
¶ Introduction
ISO 31000 (2009) / ISO Guide 73:2002 definition of risk is the 'effect of uncertainty on objectives'. Therefore, risk has the potential of gaining or losing something of value. There is normally an initial risk (inherent) before controls are applied. After application risk should reduce or remain to an acceptable risk (residual) value.
Risk can also be defined as the intentional interaction with uncertainty. Uncertainty is a potential, unpredictable, and uncontrollable outcome; risk is a consequence of action taken in spite of uncertainty.
In proper risk management, a prioritization process is followed whereby the risks with the greatest possible loss (or impact) and the greatest probability of occurring are handled first, and risks with lower probability and loss are dealt with later. In practice the process of assessing risk can be difficult as well as balancing of resources to mitigate between risks with a high probability of occurrence but lower loss versus a risk with high loss but lower probability of occurrence.
Risk management also faces difficulties in allocating resources. This is the idea of opportunity cost. Resources spent on risk management could have been spent on more profitable activities. Again, ideal risk management minimizes spending (or manpower or other resources) and also minimizes the negative effects of risks.
Intangible risk management identifies a new type of a risk that has a 100% probability of occurring but is ignored by the organization due to a lack of identification ability. For example, when deficient knowledge is applied to a situation, a knowledge risk materializes. Relationship risk appears when ineffective collaboration occurs, hence our approach to manage risk inside Dynamics 365 ERP.
¶ Navigation
¶ Specific setup
¶ Step 1: Mitigation effectiveness
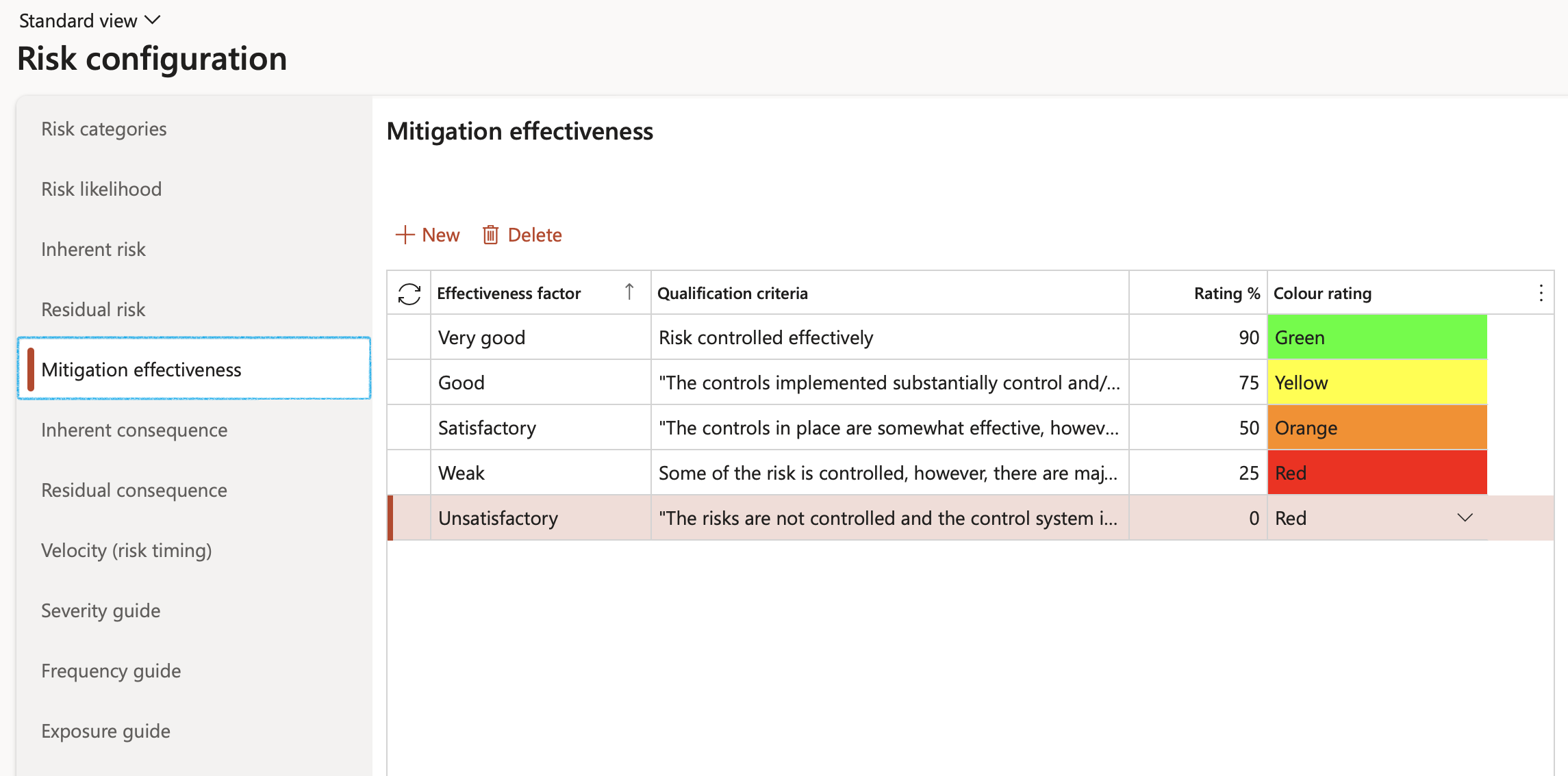
Mitigation is the action and effort entered into, with the objective to reduce loss of life and property by lessening the impact of risk. These actions and efforts must be assessed for effectiveness. At this point users must define effectiveness factors with a percentage rating.
Go to: GRC > Risk > Setup for risks > Risk configuration
- Click on the Mitigation effectiveness bullet
- Click New
- Select the Effectiveness factor from the dropdown list
- Enter a brief description of the Qualification criteria
- Enter the Rating percentage
- Click Save
¶ Daily use
¶ Step 2: Using the Risk worksheet (header)
Various Risks (Hazards) are created and identified in the Risk register. These risks needs to be maintained, mitigated and eventually closed.
The Risk worksheet is used for “quick” maintenance on and viewing of Risks (Hazards), and places focus on the responses to risks. Risk outcomes and Controls measures are defined and maintained in this form.
The Risk worksheet displays the various open Risks (Hazards) per Risk register in the top grid, with the related Additional information (Risk outcomes and Control measures) in the bottom grid. Additional Risk outcomes and Control measures can be added to each Risk line from using the bottom grid.
Go to: GRC > Risk > Worksheets > Operational risk worksheet
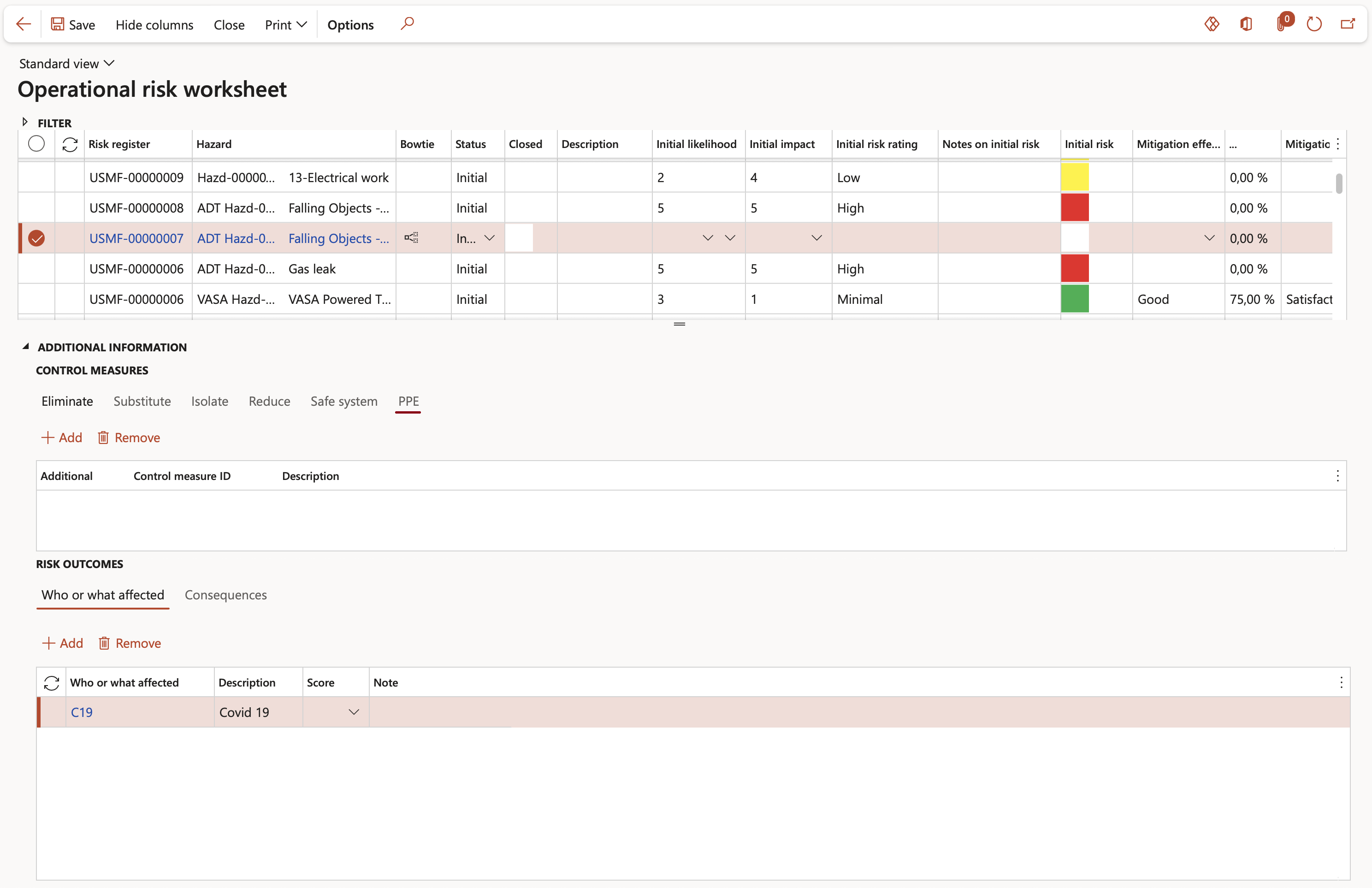
Please note the one-to-many link allowing one Risk (Hazard) to be mitigated via many Controls (Control measures)
¶ Step 2.1: Buttons on the Risk worksheet

- Hide columns – Is a toggle to control focussed form layout
- Close – Marks the Risk (Hazard) line (as well as all Controls measures) as closed. Risks which have been completed in full can be marked as closed.
After a risk (hazard) has been closed, the line will disappear from the Risk worksheet.
To view closed risks, select the Yes option under Closed in the filter area (see Step 2.2 below)
- Print – Print one of the following reports:
- Risk register
- Risk register detail
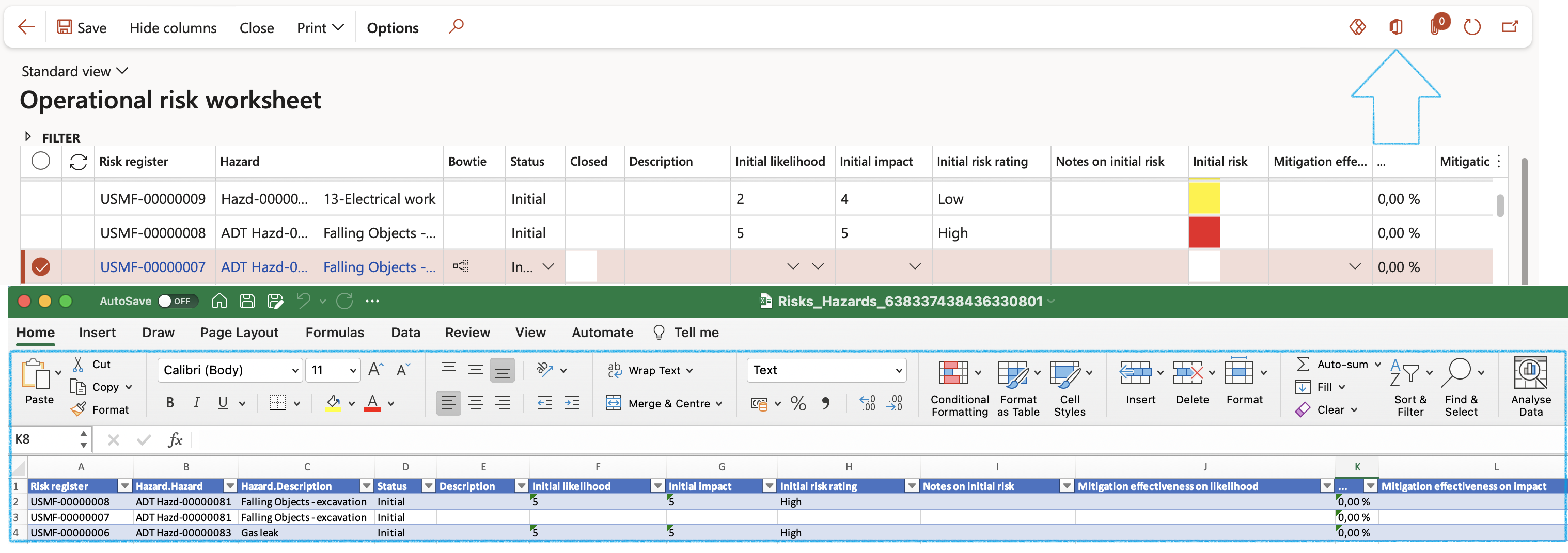
- Export to Excel – All the Risk register – Risk (Hazard) lines are exported to Excel, where data is available for further use
¶ Step 2.2: Filters on the Risk worksheet
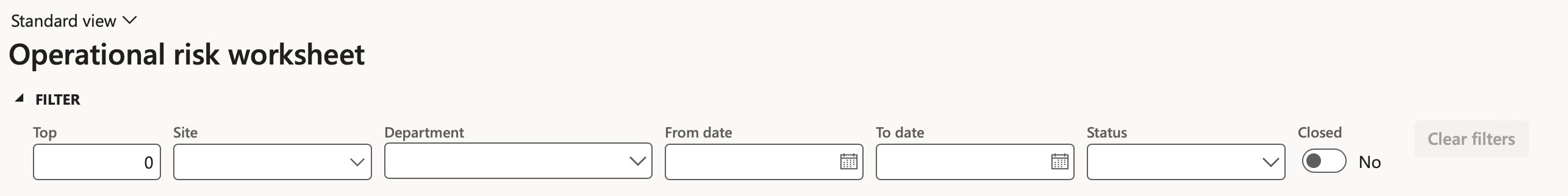
- Top – List the top X (1 to 10) lines of highest risk score. Zero/empty value will list all lines
- Site – Filter for risks as captured per Site
- Department – Filter for risks as captured per Department.
- From date and To date – search for risks in selected date period.
- Closed – The default view displays only the open risk entries. To view the closed entries, select the Yes option under Closed in the filter area.
- Status – Filter risk lines by status
- Clear filters – Removes all filters in on order to display only open risk entries
¶ Step 2.3: Display risk records
Risk information and values from the Risk register form are displayed in the top grid of the Risk worksheet.
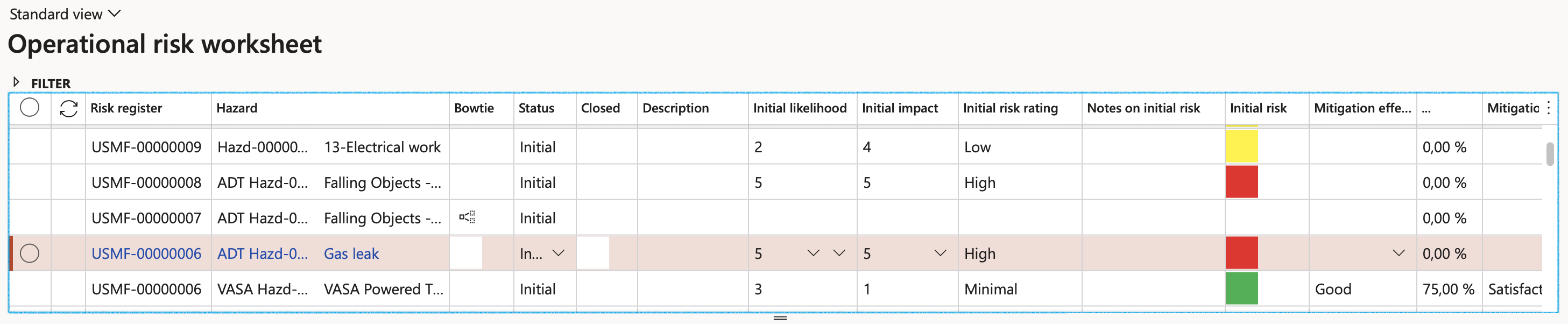
- Risk register – indicates the Risk register that groups together multiple risks (hazards)
- Hazard – Brief description of the risk (hazard)
- Description – Detailed description of the risk (hazard) as per hazard lines > General tab
- Initial likelihood, Initial impact and Initial risk rating – act as guides and display the colour under Initial risk column, just as per the register’s hazard lines, populated under the hazard lines > Initial risk tab.
- Mitigation effectiveness on likelihood and Mitigation effectiveness on impact – indicate the values selected on the register’s hazard lines, populated under the hazard lines > Control measures tab.
- Residual likelihood, Residual impact and Residual risk rating – act as guides and display the colour under Residual risk column, just as per the register’s hazard lines, populated under the hazard lines > Residual risk tab.
¶ Step 3: Using the Risk worksheet (lines)
The lower section of the Risk worksheet, Additional information:
These details are from the risk (hazard) lines inside the Risk register
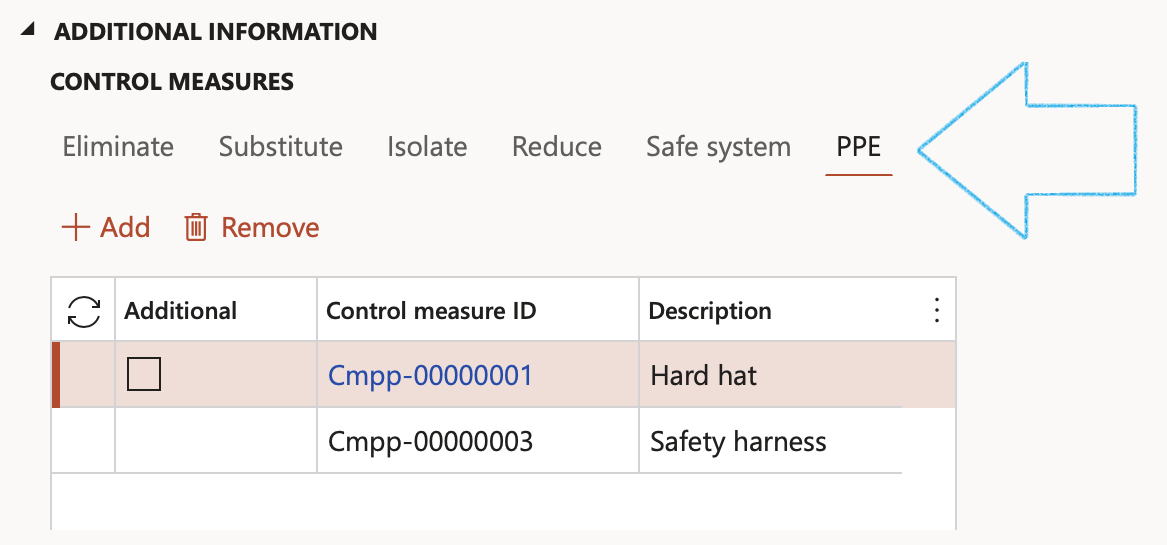
¶ Step 3.1: The Control measures
- There are six Index tabs: Eliminate, Substitute, Isolate, Reduce, Safe system and PPE
- Lines can be added or removed under each Index tab
¶ Step 3.1.1: Eliminate
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of elimination control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
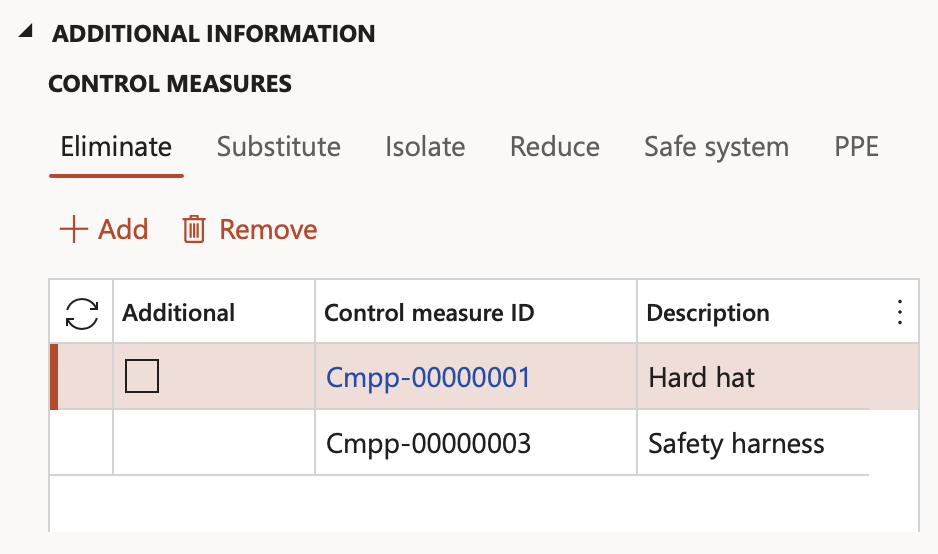
¶ Step 3.1.2: Substitute
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of substitution control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
¶ Step 3.1.3: Isolate
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of isolation control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
¶ Step 3.1.4: Reduce
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of reducing control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
¶ Step 3.1.5: Safe system
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of safe system control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
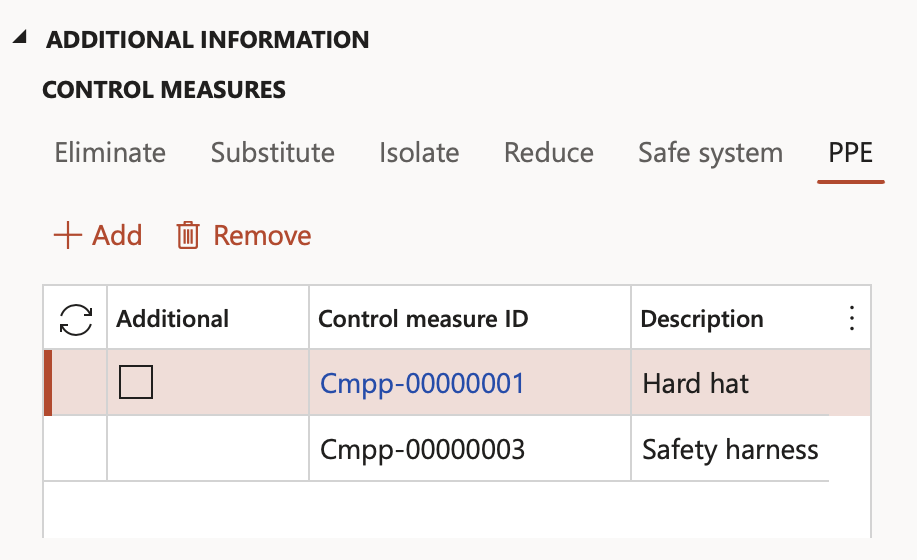
¶ Step 3.1.6: PPE
- The Control type field is a dropdown, selecting the type of PPE control required.
- The Control measure ID is a unique system generated number assigned to the selected Control type selection made per line.
- Specify the Description of each control type selected as per the previous point.
- The Item number field is a dropdown, selecting a PPE item from the list of items maintained in D365.
¶ Step 3.2: The Risk outcomes
- There are two Index tabs Who or what affected and Consequences
- Lines can be added or removed under each Index tab
These details are from the risk (hazard) lines inside the Risk register
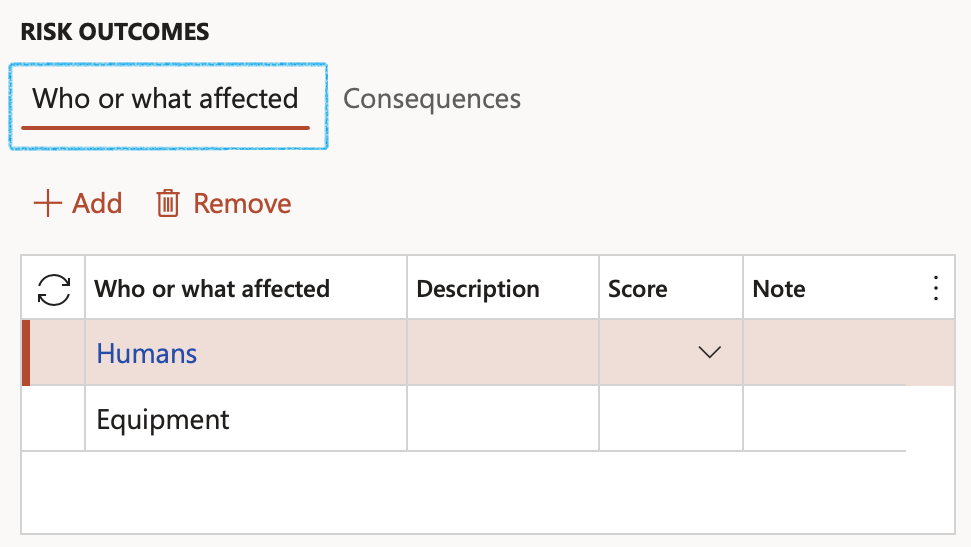
¶ Step 3.2.1: Who or what affected
- The Who or what affected field is a dropdown, selecting the type of entity which is affected.
- Specify the Description of the affected entity.
- Specify a Note for the affected entity.
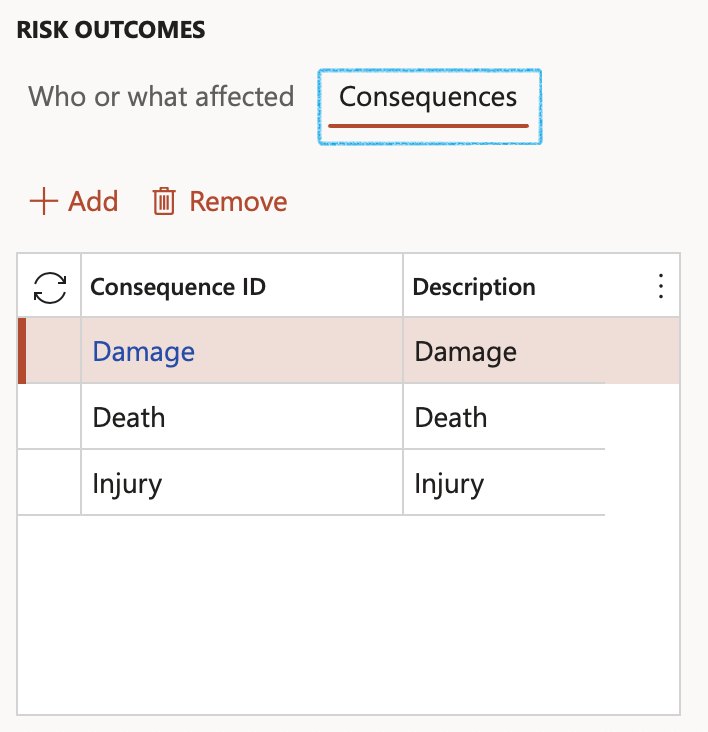
¶ Step 3.2.2: Consequences
- The Consequence ID field is a dropdown, selecting the type of consequence which is affected.
- Specify the Description of the consequence selected in the previous point.
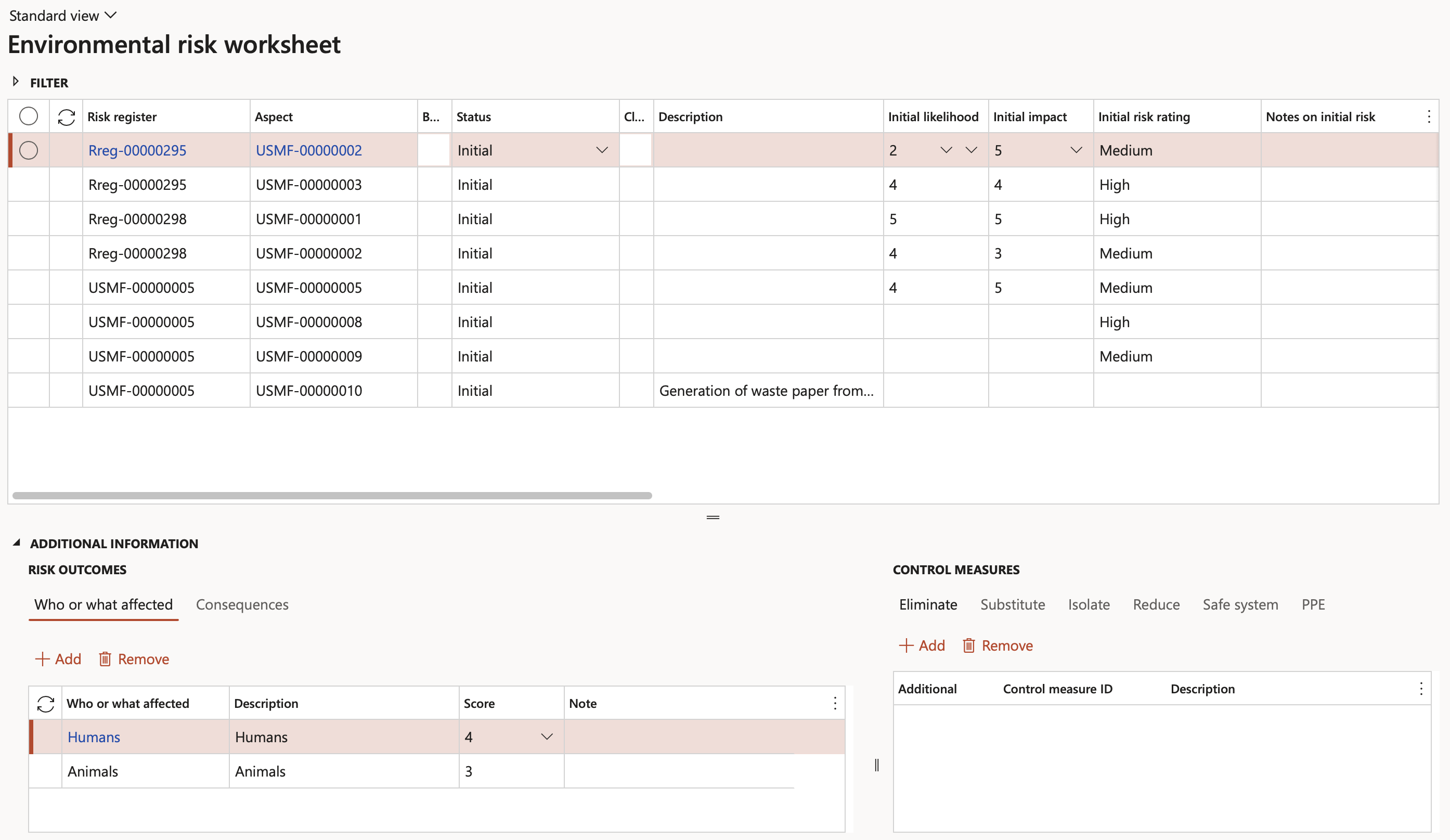
¶ Step 4: View Environmental risk worksheet
All of the above is applicable to the Environmental risk worksheet, except for the Hazard column which is replaced with Aspects (ISO 14001)
¶ Reports
¶ Step 5: Printing reports
Go to: GRC > Risk > Reports and Inquiries > Risk hazard lines graph
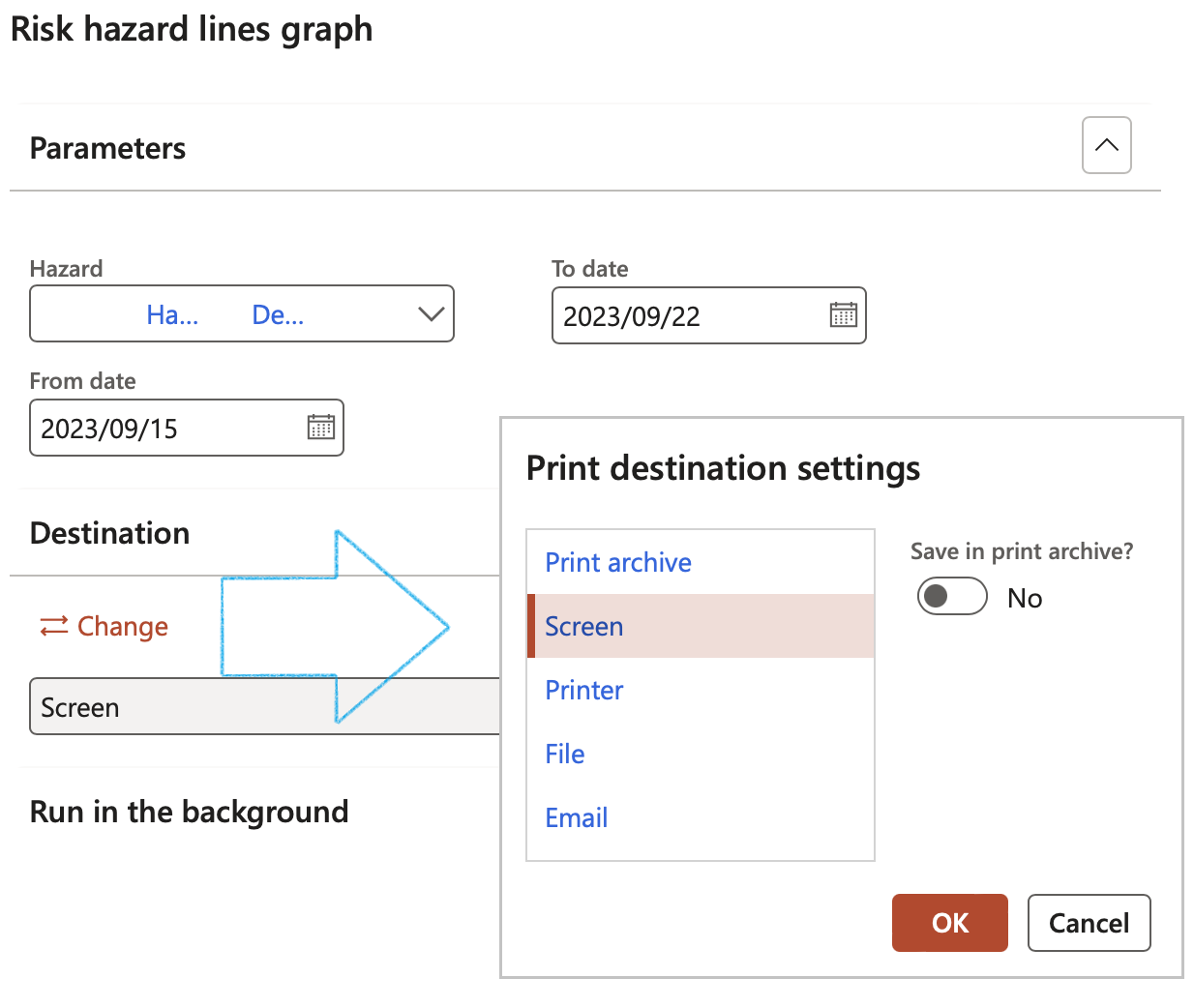
Printing any report in Dynamics 365 will display a dialogue where the parameters and filters are selected.
The Parameters:
- Make use of the dropdown options to select values, or enter Date selections. The more parameter values entered, the finer the ‘search’ becomes with more pin-pointed data printed on the reports.
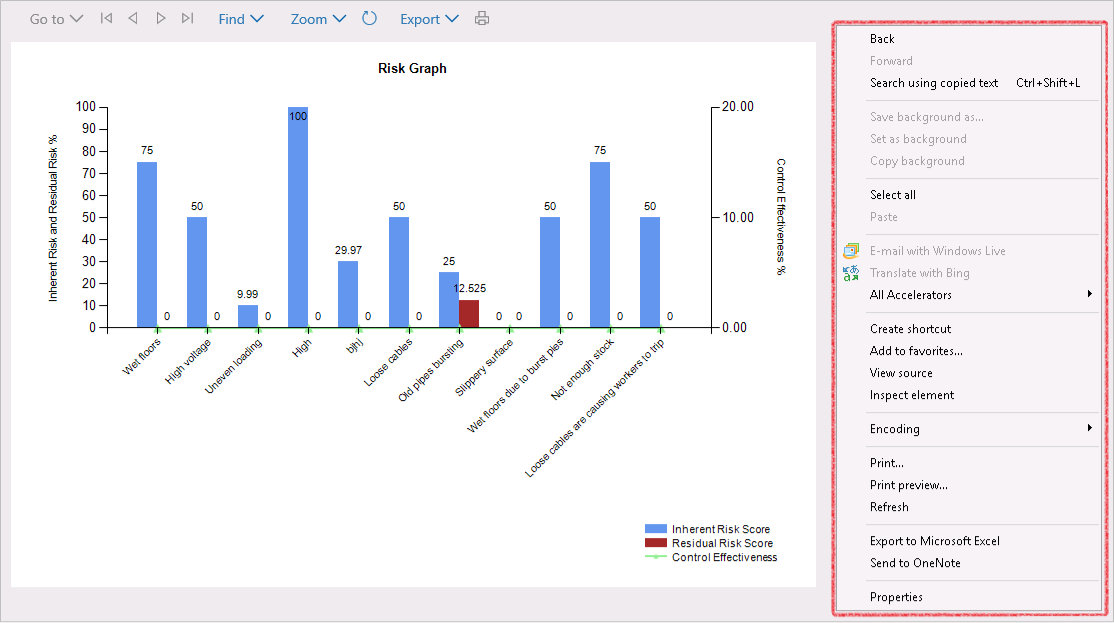
¶ Step 6: Risk hazard analysis
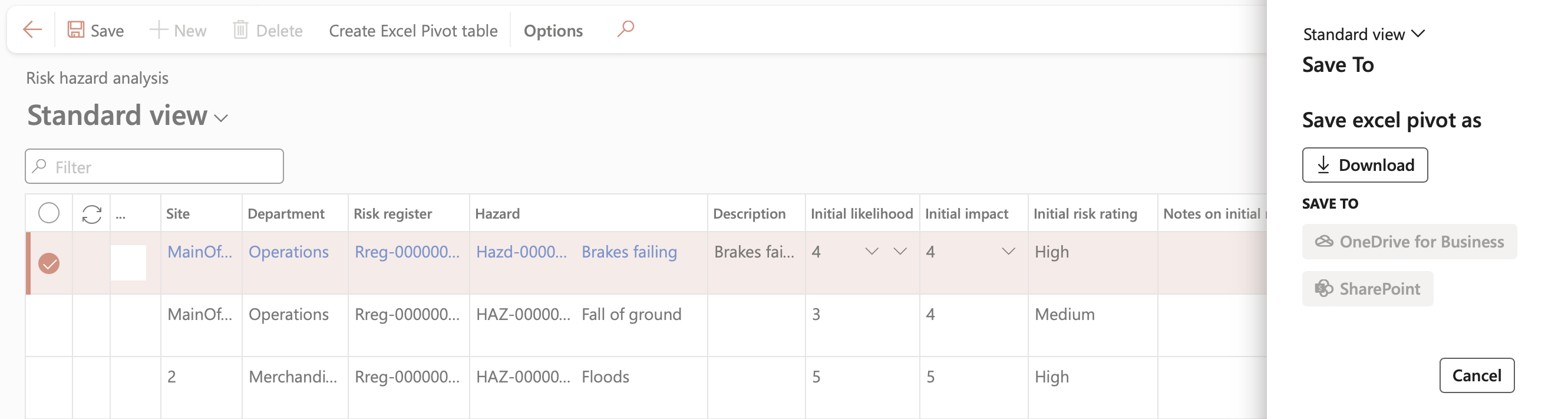
¶ Step 6.1: Create a Pivot table with the graphs you want inside Excel
Go to: GRC > Risk > Reports and Inquiries > Risk hazard analysis
- Select the relevant risk
- On the Action pane, click on the Create Excel Pivot table button
- The Save to dialog will open up where the user can select one of the following options:
- Save excel pivot as…
- Save to…
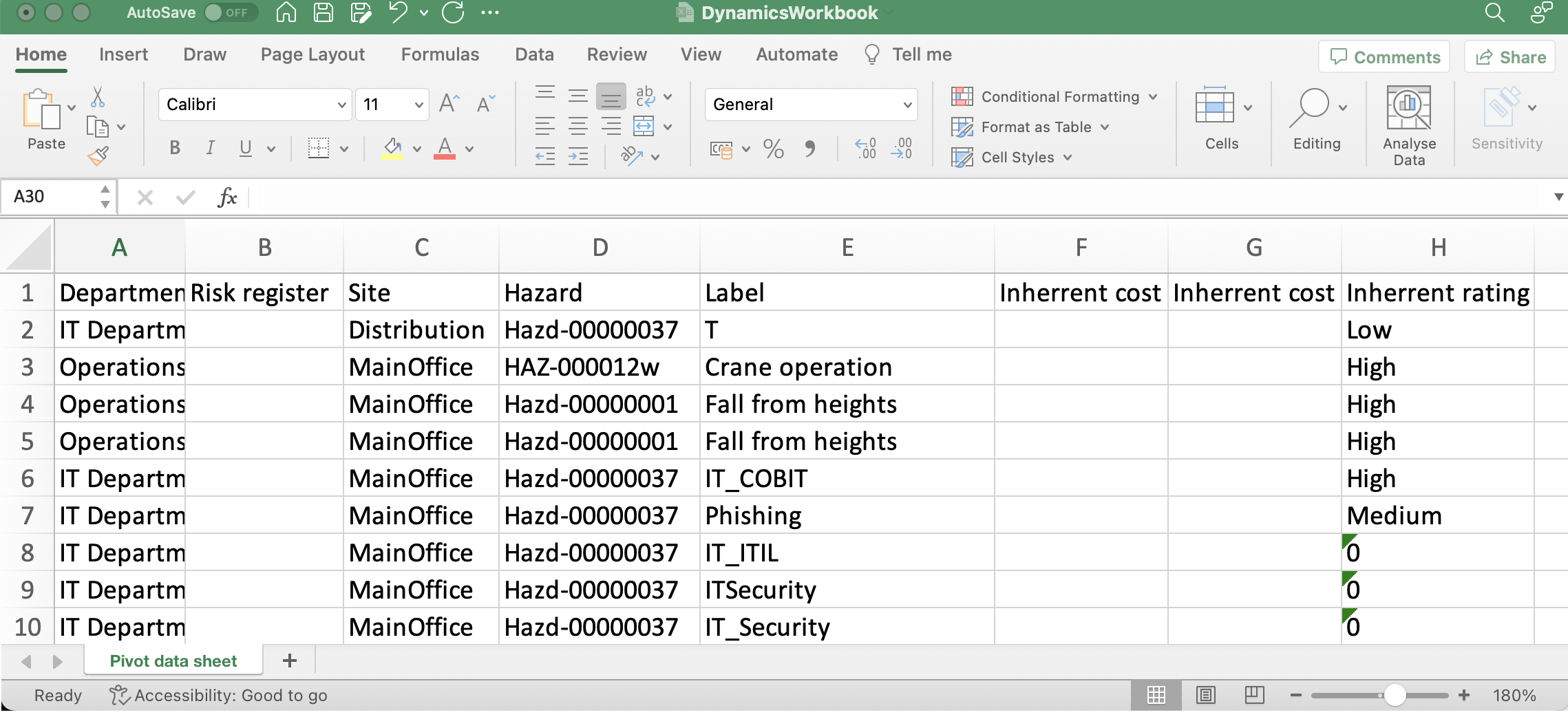
From the Excel spreadsheet generated in Dynamics 365, the user can copy the relevant data to create a pivot table template
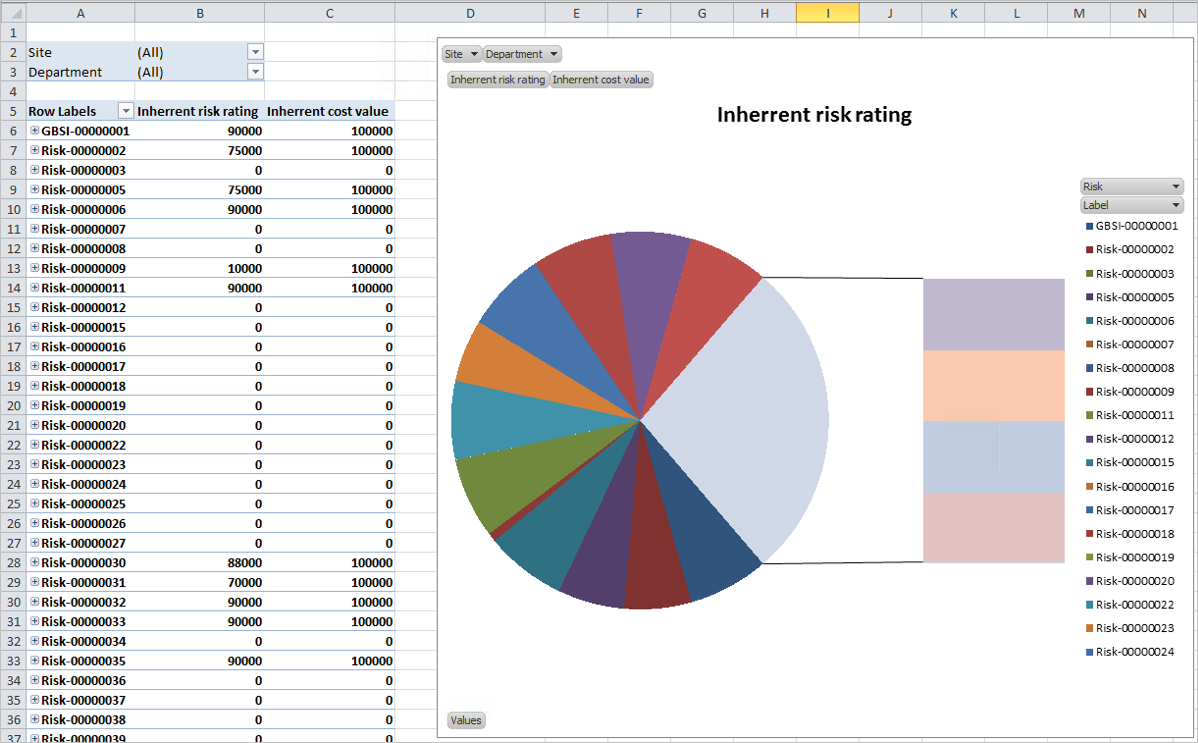
¶ Reference table
Definitions
| Hazard: | Any source or situation with a potential for harm in terms of injury/illness, damage to property/plant/equipment, or damage to the environment. |
| Risk: | A risk is the likelihood that exposure to a hazard will result in injury or disease. |
| Risk Assessment: |
The process of analyzing all of the risks associated with hazards and evaluating them to determine steps for risk control and priorities. Risk Assessment considers two (2) main factors:-
|
|
Risk Score: |
The risk score is the number allocated following risk assessment, which describes the level of risk, ranging from H (very high risk) to L (very low risk). The risk score is also used to identify the priority and timeframe of response to the identified hazard. |
| Risk Control: |
Risk Control is a method of managing the risk, which involves taking actions to eliminate &/or reduce the likelihood that exposure to a hazard will result in injury/disease. There is a hierarchy of control measures to be followed with the primary emphasis on controlling the hazards at source. Methods of Risk control in preferred priority order are:
|