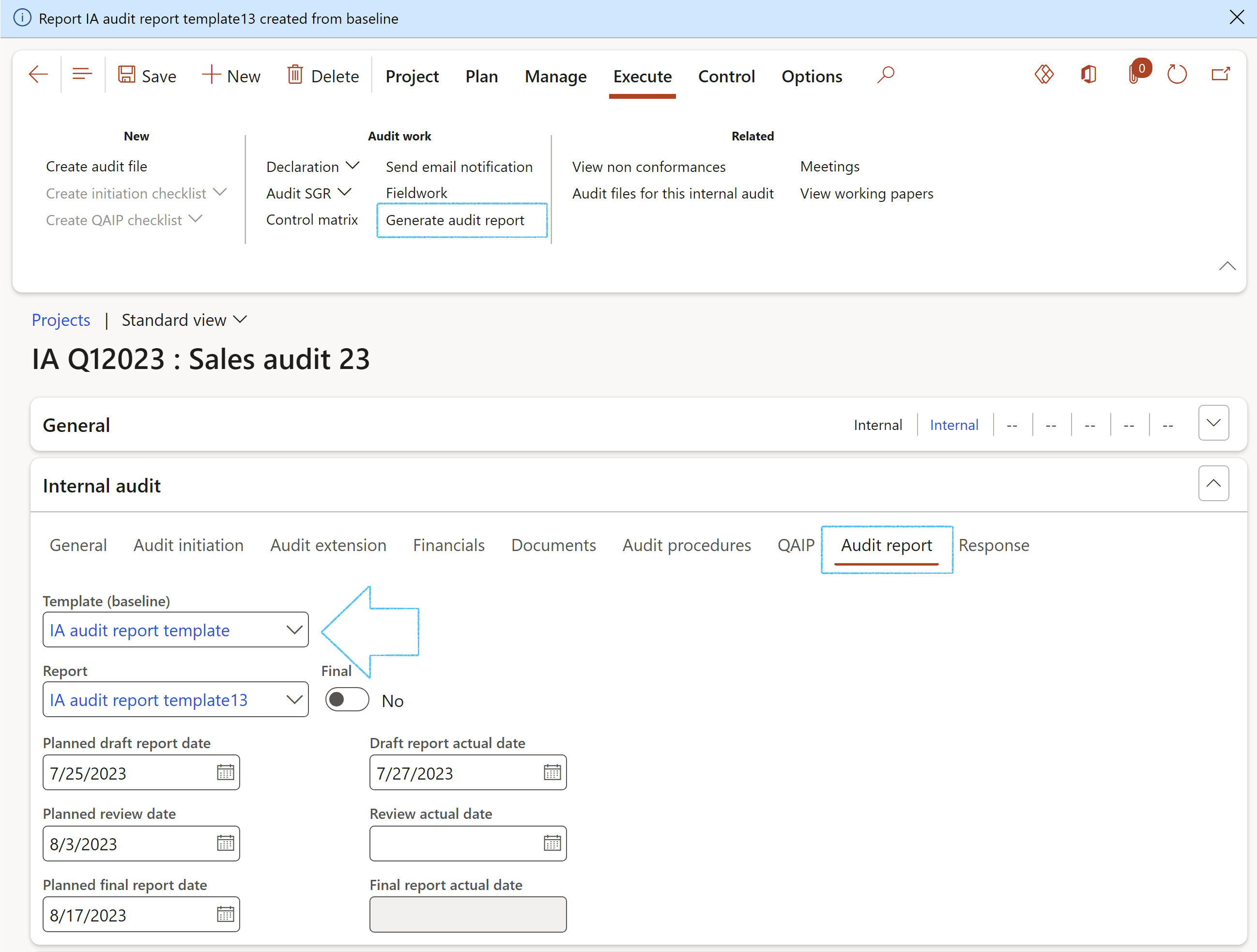
- Under the Audit report Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the Template (baseline) report from the dropdown list
- In the Action pane, click on the Generate audit report button
- The user is given the option to copy attachments from the Baseline Audit report
- A blue line will confirm that the new report has been created, and the Report field will be populated with the name of the newly created report
- Select the Planned date of the draft report
- Select the Planned review date of the report
- Select the Planned final report date of the report
- When the Final slider is set to Yes, the Final report actual date field will be populated with the current/today’s date
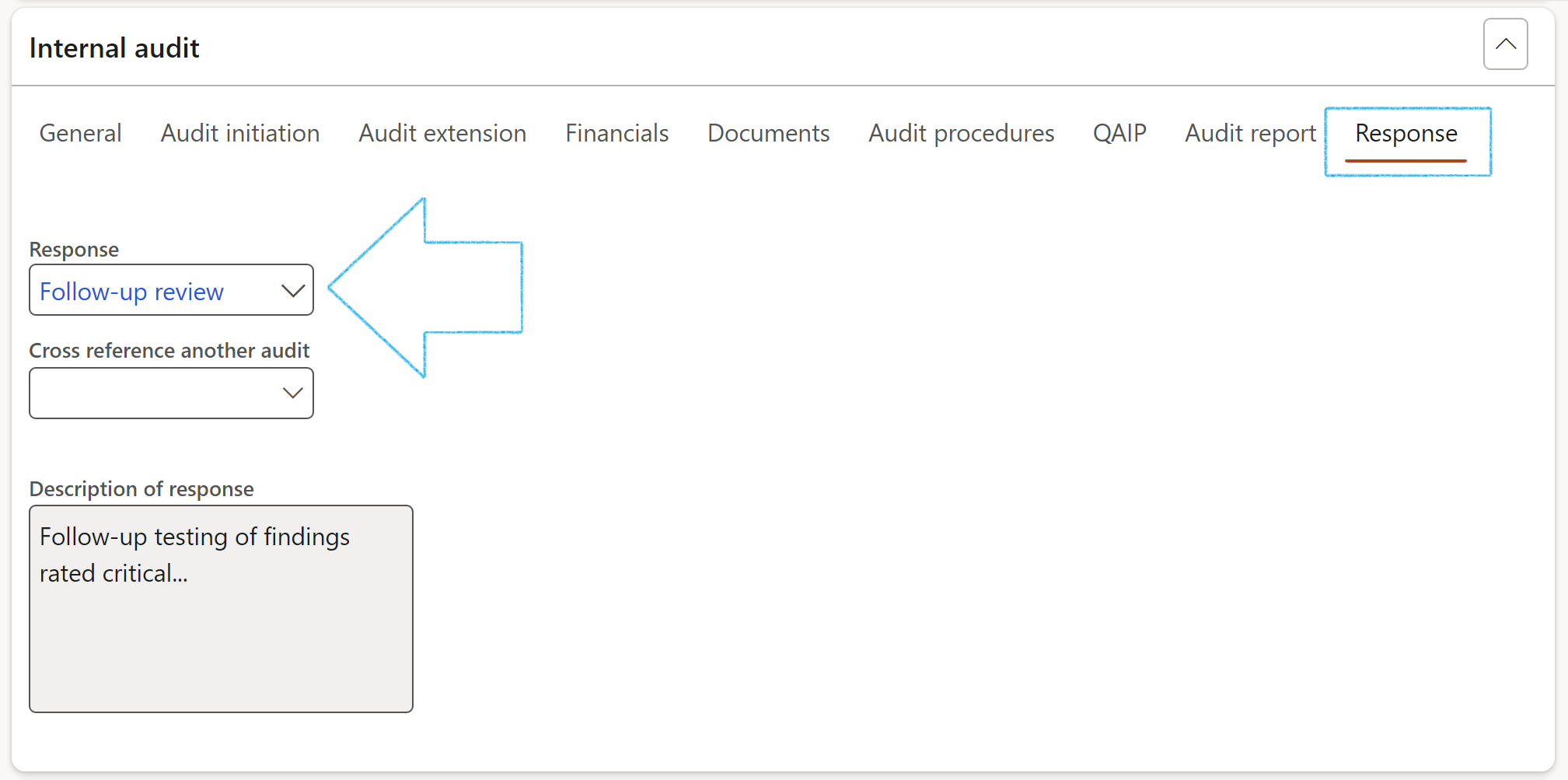
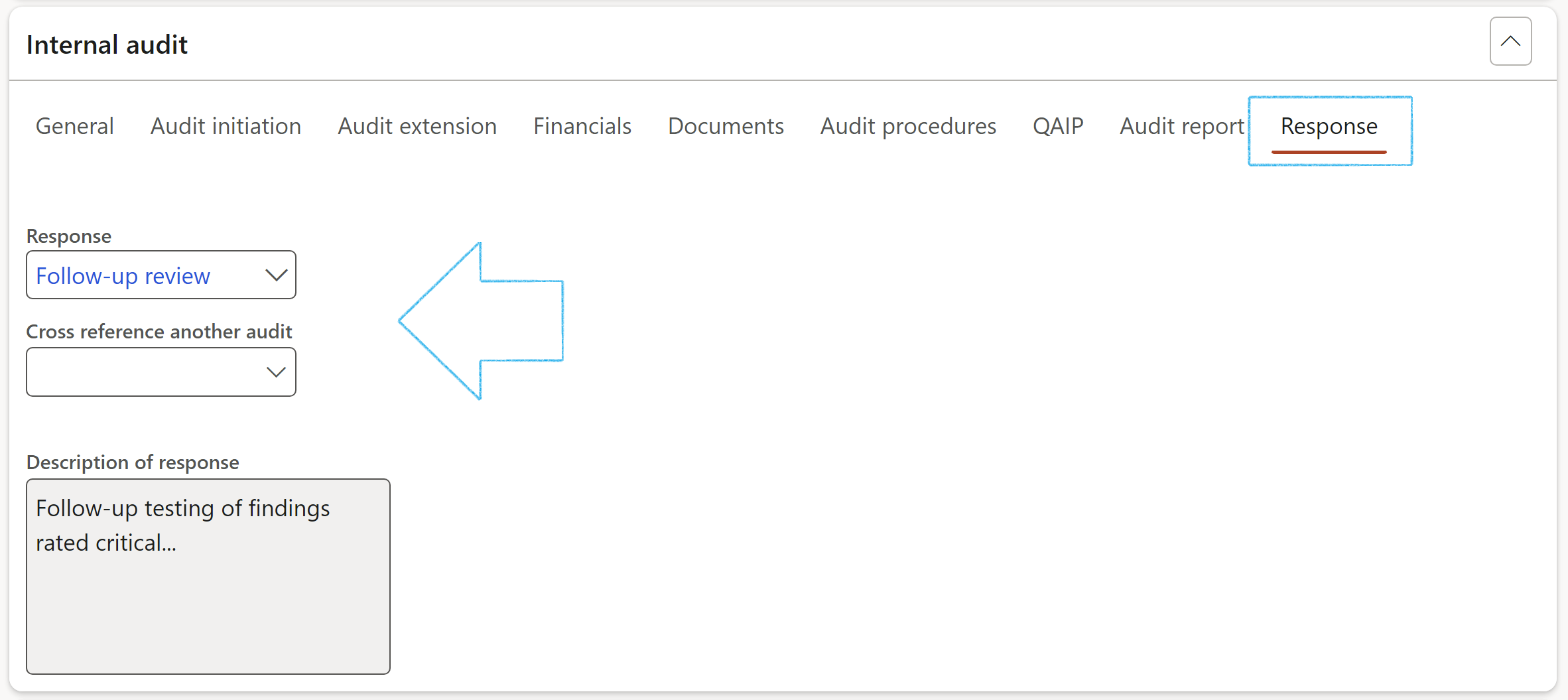
- Under the Response Index tab, enter the following:
- Select the relevant Response from the dropdown list
- Select another audit to cross reference (if applicable)
- On the Action pane, open the Execute tab
- On the Action pane, click on the Declaration button
- Click on the Agree button after reading the Declaration of interest
- On the Action pane, open the Execute tab
- In the Audit work group, click on the Audit SGR button
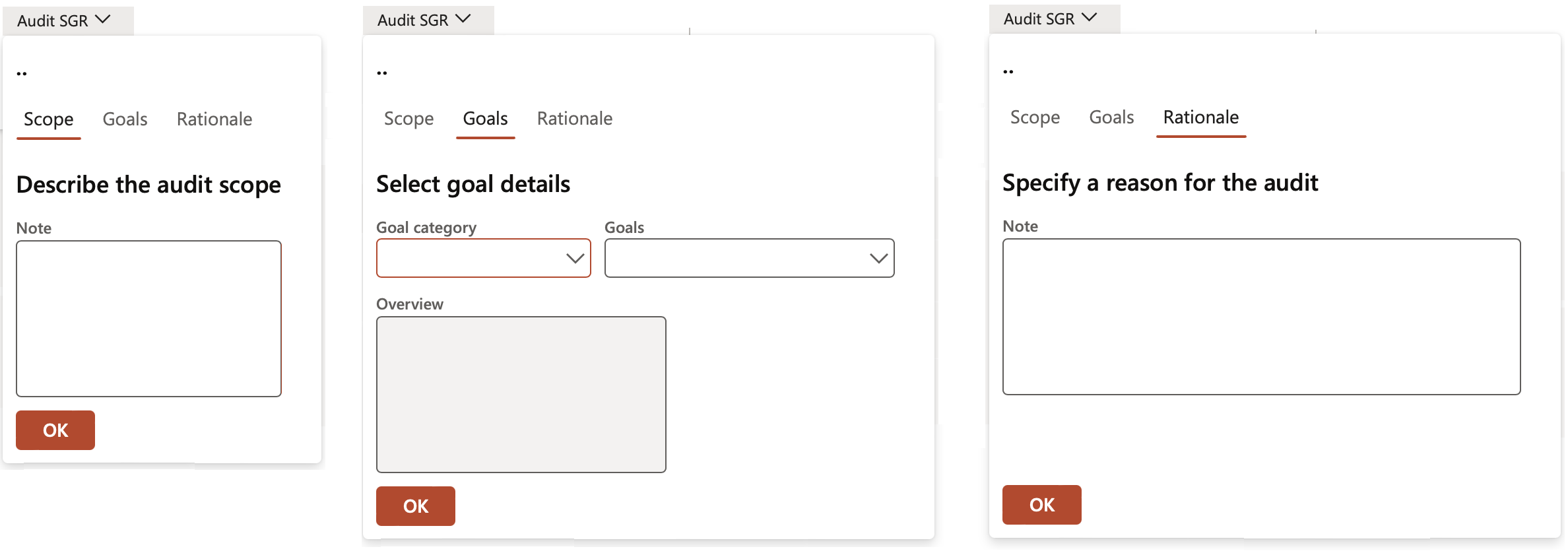
- Under the Scope Index tab, enter notes to describe the audit scope
- Under the Goals Index tab, select the Goal category and the Goal
- Under the Rationale Index tab, specify a reason for the audit
- Click the OK button
- On the Audit project, in the Action pane, open the Execute tab
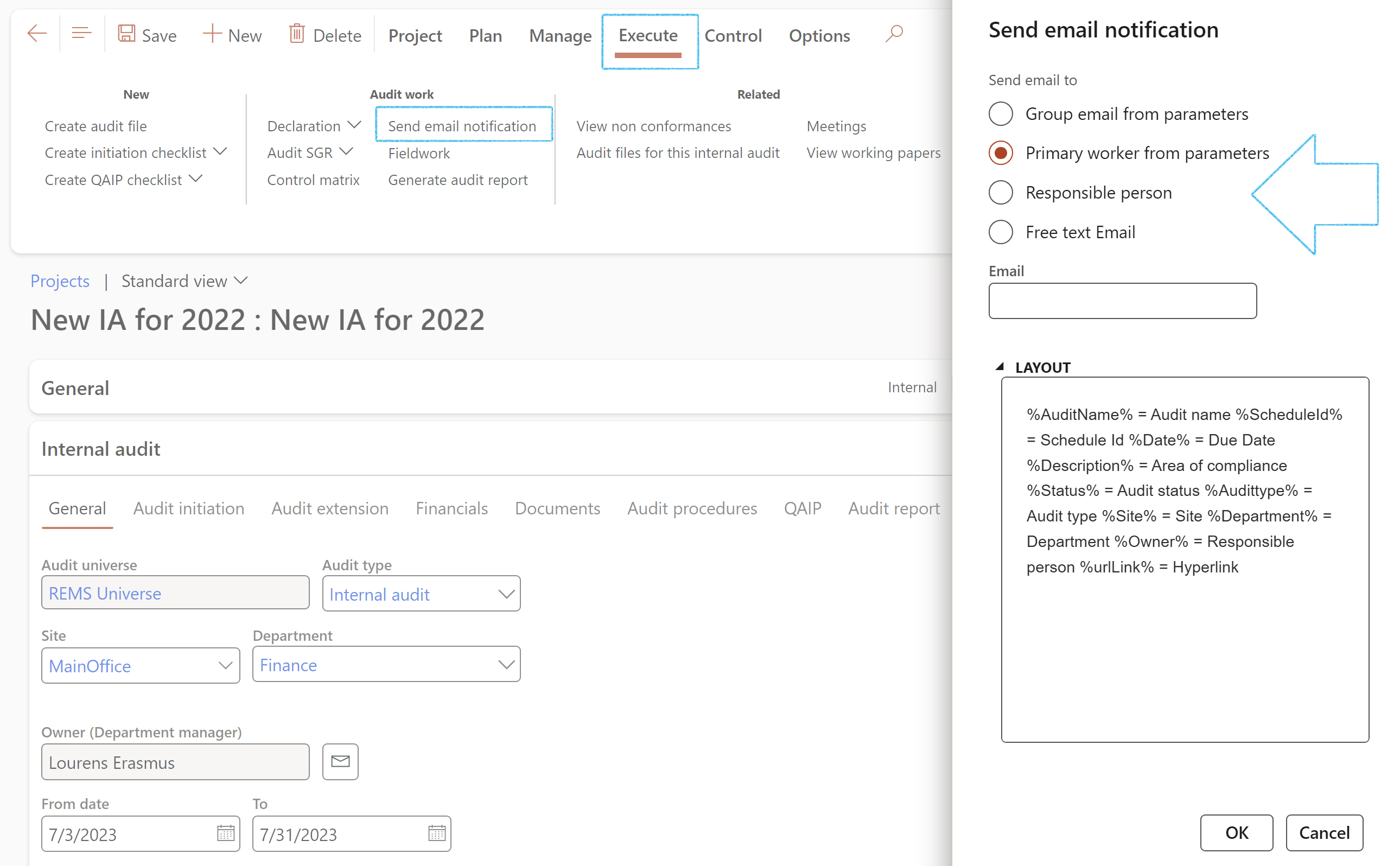
- Click on the Send email notification button
- On the dialog, select the required radio button
- Click OK
- On the Audit project, in the Action pane, open the Execute tab
- Click on the Meetings button
- On the Meetings form, on the Action pane, click on the New button
- On the Audit project, in the Action pane, open the Execute tab
- Click on the Fieldwork button
- On the Fieldwork form, the Audit project name will pull through from the Internal audit project
- Select the relevant Auditable entity from the dropdown list
- Do the scoring for each Clause line
- Complete the header information
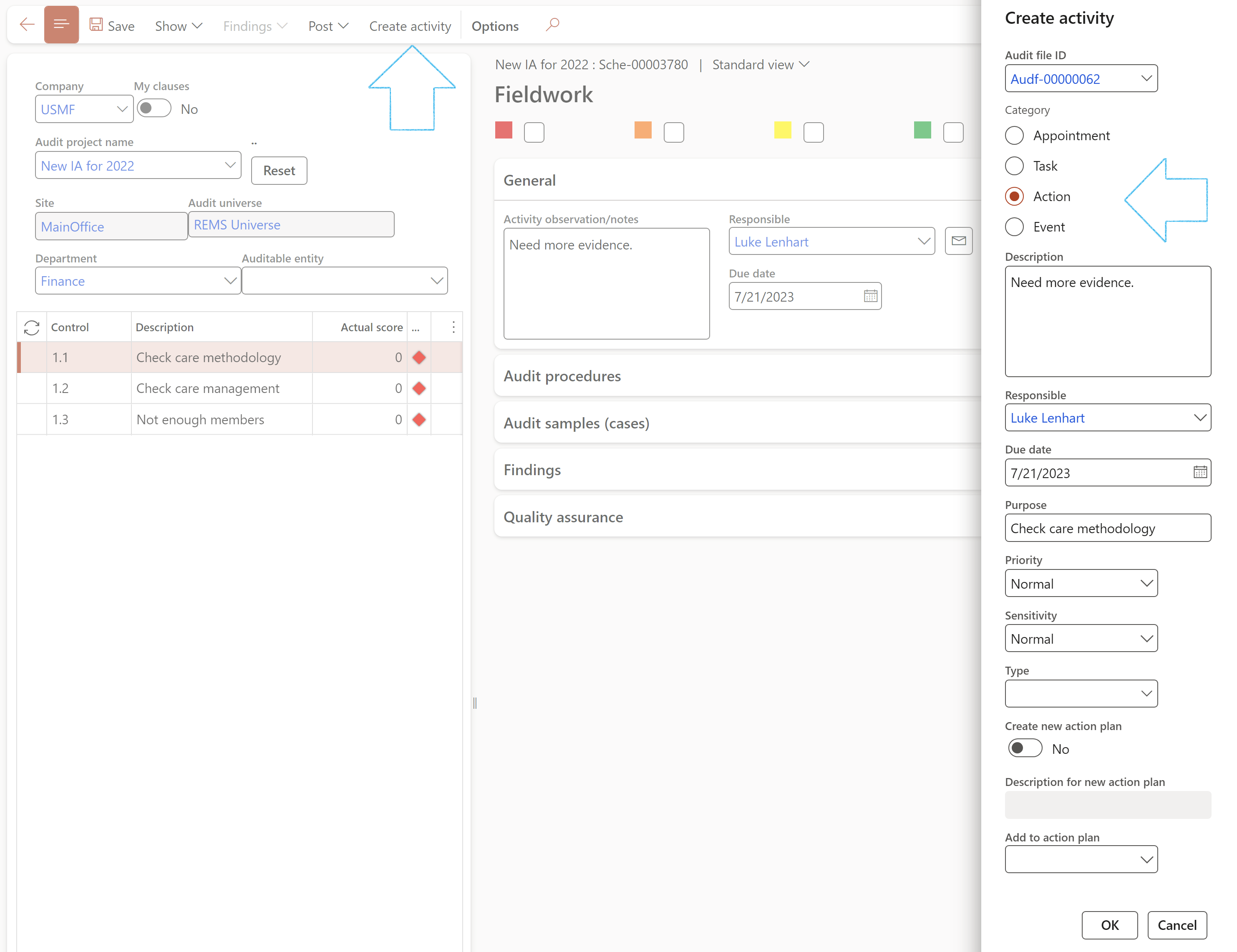
- Select the clause that you want to create the activity for
- On the Action pane, click on the Create activity button
- On the Create activity dialog, select the relevant Audit file ID from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Category
- The Description field is populated with the information entered in the Suggested improvements field under the General Fast tab on the scoring form
- The Responsible field is populated by the person selected under the General Fast tab on the scoring form
- The Due date field is populated by the due date selected under the General Fast tab on the scoring form
- Select the relevant Priority for the activity
- Select the relevant Sensitivity for the activity
- The user has the option to Create a new action plan, OR
- Select the Action plan that you want to add the activity to
- Click OK
- On the Action pane, in the Execution Tab, click on the Audit files for this internal audit button
- Under the Internal audit Fast tab, open the Audit initiation Index tab
- Select the relevant Job plan from the dropdown list
- On the Action pane, click on the Create initiation checklist button
- Enter the relevant detail on the Create new checklist dialog
- Click Create
- Under the Internal audit Fast tab, open the QAIP Index tab
- Select the relevant Job plan from the dropdown list
- On the Action pane, click on the Create QAIP checklist button
- Enter the relevant detail on the Create new checklist dialog
- Click Create
- The Time and material group
- On the Action pane, click on the Generate audit report button
- A pop-up will ask the user if it is required to copy the attachments from the selected Baseline audit report
- A blue line will confirm that the report has been created
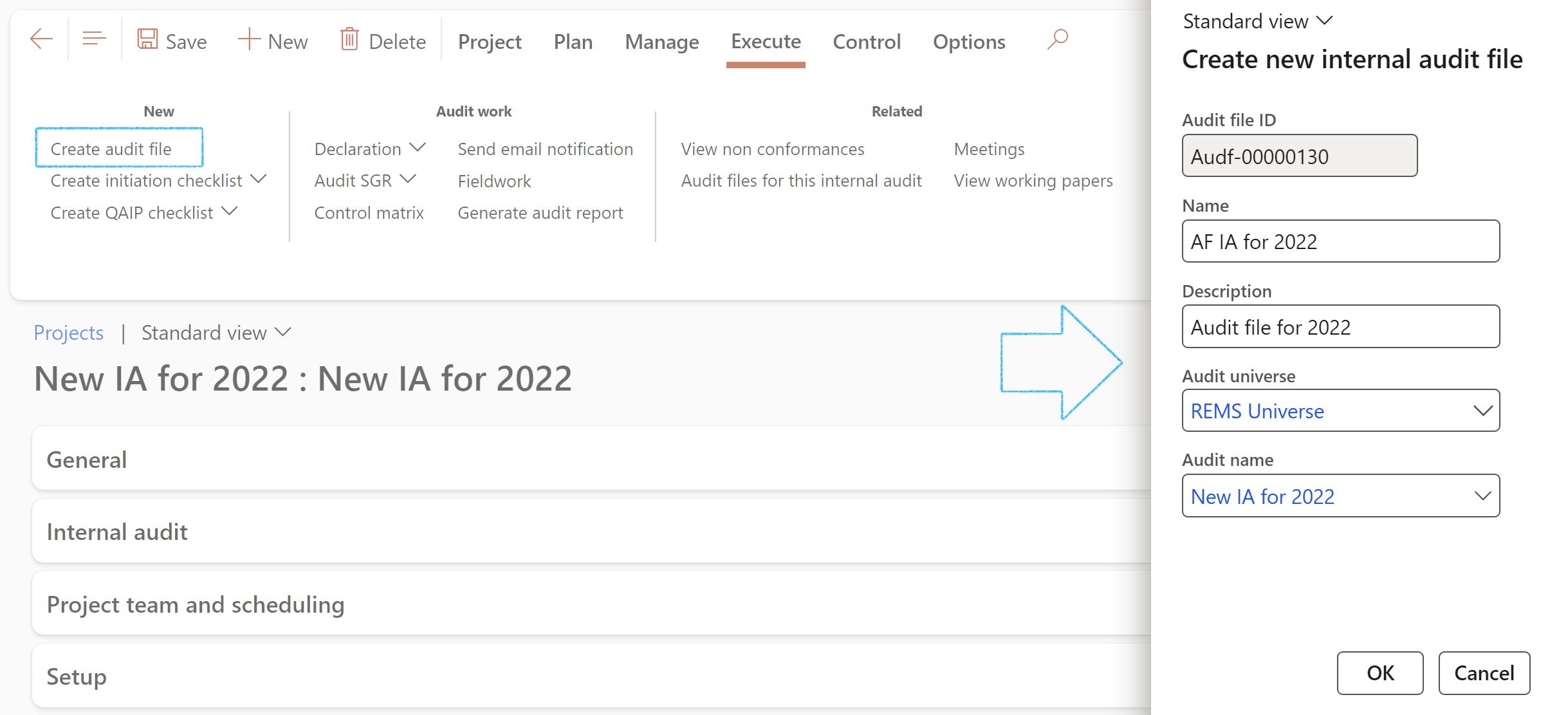
- On the Action pane, click on the Create audit file button
- On the Create new internal audit file dialog:
- The audit file Name field will be populated but can be edited
- Enter a Description for the new Audit file
- Click OK
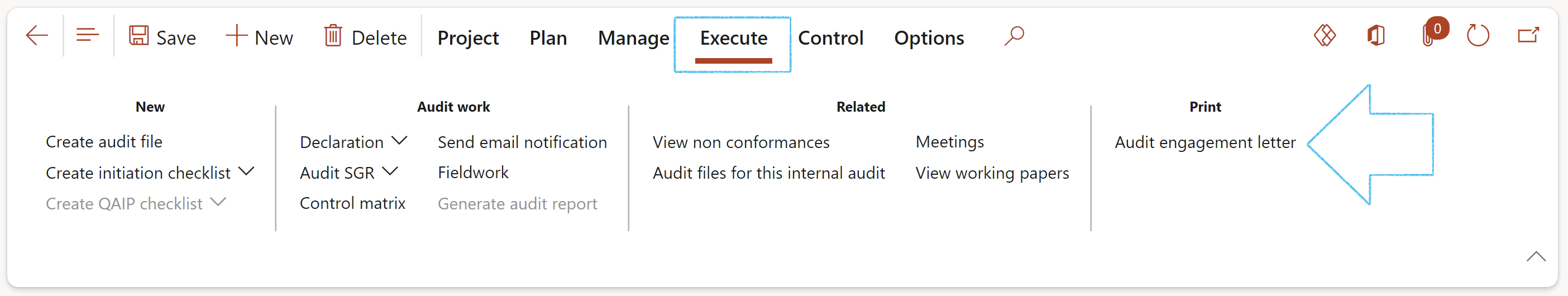
- On the Action pane, under the Execute tab, click on the Audit engagement letter button
- On the Action pane of the Audit project, open the Execute Tab
- Click on the Control matrix button
- To add a missing control: on the Action pane, click on the New button
- Select the relevant Auditable entity from the dropdown list
- Enter the new Control
- Enter a brief Description for the new control
- Select the relevant Control category from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Control frequency from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Control objective from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Business process from the dropdown list
- Select the control Owner from the dropdown list
- Indicate whether this control is CAATs applicable
- Indicate whether this control is Manual
- Indicate whether this control is a Key control
- Indicate whether this control is a Fraud case
- Enter details of the Control walk through in the box provided
- The Missing slider will automatically be on Yes for newly added controls
- Once controls have beenn saved they cannot be deleted
- Expand the Risk Fast tab
- Select the relevant Inherent likelihood from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Inherent consequence from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Risk register from the dropdown list (if applicable)
- Click on the Risk assessment button on the Action pane
- If a Risk register already exists, click on Add risk line
- If a Risk register does not exist, click on New risk register and line
- Enter the Line details on the risk assessment form
- Select the relevant Inherent likelihood from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Inherent consequence from the dropdown list
- Click on the Create button
- Expand the Audit procedures Fast tab
- Select the relevant Testing procedure from the drop-down list. The "Planned auditor" might be pre-populated based on the the planned auditor on the Audit universe
- Click on the New audit procedure button in then Action pane
- Complete the New audit procedure dialog and click on Create
- Click on the Feedback button to work on the created audit procedure (checklist)
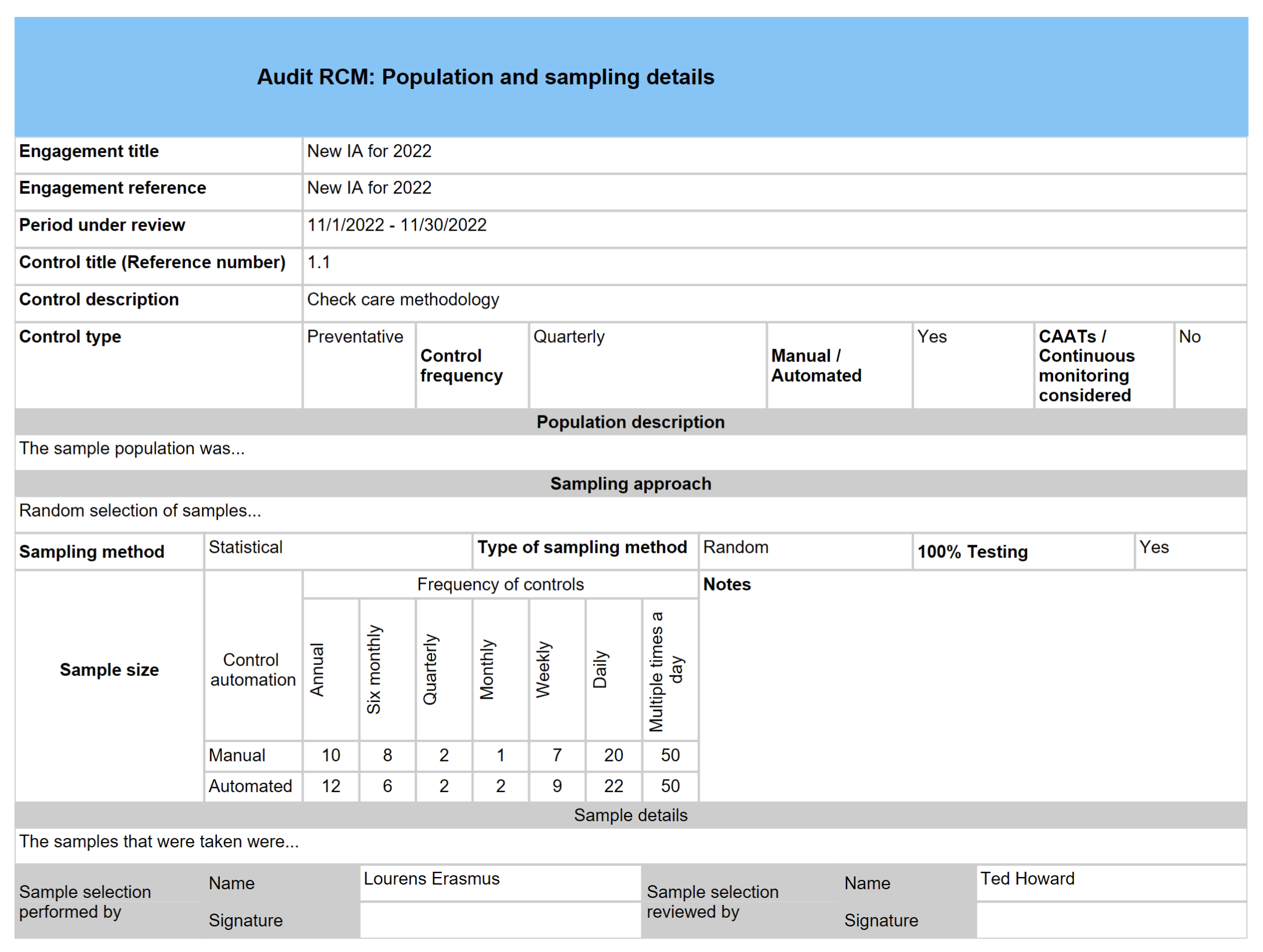
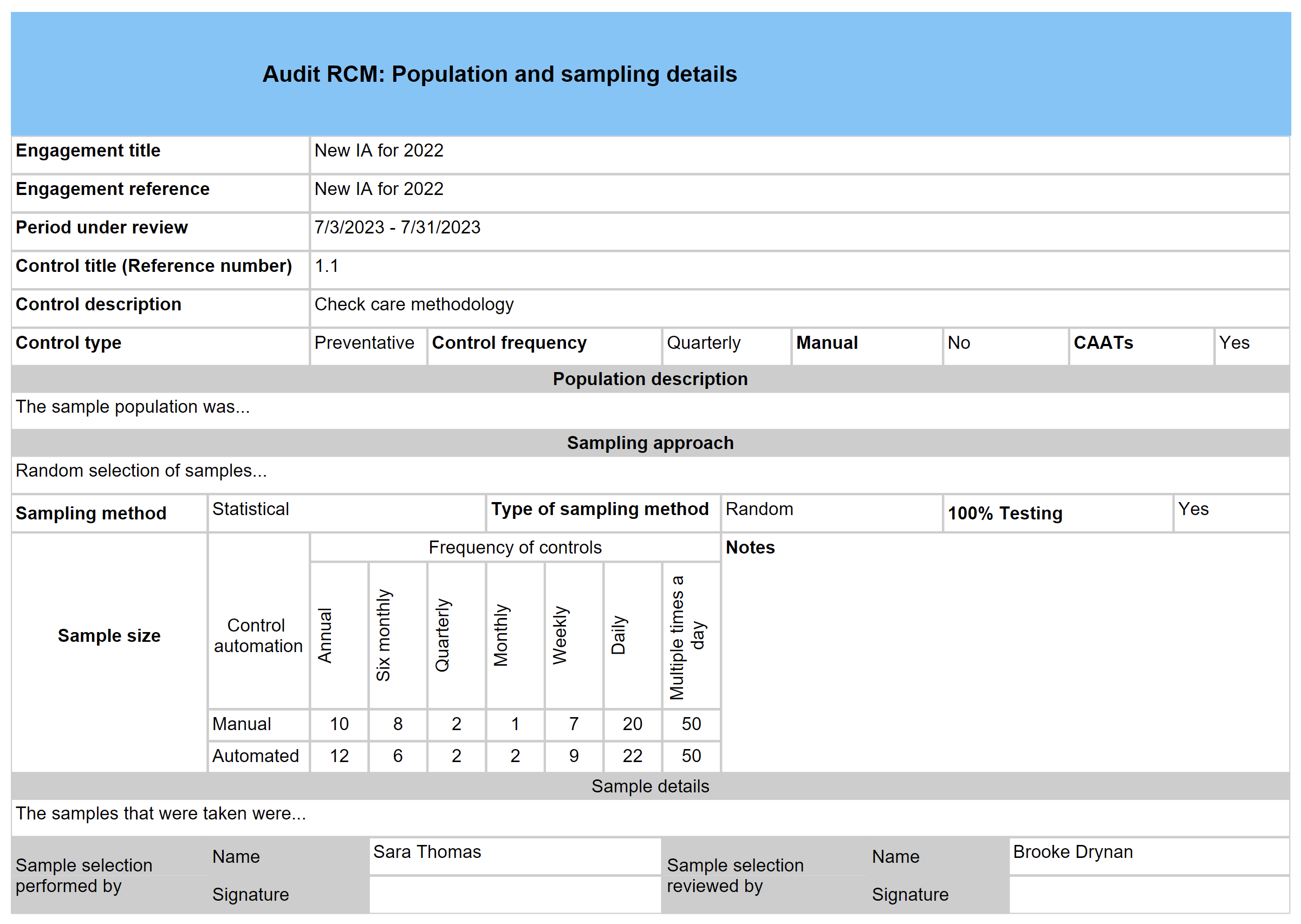
- Expand the Population detail Fast tab
- Enter a description of the sample population
- Expand the Sample sizes Fast tab
- Select the relevant Sampling method from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Sample type from the dropdown list
- Enter details regarding the approcah followed
- Enter details regarding the sample
- Select the relevant Sampling rules (Audit policy) from the dropdown list
- Enter the sample sizes under the Manual controls Field group
- Enter the sample sizes under the Automated controls Field group
- Indicate whether the testing was done on 100% of the samples taken, by moving the 100% Testing slider to Yes
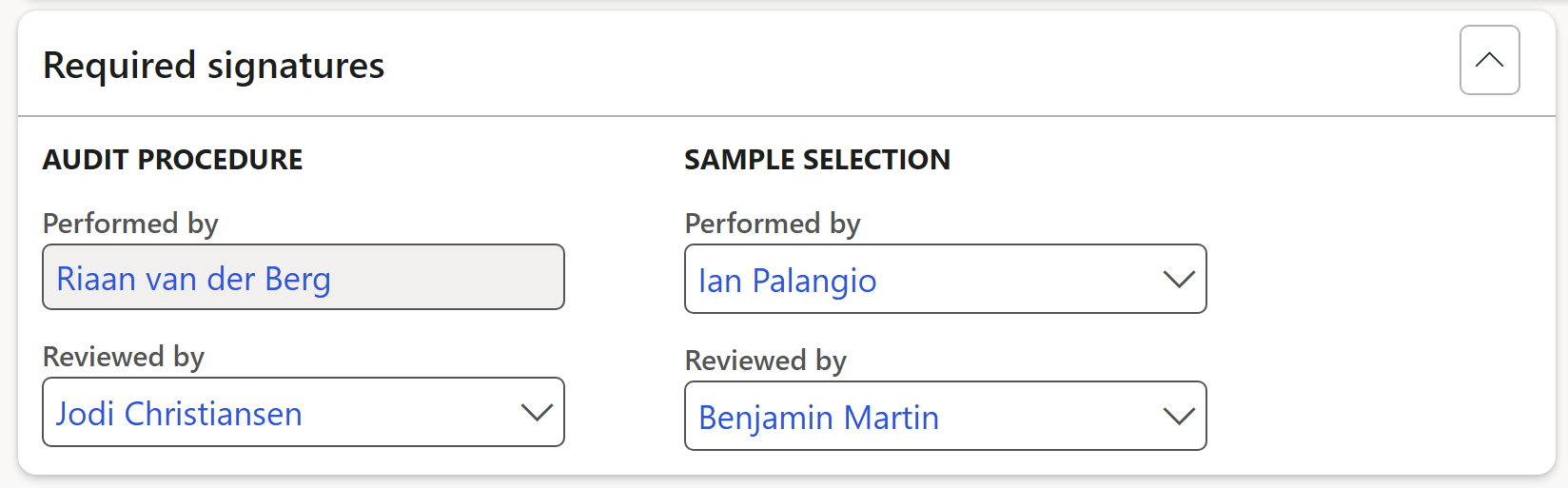
- Expand the Required signatures Fast tab
- Select the name of the worker who performed the audit procedure, from the dropdown list
- Select the name of the worker who reviewed the audit procedure, from the dropdown list
- Select the name of the worker who performed the sample selection, from the dropdown list
- Select the name of the worker who reviewed the sample selection, from the dropdown list
- Click on the Print button on the Action pane
- On the Action pane of the Audit project form, under the Execute tab, in the Related button group, click on the Audit files for this internal audit button
- It is automatically created from the Audit universe when users select the Manual audit function from the Functions button dropdown list
- When a scheduled/planned audit is Approved
- Manually, by clicking the New button on the Audit file
- To send an email to users selected under Administration, click on the email icon next to the relevant name
- The selected worker must have a primary email address
- Select the relevant Improvement plan from the dropdown list
- In the Action pane, click on the Create QAIP checklist button
- Complete the Create new checklist dialog
- Feedback can be done on the checklist by clicking on the feedback button
- Expand the Audit file comments Fast tab
- Click on the Comment button in the Action pane
- Enter comments on the Comment on audit file dialog
- Click on the OK button
- Enter Lessons learned in the box provided
- Enter the Action taken by employer in the box provided
- Enter the Due date for the activity
- Select the Responsible person for the activity
- Enter a Description
- Select the Priority
- On the Action pane, click on the Create activity button and select the relevant action from the dropdown list
- The Completed scores Fast tab displays the actual score for the Auditable entity
- The Scores detail Fast tab displays the actual scores per clause
- Select the Audit file to be worked on from the list page (note the column indicating the quantity of working papers inside the file)
- Open the "Working paper and samples" Fast tab
- Void = Cancelled
- Completed = Closed
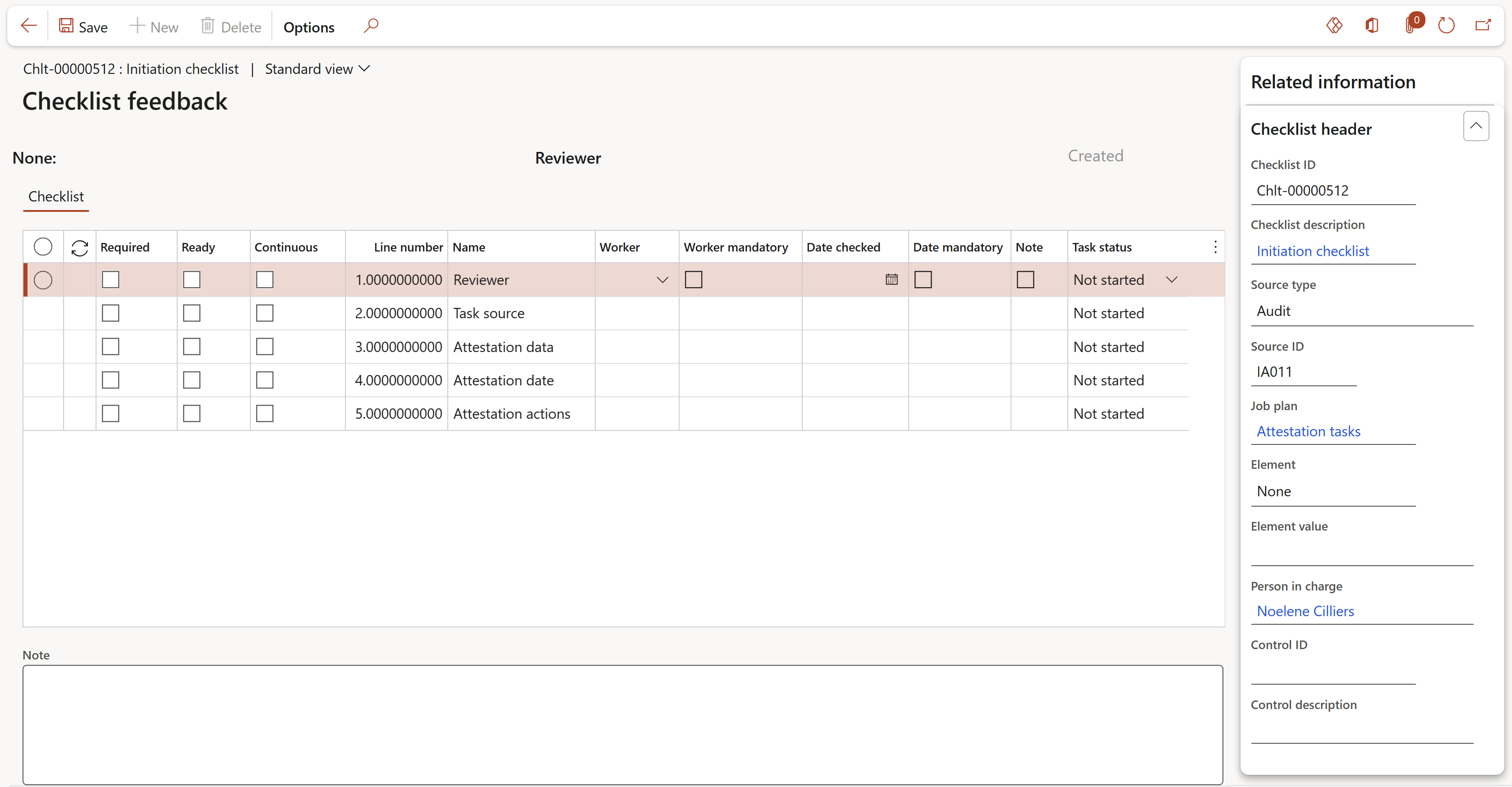
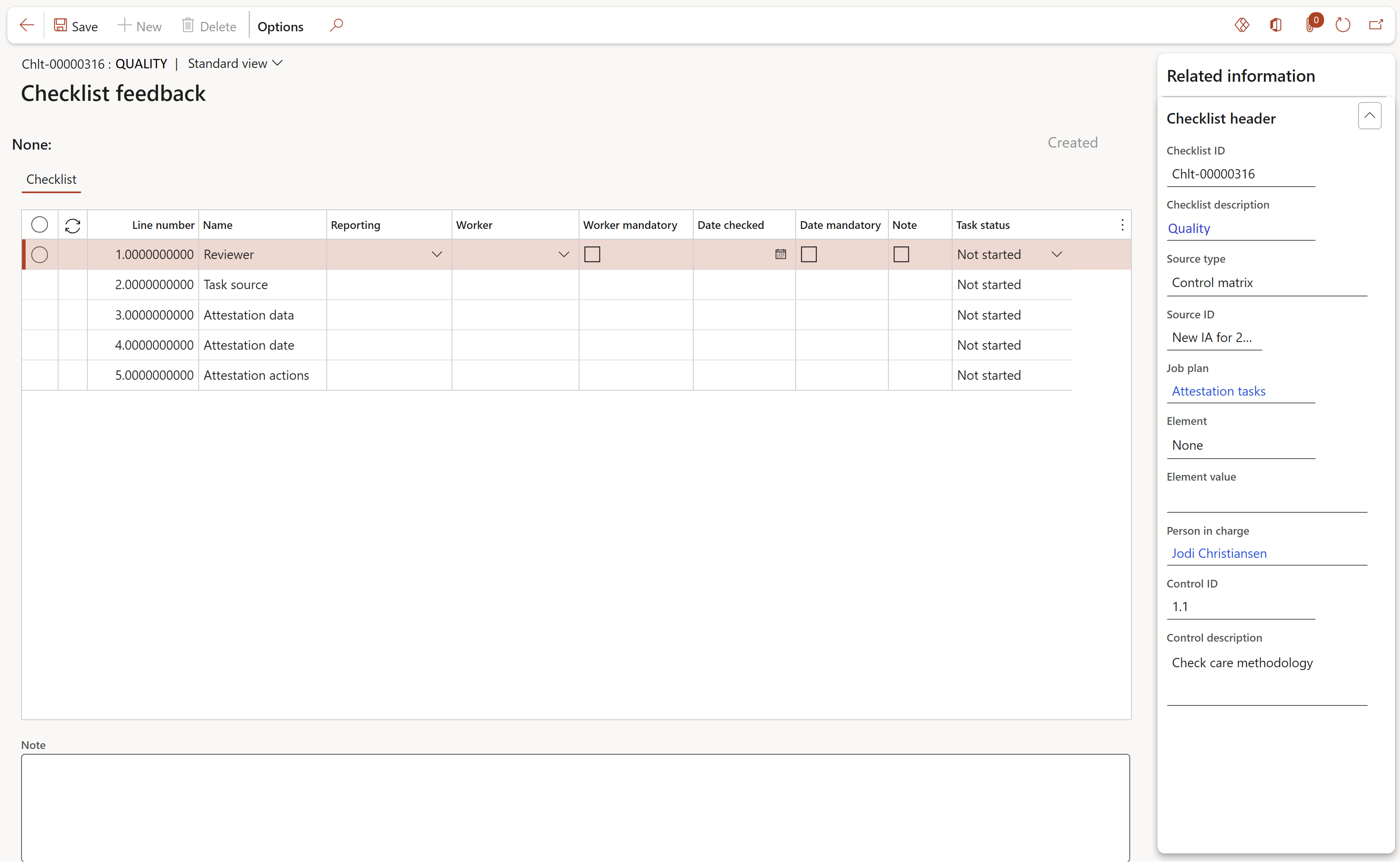
- The checklist header information can be viewed in the Related information pane
- Under the Checklist section:
- A Worker can be specified for every line
- In the Reporting column, the user can specify which line to use on the working paper report for control Adequacy, for control Effectiveness and also the line with the key audit finding.
- The Task status can be changed
- Under the Assertions section:
- Move the relevant sliders to Yes. The following will be printed on the Working paper report:
- Accuracy = Is it the right control
- Cut-off = Is it performed by the appropriate person at the right time and frequency?
- Sustainable = Is it sustainable
- Existence = Is it evidenced
- Sample details can be entered under the Sampling section. The sample size will be populated from the RCM
- Audit results can be entered under the Result section
- Additional notes can be added in the note box at the bottom of the form
- Open the Observations Index tab and enter details of the finding in the six note boxes provided
- In the Action pane, click on the Create audit finding button
- On the Create non conformance dialog:
- Enter a Description of the non conformance
- Select the relevant Site from the dropdown list
- Click on the OK button
- Select the relevant record and open the Audit observation Index tab
- Open the Execute tab
- Click on the View working papers button
- Activities can be created for each clause:
- Enter Activity observations/notes
- Select the Responsible person
- Enter the Due date
- Select the relevant Audit file from the dropdown list
- In the Action pane, click on the Create activity button
- On the Create activity dialog:
- Select the relevant activity category
- The user can choose to create a new Action plan for the activity, or add the Activity to an existing Action plan
- Click on the OK button
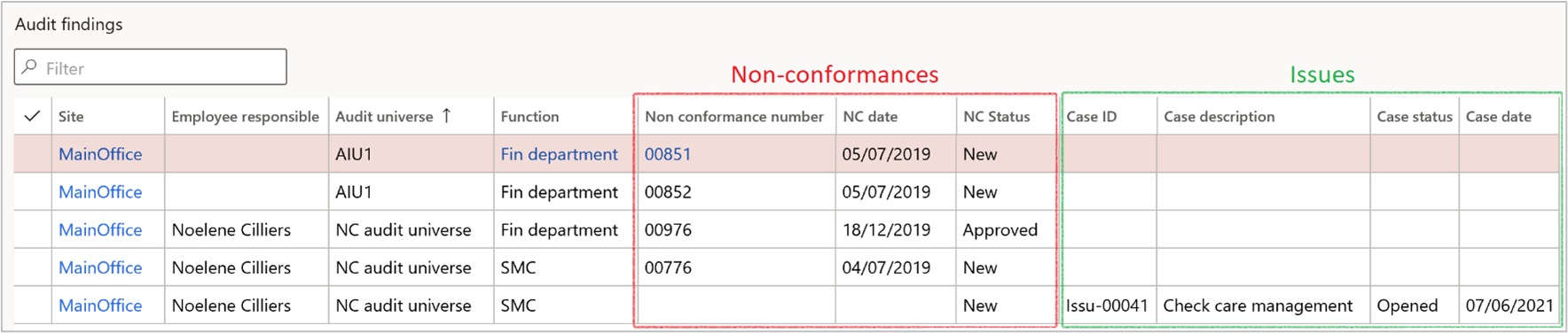
- Non conformance
- Findings
- Recommendation
- Raise a non-conformance inside Dynamics or,
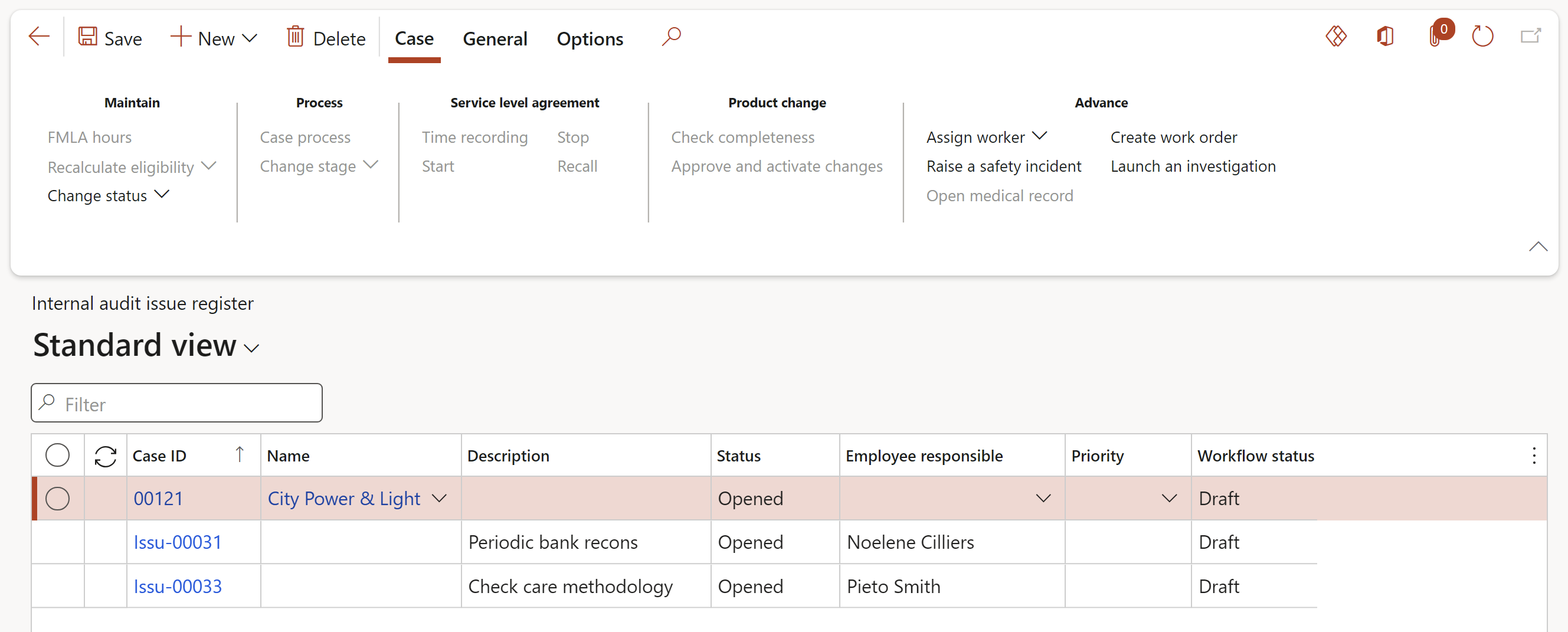
- Record an issue in the Internal audit register if the outcome is less critical and of lesser significance
- Open the Audit observation Index tab to see the details of the selected Non conformance record
- Expand the Quality assurance Fast tab
- Select the relevant Improvement plan from the dropdown list
- Click on the Save button
- Commits the scores and the audit to the database
- Gives the user the option to record working papers to an open audit file
- Helps with improvement plans by creating a formal checklist on the Checklist list page
- are necessary for audit quality control purposes
- provide assurance that the work delegated by the audit partner has been properly completed
- provide evidence that an effective audit has been carried out
- increase the economy, efficiency, and effectiveness of the audit
- contain sufficiently detailed and
- up-to-date facts which justify the reasonableness of the auditor’s conclusions
- retain a record of matters of continuing significance to future audits.
- Select the record that you want to print the working paper for
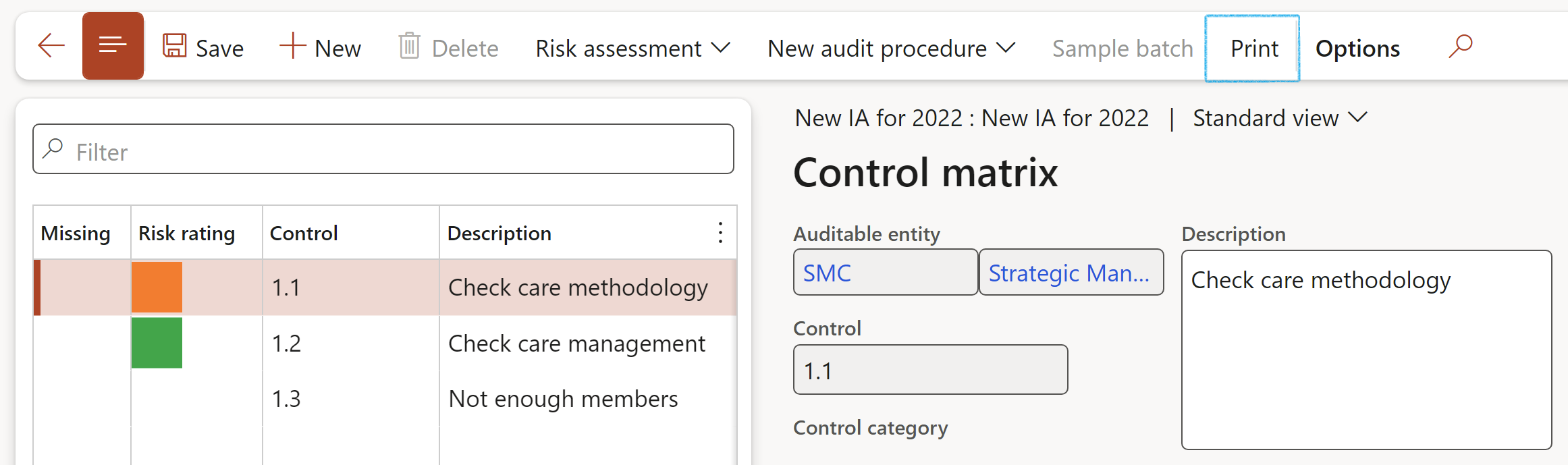
- On the Audit project, in the Action pane, under the Execute tab, click on the Control matrix button
- On the Control matrix, in the Action pane, click on the Print button
- On the Action pane, click on the Audit button and select Generate follow up review from the dropdown list
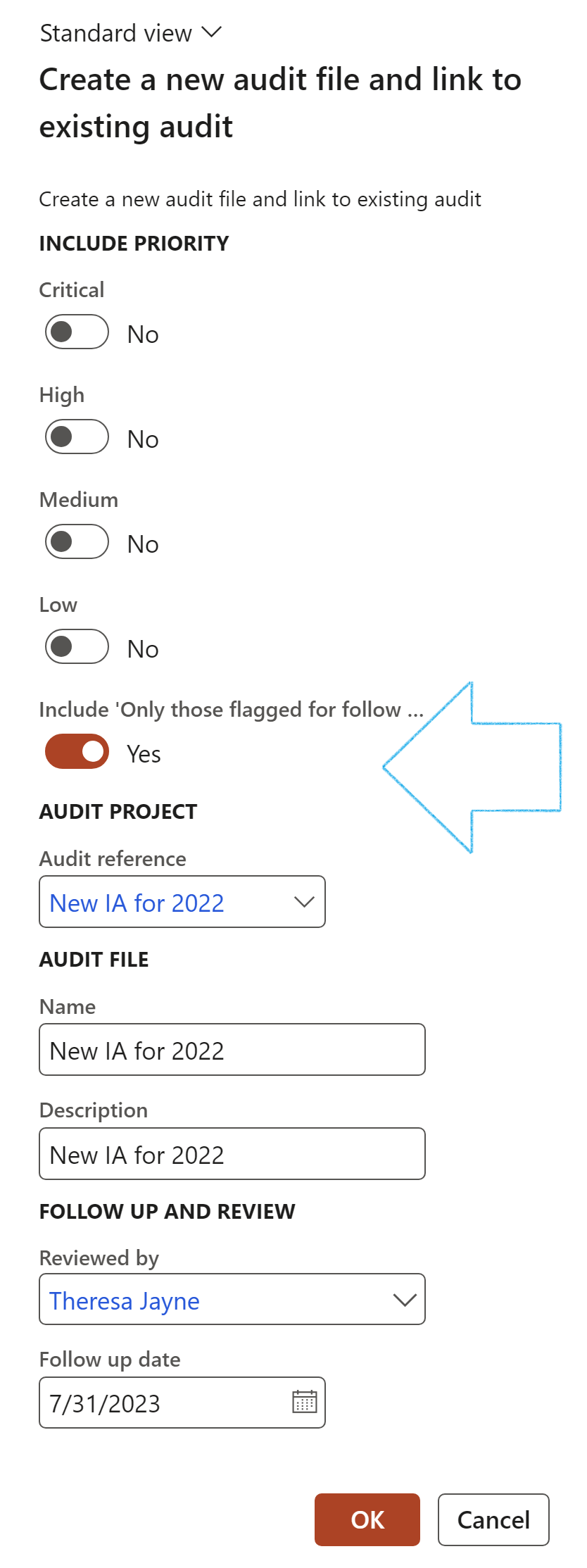
- On the create dialog that opens, enter the following:
- The user can choose to only include records that have flagged for follow up
- Select the relevant Audit reference from the dropdown list
- Enter the Name of the new audit file that will be created for these follow up records
- Enter a brief Description for the Audit file
- Select the person who is going to Review this follow up
- Enter the Follow up date
- Click on OK
- Audit procedures feedback form (Refer to Step 21.1.4)
- Fieldwork form (Refer to Step 22)
- On the Audit project, expand the Internal audit Fast tab
- Under the Audit report Index tab, enter the following:
- Select a Template (baseline) Audit report from the Policies, reports and other tool
- On the Action pane, click on the Generate audit report button
- The created Audit report will populate the Report field
- Move the Final slider to Yes if this is the final report
- Select the relevant dates for the report
- On the Audit project, expand the Internal audit Fast tab
- Under the Response Index tab:
- On the Audit project, on the Action pane, open the Project Tab
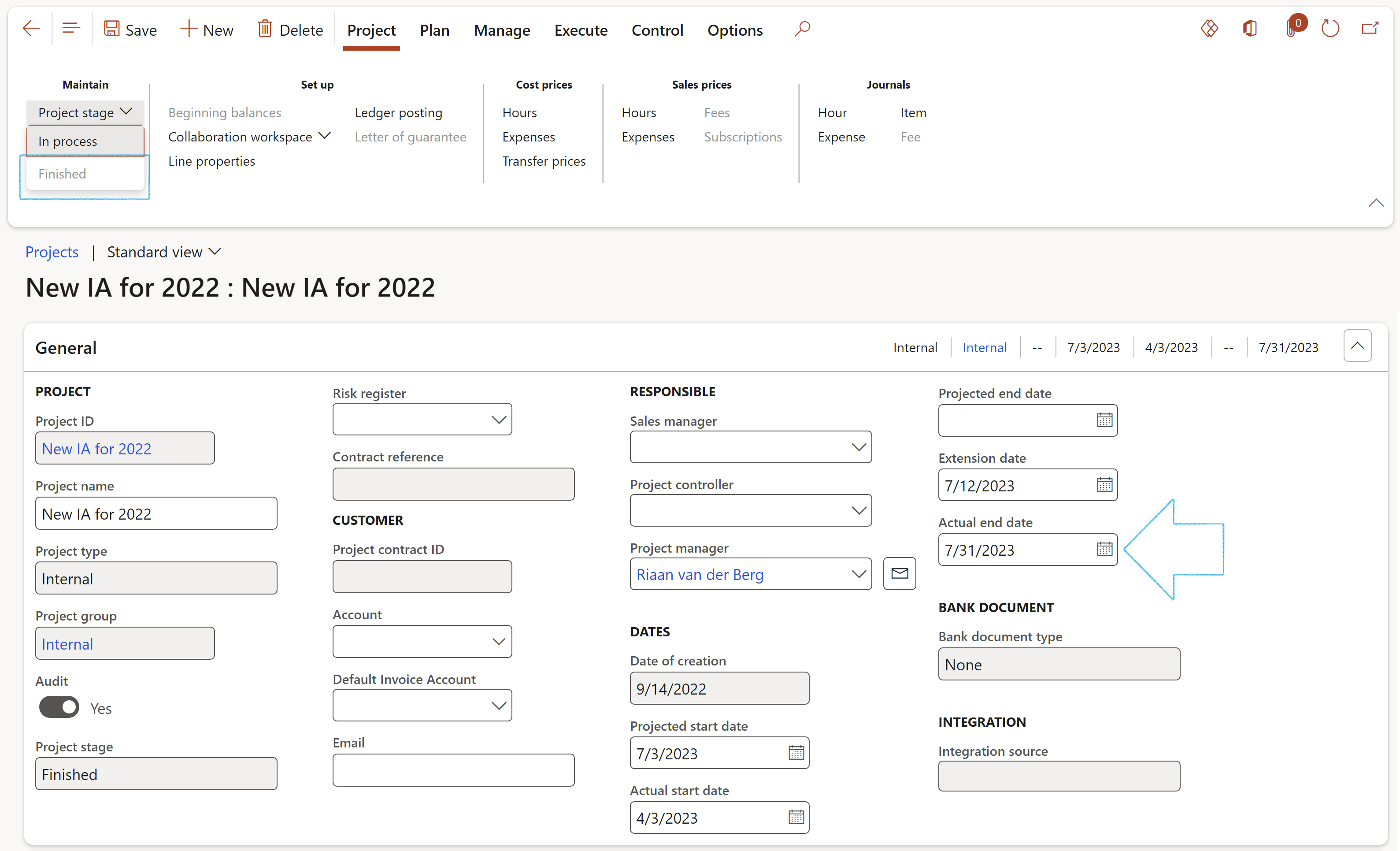
- In the Maintain button group, click on the Project stage button and select Finished
- On the Audit, the Actual end date under the General Fast tab will be populated with the current date
- On the Audit universe, General Fast tab, the Last audited date will be populated with the current date
- Audit plan (not approved)
- Risk control matrix
- Audit universe
- Audit plan delivery
- Internal audit findings
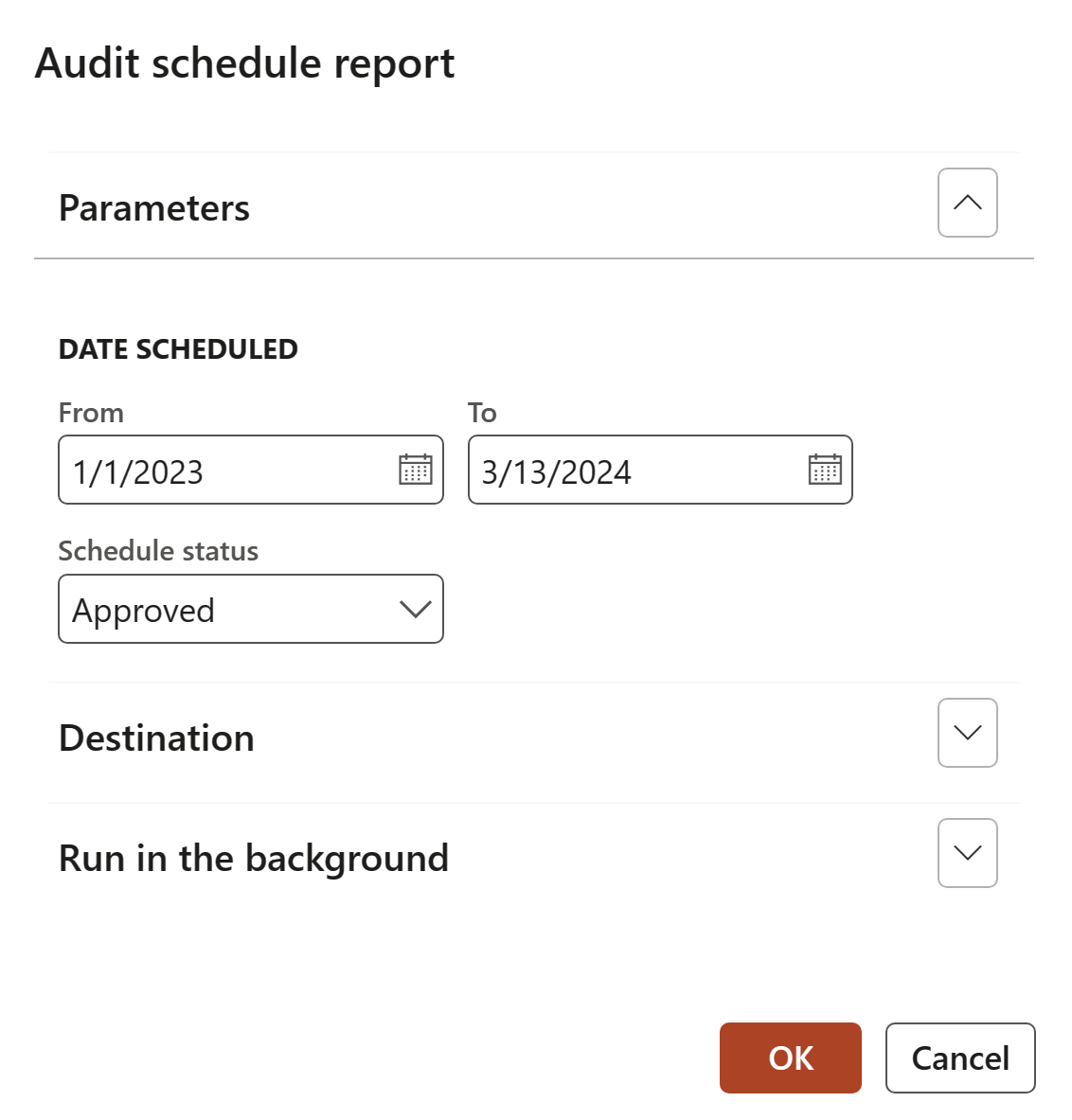
- Select the scheduled From and To dates for the report
- Select the Schedule status from the dropdown list
- Click on the OK button
- Select the Parameters for the report
- Select the From and To dates on the Parameters
- Click on OK
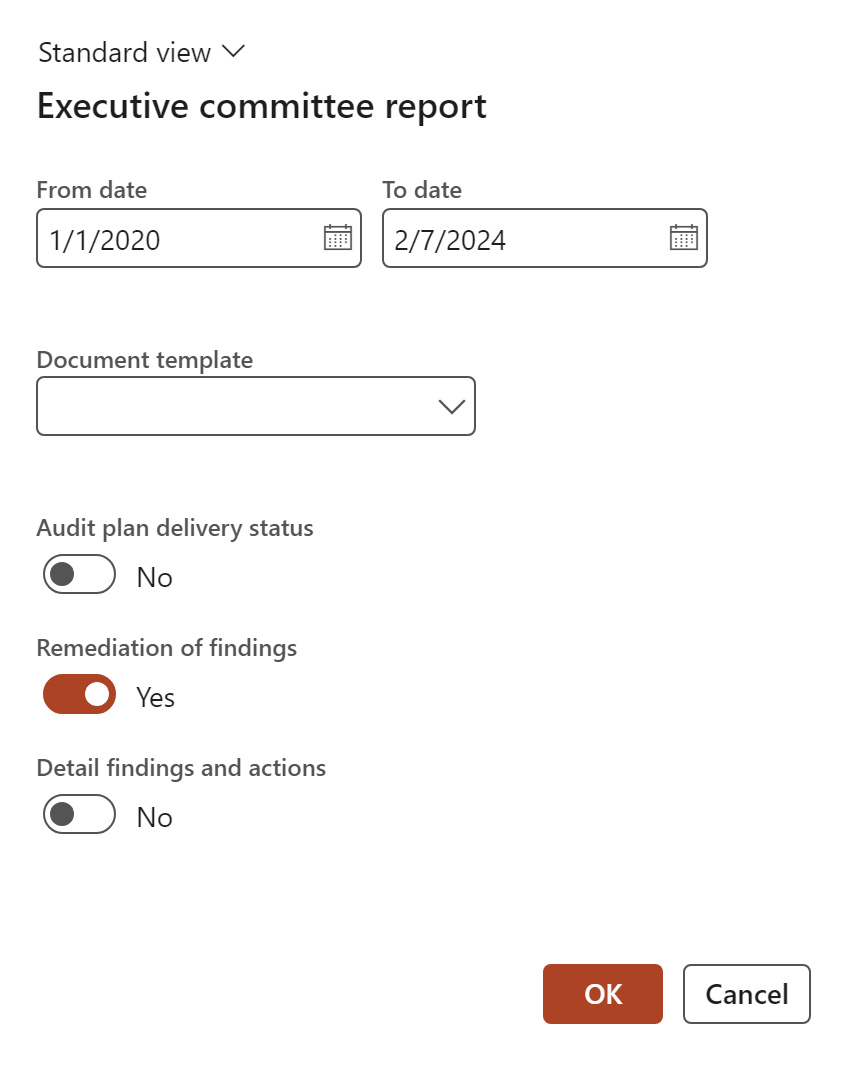
- Audit plan delivery status
- Remedies of findings (Findings age analysis)
- Detail findings and actions
- Select the Audit universe from the dropdown list
- Select the Audit type from the dropdown list
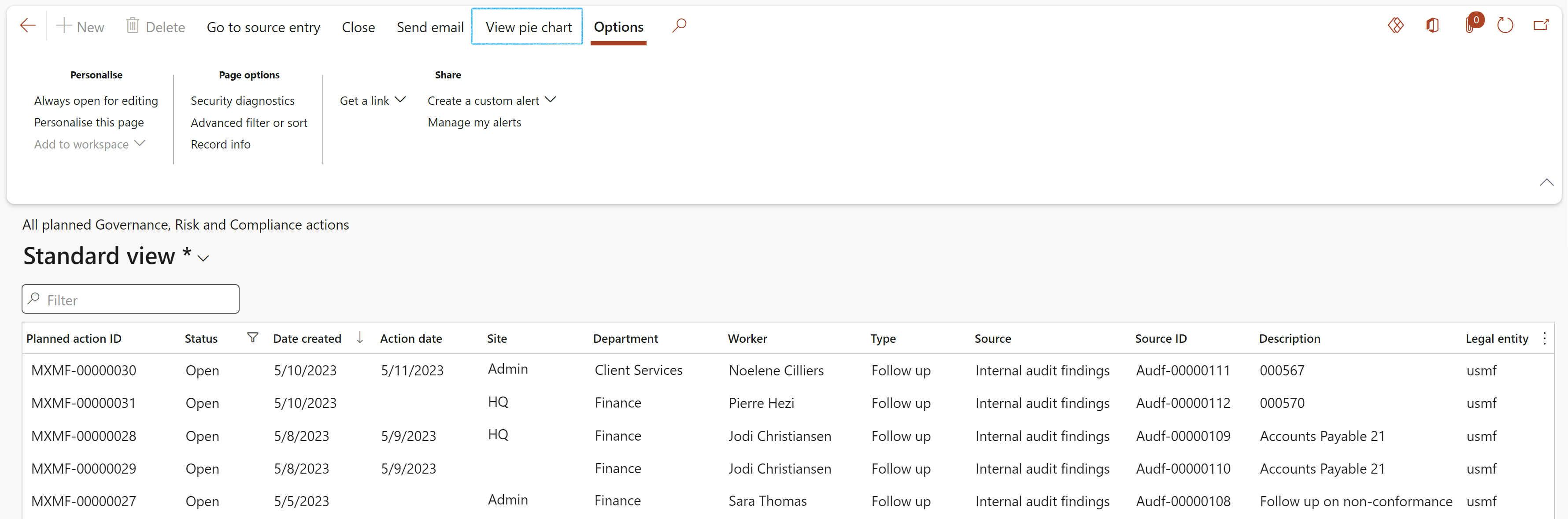
- Buttons on the All planned GRC actions list page:
- Go to source entry – Opens the form from which the follow up action was created
- Close – Closes the action and removes the record from the list
- Send email notification – Sends an email notification to the selected worker in the Reviewed by field
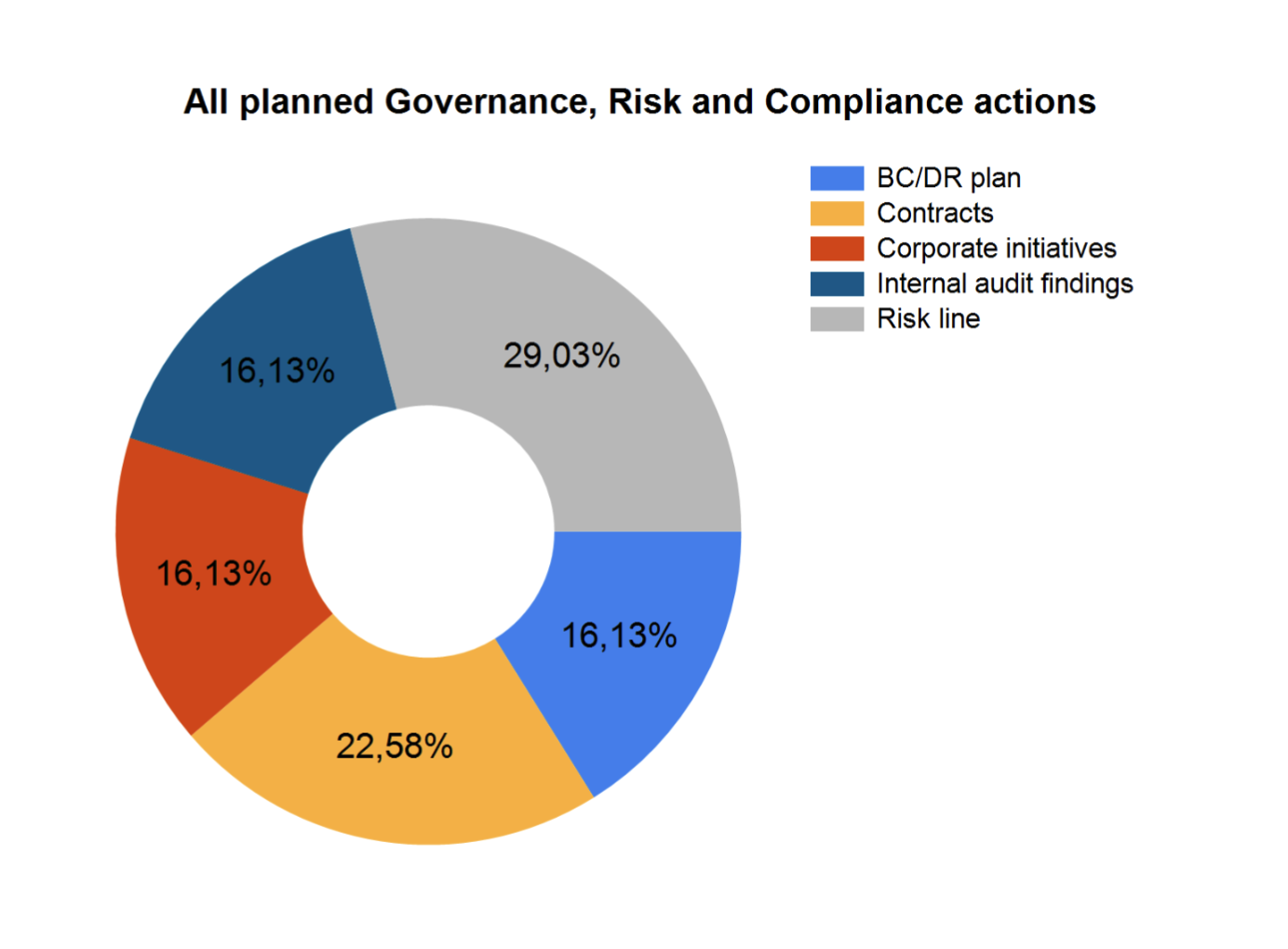
- View pie chart – Displays a pie chart of all the planned GRC actions
The Last audited date field will be populated with the end date entered on the Internal audit project, and the project stage is set to finished. The last posted scores per Auditable entity control is also visable on the lines.
A responsibility assignment matrix describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for an audit.
(On the All audit schedules list page, this person is the Owner)
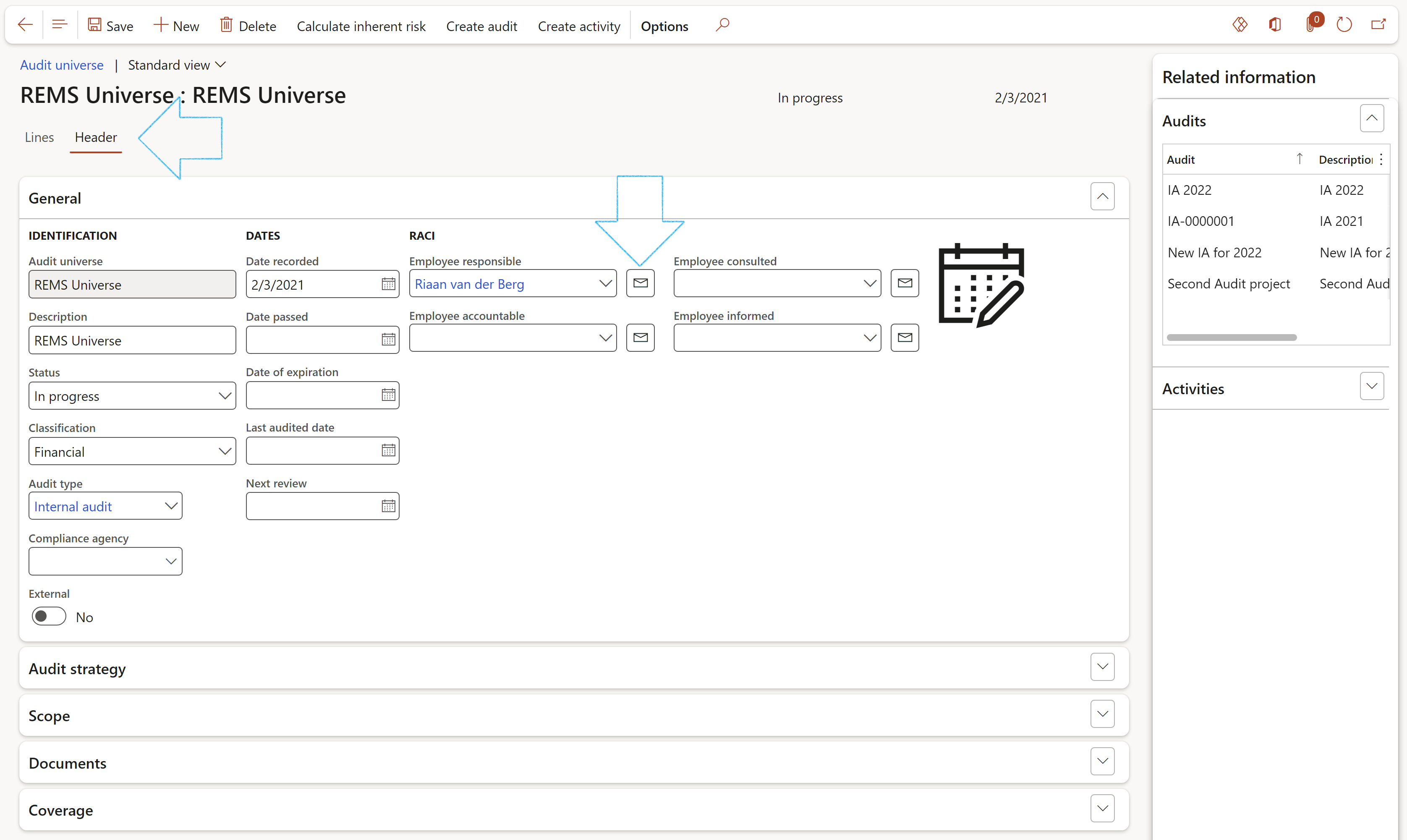
¶ Step 16.1.2: Header – Audit strategy Fast tab
The overall audit strategy includes consideration of planned audit responses to specific risks through the development of the audit plan. The overall audit strategy also helps the auditor determine the resources required for the engagement, including engagement staffing. Therefore, at a minimum the following matters should be included in the overall audit strategy:
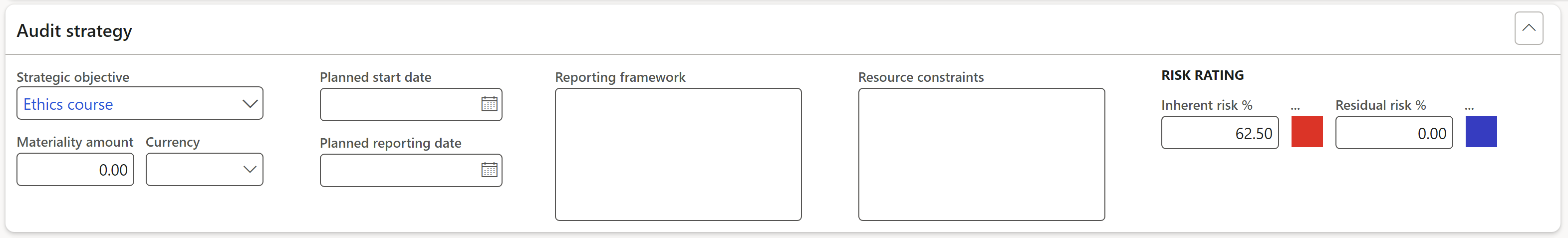
Risk rating:
¶ Step 16.1.3: Header - Scope Fast tab
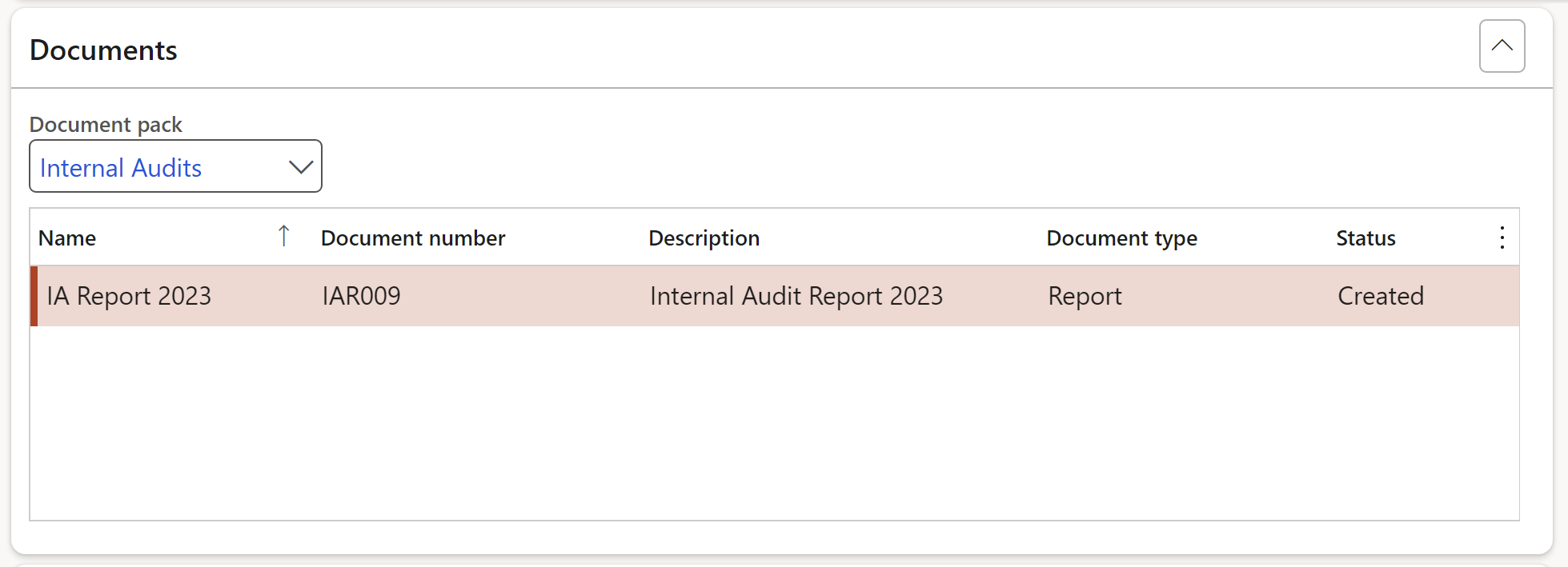
¶ Step 16.1.4: Header - Documents Fast tab
The Document pack relevant to the Audit universe can be selected from the dropdown list.
For more information on how documents and document packs are created in Dynamics 365, please refer to the GRC wiki page for Other documents
¶ Step 16.1.5: Header - Coverage Fast tab
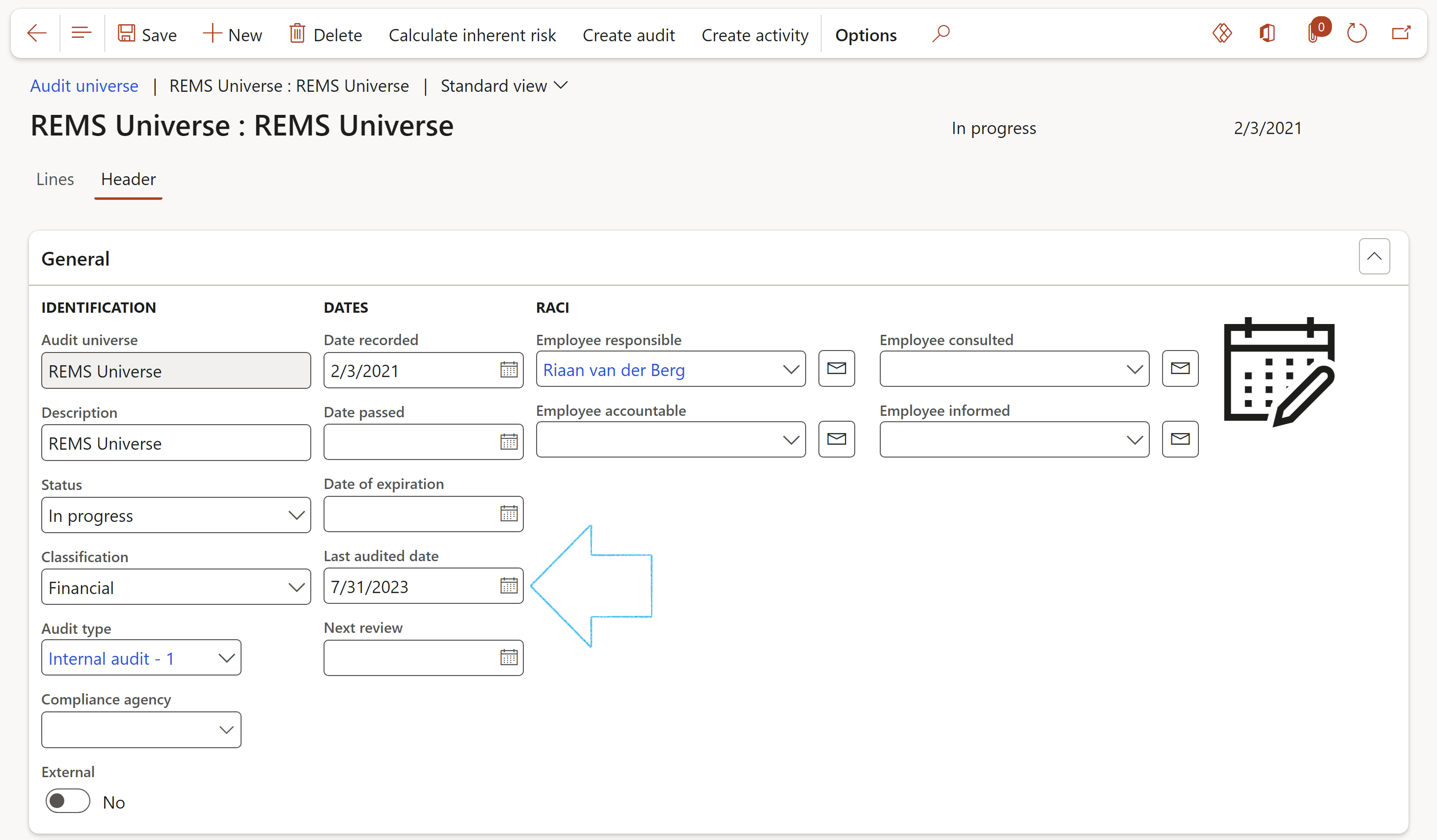
This is an indication of the level of coverage of the previous audit that was done on the selected auditable entity
Three years’ coverage can be entered as well as the worker who did the scoring
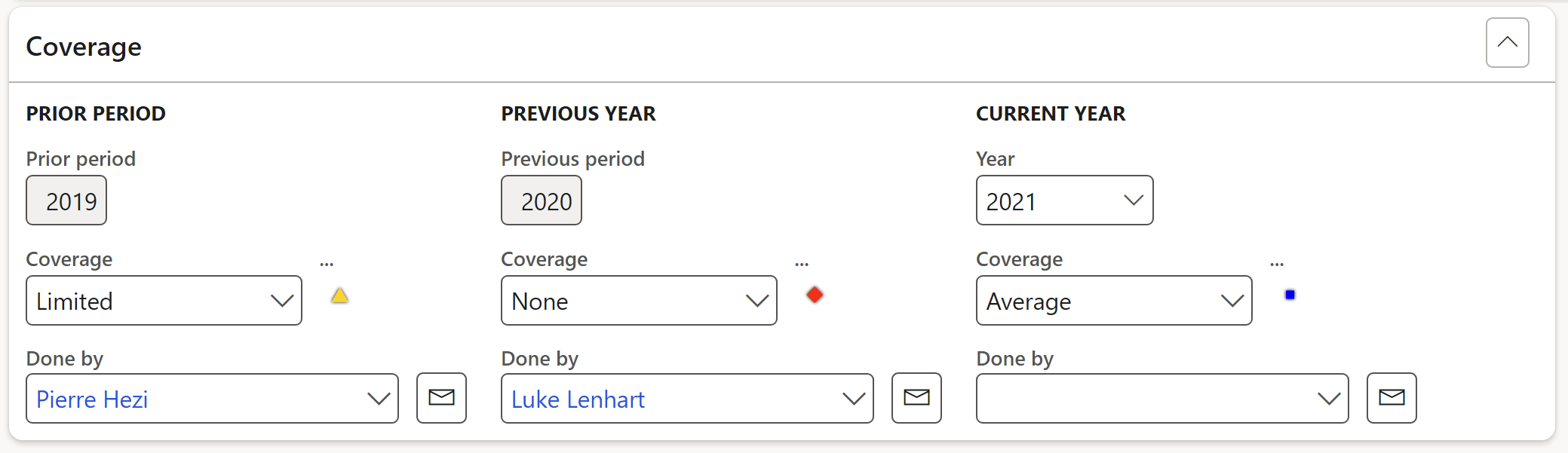
The department manager will be displayed when a Department being audited is selected. The email address linked to this manager will be used when sending out the Audit notification.
Users can also choose an “audit budget”. This will show the total hours and cost associated with doing the budget. Remember that the lookup here is filtered based on the value in the Dynamics 365 GRC parameters form.
¶ Step 16.1.6: Header - Create activities
¶ Step 16.2: Create the Audit universe lines
¶ Step 16.2.1: Lines – Auditable entity Fast tab
¶ Step 16.2.2: Lines – Controls Fast tab
¶ Step 16.3: Automated functions
¶ Step 16.3.1: Update manual risk
To adjust/update the manual risk rating on the Audit universe
¶ Step 16.3.2: Audit need assessment
Based on the Audit needs assessment, Dynamics 365 will update the need assessment from the auditable entities into the Audit universe. Thus, effectively proposing to the user which area needs focused audit attention.
¶ Step 16.3.3: Manual audit
Clicking on the Manual audit button creates a manual/ad-hoc schedule on the form. It also creates an audit and an audit file.
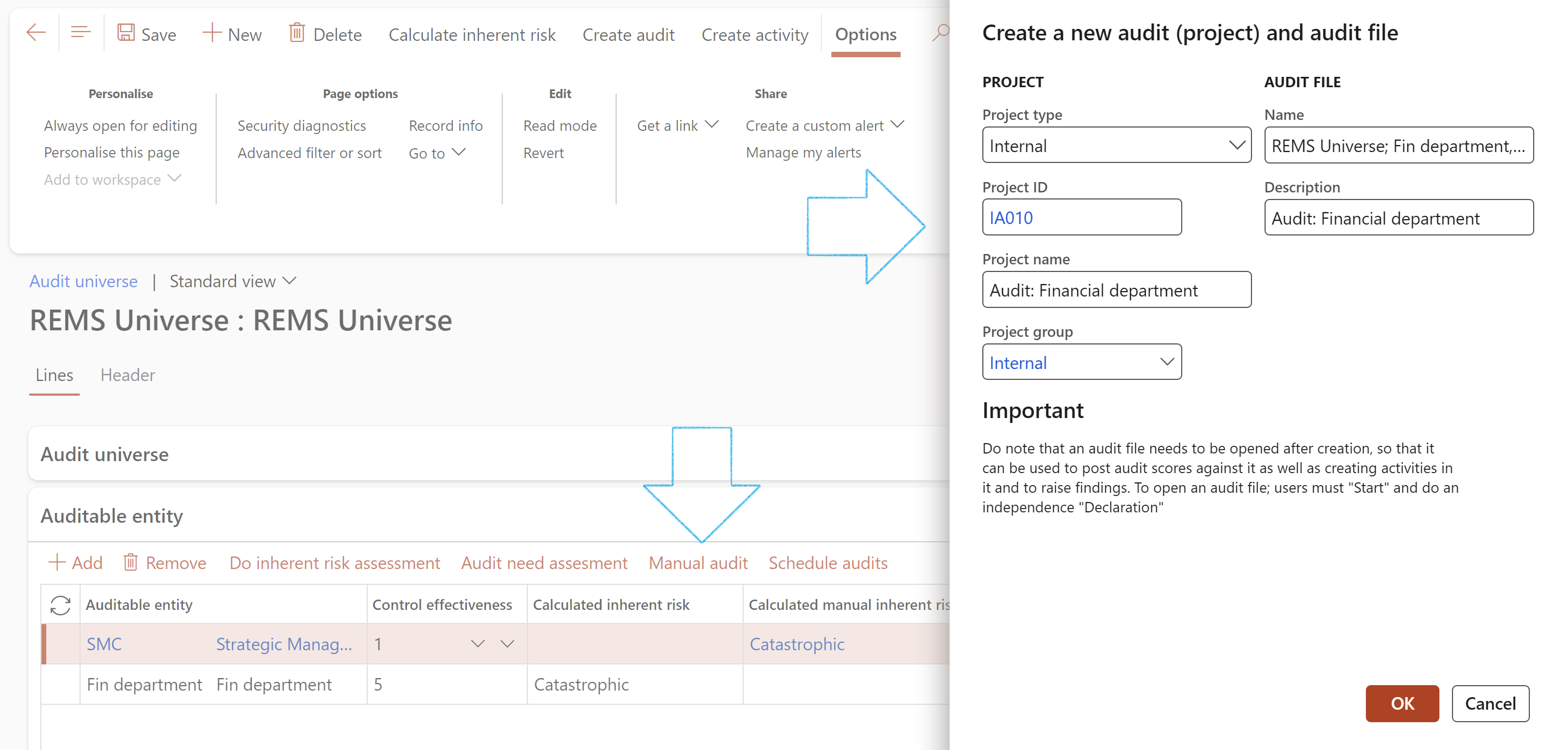
A Manual audit can also be created by clicking on the Create audit button on the Action pane of the Audit universe list page.
By completing the dialog, a manual/ad-hoc schedule is created on the form. It also creates an audit and an audit file.
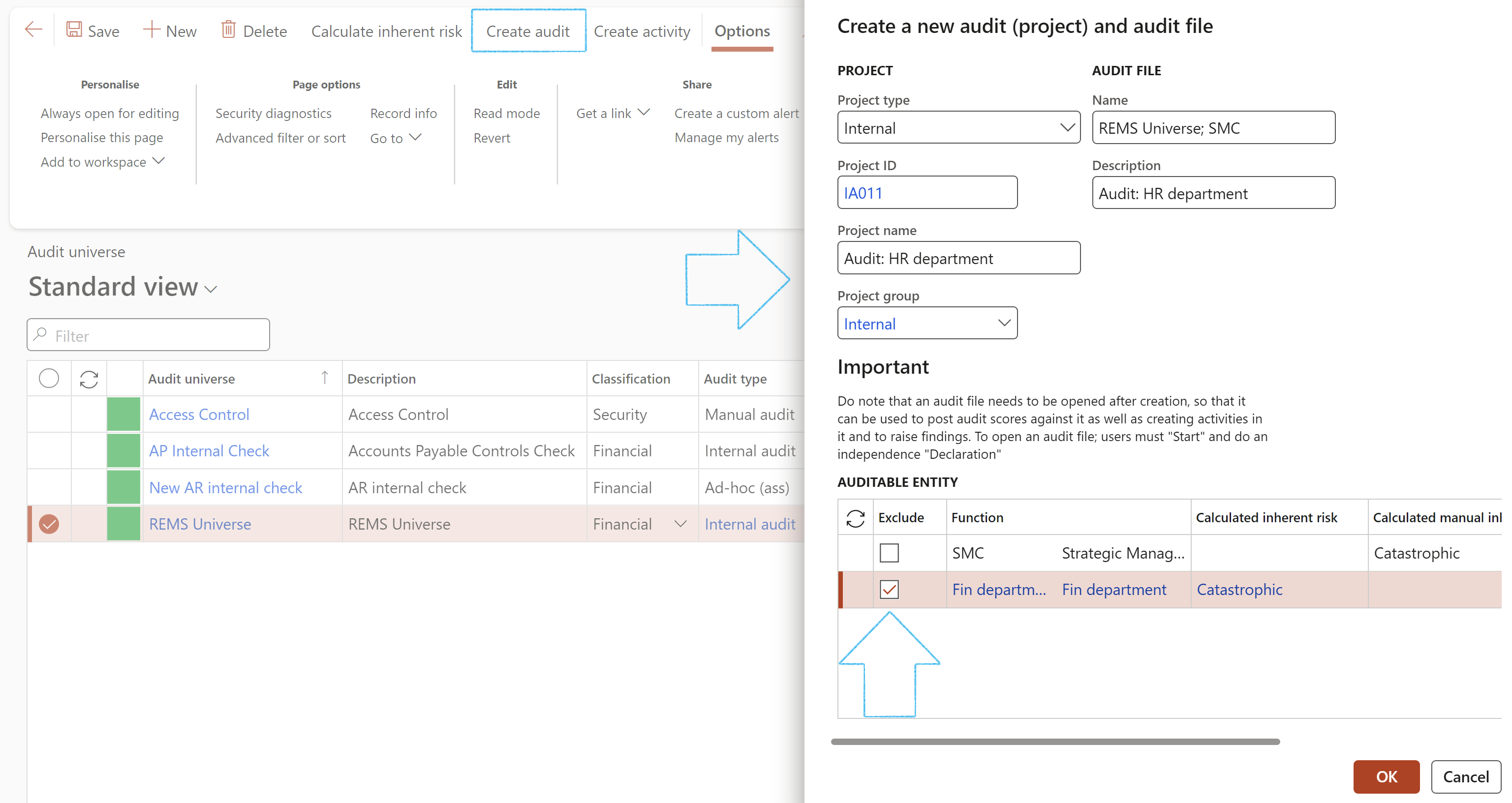
¶ Step 16.3.4: Schedule audits
The Schedule audits button gives users access to the periodic scheduling form to allow them to schedule future audits.
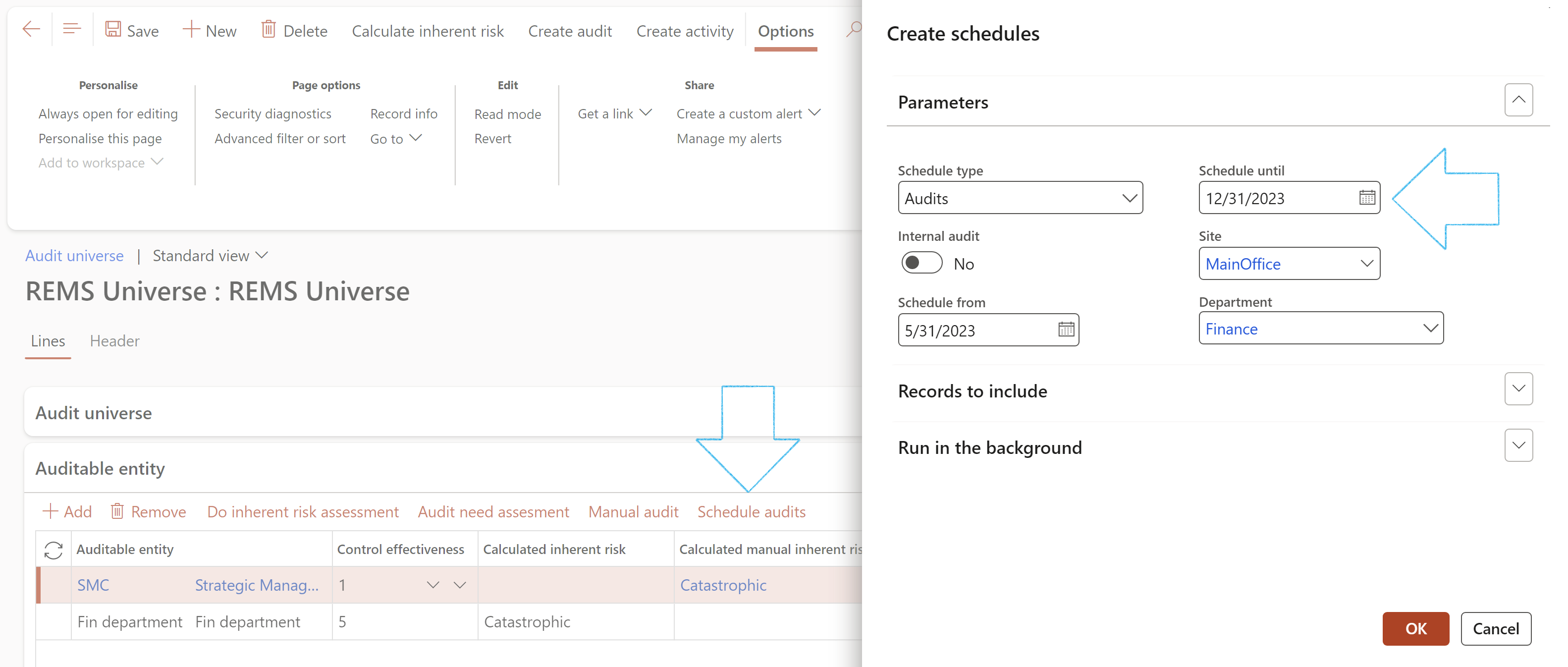
If the Scheduling period on the Audit universe is different to that on the Auditable entity, a yellow line with a warning message will appear across the screen.
The system will use the scheduling period as set up on the Audit universe.
¶ Step 17: Planning & Scheduling
The purpose of an internal audit is to provide independent assurance that an organization’s risk management, governance and internal control processes are operating effectively. It starts with having a budget.
¶ Step 17.1: Create Audit budget entries
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All audit budget entries
¶ Step 17.2: Planning
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Periodic > Audit planning
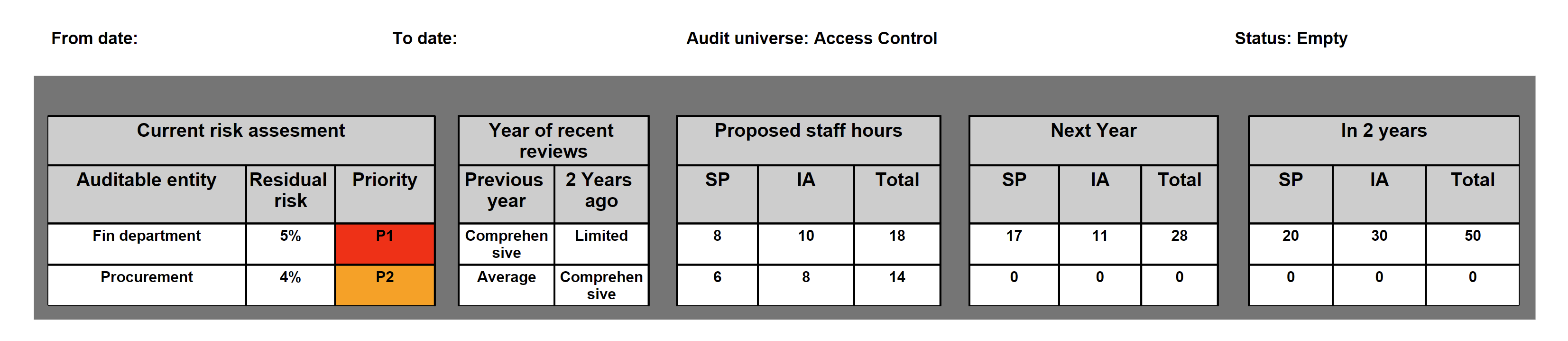
To print the audit plan report, go to: GRC > Internal audits > Reports and Inquiries > Audit three year plan report
¶ Step 17.3: Scheduling
Enterprises require scheduled audits to be created based on user specific frequency rules. In addition, automation (recurring and batch driven) of scheduling is also needed. For this to work users must have scheduling rules defined on the Compliance group form.
Both these requirements are supported in Dynamics 365 GRC.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Audit universe
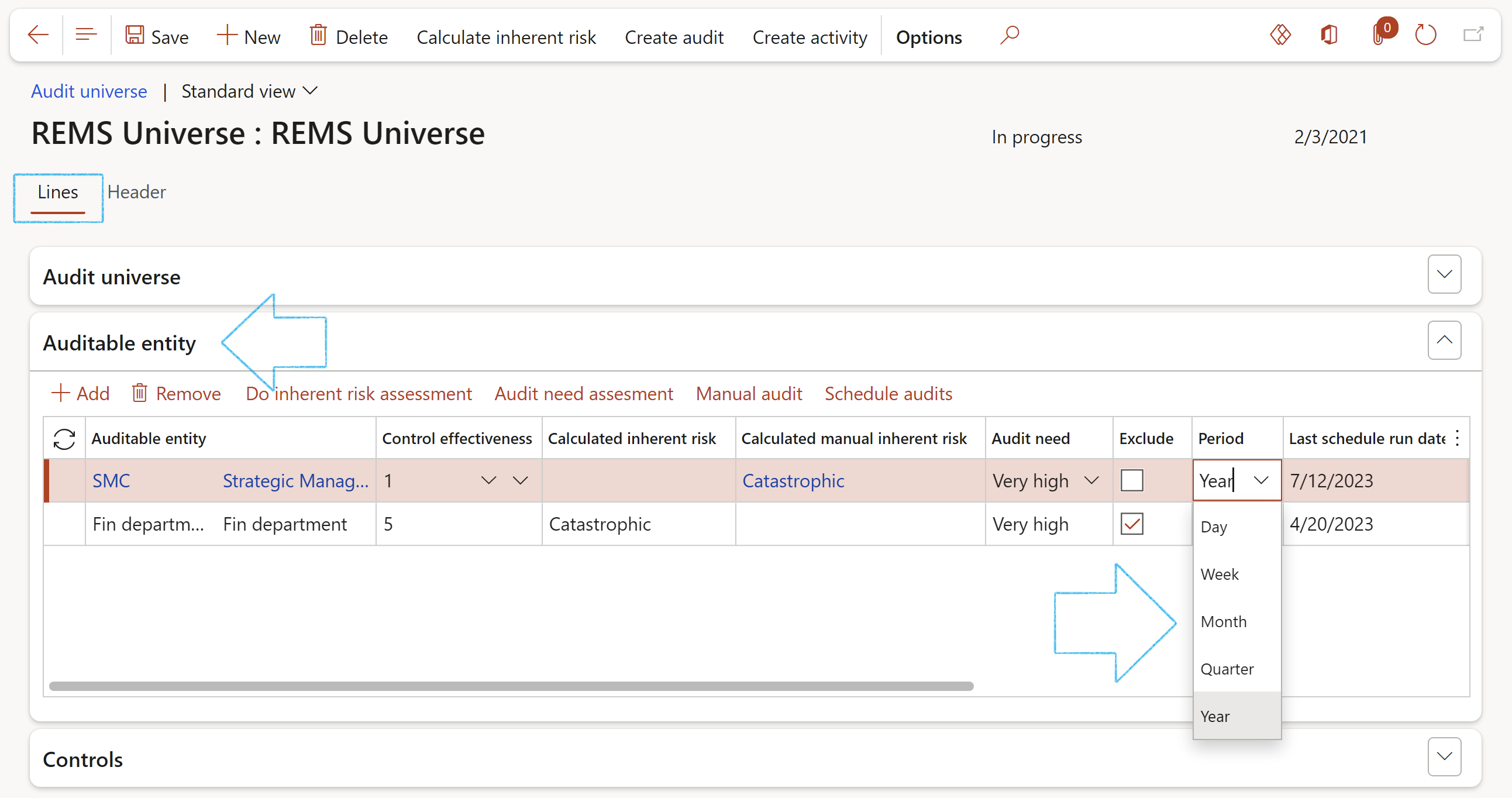
¶ Step 17.4: Run the schedule
Go to: GRC > Create schedules
¶ Step 17.5: View schedule results
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Schedules > All audit schedules
(The Owner is selected on the Audit universe as the Employee responsible in the RACI group under the General Fast tab)
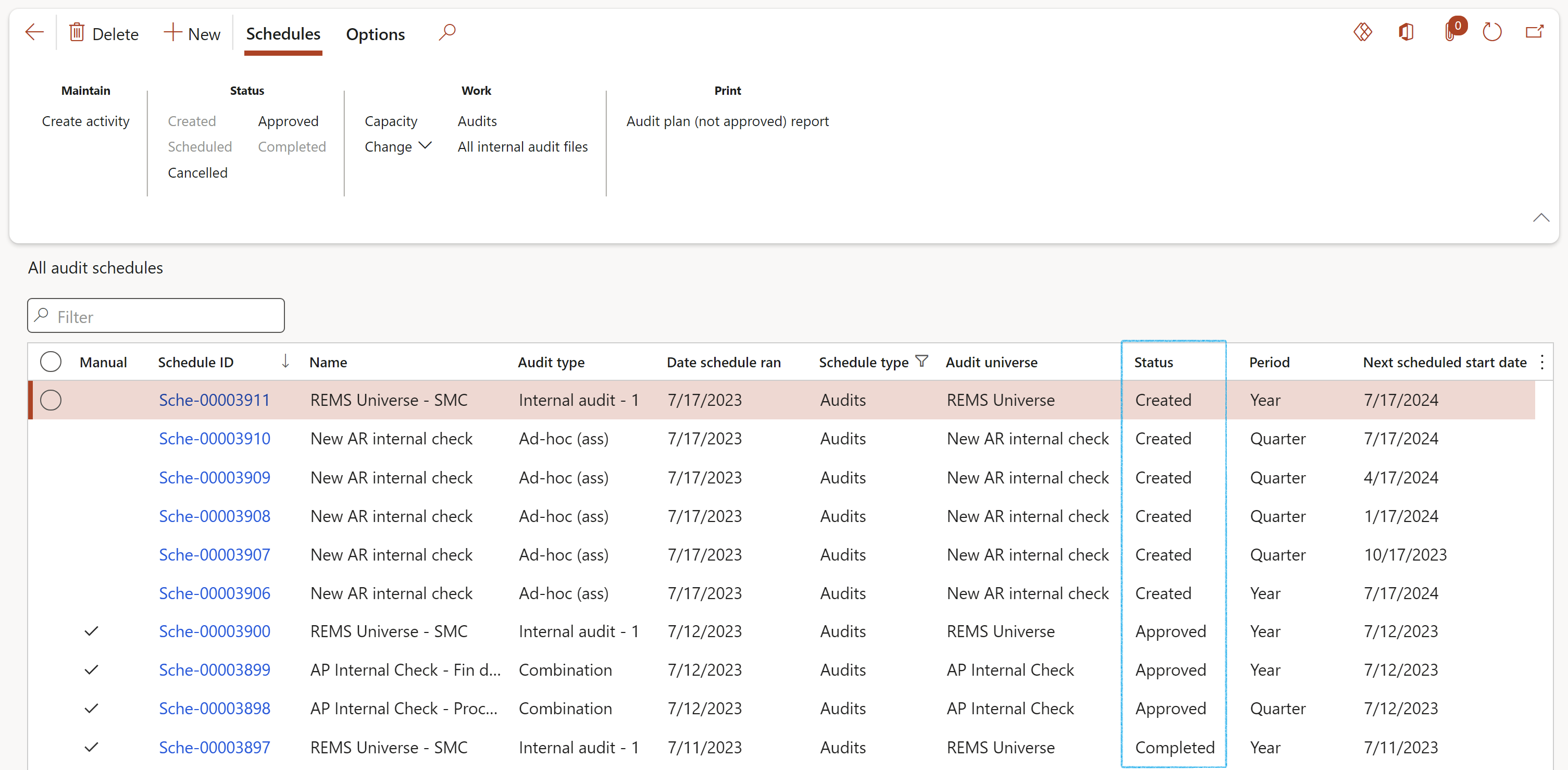
The status is important:
Also please note that Dynamics 365 will propose a Name and ask for a Description for the new Audit file to be created.
Buttons in the Work group on the Action pane:
On the Scheduled capacity load form:
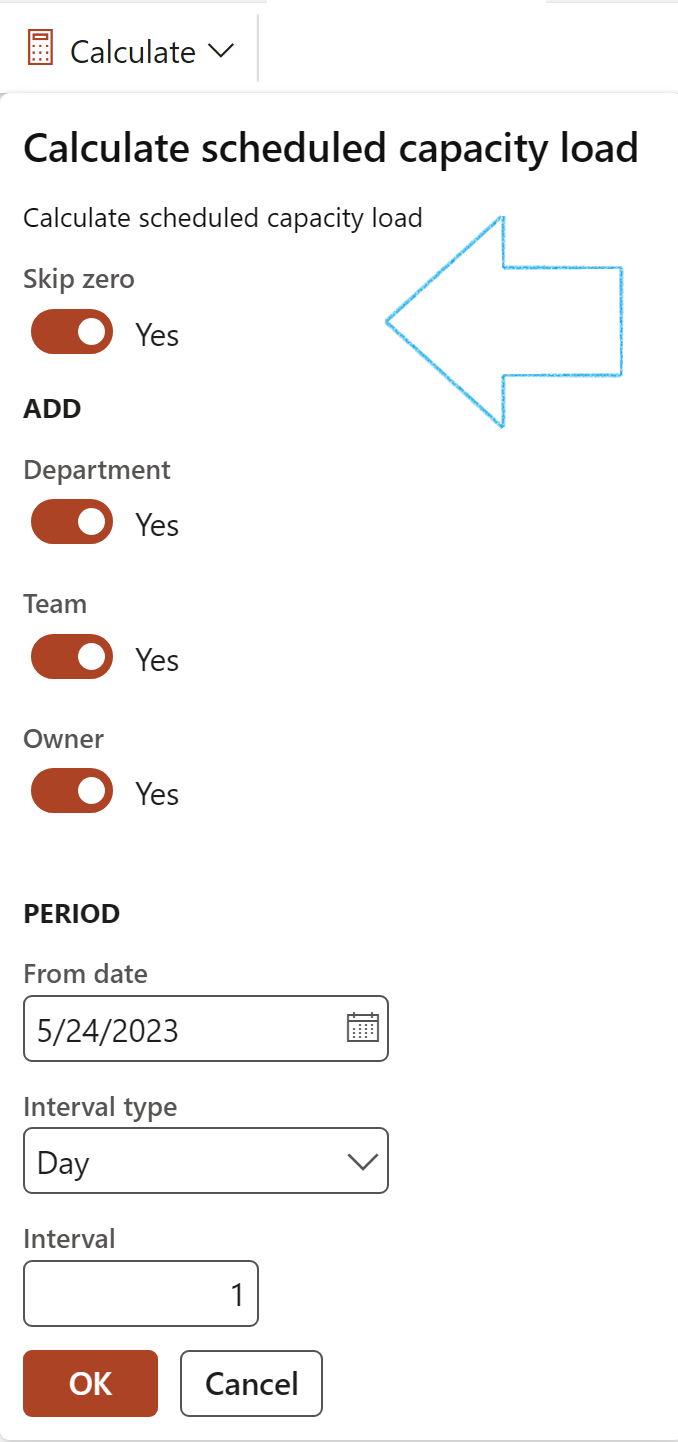
If the Skip zero check box is NOT ticked, details for all the audits will be displayed – those without budgeted hours as well
¶ Step 18: Audits
The word audit is derived from a Latin word "audire" which means "to hear". During medieval times when manual book-keeping was prevalent, auditors in Britain used to hear the accounts read out for them and checked that the organization’s personnel were not negligent or fraudulent.
An Audit is an official examination/inspection of an individual or organization's accounts, controls, and processes, typically by an independent body. Any subject matter may be audited. Audits aim to provide objective 3rd party assurance to various stakeholders that the subject matter is free from material misstatement.
A new Internal audit can be created from the Internal audit workspace by clicking on the New internal audit tile
OR a new Internal audit can be created by clicking on the New button on the All internal audits list page
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All internal audits
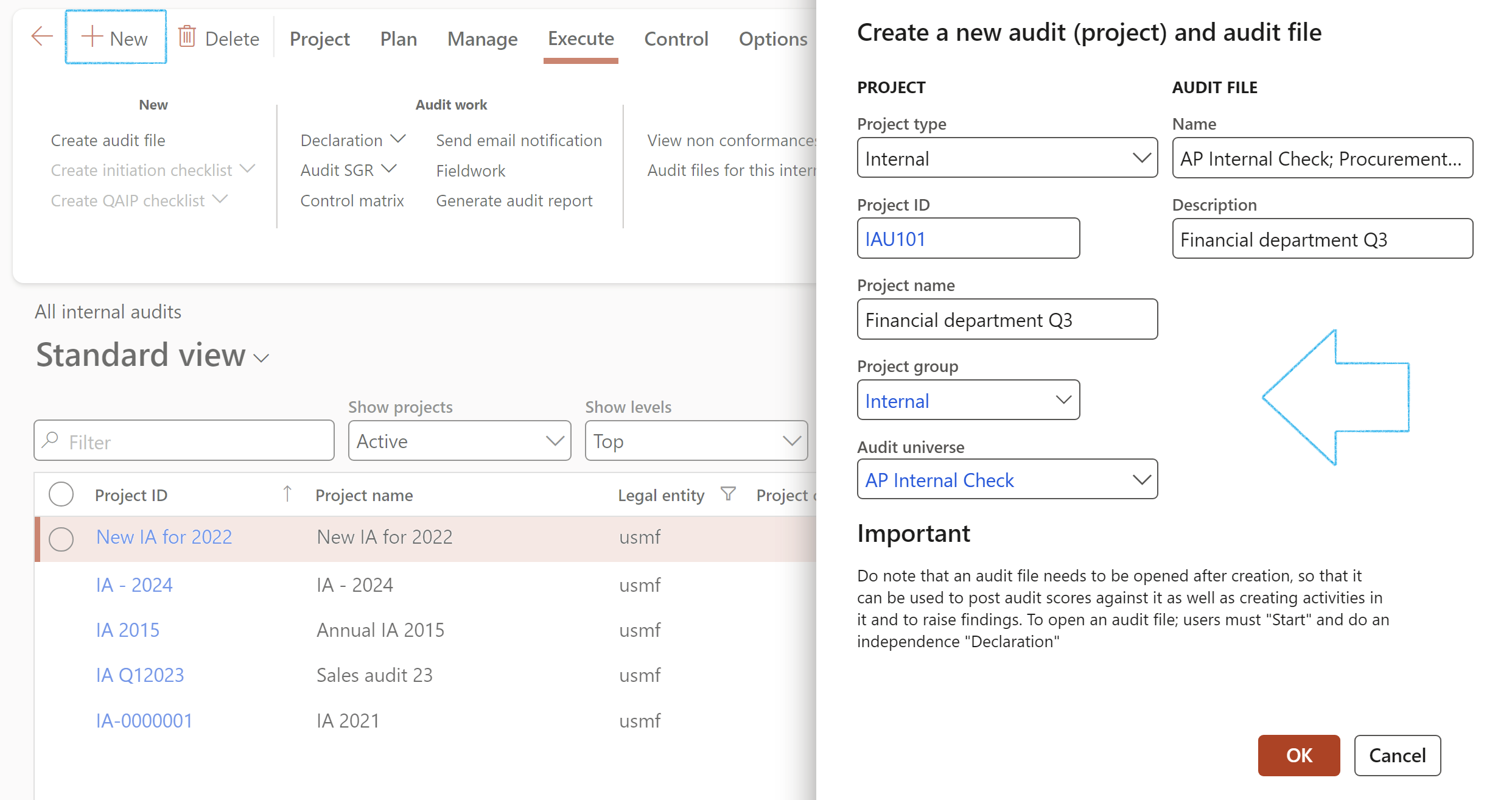
Audits can also be created:
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All internal audits
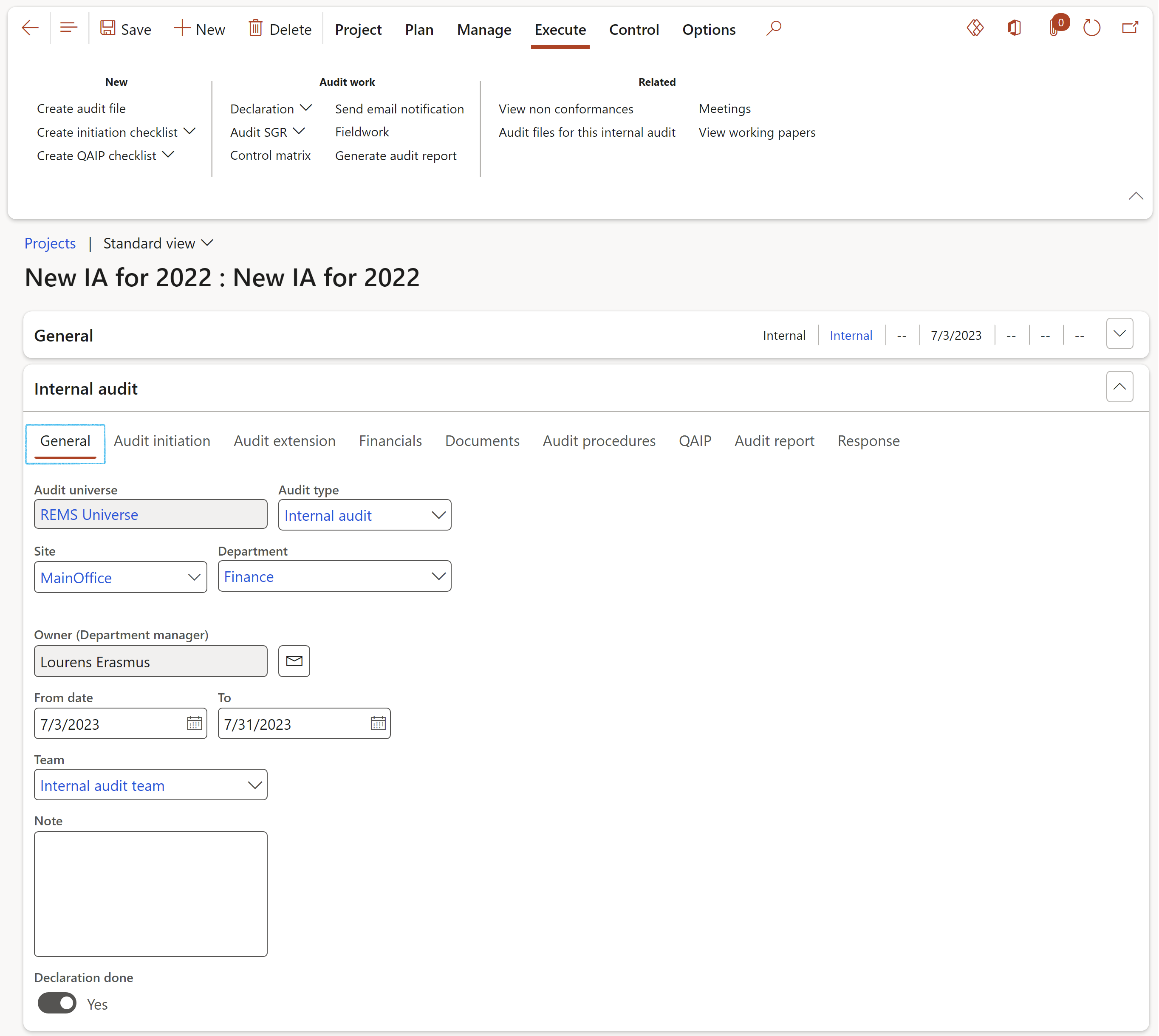
¶ Step 18.1: The Internal audit Fast tab
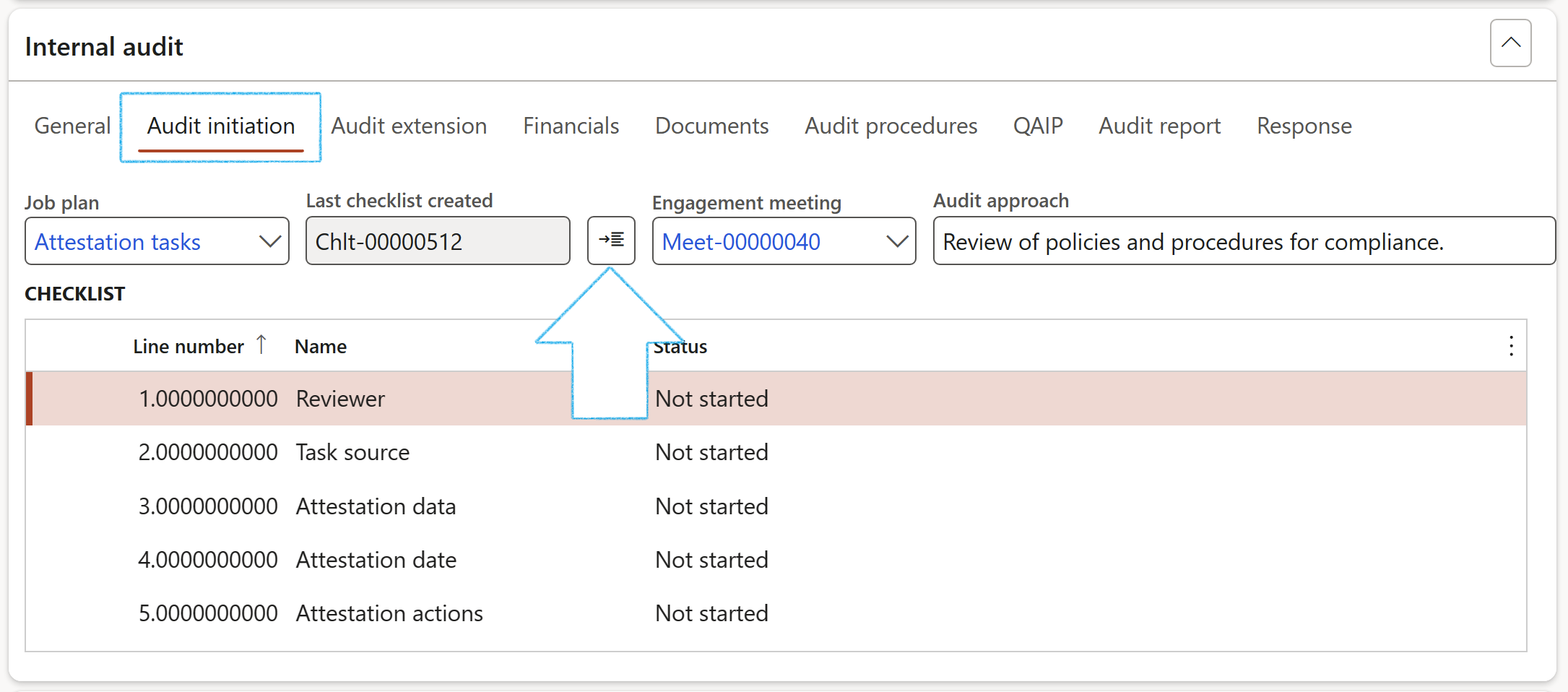
The Checklist number and the created Checklist lines will be displayed under the Audit initiation Index tab
Do feedback by clicking on the Feedback button
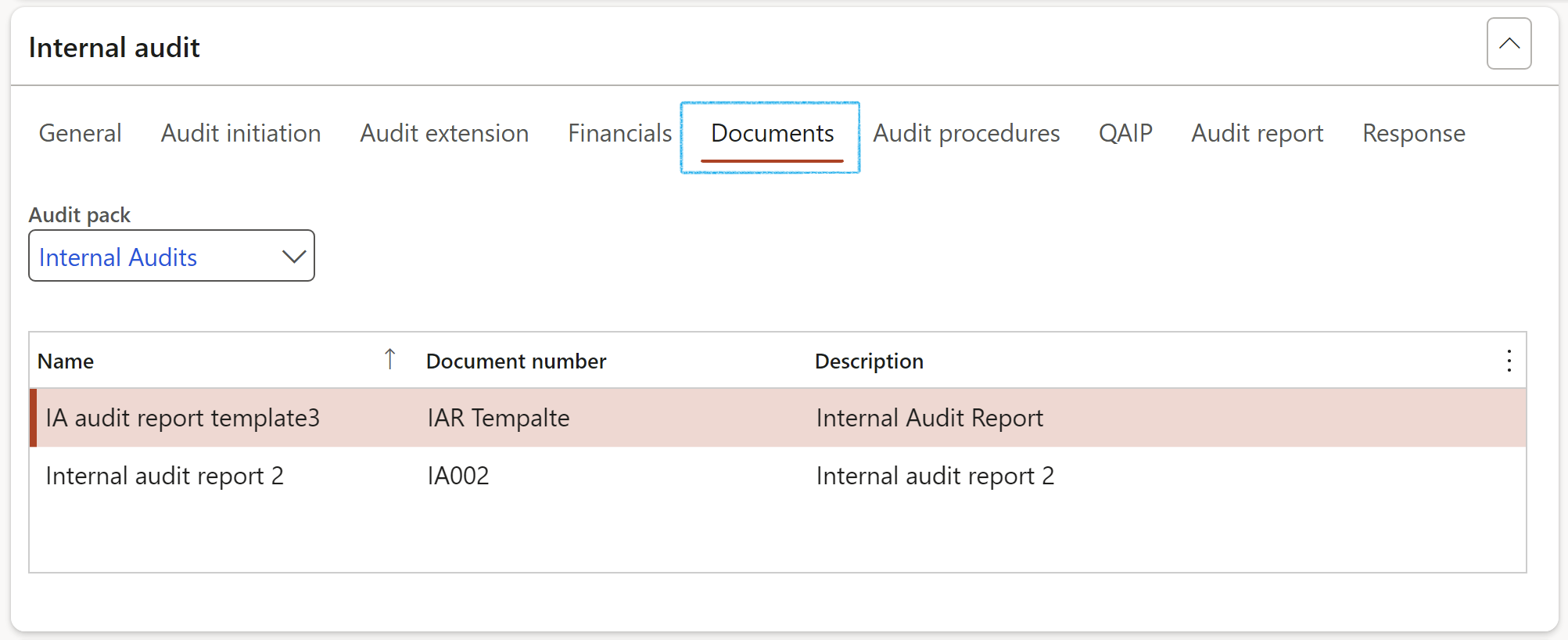
The Document pack selected on creation of the Audit universe will be displayed, as well as the list of documents in the document pack
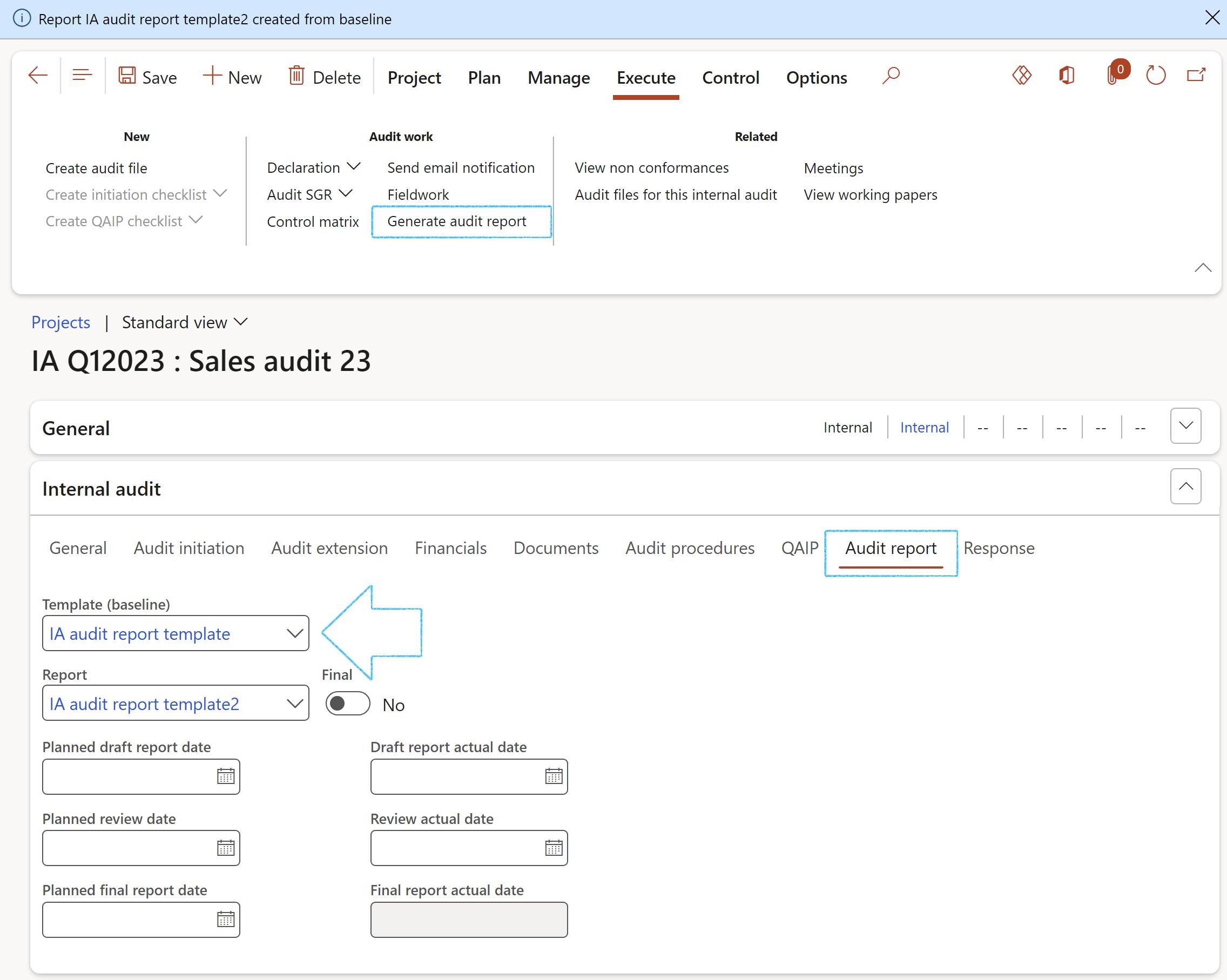
Before clicking the Generate audit report button, make sure that the relevant clauses on the baseline audit report have the Copy tick on
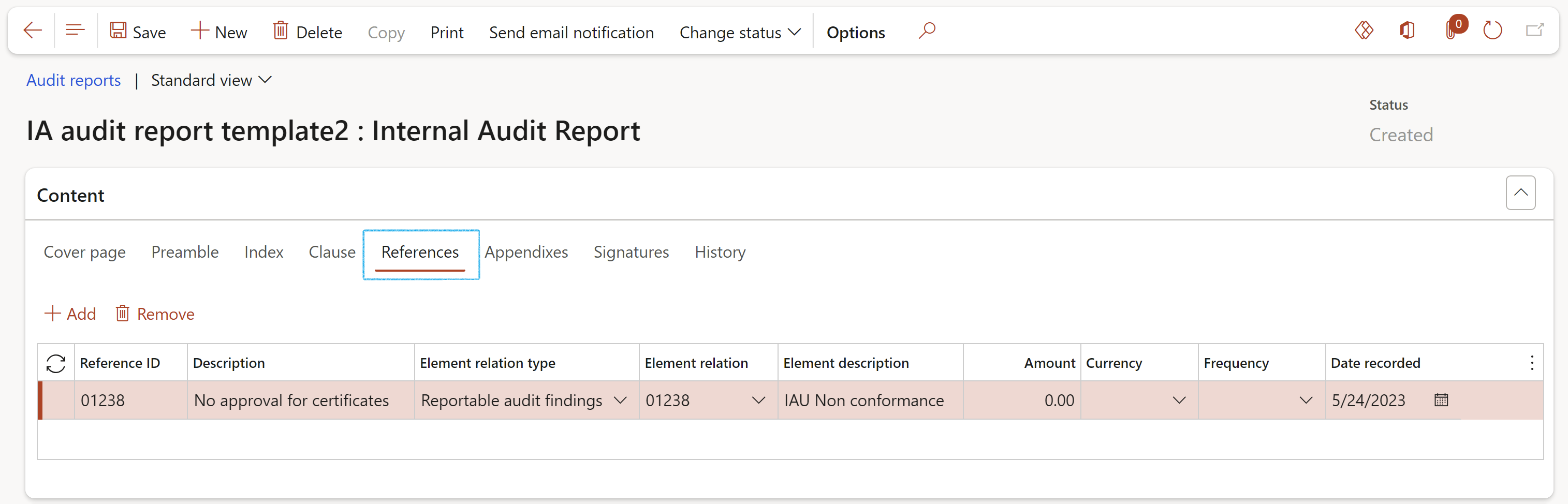
All the open and reportable Non conformances on the Internal audit will be copied to the References index tab on the Internal audit report when users click the Generate audit report in the action pane.
¶ Step 18.2: Buttons
¶ Step 18.2.1: Declaration
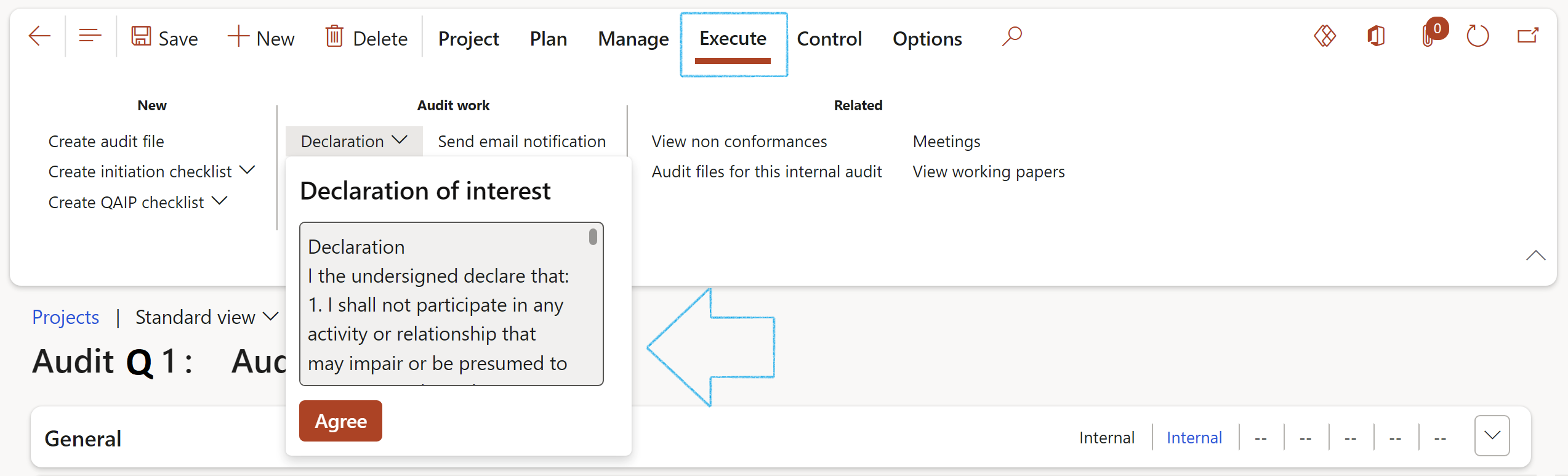
When the user clicks on the Agree button, this user’s name will populate the Project manager field in the Responsible group under the General FastTab, and the Declaration done slider will be moved to Yes.
¶ Step 18.2.2: Audit scope, goal and rationale
¶ Step 18.2.3: Control matrix
Refer to Step 19 below. Risk and control matrix ('RCM')
¶ Step 18.2.4: Send email notification
¶ Step 18.2.5: Meetings
Refer to the page on Meeting management for details on meetings
¶ Step 18.2.6: Fieldwork
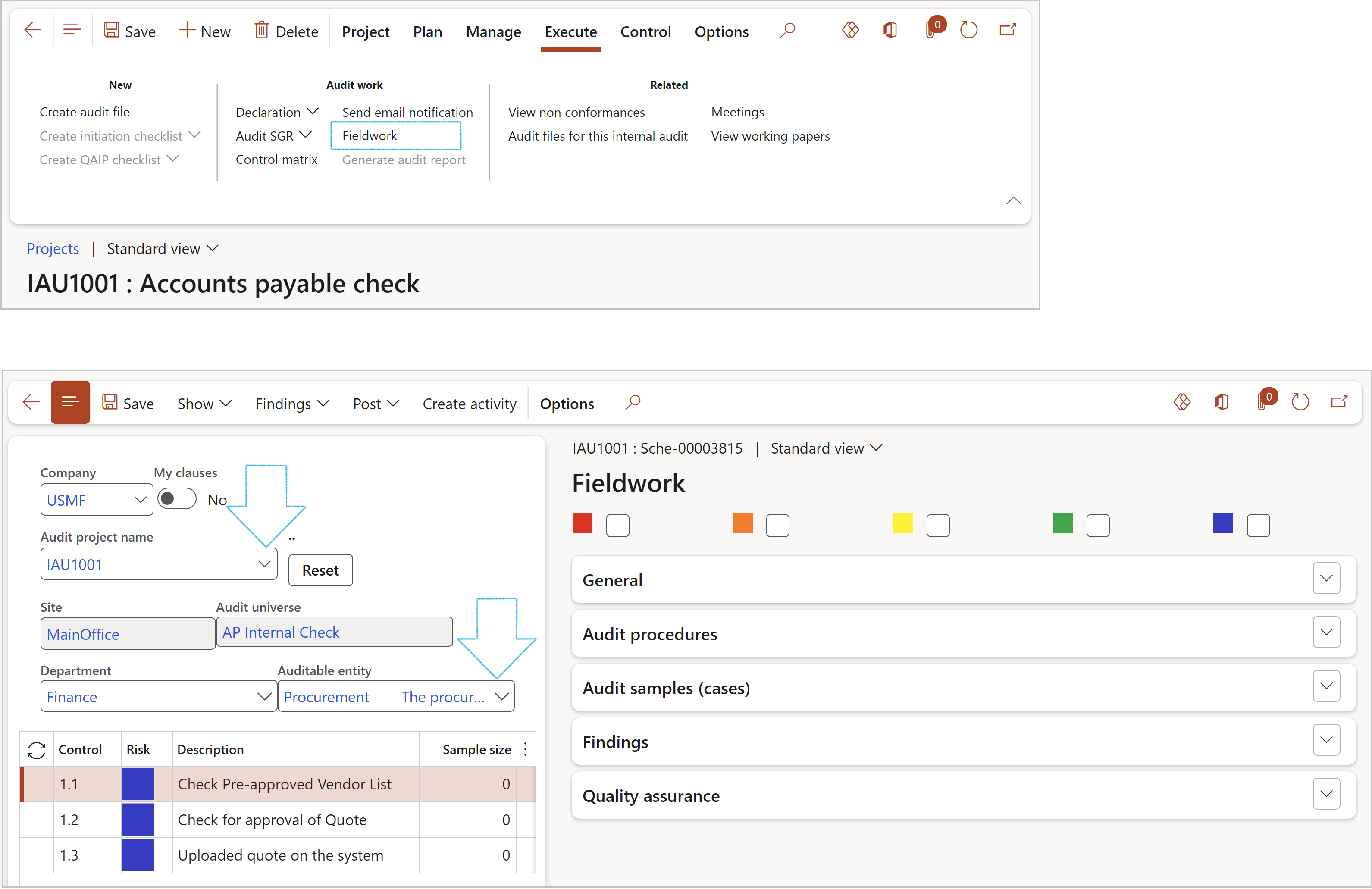
If no scoring method is specified on the Audit type, the scoring method specified on the Parameters will be used
For more detail on the Fieldwork form, refer to Step 22 below
¶ Step 18.2.7: Creating activities from the Fieldwork form
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Periodic > Fieldwork

¶ Step 18.2.8: Audit files for this internal audit
¶ Step 18.2.9: Create initiation checklist
¶ Step 18.2.10: Create QAIP checklist
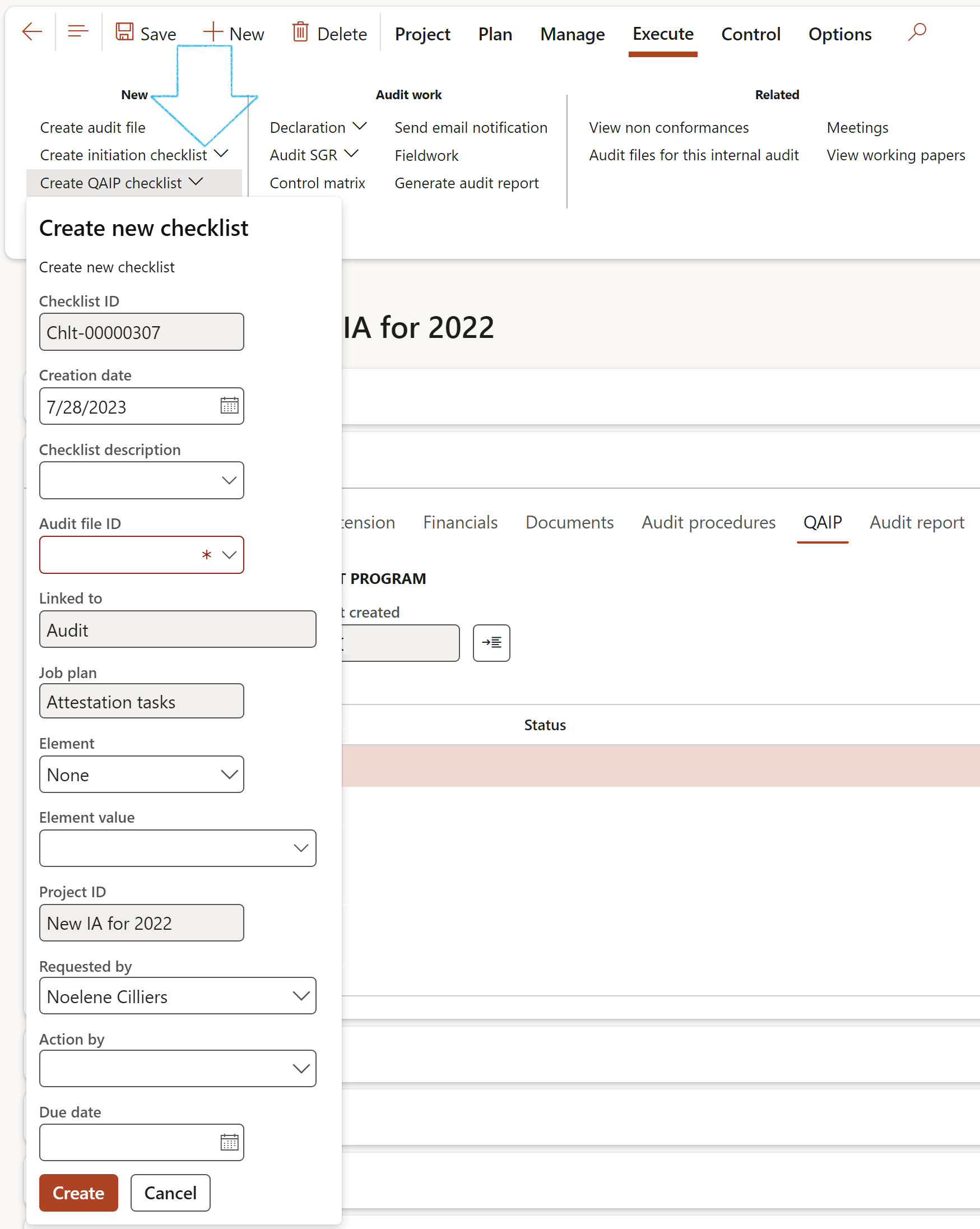
Based on the specified budget in the Scope of the audit file, Dynamics 365 will calculate the % utilized for the particular audit by considering the actual hours against the budgeted hours
¶ Step 18.2.11: Generate audit report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Audit reports to view the created report
¶ Step 18.2.12: Create Audit file
¶ Step 19: Audit engagement letter
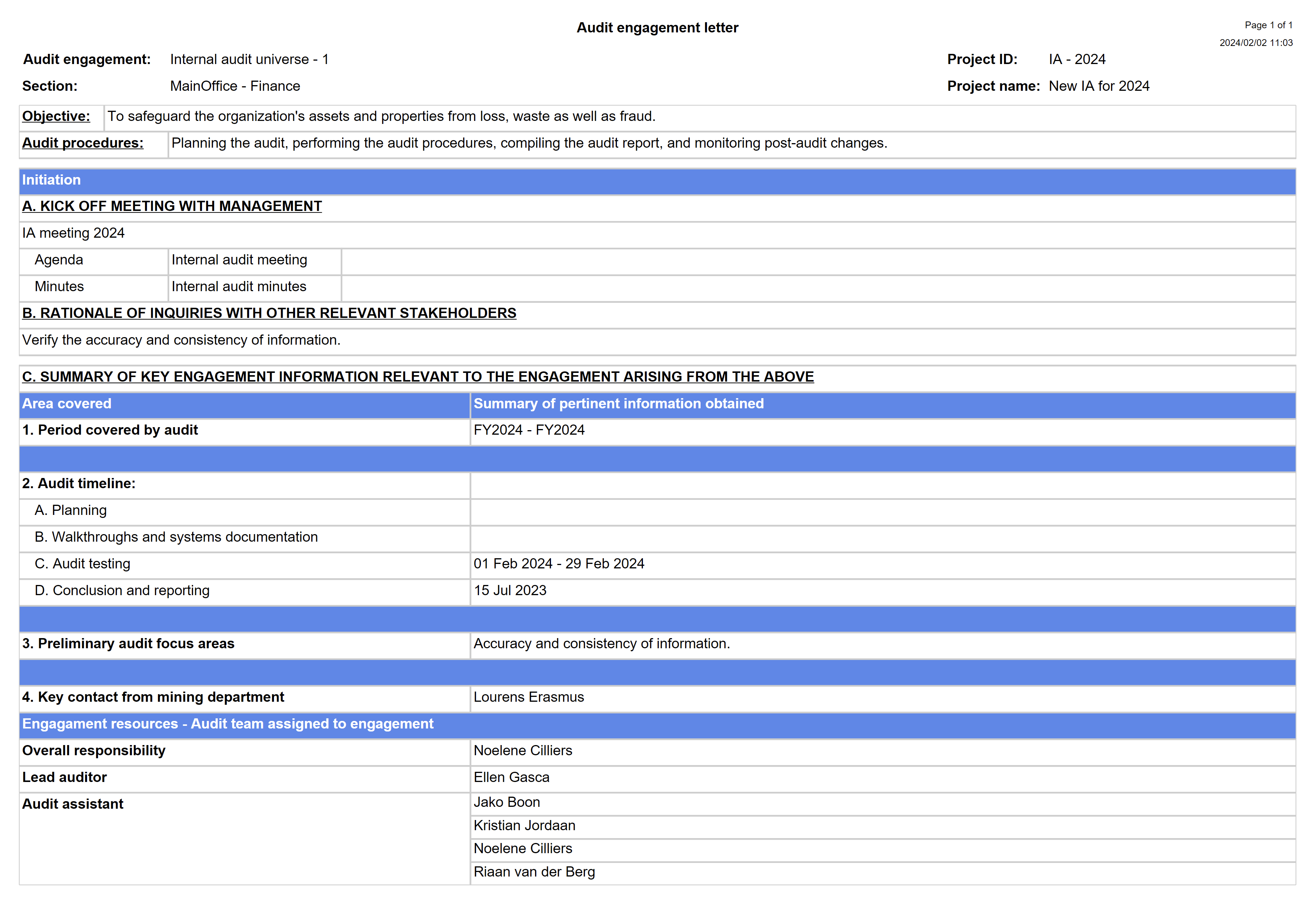
The Audit engagement letter documents and confirms the auditor's acceptance of the appointment, the objective and scope of the audit, the extent of the auditor's responsibilities to the client and the form of any reports.
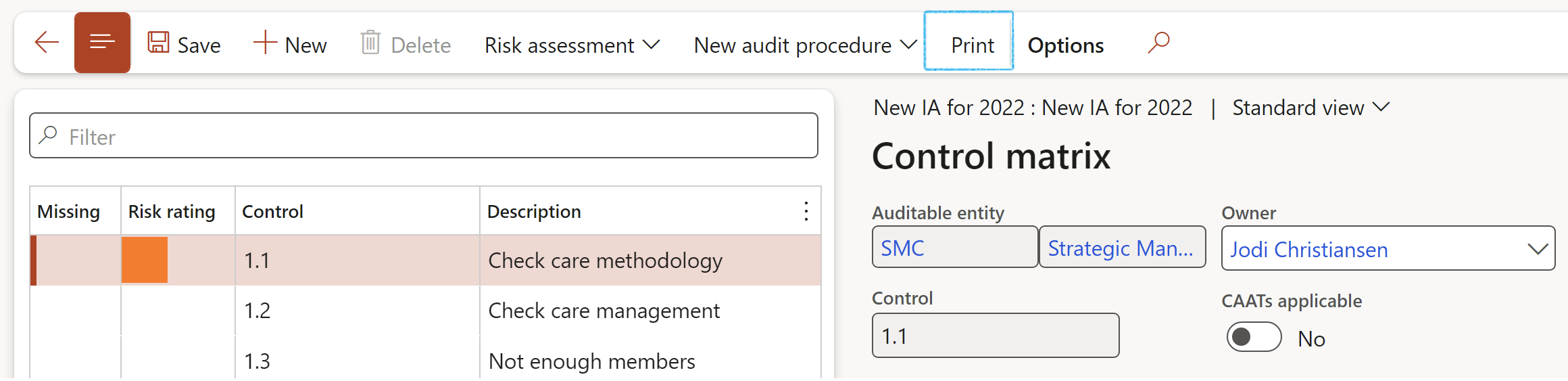
¶ Step 20: Risk and control matrix
The Risk Control Matrix ('RCM') is an essential element of the Internal Audit module. A RCM enables auditors to perform a "data-driven" analysis for a given process, IT system, control or event. This analysis is focused on determining objectives, identifying related risks, documenting mitigating controls and loading supporting test information that validates the adequacy and effectiveness of controls.
Inside Dynamics 365 GRC the RCM is key to the execution of an audit. Here audit managers can create sample, audit procedures and more. Auditors can accepts the controls to be audited (ones listed on the Audit universe that created this audit RCM) or add more controls here on the RCM.
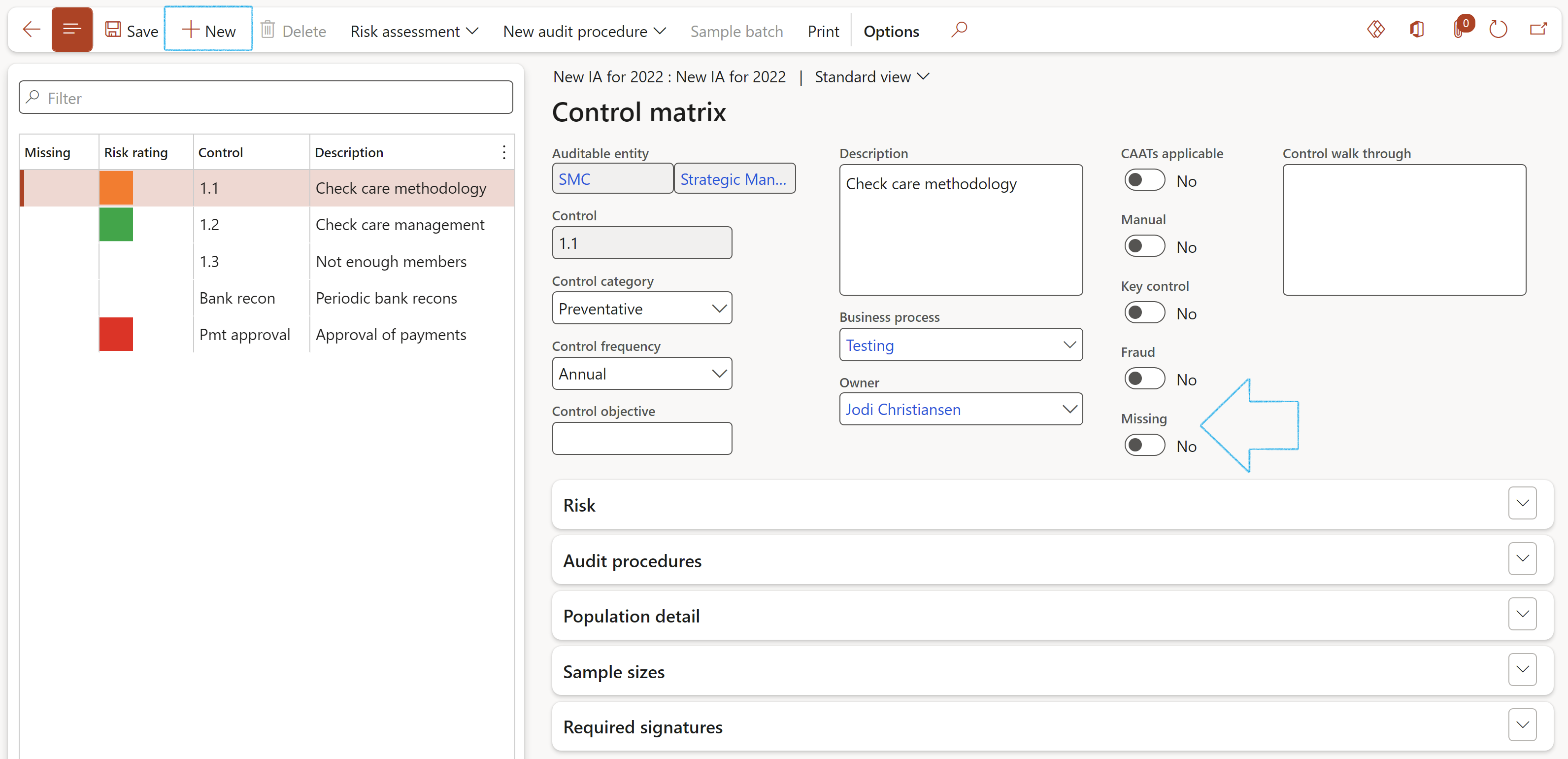
¶ Step 20.1: Control risk assessment
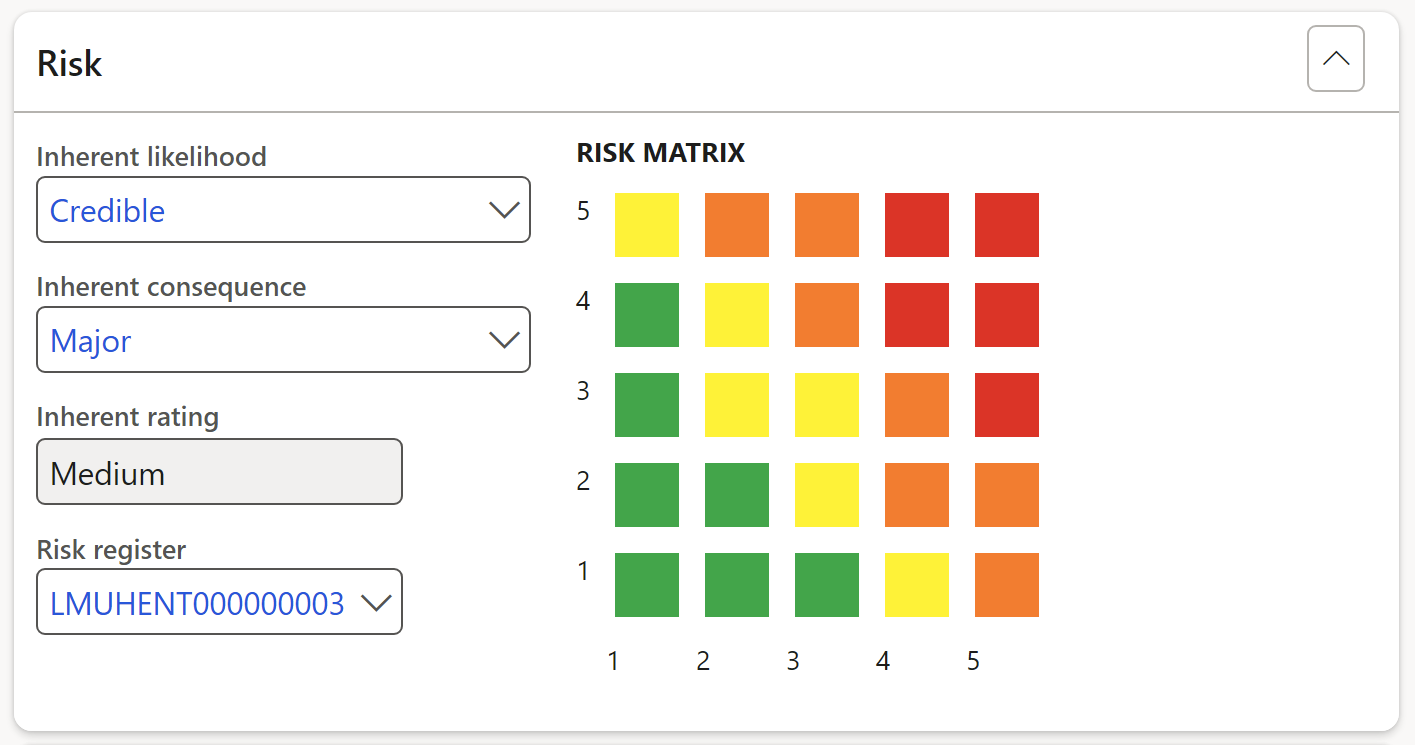
The risk rating is done per selected control on the left-hand side of the screen
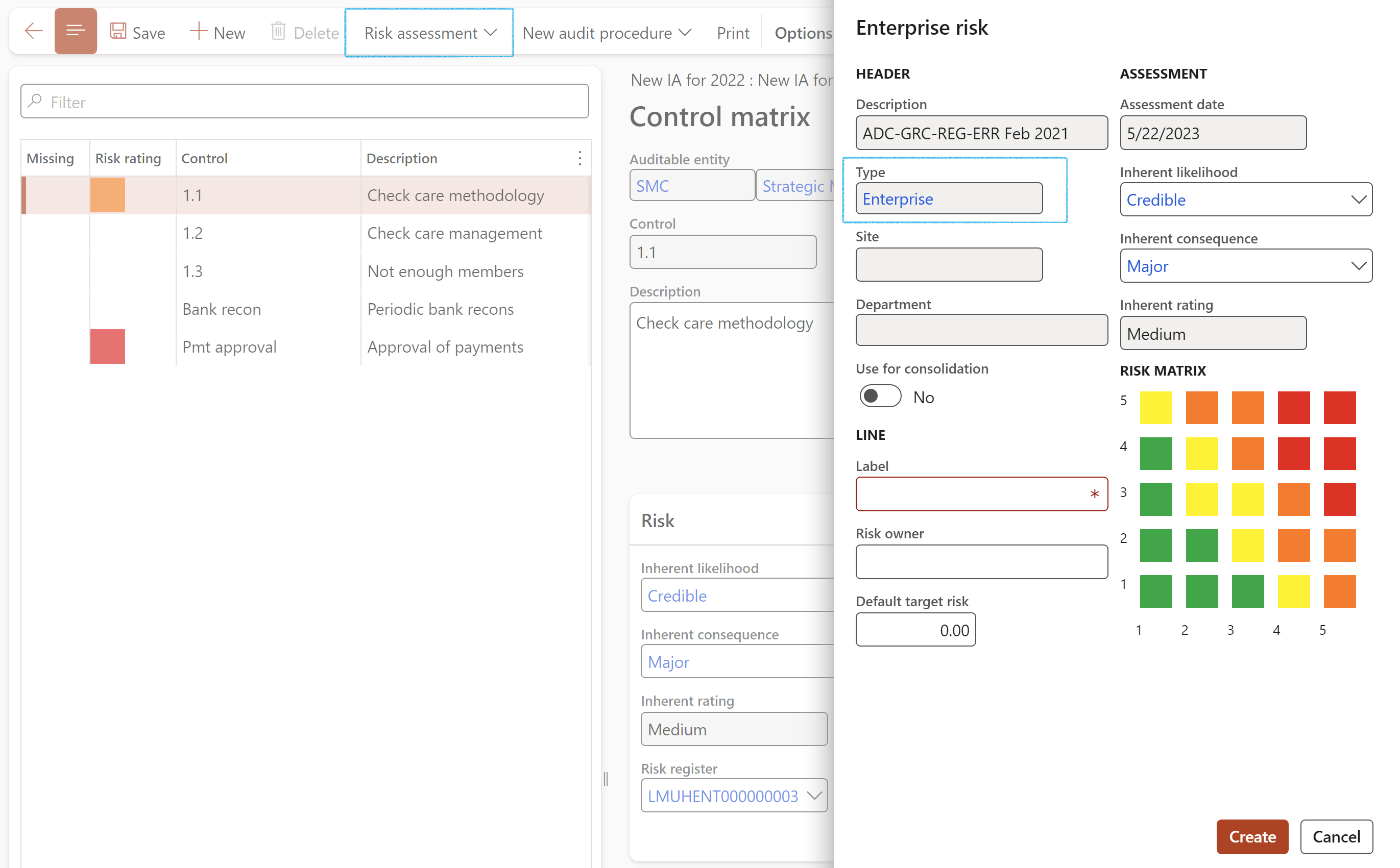
A record will be added on the Risk register line under the Associations Fast tab
The Risk type when doing a risk assessment, is selected on the GRC parameters under the Compliance and audit tab
The risk registers and lines that are created can be found under GRC > Risk > Registers > All enterprise risk registers
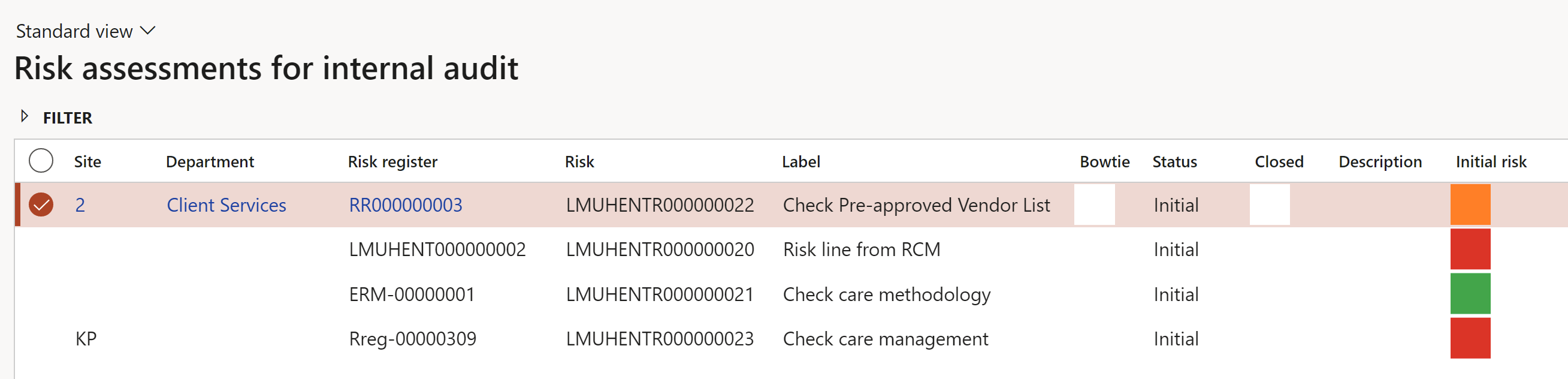
All risk assessments for internal audits can be viewed on the Risk assessments for internal audit worksheet.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Risk assessments for internal audit
¶ Step 20.2: Audit procedures
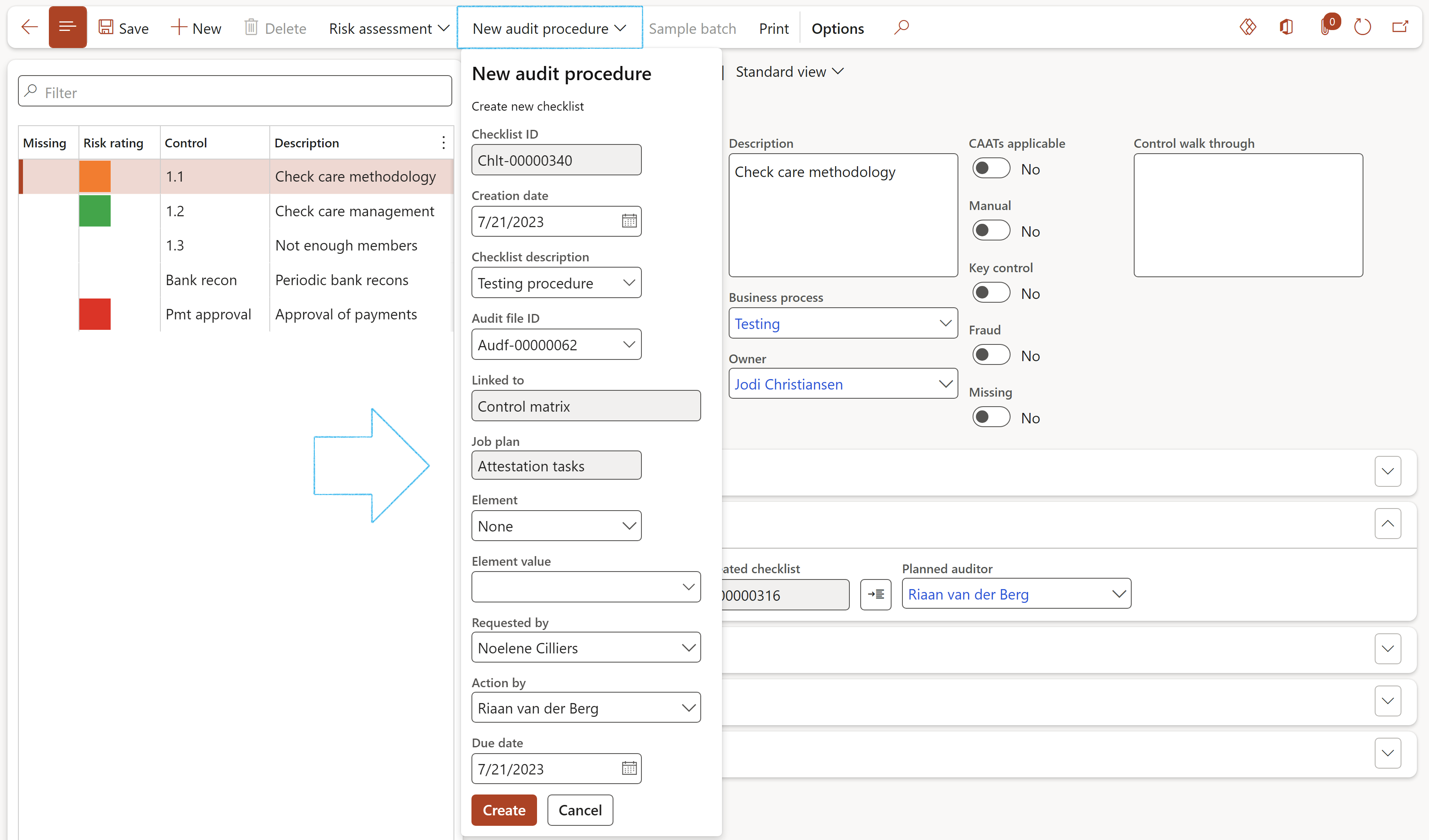
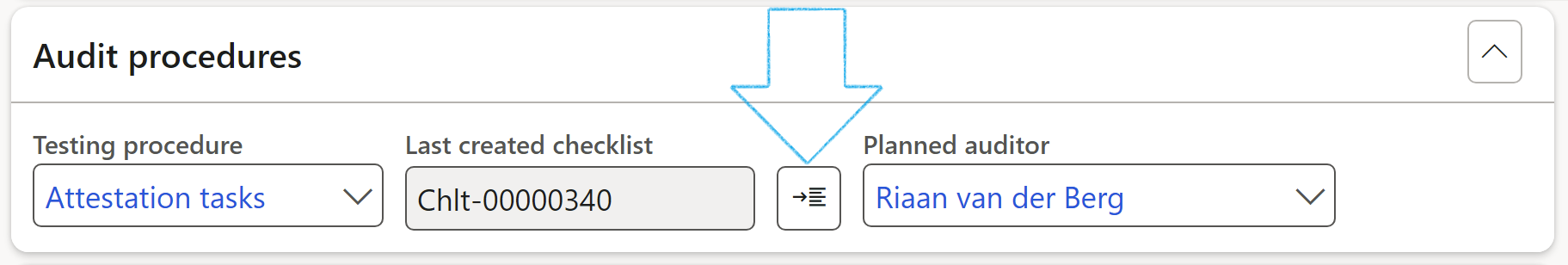
¶ Step 20.3: Population detail for audit procedure sample
¶ Step 20.4: Sample sizes
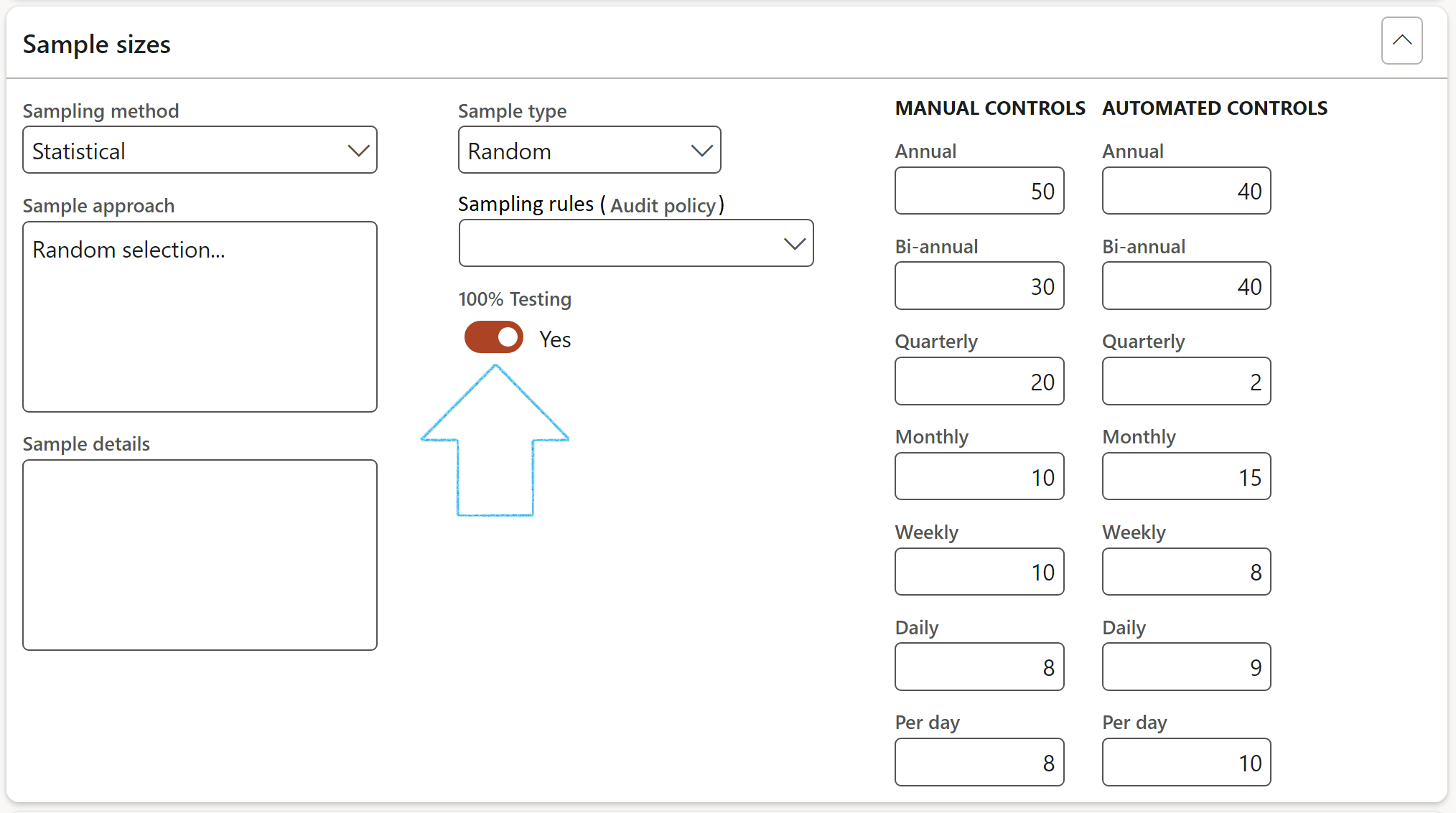
¶ Step 20.5: Required signatures
¶ Step 21: Audit files
Audit files is a crucial element of an Audit (project). It groups together related audit activitites. Every applicable internal control and Working paper is listed in the Audit file.
Audit files have a header with lines. Working papers and Audit findings are found on the header. On “posting” of audit test results, users choose which audit file to update with test results; posted as scores to the lines.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All internal audit files
OR
To view the Audit files linked to the Audit:
There are three methods to create an Audit file in Dynamics 365 GRC:
Users can also attach any additional documents, including scanned invoices, delivery notes, MS Outlook emails, photos etc. using the attachment icon.
¶ Step 21.1: Audit file Header
The Audit file has a lifecycle with a number of stages that it cycles through. Each stage is represented by a status which is changed on the General FastTab.
The statuses of the Audit file are as follows:
|
Not started |
The Audit has been approved but has not been started. This is the default status and cannot move to another status unless a Declaration of interest was done. Please note that the Audit file is locked for editing. |
|
Planning |
The Audit is being planned. The budget for an audit can be changed in the this cycle |
|
Started |
Fieldwork commences |
|
Completed |
Fieldwork has been completed |
|
Draft report |
A Draft Audit report is generated |
|
Final report |
A Final Audit report has been published |
|
Closed |
No more changes can be made to the Audit file |
|
Archived |
The Audit file is archived |
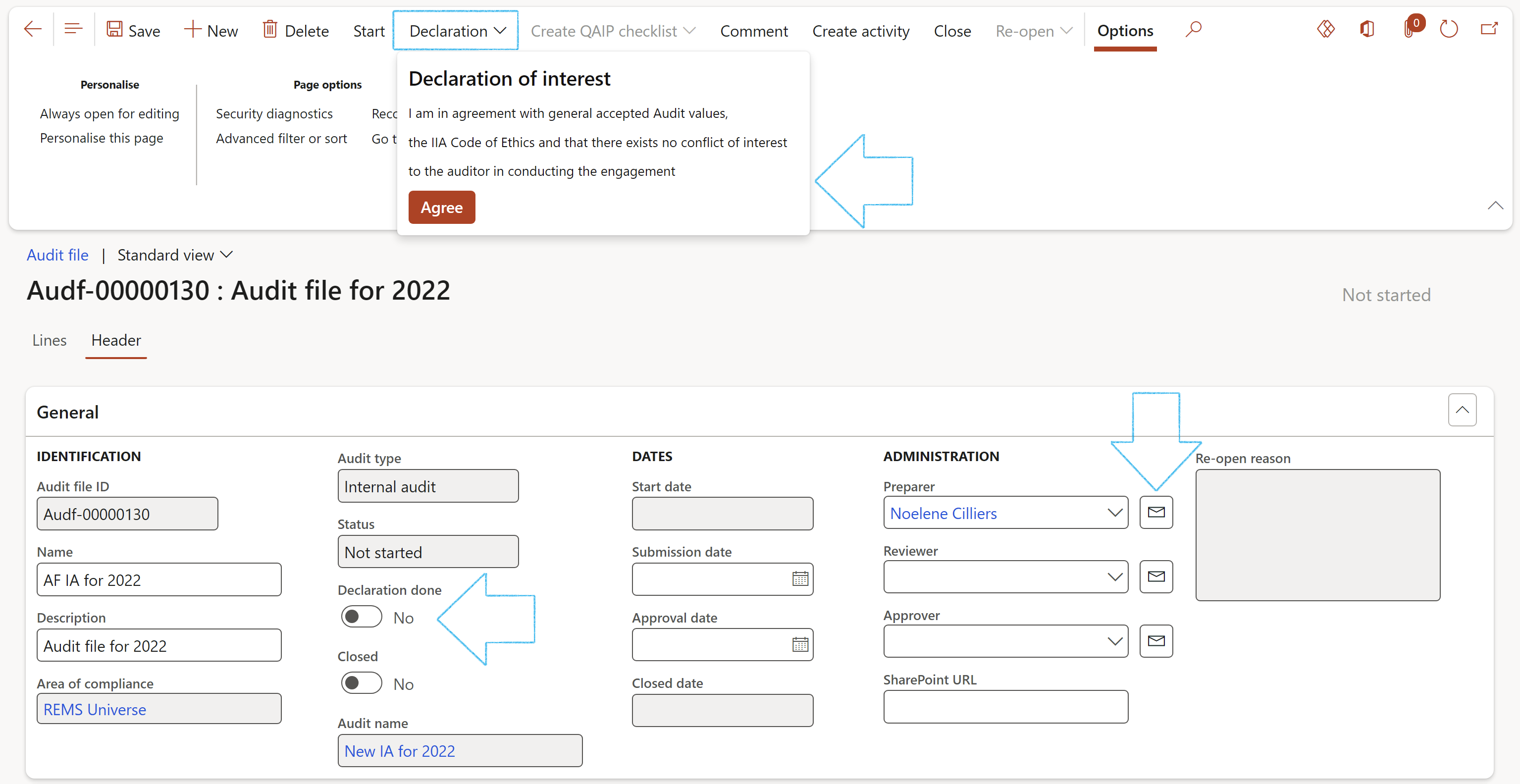
When the user clicks on the Declaration of interest button on the Button strip, this user’s name will populate the Preparer field in the Administration group under the General Fast tab, and the Declaration done slider will be on Yes. The audit file will now be open and ready to receive working papers.
¶ Step 21.1.1: The Documents Fast tab
Details of the Audit report that will be influenced by work done on the audit file, are displayed
The Document pack is passed on from the Audit universe
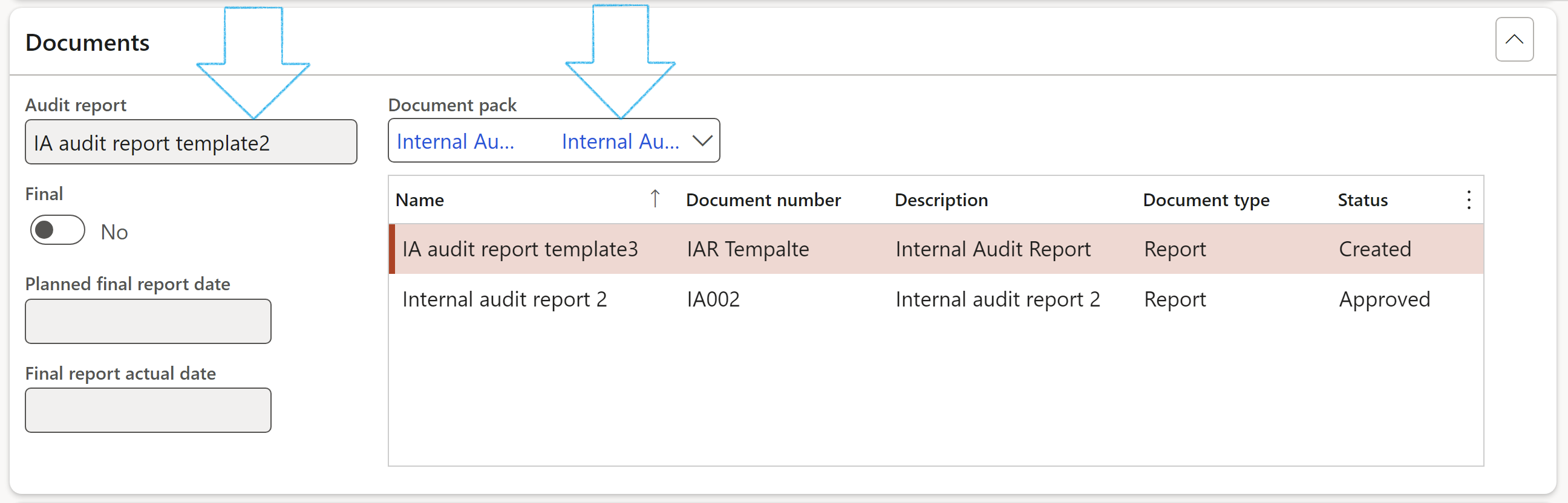
¶ Step 21.1.2: The Working paper and samples Fast tab
This is the “heart and soul” of the Audit file. It lists all system generated working papers grouped by an Auditable entity, and also lists the applicable Audit procedures. Refer to step 21 for detail on Working papers.
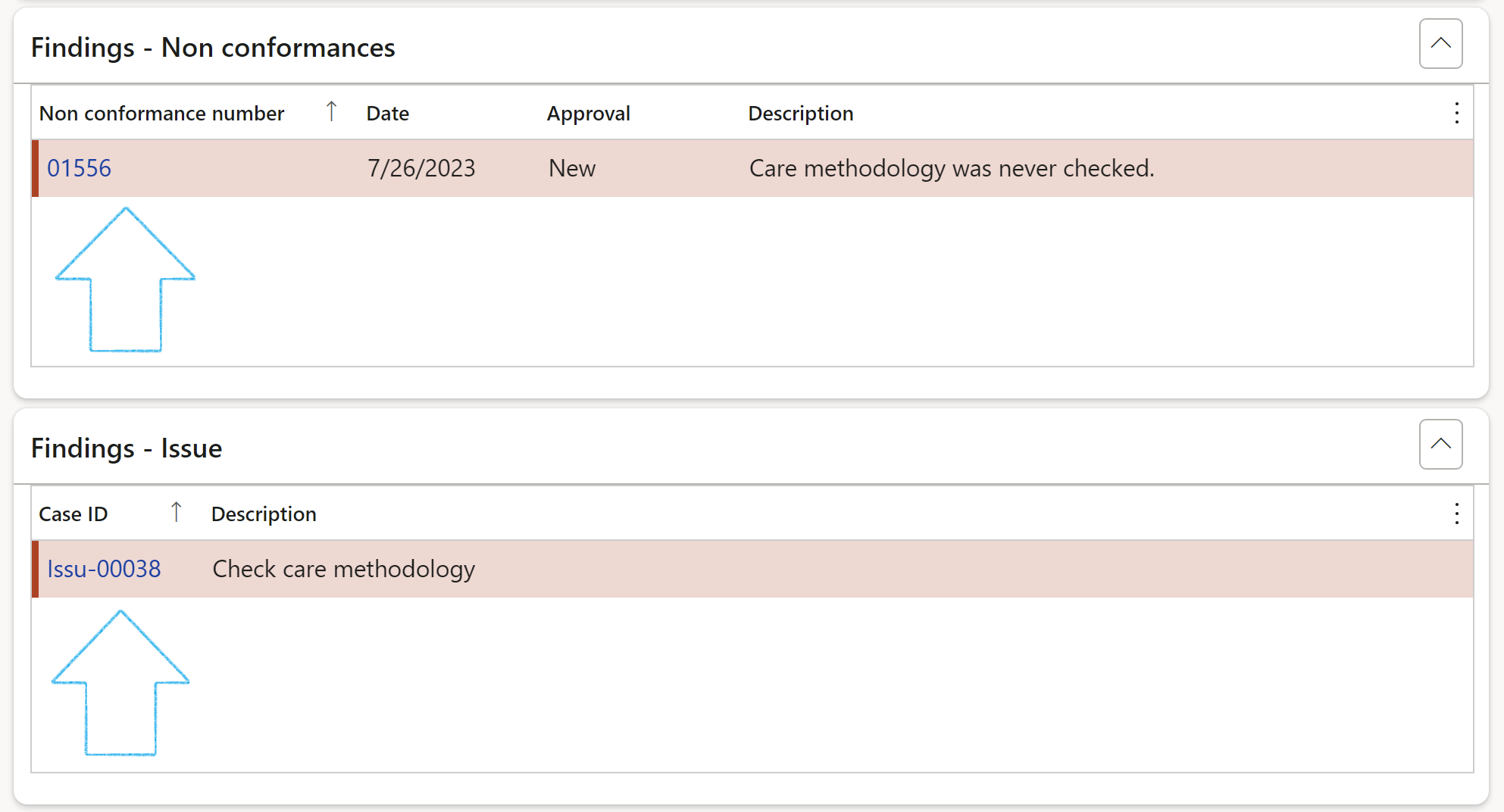
¶ Step 21.1.3: The Findings – Non-conformances/Issue Fast tabs
When fieldwork is done, and findings (non-conformances/issues) are created, the details are displayed under these two Fast tabs on the Audit file.
¶ Step 21.1.4: The Quality Assurance and Improvement Program (QAIP) Fast tab
A Quality Assurance and Improvement Program (QAIP) enables an evaluation of the internal audit activity's conformance with the Definition of Internal Auditing and the International Standards for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing (Standards) and an evaluation of whether internal auditors apply the Code of Ethics.
_fast_tab.png)
¶ Step 21.1.5: The Audit file comments Fast tab
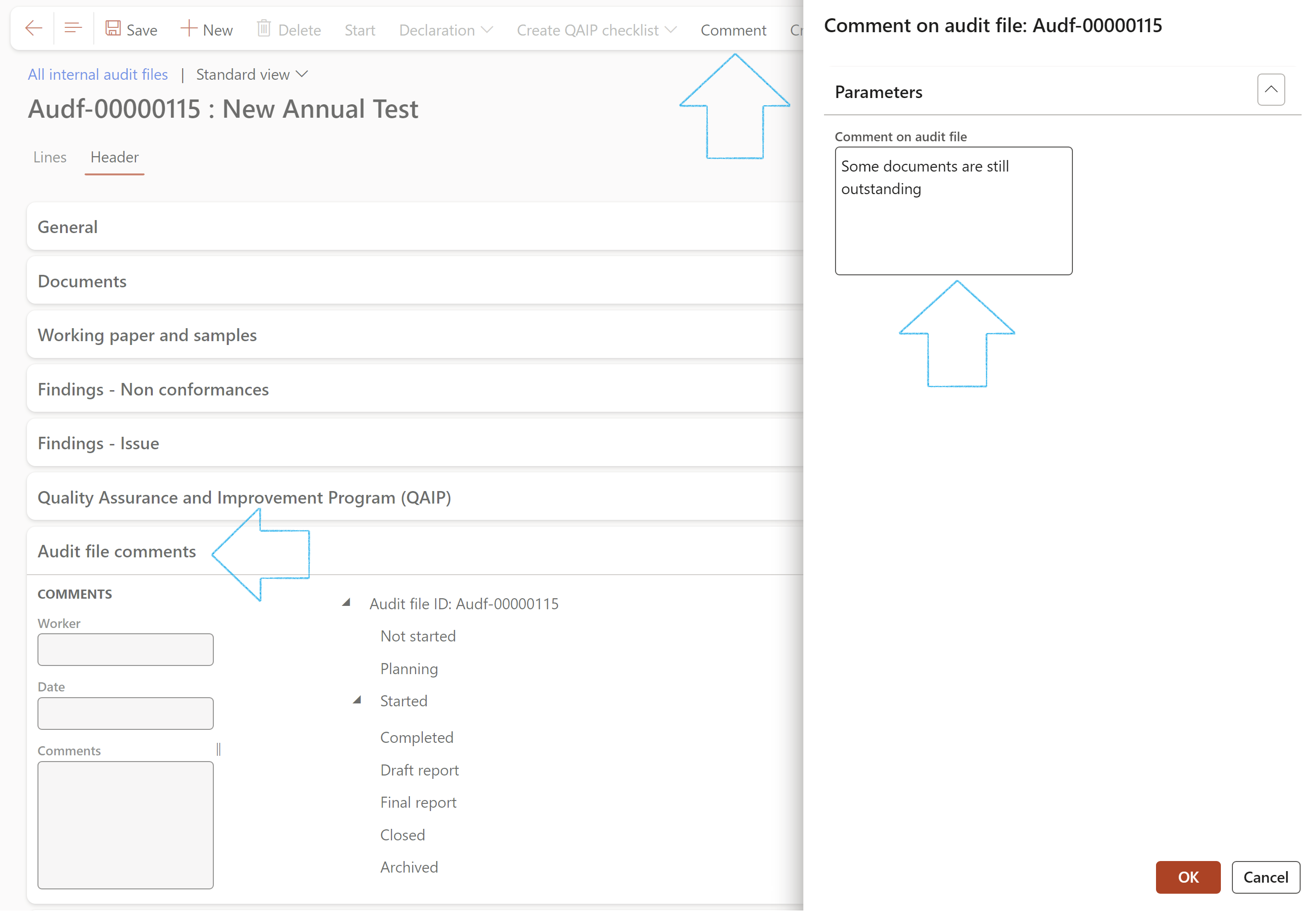
Comments are displayed under the status in which the Audit file was when the comment was added
¶ Step 21.1.6: The Conclusion Fast tab
Open the Lessons learned Index tab
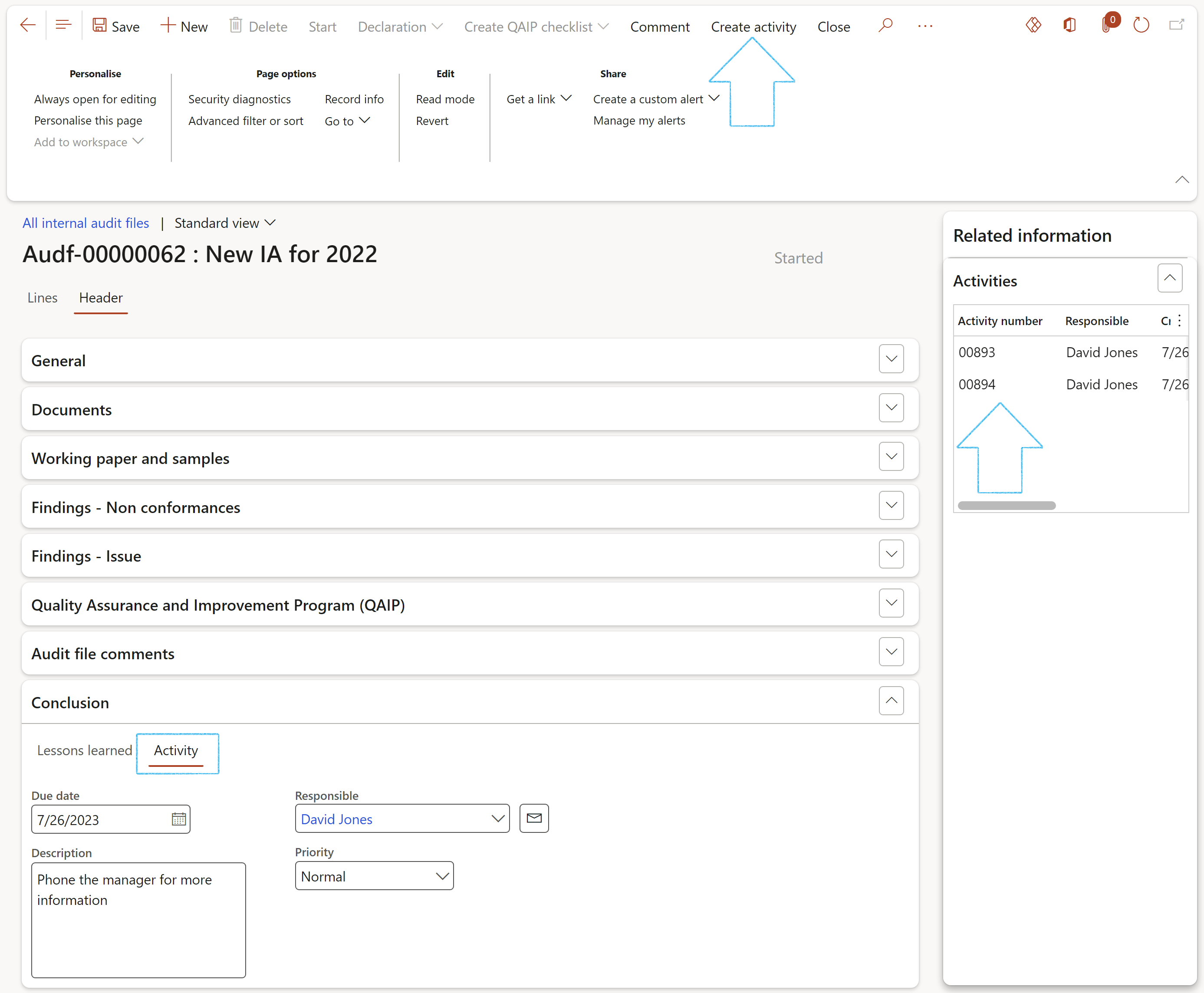
¶ Step 21.1.7: The Signatures Fast tab
Select the workers who Performed the audit tasks, as well as the workers who Reviewed the tasks
¶ Step 21.2: Audit file Lines
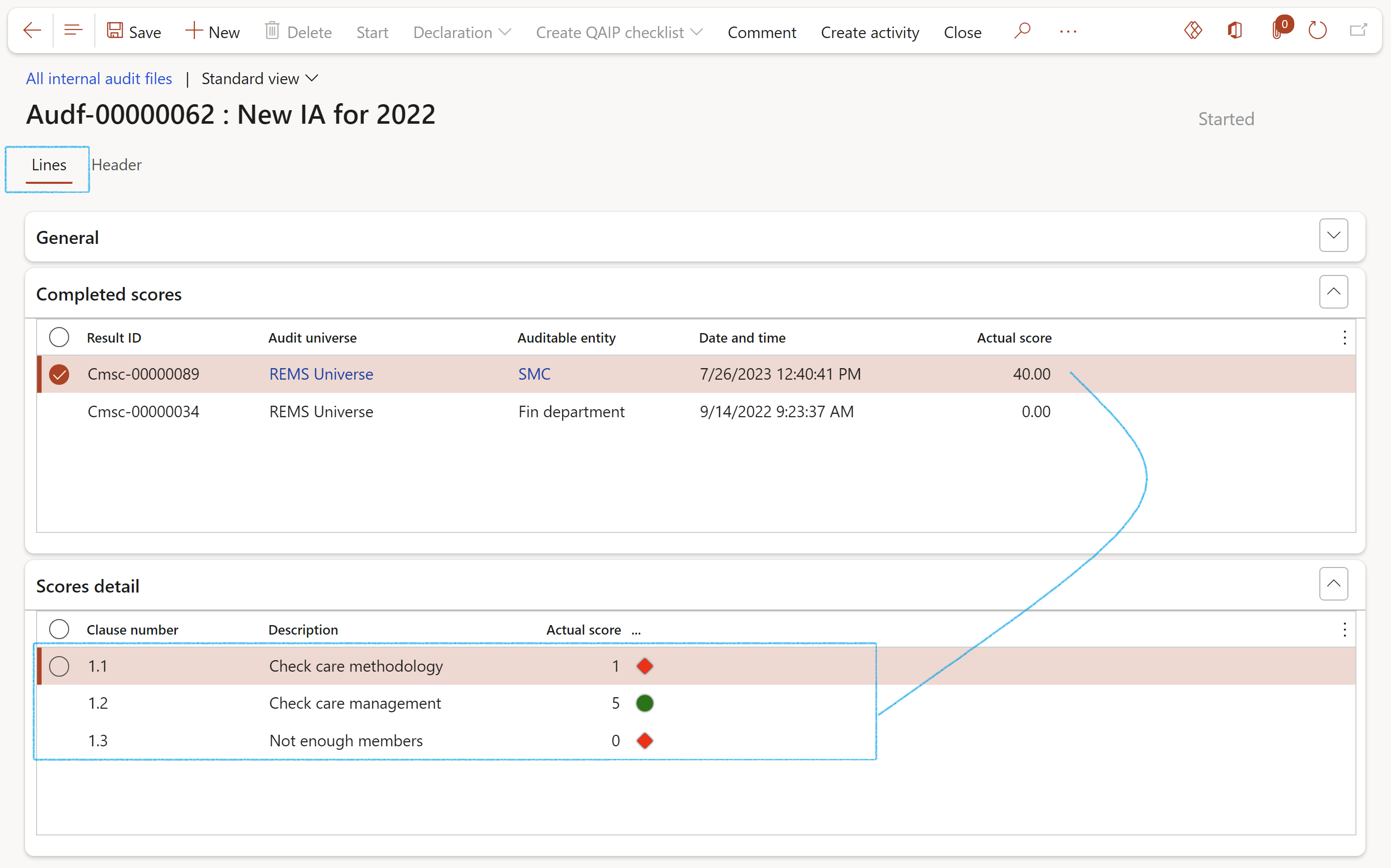
The lines view provides a list of all the posted scores (from the Fieldwork form) of the inidividual control adequacy.
¶ Step 22: Working papers
Audit working papers are used to document the information gathered during an audit. They provide evidence that sufficient information was obtained by an auditor to support his or her opinion regarding the underlying financial statements. Inside Dynamics 365 GRC auditors can view and use working papers by going to the Audit and clicking on View working papers or by opening the Audit file for a selected audit.
¶ Step 22:1 Working papers on the Audit file
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Internal Audit files
¶ Step 22.1.1: Print the Audit working paper
In the Button strip, click on the Print working paper button
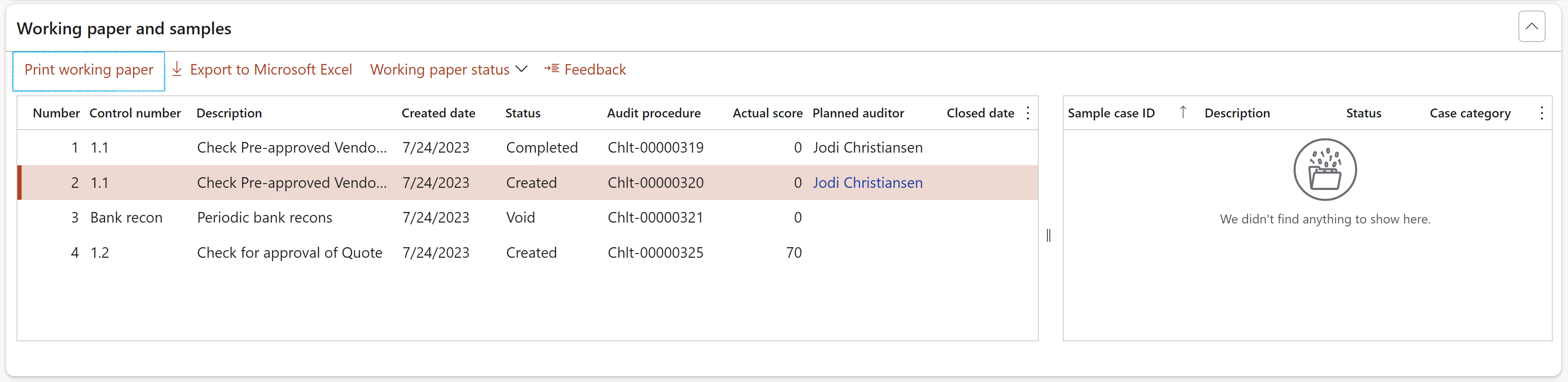
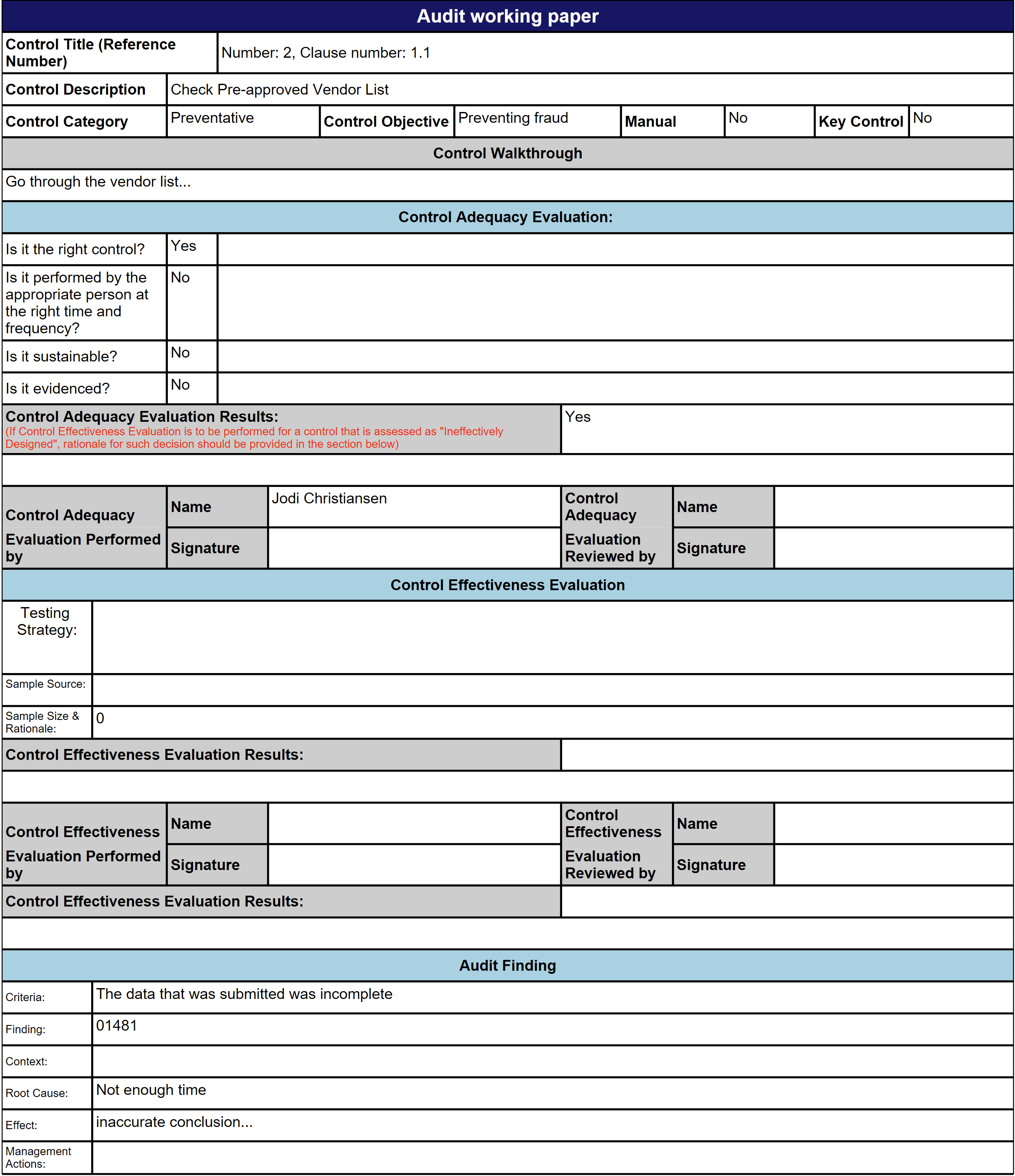
Note that the information printed on the working paper is derived from control description on the RCM and auditing clerks filling in fields on the Audit procedure lines (refer to Step 21.1.4)
If the working paper status = Void (cancelled), Voided will be printed in red at the top of the report
¶ Step 22.1.2: Export to Excel
Click on the Export to Microsoft Excel button to export the grid to Excel
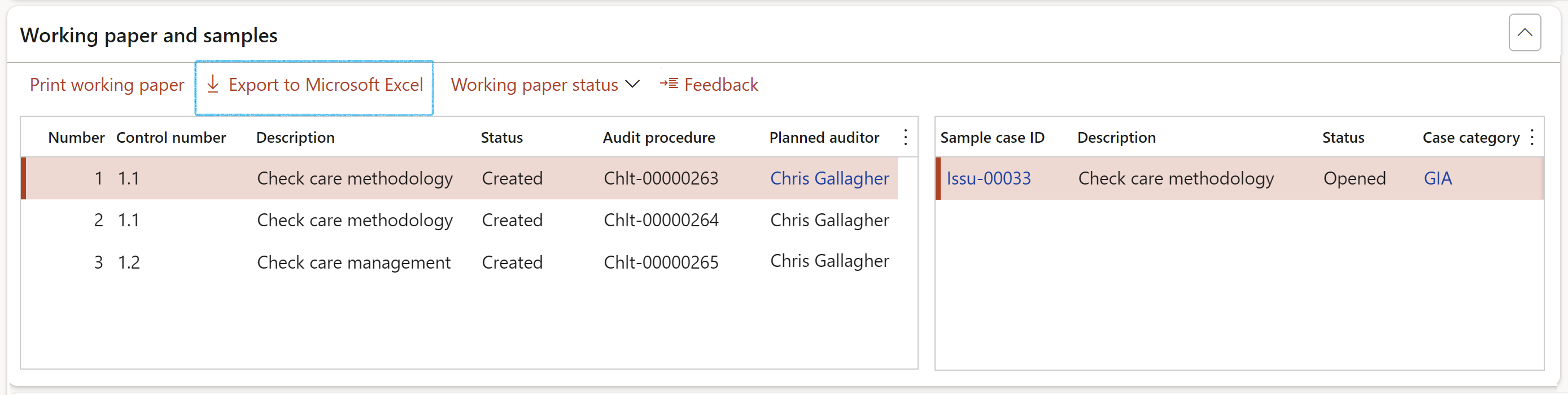
¶ Step 22.1.3: Status of the Audit working paper
The status of each Working paper can be changed by clicking on the Working paper status button
When a working paper status changes to "Void" all lines in the underlying audit procedure will also be cancelled.
¶ Step 22.1.4: Do feedback on Audit procedures checklist
Audit control testing is done here. Audit clerks will have received a list of Audit procedures (per control) to execute. These are created by the Audit manager via the RCM.
Click on the Feedback button in the Button strip.
The Checklist feedback (individual audit procedures steps) form will open.
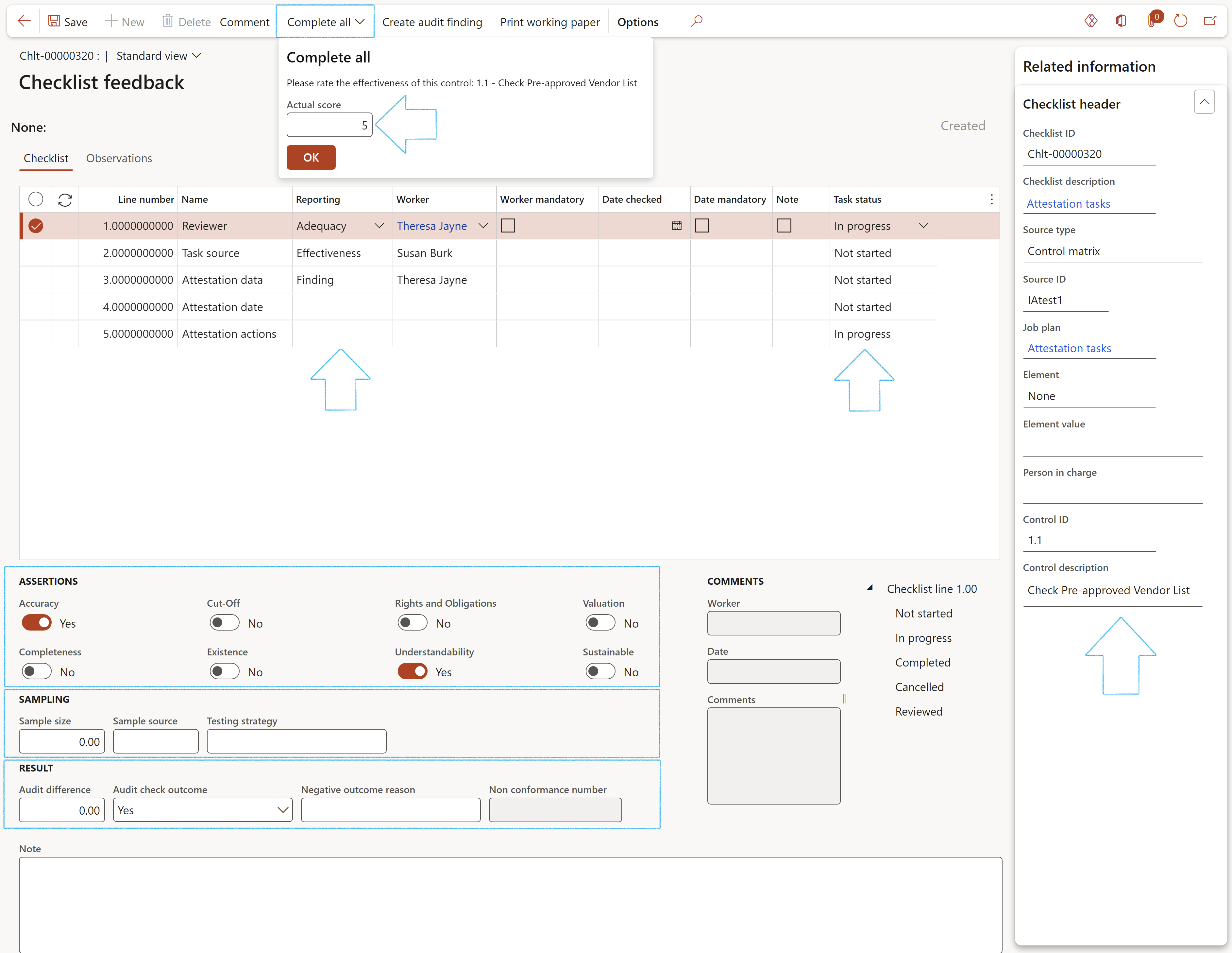
Click on the Comment button in the button strip to add comments on the selected checklist line
By clicking on the Complete all button in the button strip, all the checklist lines can be marked as Completed and a control effectiveness score given
Use Create audit finding button in the button strip, to create a non-conformance
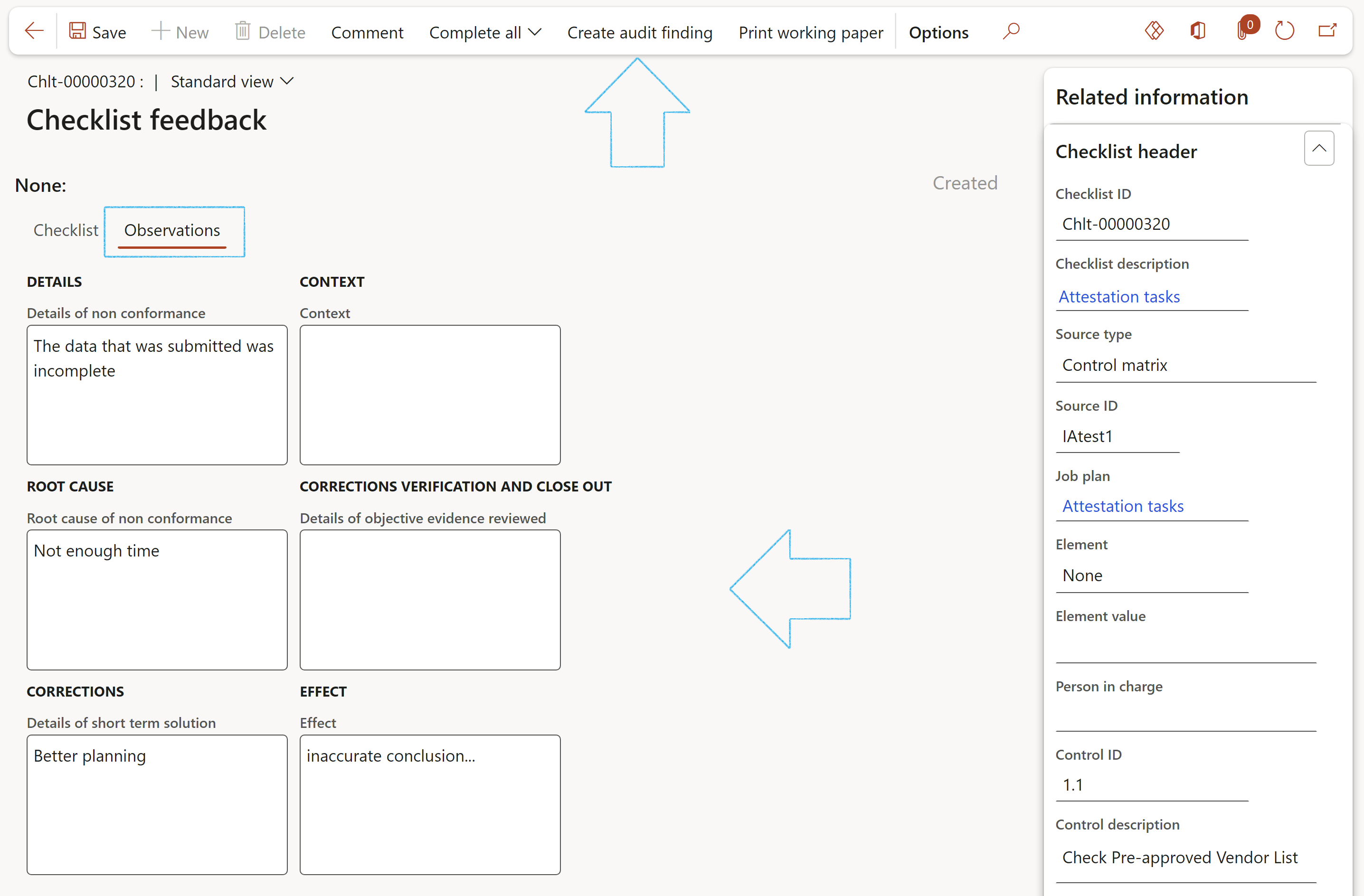
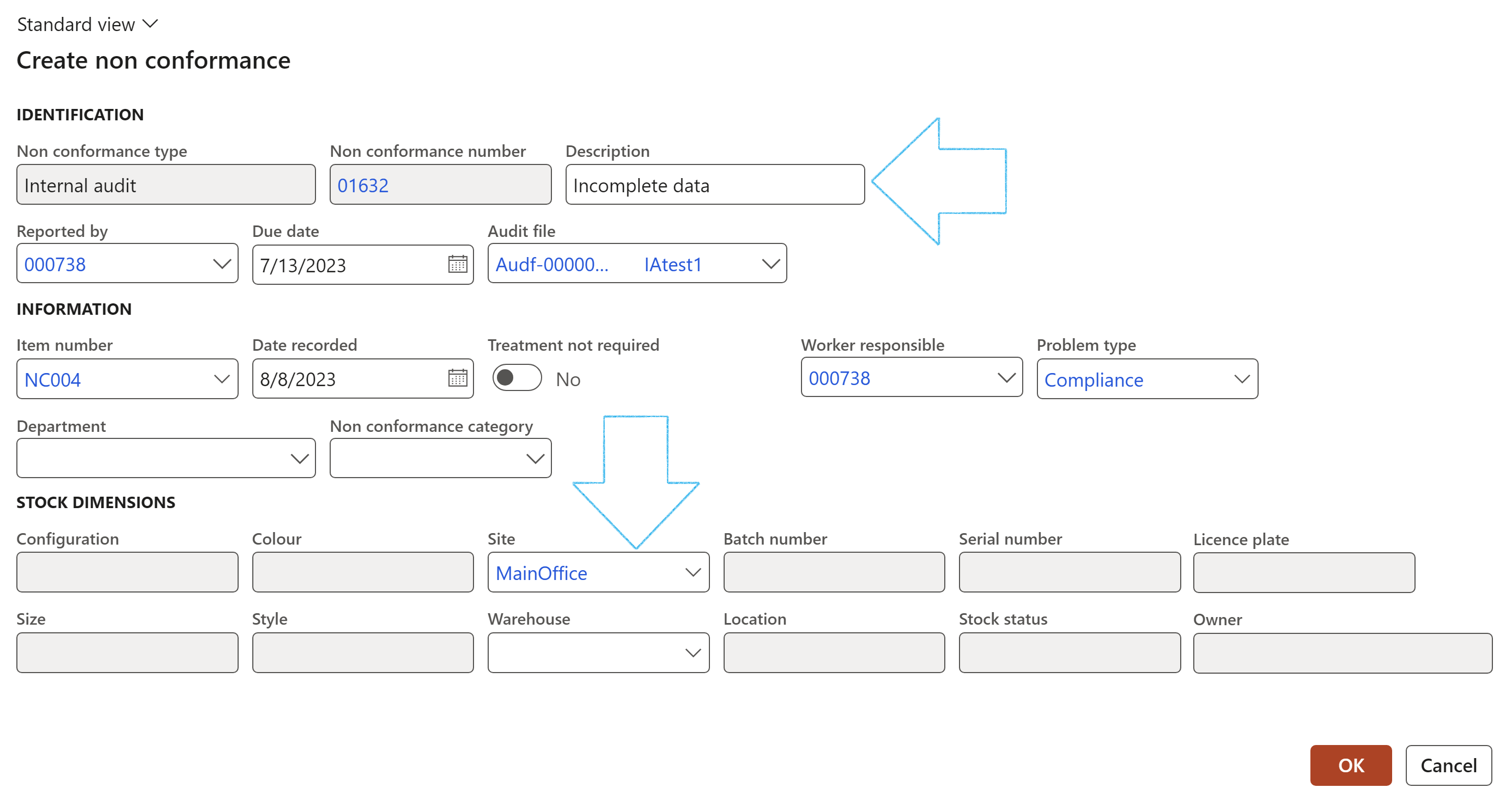
The Non conformance number will be dislayed under the Checklist Index tab, Result field group
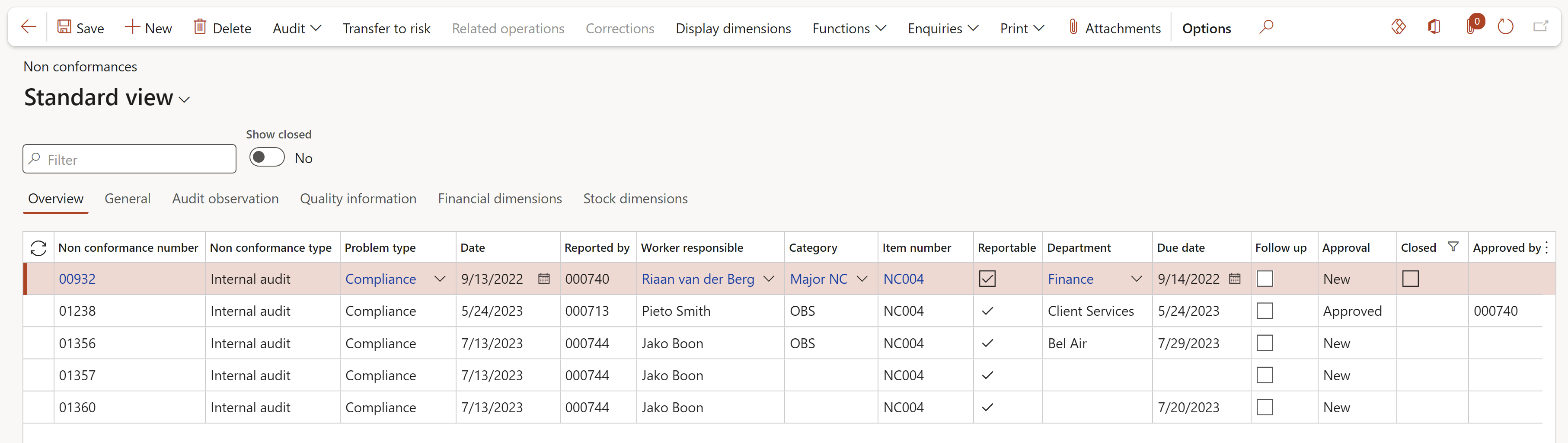
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Findings > Non conformances
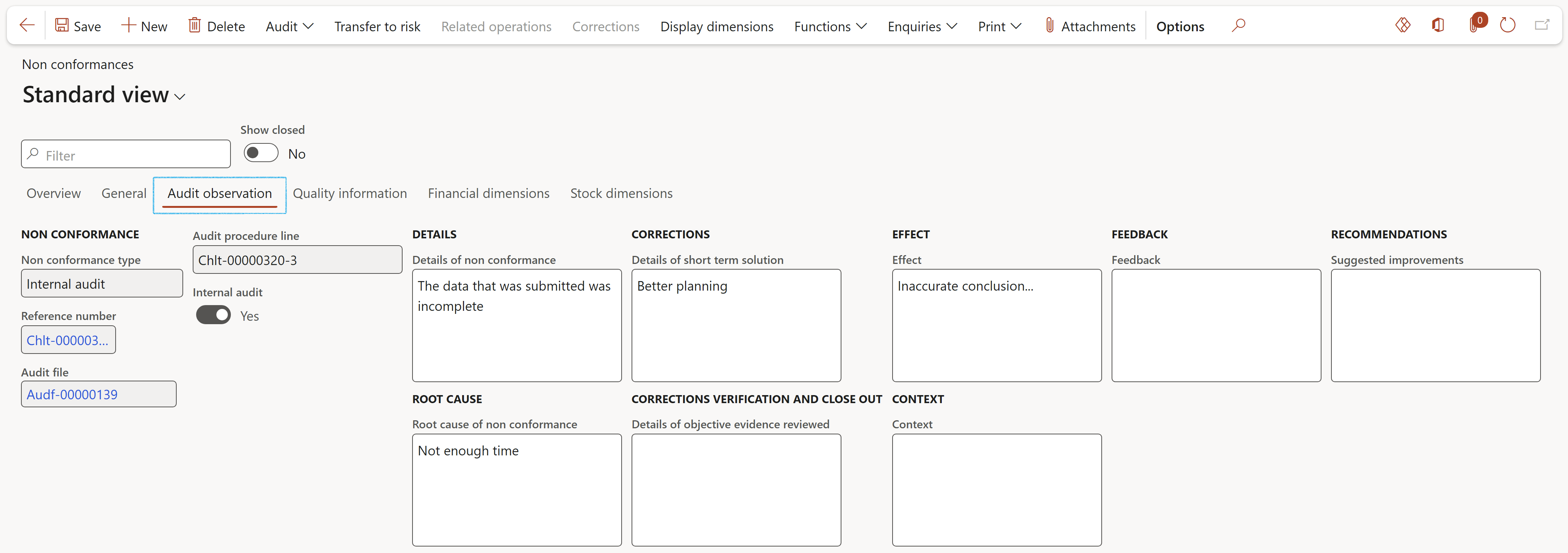
¶ Step 22:2 Working papers on an Audit
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All internal audits
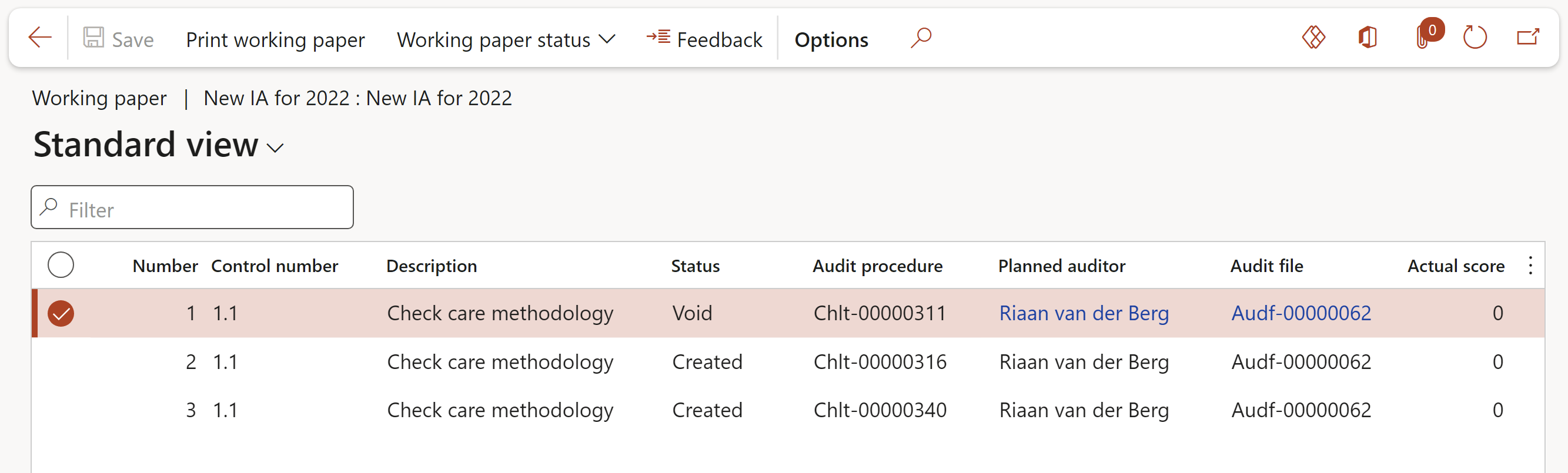
All the same steps and actions as per above is applicable when working on an audit procedure via the working papers of a specific audit.
¶ Step 23: Fieldwork
Internal auditors must identify, analyze, evaluate and document sufficient information to achieve the engagement’s objectives. This includes assisting the organization in maintaining effective controls by evaluating their effectiveness and efficiency, and by promoting continuous improvement.
Engagement findings and recommendations emerge through a process of comparing “what should be” with “what is”. Whether or not there is a difference, the internal auditor now has a foundation on which to build the report.
When conditions meet the criteria, applicable test programs will be marked as “Effective”, and no findings will be raised. However, in cases where the conditions do not meet the criteria, internal audit findings will be raised, and any issues to be reported verbally based on their materiality, will be taken into consideration.
Internal audit findings will be raised as and when the individual test programs are completed and reviewed by the audit manager. This is done in two ways; Dynamics 365 can log a formal (more serious) non-conformance, or just log an issue via the Audit register.
Audit managers would most likely use this Fieldwork form to review audit clerks working papers and rate internal controls.
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Periodic > Fieldwork
OR
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > All internal audits and click on Fieldwork button inside the Execution tab.
The user can choose which columns to see in the left-hand side grid by clicking on the Show button in the Action pane and moving the relevant sliders to Yes
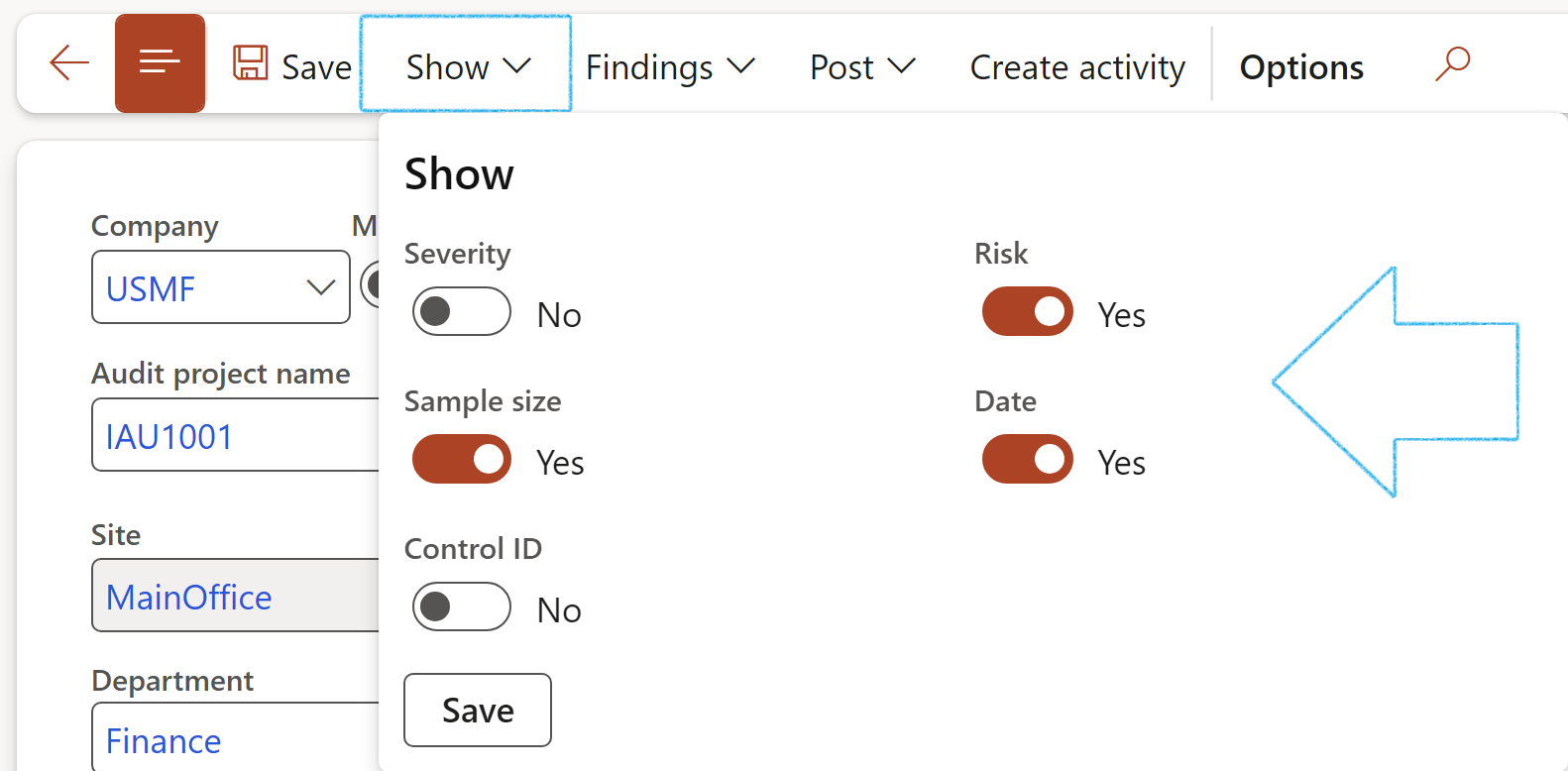
¶ Step 23.1: General Fast tab
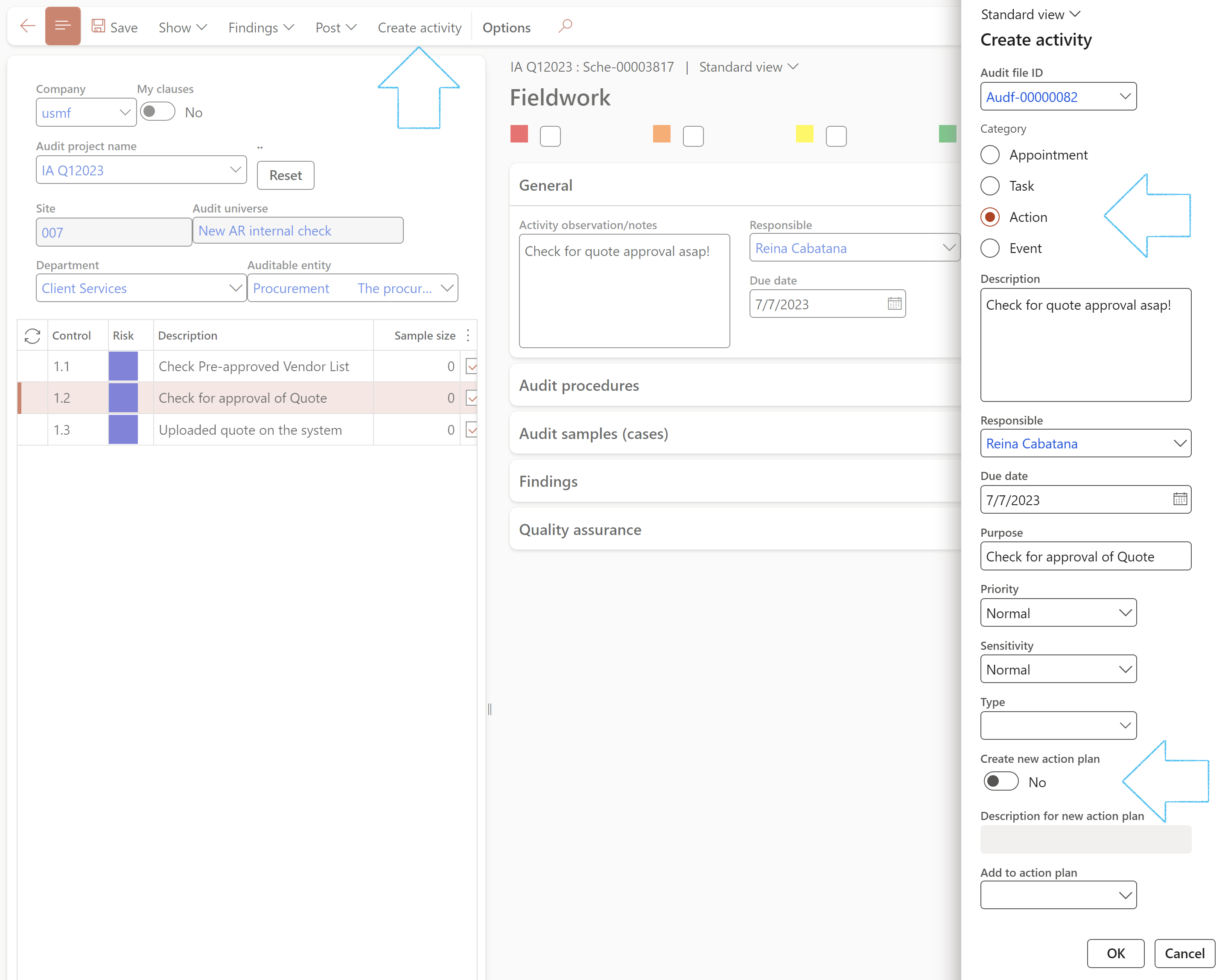
¶ Step 23.2: Audit procedures Fast tab
The checklists that are displayed under the Audit procedures Fast tab, are per selected control.
Feedback can be done on the selected checklist by clicking on the Feedback button.
¶ Step 23.3: Audit samples (cases) Fast tab
For future use
¶ Step 23.4: Findings Fast tab
There are three Index tabs under the Findings Fast tab for capturing the following details per control:
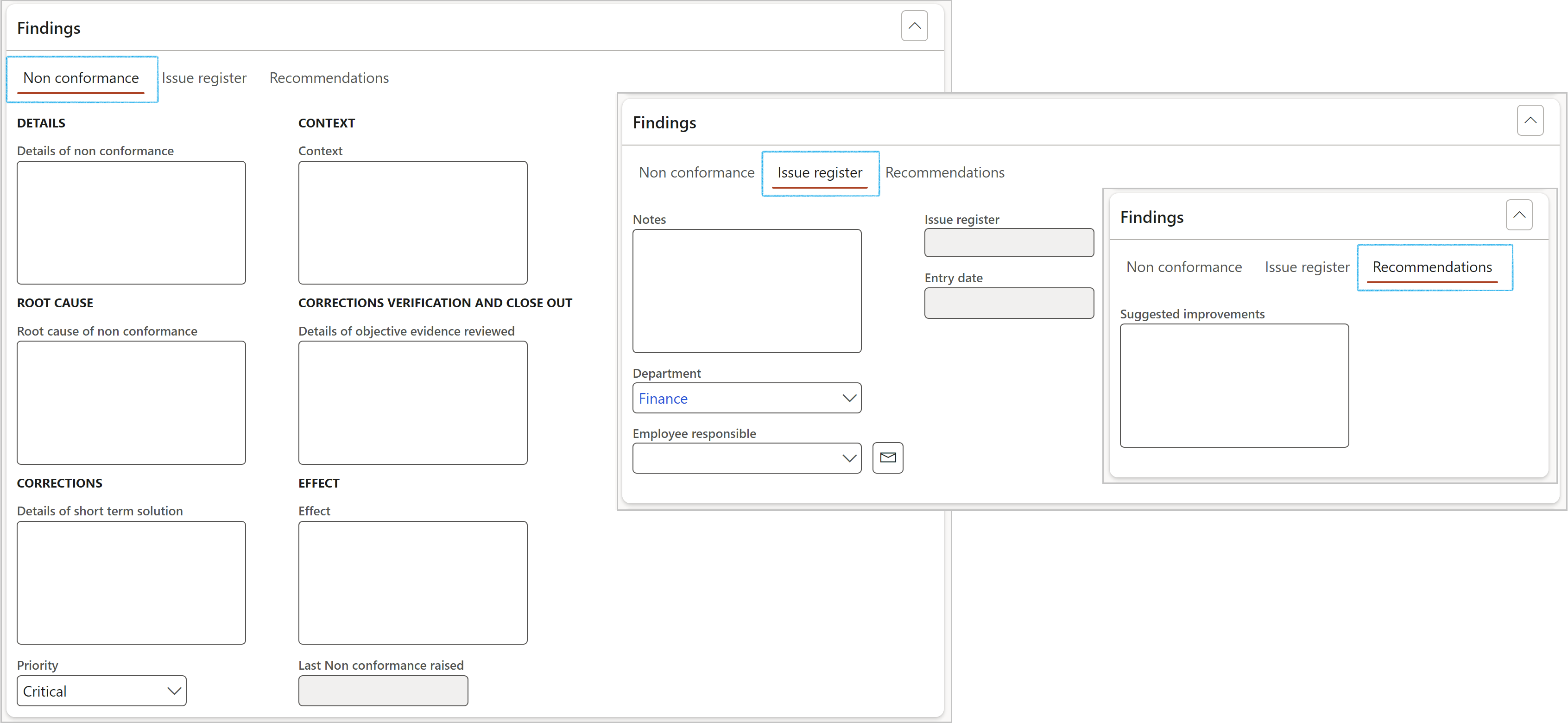
¶ Step 23.4.1: Create audit findings
After an audit team collects the facts and completes its investigation, it is time to determine the results of the investigation. For audits, the results are called audit findings.
The first step is to evaluate the evidence against the audit criteria. The evidence is the factual information collected or observed during the performance of the audit. The audit criteria are the standards, procedures, regulations or objectives which the organization was audited against. The criteria represent requirements the organization must comply with.
Using the Findings button on the Fieldwork form, users can choose to
Note that these reported outcomes are counted and recorded as findings
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Findings > Non conformances
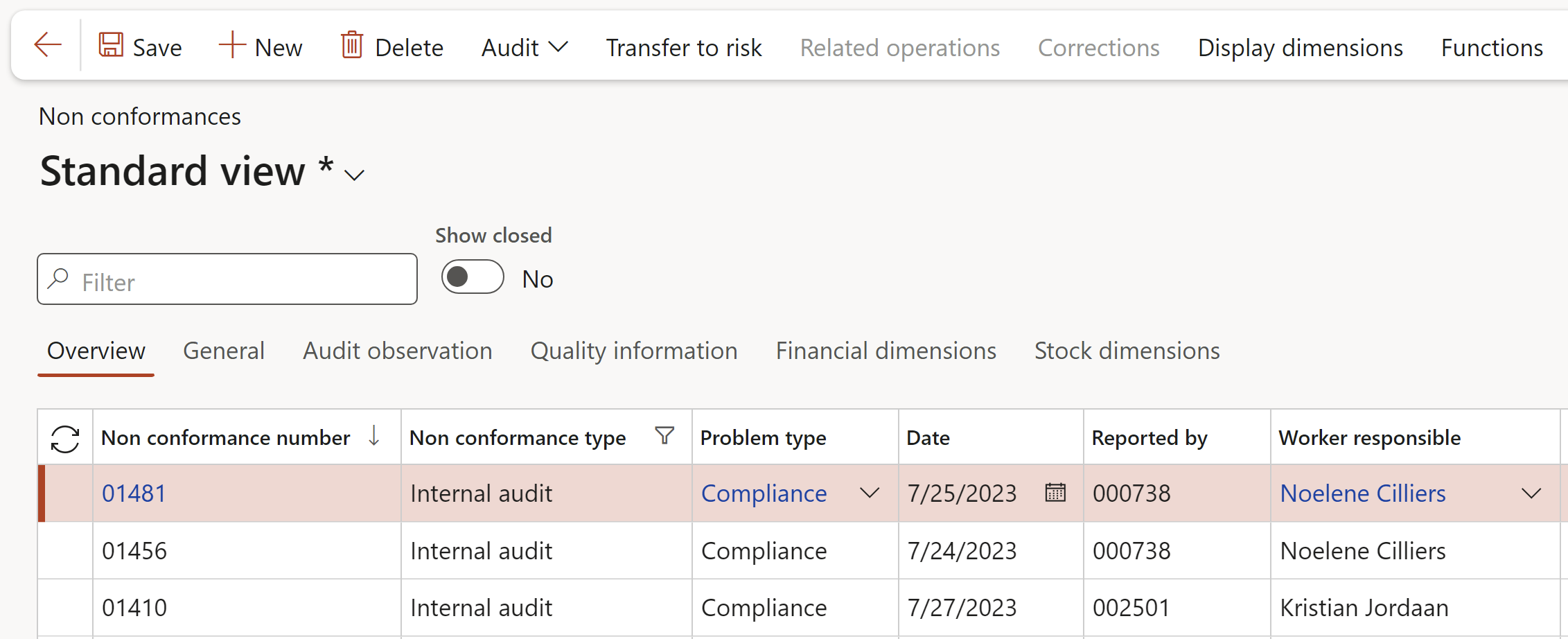
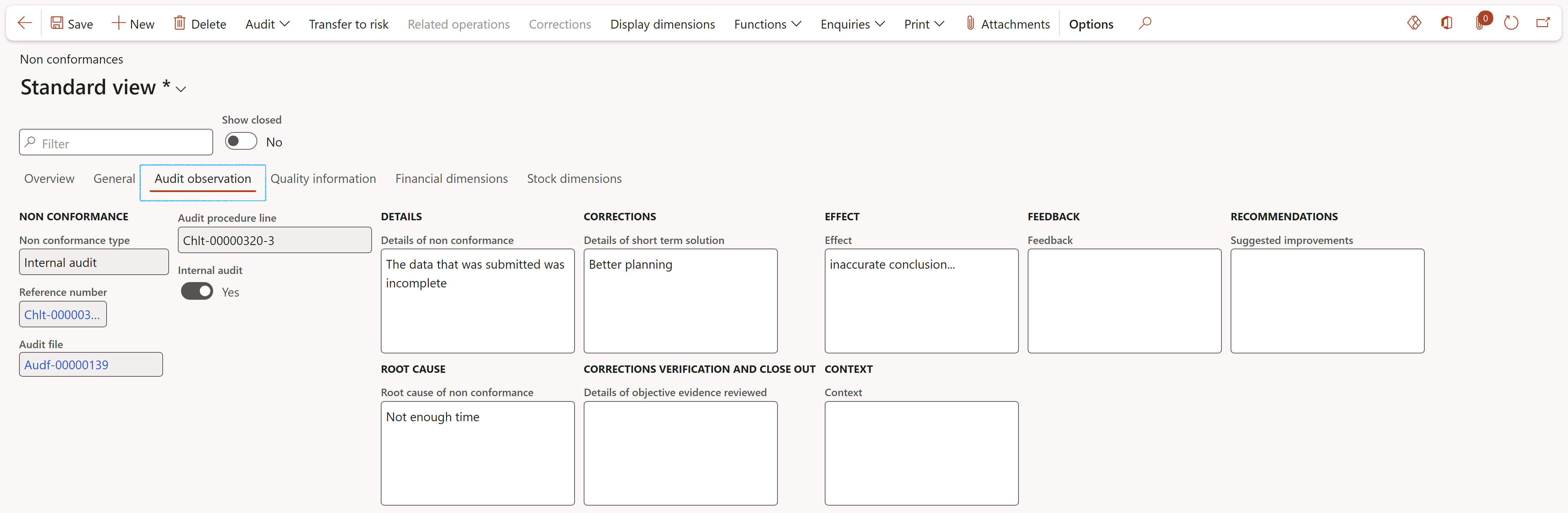
¶ Step 23.5: Quality assurance
A quality assurance and improvement plan should be designed to compare the audit activity’s conformance with applicable Audit standards and an evaluation of whether internal auditors apply the Code of Ethics. The plan also assesses the effectiveness of the audit activity and identifies opportunities for improvement.
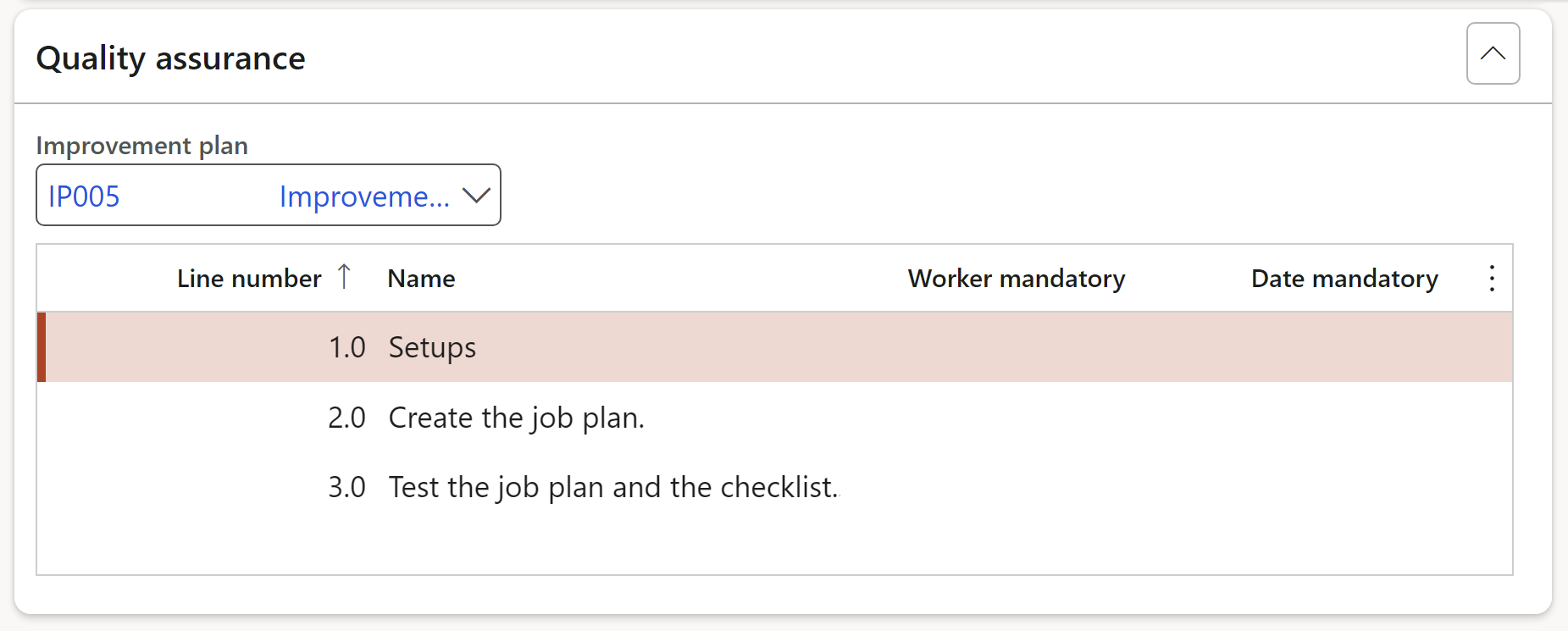
Future releases will see dedicated audit test (from the RCM above) extended into the field work form and test results posted to the audit files.
¶ Step 23.6: Posting fieldwork
Posting does three things:
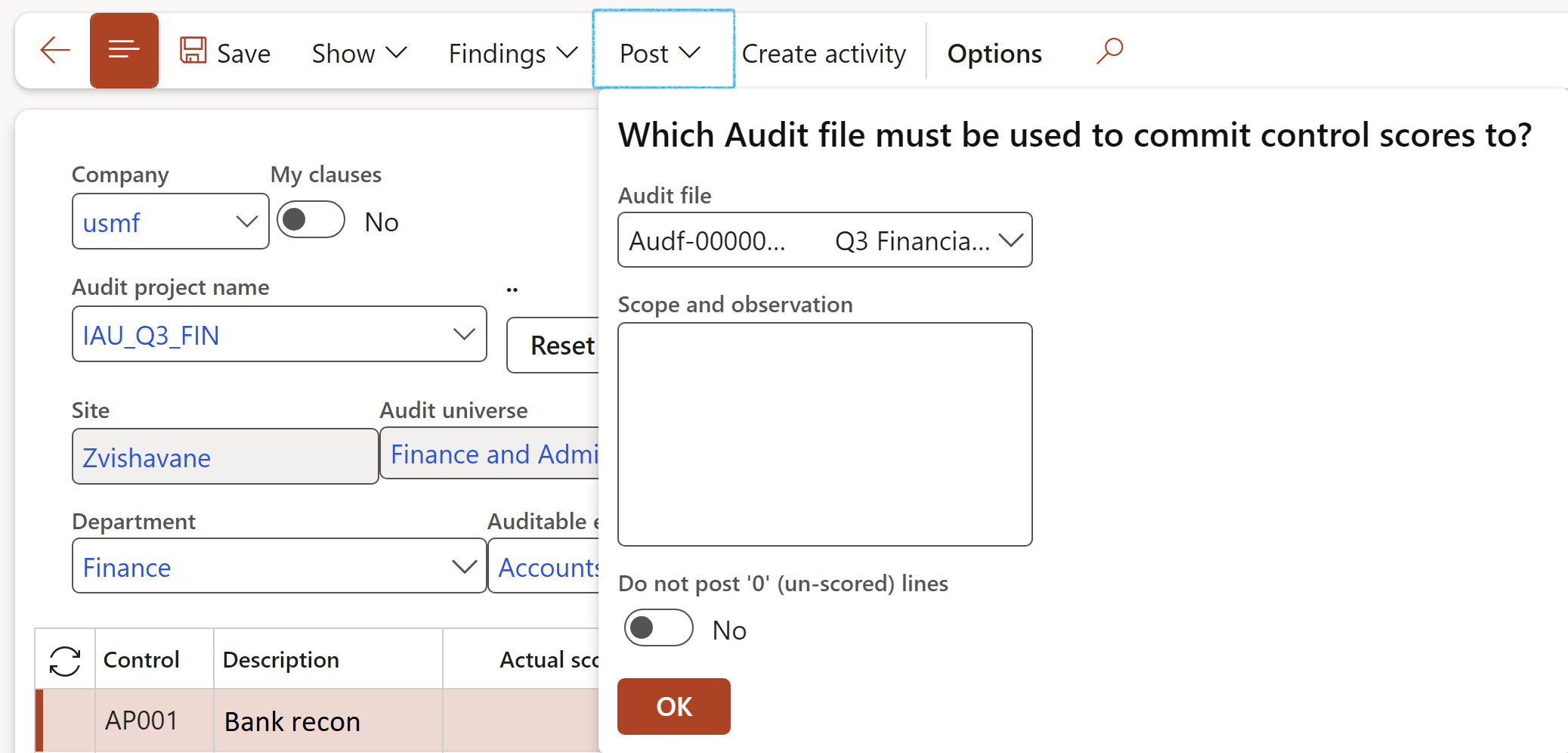
Fieldwork cannot be posted if an Auditable entity has not been selected.
¶ Step 24: Fieldwork results and completed scores
¶ Step 24.1: Audit working papers
Audit working papers are the documents which record all audit evidence obtained during internal auditing, information systems auditing, financial audits and investigations. Audit working papers are used to support the audit work done in order to provide assurance that the audit was performed in accordance with the relevant auditing standards.
Working papers are important because they:
To print the Internal audit population and sampling working paper:
Go to: GRC > Internal audits
¶ Step 25: Audit findings
Go to: GRC > Internal audits > Findings > Internal audit issue register
Go to: GRC > Internal audits > Findings > Non conformances
¶ Step 25.1: Generate follow up reviews
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Findings > Non conformances
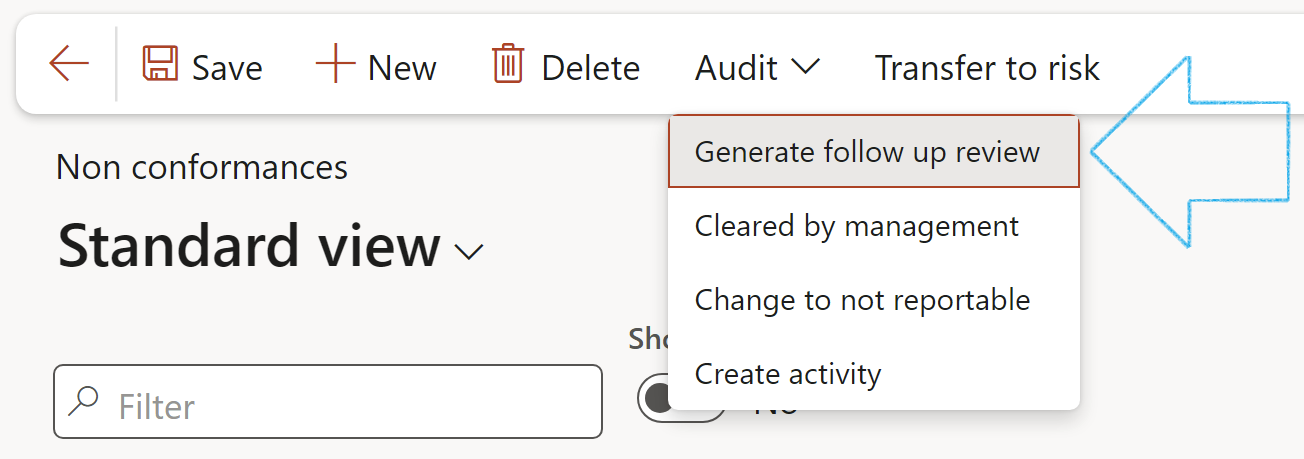
A blue line will appear confirming that a Planned action has been created for the follow up

Findings are created from two sources:
¶ Step 26: Audit report
The auditor's report is a document containing the auditor's opinion on whether a company's statements comply with complaince obligations (e.g. IFRS, GAAP) and are free from material misstatement.
The report can be printed by clicking on the Print icon
On the Audit report, under the Content Fast tab, open the References Index tab to see the lines created with Reportable findings
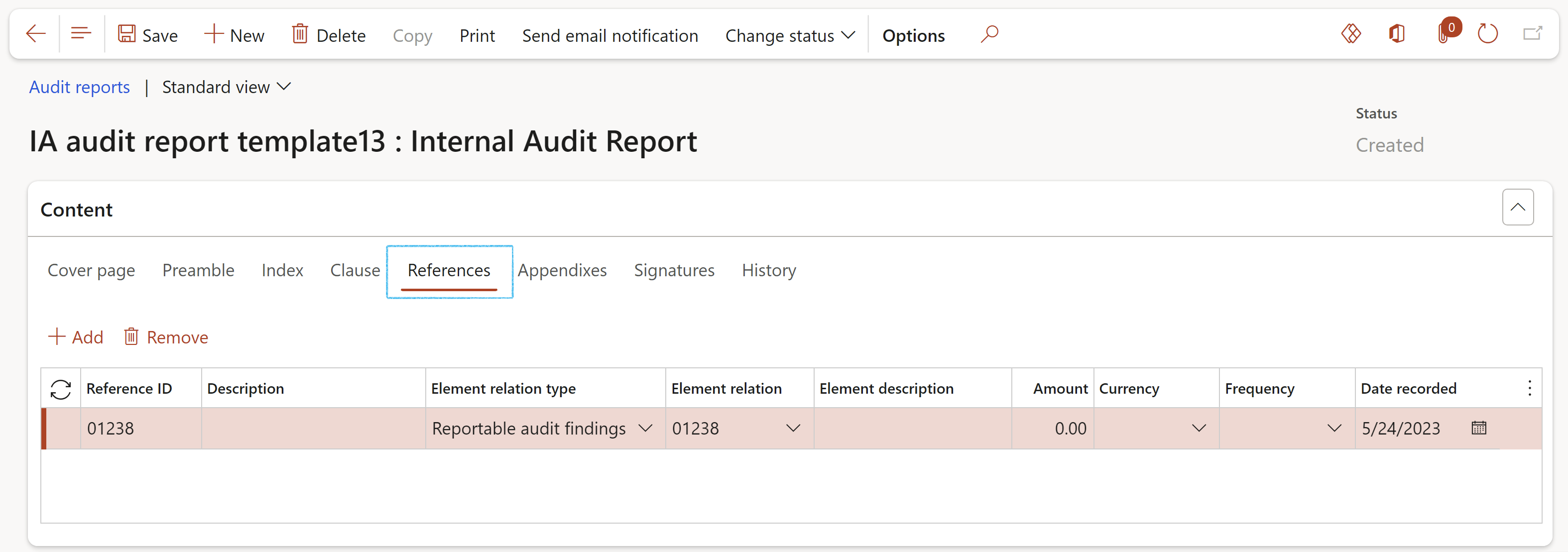
When the status of the Internal audit report is changed to Approved, the status of the referenced findings will also be changed to Approved
The Internal audit and linked Audit files, where the Audit report was generated from, will also be displayed under the References Index tab


¶ Step 27: Audit response
The auditor can select an audit response type from the dropdown list. The response is linked to a job plan (checklist) that can be used for detail step by step actions to be taken.
Another audit can be selected as cross reference.
¶ Step 28: Complete the audit
¶ Reporting
Internal audit reports provide a formal means of communicating to management the results arising from audits undertaken. Such reports should include audit findings, recommendations and conclusions relating to the adequacy of and compliance with the system of internal control and the efficiency, effectiveness, and economy of operations in the area covered by the audit. From a completeness point of view; management response to the audit findings should preferably also be included in the report.
Reports:
Inquiries:
¶ Step 29: Audit schedule report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Audit schedule report
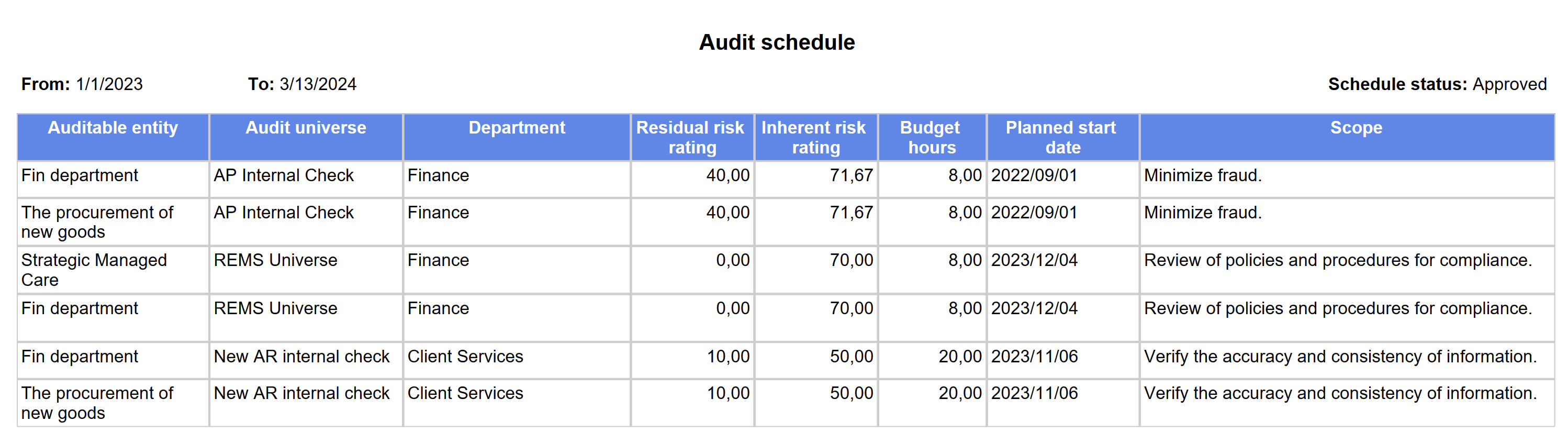
¶ Step 30: Risk control matrix report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Risk control matrix report
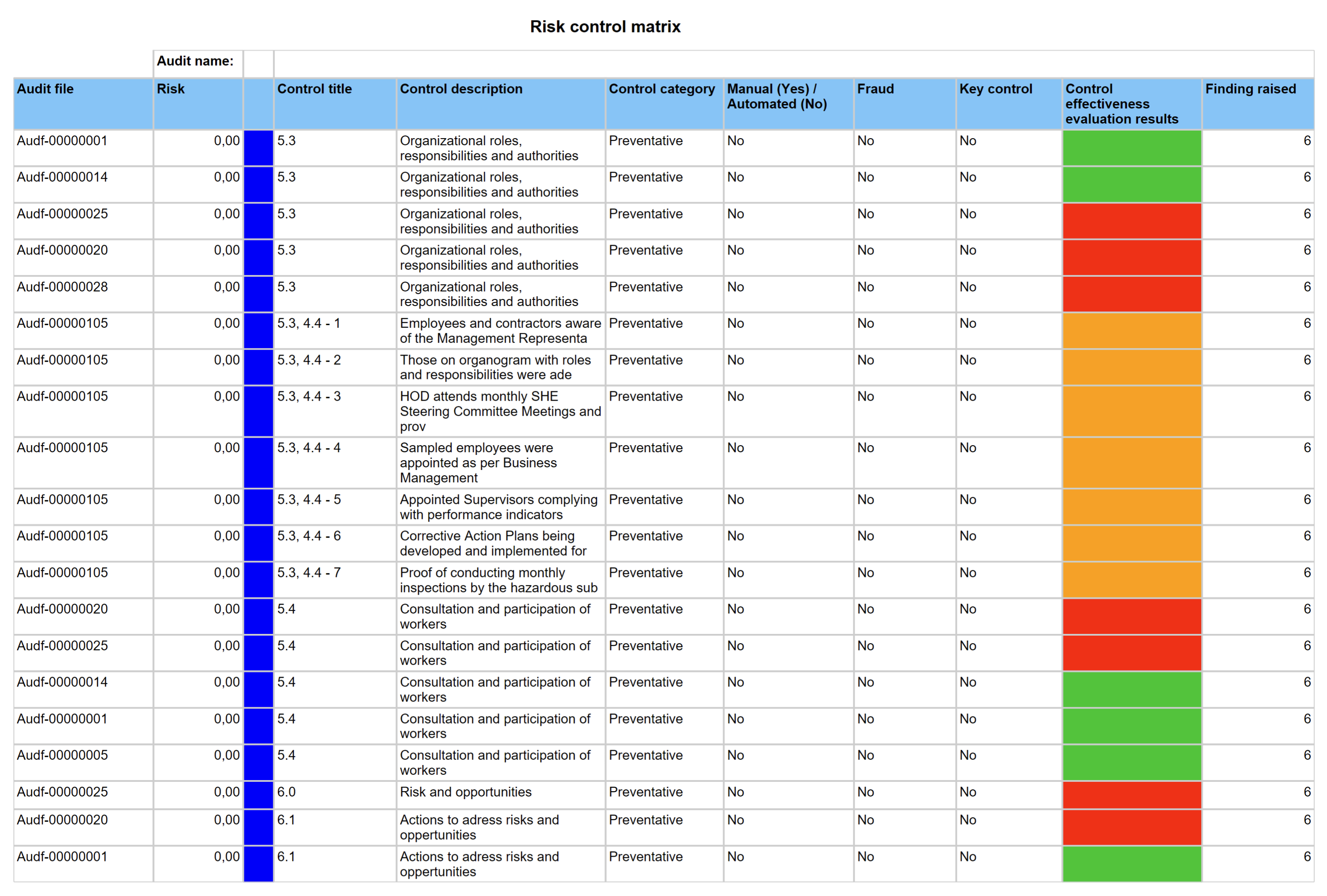
¶ Step 31: Risk assessments for internal audit
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Risk assessments for internal audit
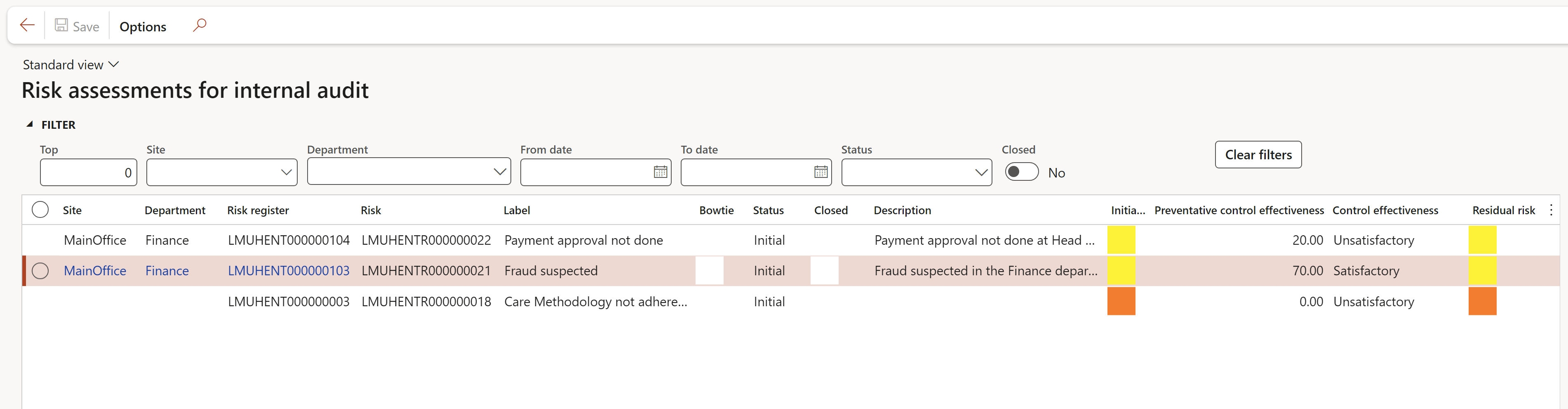
¶ Step 32: Detailed findings and action plans report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Detailed findings and action plans report

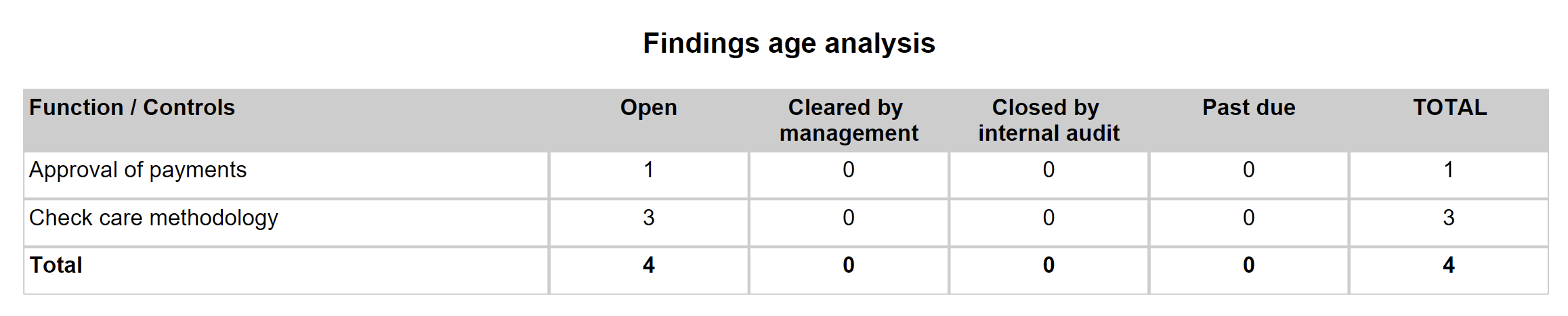
¶ Step 33: Findings age analysis report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Findings age analysis report
¶ Step 34: Executive committee report
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Executive committee report
GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Executive committee report
The Executive committee report dialog allows the user to print three reports (one at a time)
Select the parameters and then click OK
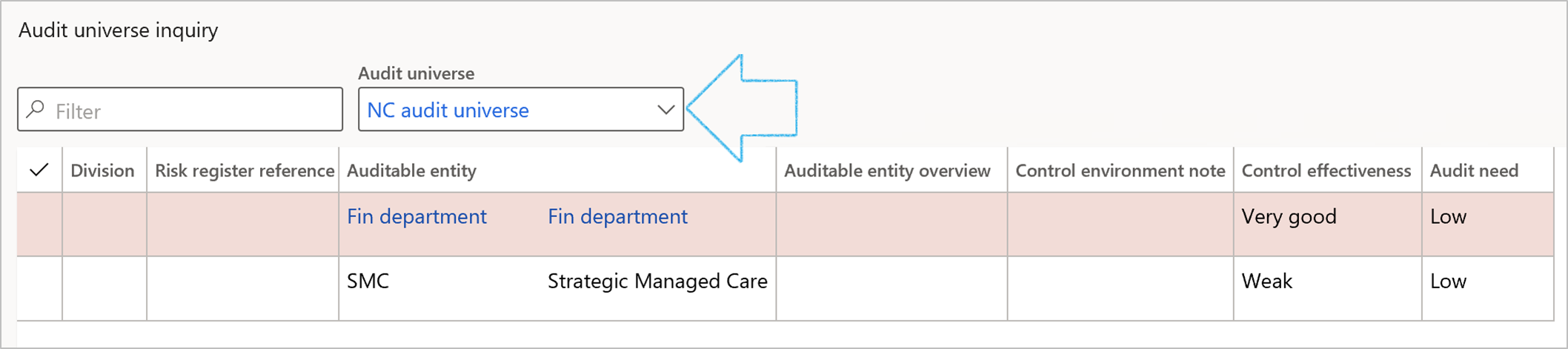
¶ Step 35: Audit universe inquiry
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Audit universe inquiry
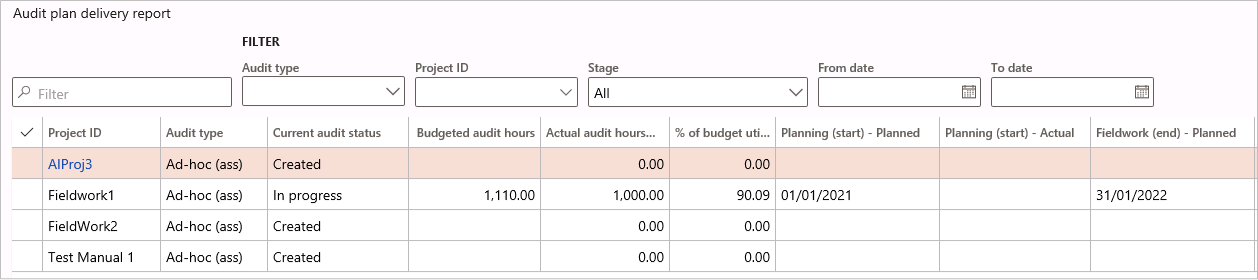
¶ Step 36: Audit plan delivery
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and Inquiries > Audit plan delivery
¶ Step 37: Audit findings
Go to: GRC > Internal audit > Reports and inquiries > Internal audit findings
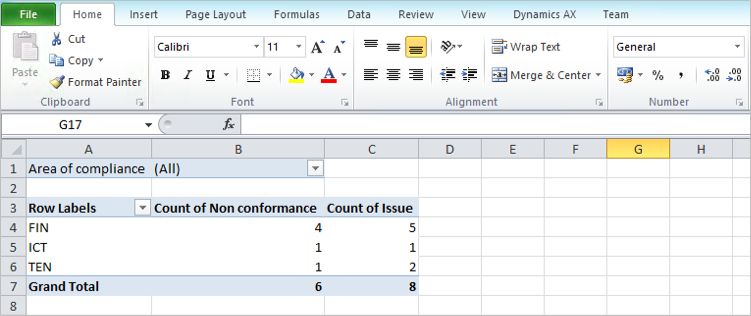
¶ Step 38: Internal Audit workspace
A dedicated workspace is given to Internal Audit. Future release will see more features being added.
¶ Step 39: Planned actions
Go to: GRC > All planned Governance, Risk and Compliance actions