
¶ Introduction
Definitions
A Performance scorecard is a graphical representation of the progress over time of some entity (such as an enterprise, an employee or a business unit) toward some specified goal or goals. Performance scorecards are widely used in many industries throughout both the public and private sectors.
Key Performance Areas (KPAs) are the areas (maybe a business unit or department or pockets inside these) within the enterprise, for which an individual or group is logically responsible.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are used for each Key Performance Area (KPA) to determine where the organization ranks.
The above can also be referred to as goals with specific measurements.
Detail
Corporate performance management (CPM), also referred to as business performance management (or enterprise performance management), is an “umbrella term” used to describe the methodologies that help an enterprise manage the success of an organization. You can think of corporate performance as the collaborative accomplishments, successes, and failures of an organization.
It includes tools that help with identification of Strategy, Planning, increase of shareholders value, and improvement to business performance, insights into past performance and more.
Traditionally CPM tools live outside of ERP and require “plumbers” to connect the flow of data from ERP systems to the CPM platform.
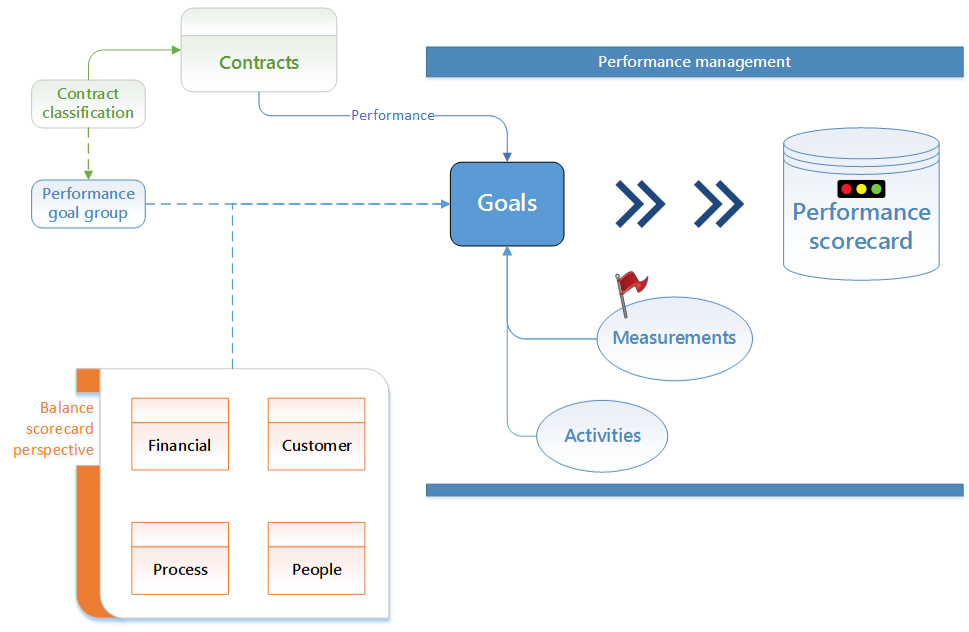
Axnosis developed Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC 365) inside Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations. It includes a sub module that deals with Corporate Performance Management (CPM). It includes a Performance scorecard. It is based amongst others on goals and measurements inside of D365 as well as balance scorecard principles.
¶ Navigation

¶ Specific setups
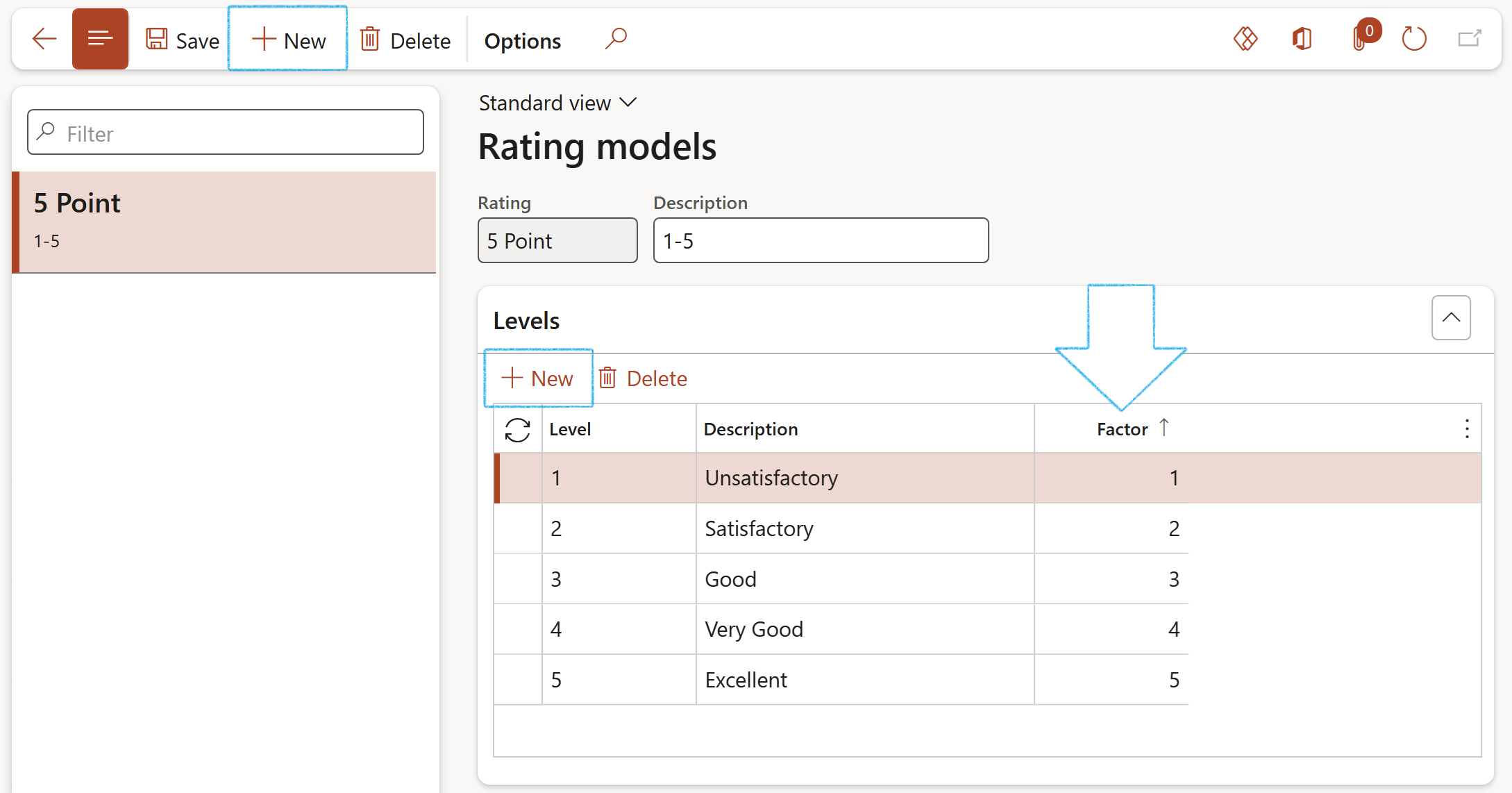
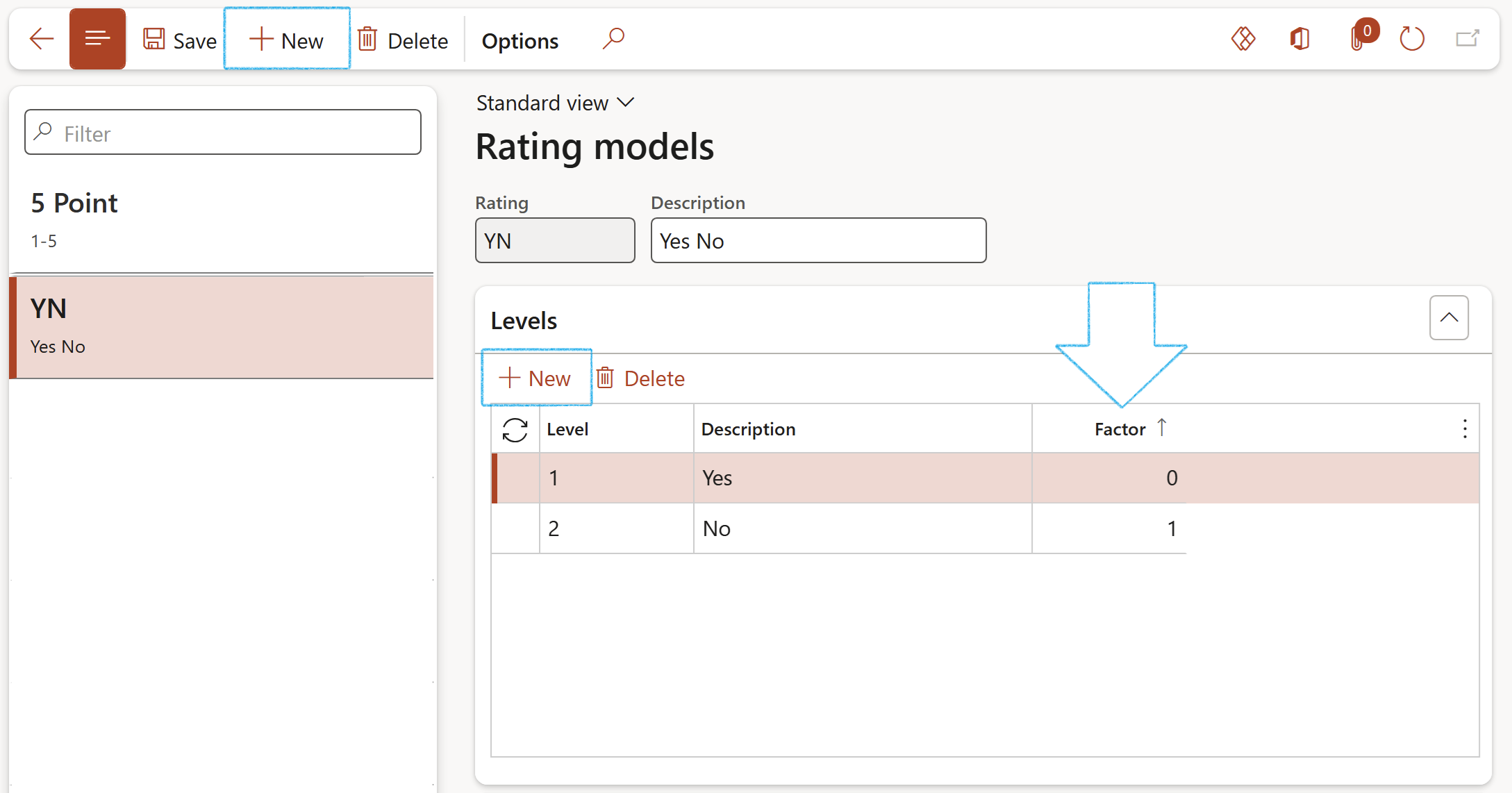
¶ Step 1: Rating models
Rating models help evaluate a person's actual level of skill, the level they should work to achieve, or the level of skill required for a job. Each level in a rating model is assigned a factor.
Rating models with levels such as 1 to 5 can be set up, as well as a simple Yes/No rating model
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Rating models
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a name for the Rating model
- Enter a brief Description for the Rating model
- Expand the Levels Fast tab and click on the New button
- Enter the Level number
- Enter a Description for the level
- Enter the Factor for the rating level. When you compare items with a different number of rating levels, the factor is used to normalise scores. The factor must be a number between 0 and 9, or it can be Yes/No.
See two examples below
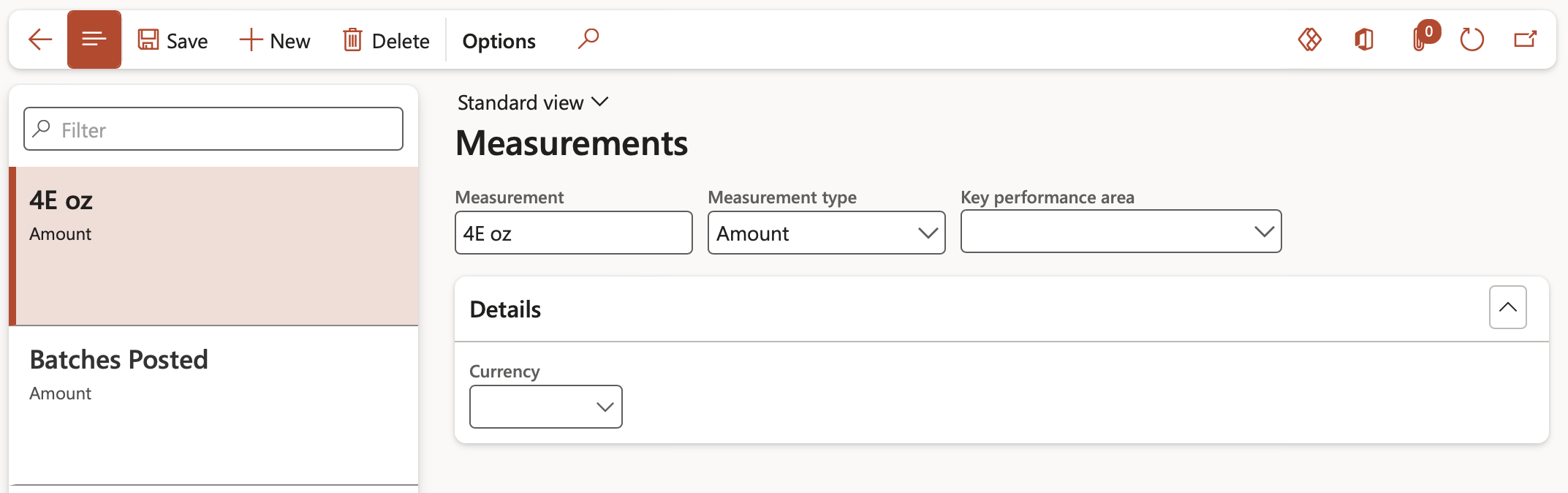
¶ Step 2: Measurements
The Measurements page in GRC lets you create standard measurements that will be used on the performance goals and reviews pages. You can create measurements that are dates, amounts, quantities or percentages, or measurements that are based on a rating model.
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Measurements
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a name/brief description for the Measurement
- Select the relevant Measurement type from the dropdown list
- Expand the Details Fast tab and select the relevant Rating from the dropdown list
- Enter a Long description for the Measurement
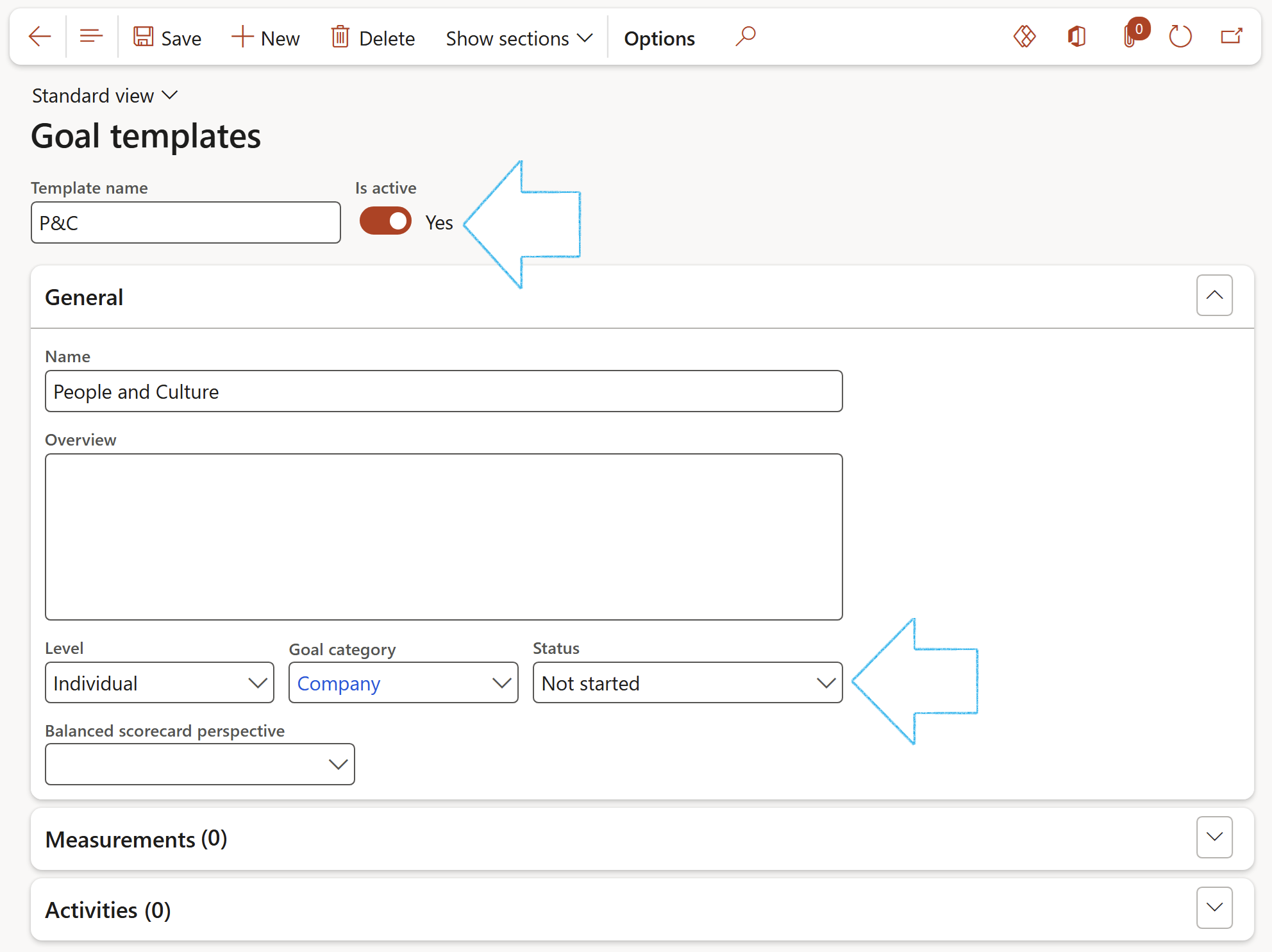
¶ Step 3: Goal templates
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Goal templates
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a Template name
- Move the Is active slider to Yes
- If the measurements are to be scored with Yes/No, then move the Is yes/no type slider to Yes
- Expand the General Fast tab
- Select the relevant Level from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Goal category from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Status from the dropdown list. When just created, it should be Not started
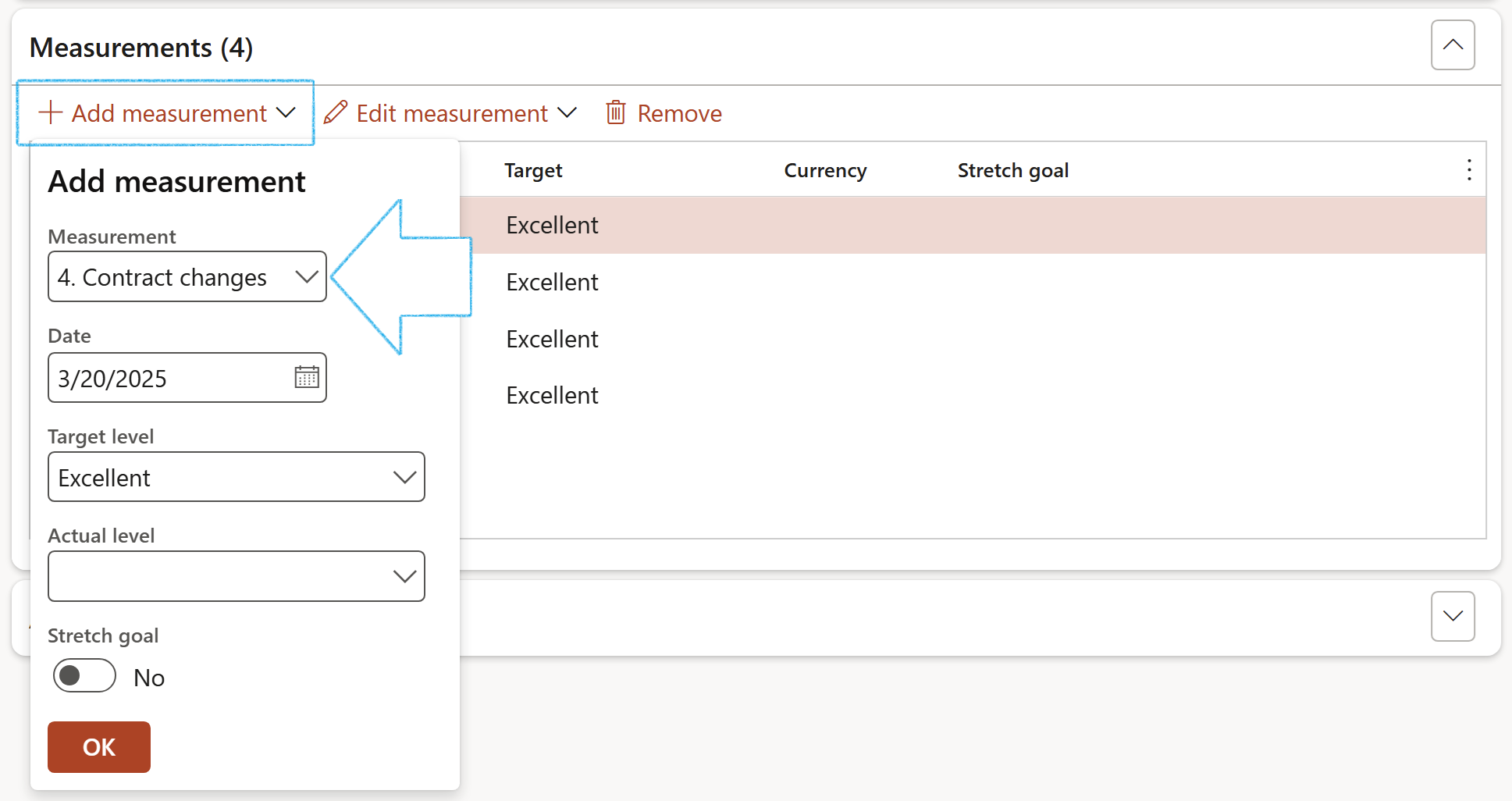
- Expand the Measurements Fast tab
- In the Button strip, click on the Add measurement button
- On the Add measurement dialog, enter the Number of the measurement (This is the order in which the Measurement should be printed under the Goal template, on the report)
- select the relevant Measurement from the dropdown list
- Enter a Date
- Select the relevant Target level from the dropdown list
- Click on the OK button
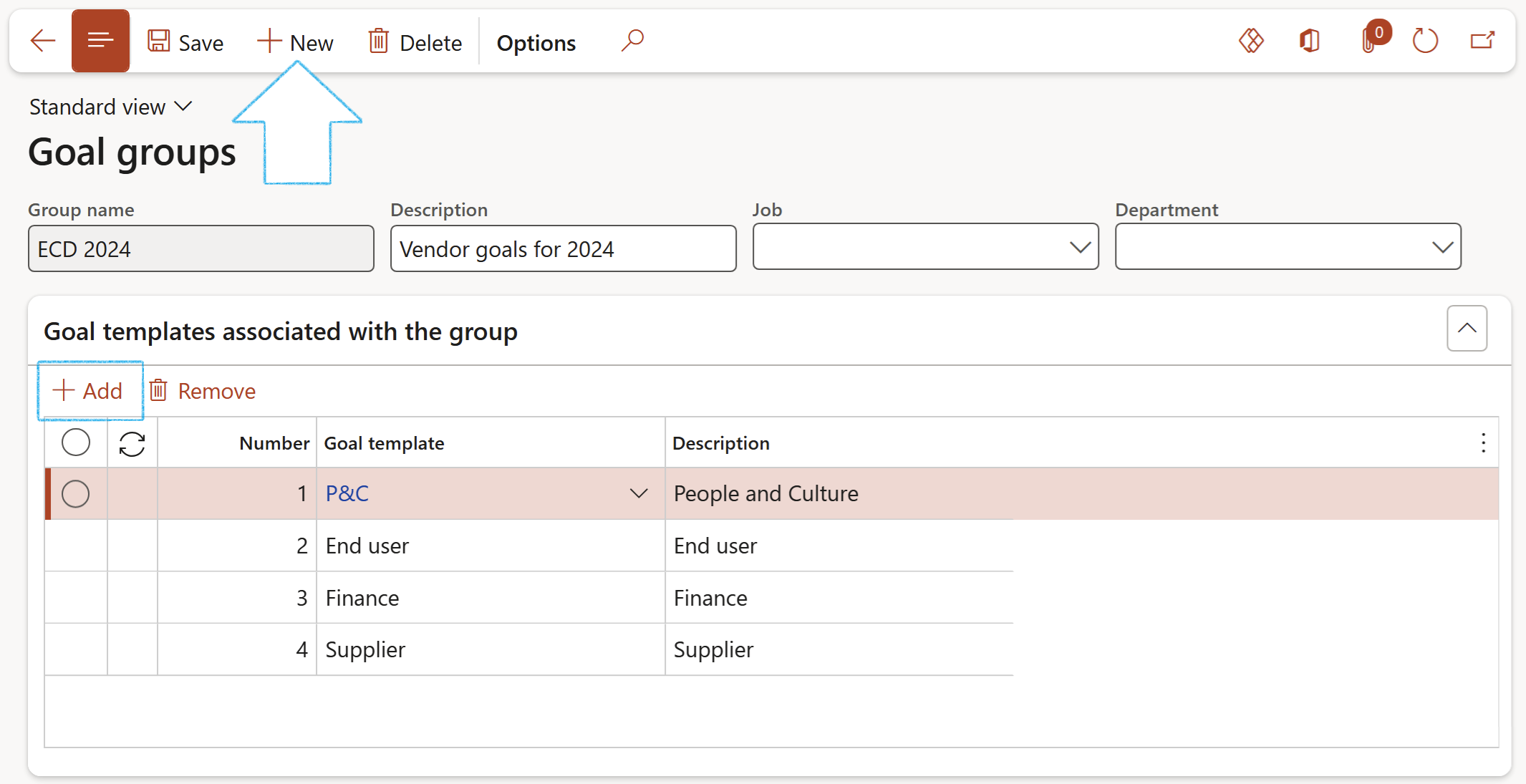
¶ Step 4: Goal groups
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Goal groups
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a Group name
- Enter a Description for the group
- Under the Goal templates associated with the group Fast tab, click on the Add button
- In the Number field, enter the number for the Goal template. (This is the order in which the Goal template should be printed under the Goal group, on the report)
- Select the Goal template that you want to add to the group, from the dropdown list
¶ Step 5: Goal categories
Use goal categories to categorize goals. For example, if you set quarterly goals, the goal heading for a goal might be the quarter in which the trading partner (Suppliers and customers) is to achieve the goal.
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Goal category
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a name for the new Goal category
- Enter a brief Description for the new Goal category
- In the Active field, select the option to allow employees and managers to assign goals to the heading
- Click Save
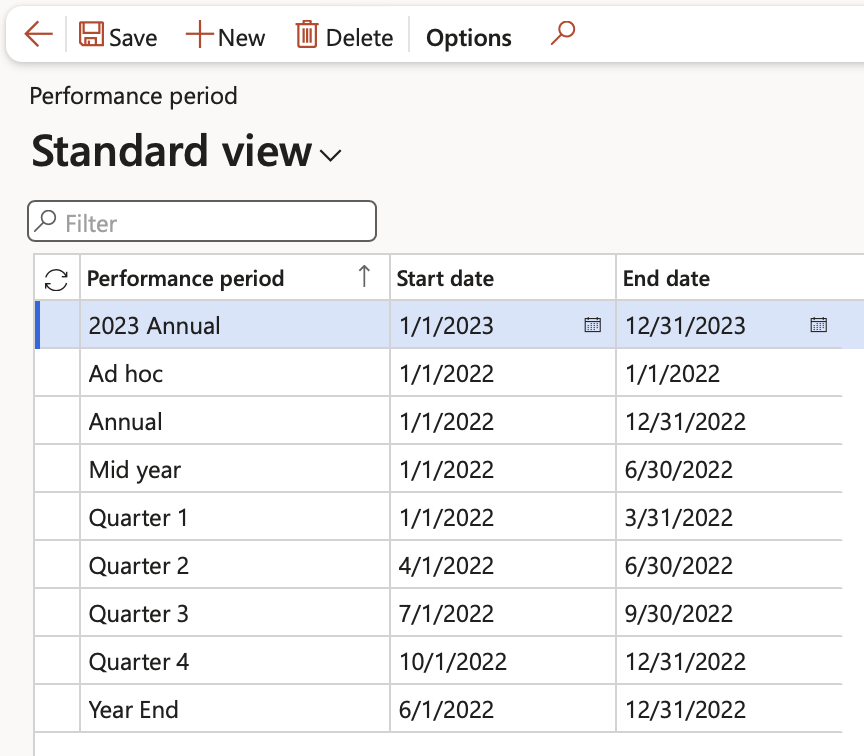
¶ Step 6: Performance periods
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Performance period
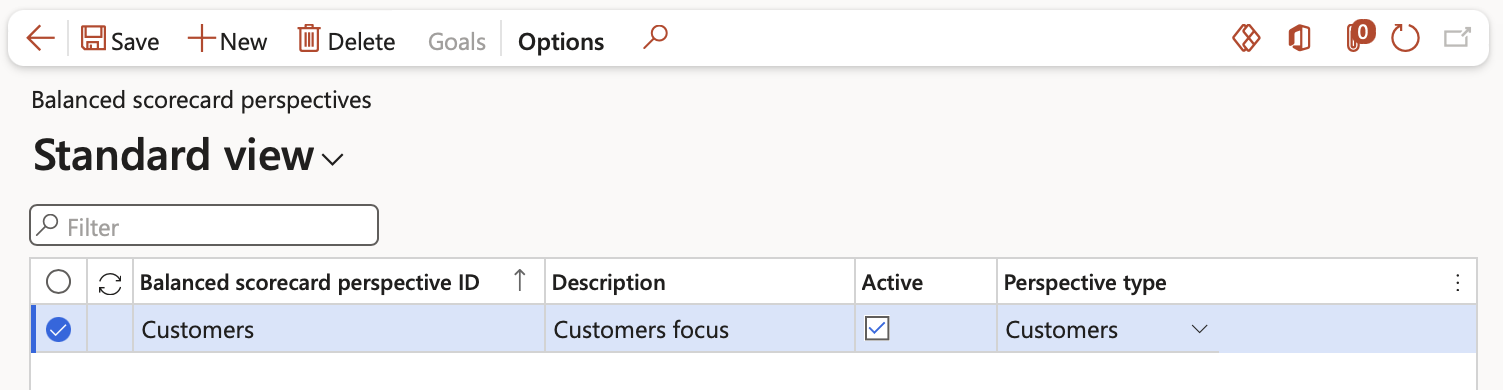
¶ Step 7: Balance scorecard perspective
Go to: GRC > Performance > Balanced scorecard > Balanced scorecard perspectives
- Click New
- Complete the following:
- Balanced scorecard perspective ID - Enter a unique identification
- Description – Enter a relevant description
- Active – Tick if this record will be used
- Perspective type – Select one of the four values from the dropdown list
¶ Step 8: Key performance area (KPA)
Go to: GRC > Performance > Balanced scorecard > Key performance areas
- Click New and complete the following:
- Key performance area - Create a unique name & Description
- Link this KPA to the above created Balanced scorecard perspective by selecting the relevant Balance scorecard perspective from the dropdown list
- Expected weight % – Normally KPA’s roll up into a Perspective. This indicates the weight relative to other KPA’s in the group

¶ Step 9: Create Key performance indicators list
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Key performance indicators list
- Click on the New button in the Action pane
- Under the Key performance indicators list section:
- Select the relevant Key performance area from the dropdown list
- Enter the KPI name
- Enter a brief Description
- Select which of the following should be displayed on the Performance scorecard workspace under the Key performance indicators Index tab
- Actual vs Budget
- Actual only
- Budget only
- Select the relevant KPI element 1 from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Operator from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant KPI element 2 from the dropdown list
- Enter the Constant value
If the selected KPI list element should be published on the Performance scorecard workspace under the Key performance indicators Index tab, tick the Publish tick box.
The following is done for each line under the Key performance indicators list section:
- Under the KPI list elements section, click on the Add button
- Select the relevant Element grouping from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant KPI element from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Element lookup from the dropdown list
- Indicate whether this KPI list element should be Excluded from the KPI calculations
- Choose the relevant Sign for adding or subtracting amounts when calculating KPI totals
- Select the relevant Balance type for the KPI element
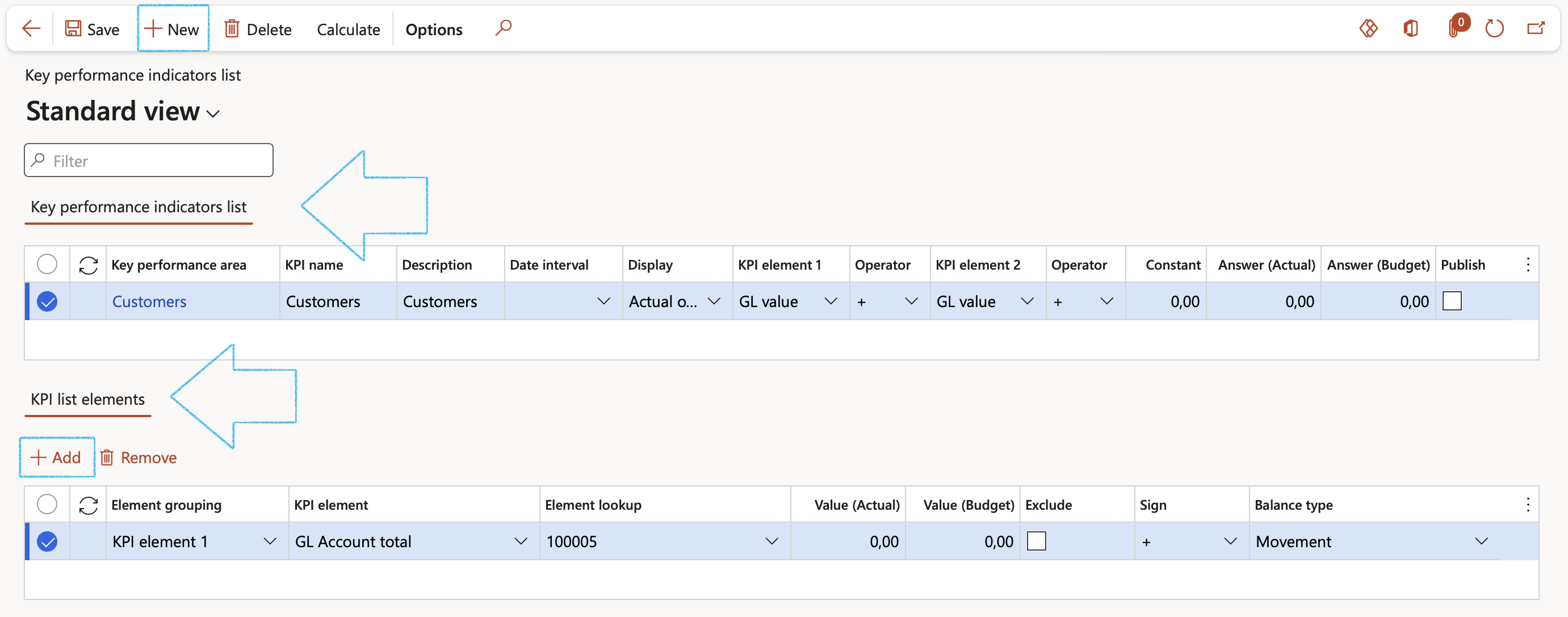
Click on the Open performance scorecard button in the Action pane to open the Performance scorecard workspace
To update the Answer (actual) column for the selected Key performance indicator line:
- Click on the Filter button in the Action pane
- On the Filters dialog, select the Date interval that you want to get the answer for
- Click on the OK button
- In the Action pane, click on the Calculate button
The Answer (actual) column will be updated
In the example in the screenshot below:
- The total of GL account 132999 (of the previous year (PY)): 199,235,628.63
- divided by the total of GL account 222999 (of the previous year (PY)): -200,636,516.28
- equals the amount in the Answer (Actual) column: -0.99
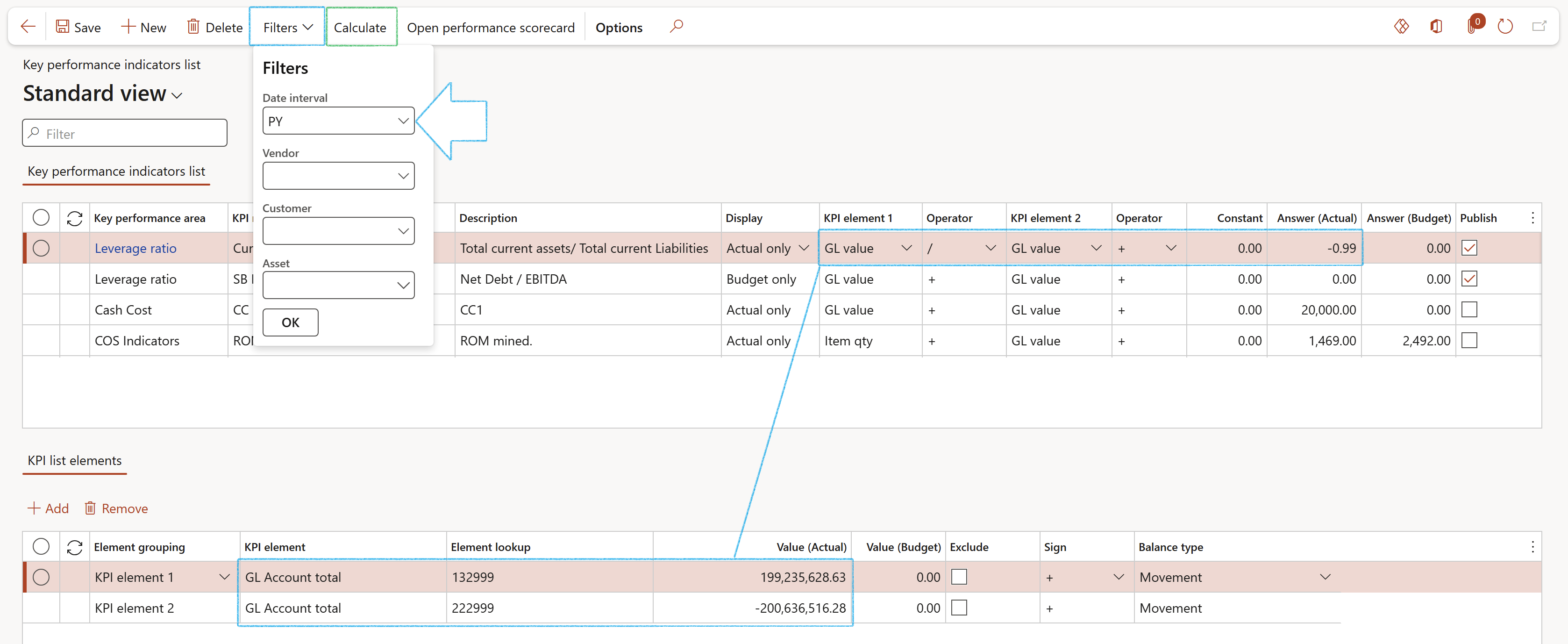
The following filters are for future use: Vendor, Customer and Asset
¶ Step 10: Setup Approval group
Users have to be members of the Approval group in order to make changes on Performance transactions
Go to: GRC > Setup > Governance, risk and compliance parameters
- Under the General tab, expand the Corporate performance management Fast tab
- In the Approval group field, select the relevant approval group from the dropdown list
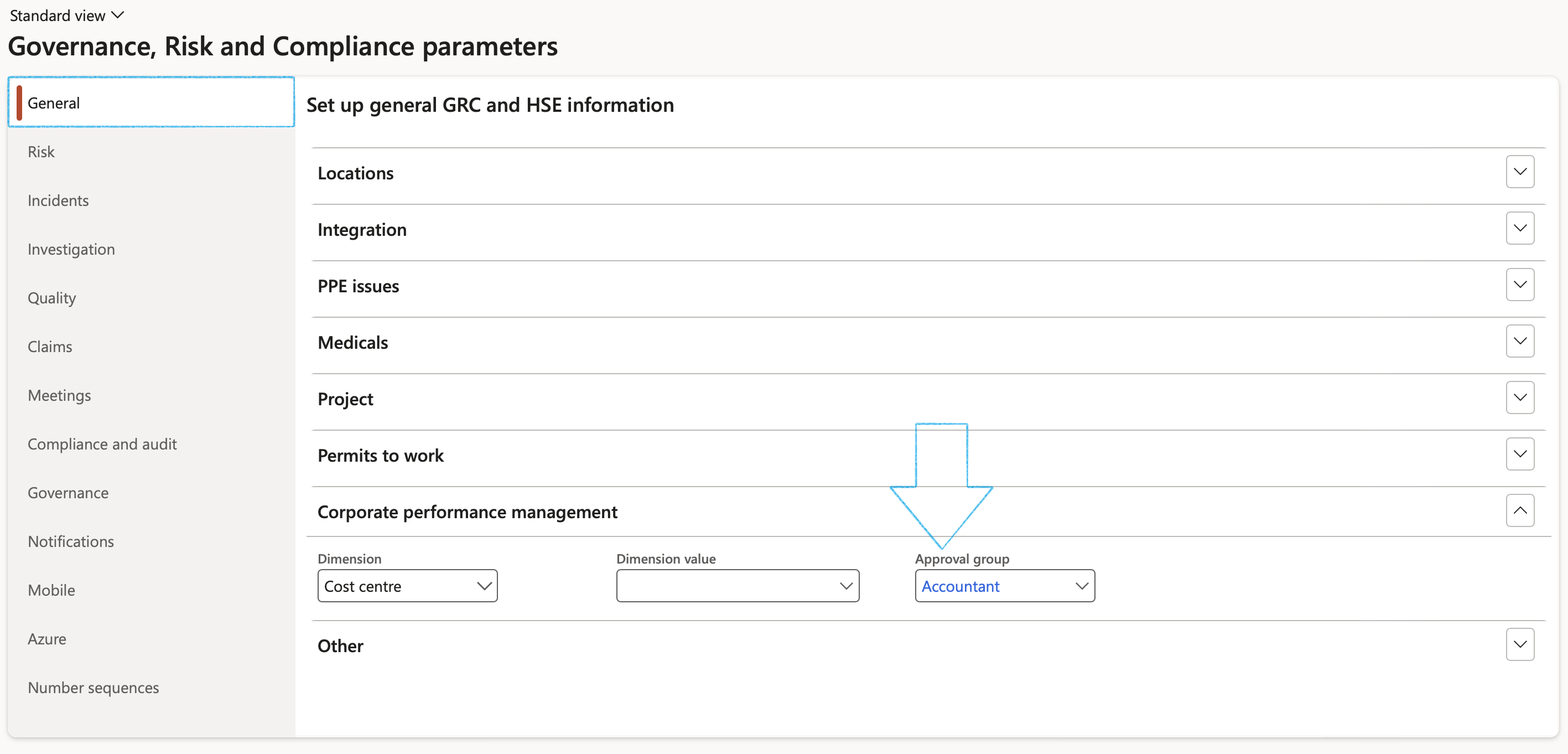
The Mining perspective Index tab will be hidden on the Performance scorecard workspace if the Show mining perspective slider is set to No
¶ Step 11: Signature types
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Signature type
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Under the Signature type Index tab:
- Enter a unique Signature type ID
- Enter a brief Description for the signature type
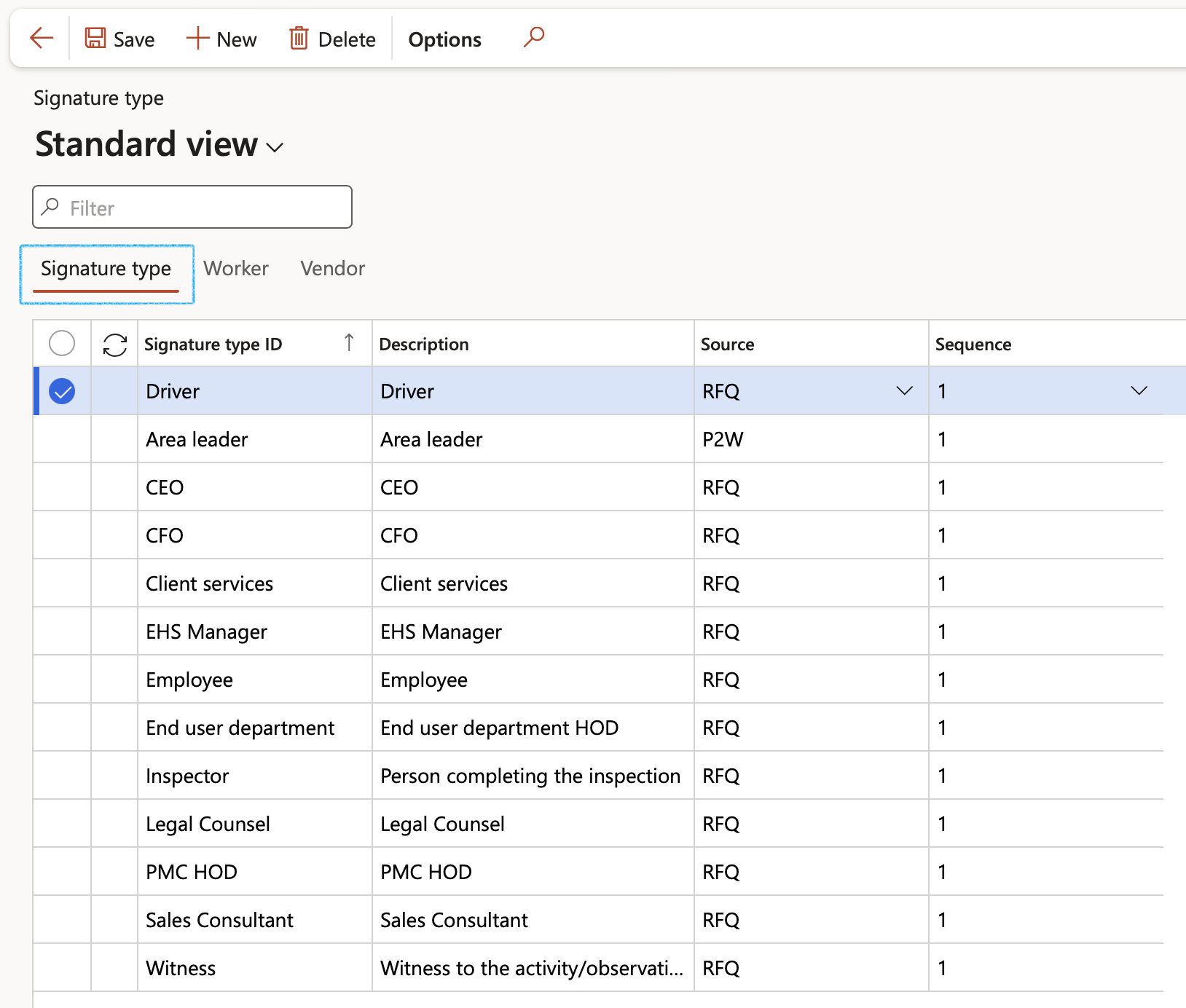
- Select the Signature type that you want to add workers to
- Open the Worker Index tab:
- In the Remaining workers column, select the Worker that you want to link to the Signature type
- Click on the < button to move the Worker across to the Selected workers column
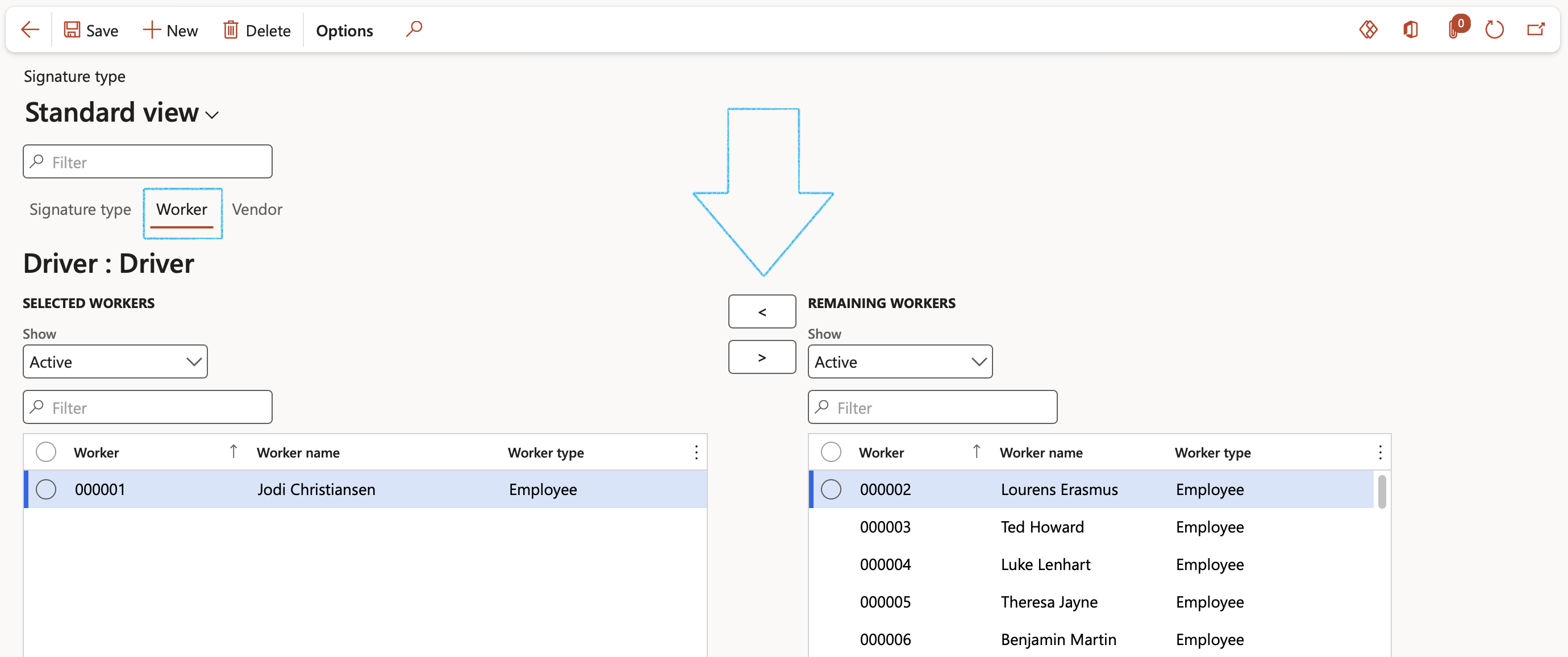
Only workers that have been linked to a Signature type can be selected under the Signatures off Fast tab on the KRI & Goals
¶ Daily use
¶ Step 12: Performance transactions
For future use
¶ Step 13: Create a Goal and associated Measurements
Creating a Goal (objective)
The performance management process enables employees to document and discuss performance. This is done by aiming for a goal and then having specific (measurements) that will track the performance against each goal.
You can create any number of goals. These goals can span different periods and performance reviews. You can also create simple or complex goals, depending on the amount of information that you want to enter about the goal.
¶ Step 13.1: Create Goals
Go to: GRC > Performance > KRI & goals
- The grid will only show all GRC related goals
- On the Action pane, click New
- Under the General Fast tab enter at least the following:
- Name of the goal
- Select the relevant Worker from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Department from the dropdown list
- Select the Planned assessor form the dropdown list
- Brief Overview of the goal
- Select the relevant Goal category from the dropdown list
- Anticipated Start date and End date
- Link goal to a previously created Balance scorecard perspective
- Link a goal to a Risk line
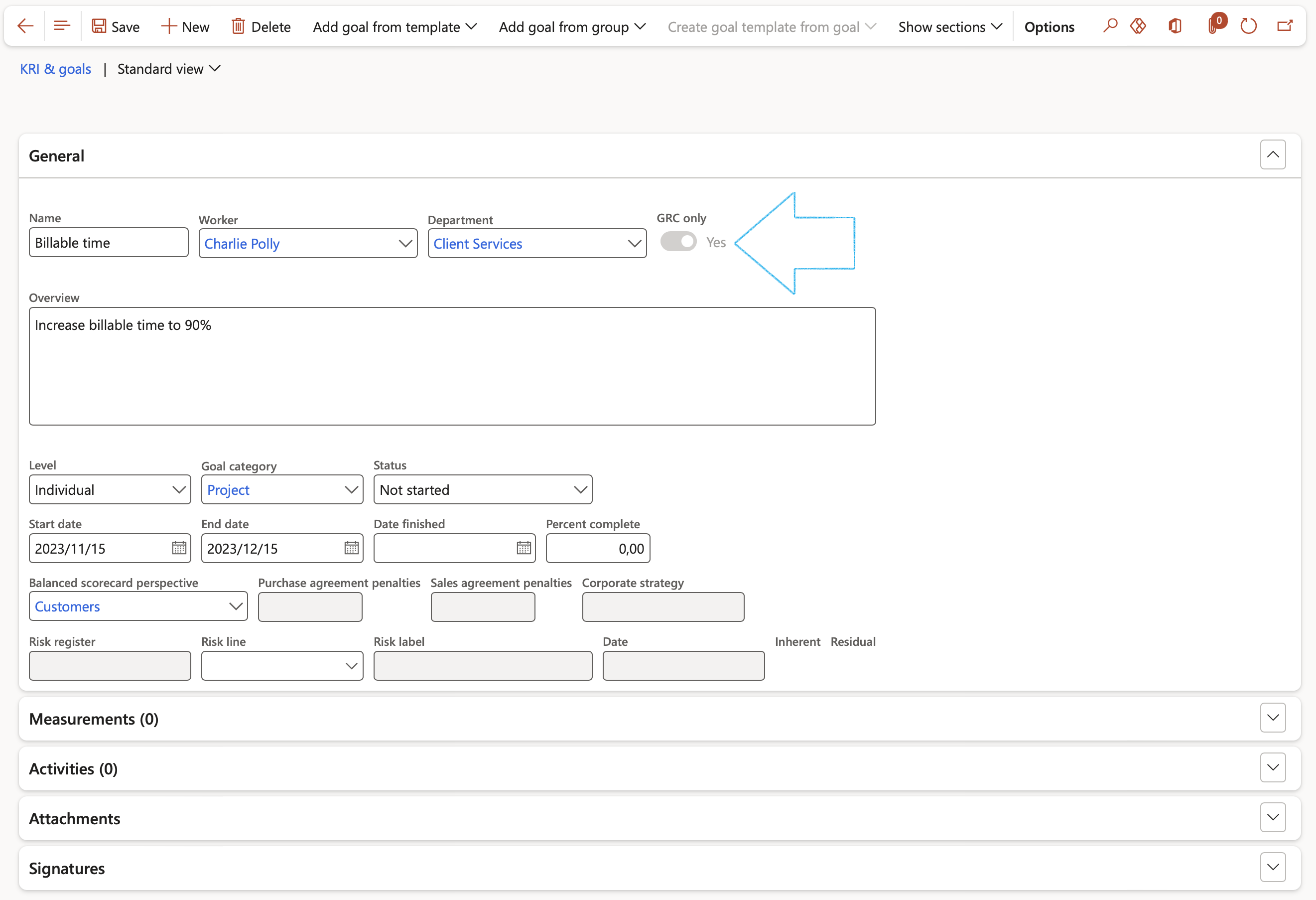
- Goals created from the GRC KRI & goals menu item will only be visible on the GRC > Performance > KRI & goals list page, and not on the HR Goals list page.
- The GRC only slider will by default be on Yes.
¶ Step 13.2: Create Measurements
Goals often have measurable results. You can add measurements to track the target goal results and the actual results. If the measurement is a stretch goal, you can mark the measurement by using the Stretch goal option.
In order to keep track of performance goals users must add Measurements:
Go to: GRC > Performance > KRI & goals
- Select the goal created above
- Open the detail form by clicking on the Name of the goal
- Expand the Measurements Fast tab
- Click on the Add measurement button
- Select the relevant Measurement from the dropdown list
- Enter the Target and Actual values
- Indicate whether this is a Stretch goal
- Click OK and repeat for additional measurements
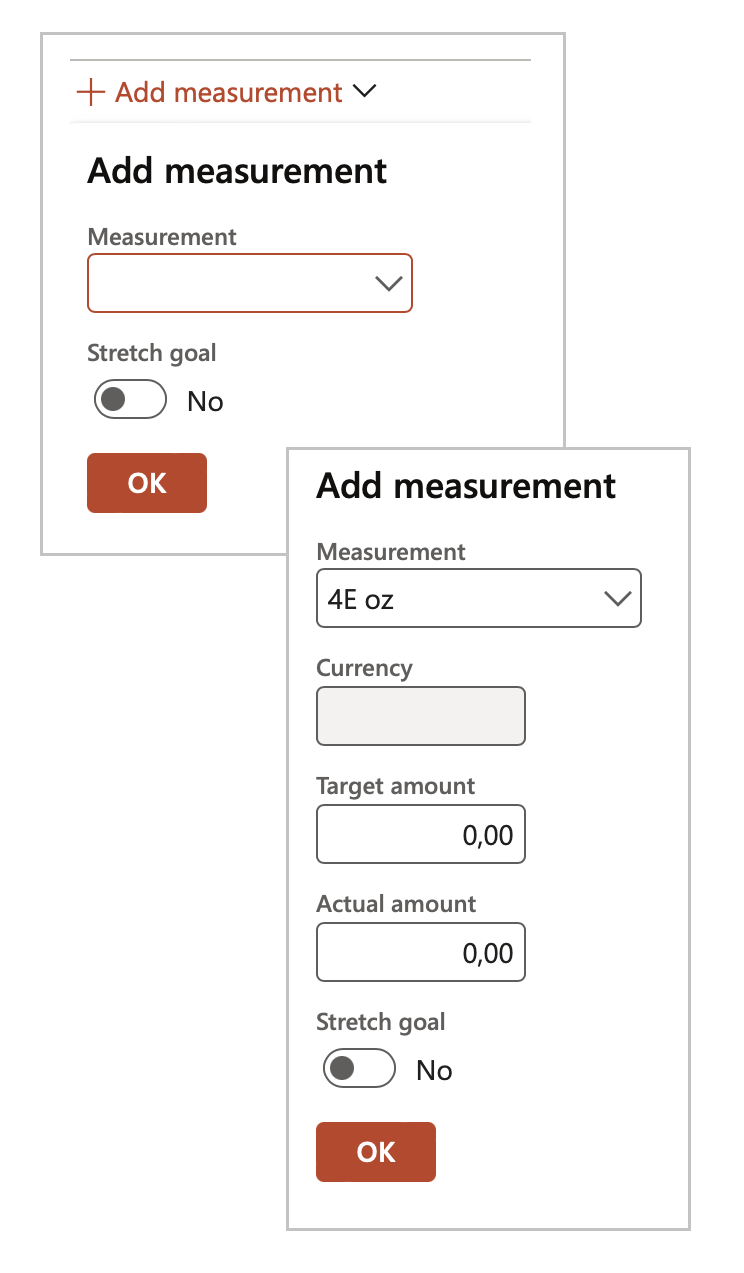
Once the scoring has been done, actual scores will go into the Actual column
¶ Step 13.3: Signatures on KRI & goals
It is sometimes required that the measurements on goals be signed. This can be done under the Signatures Fast tab.
- Expand the Signatures Fast tab
- In the Button strip, click on the Add button
- Select the relevant Signature type from the dropdown list
- Select either a Worker or a Vendor from the dropdown list
- If a Vendor is selected, enter the name of the Contractor employee
- Enter the Date on which the record was signed
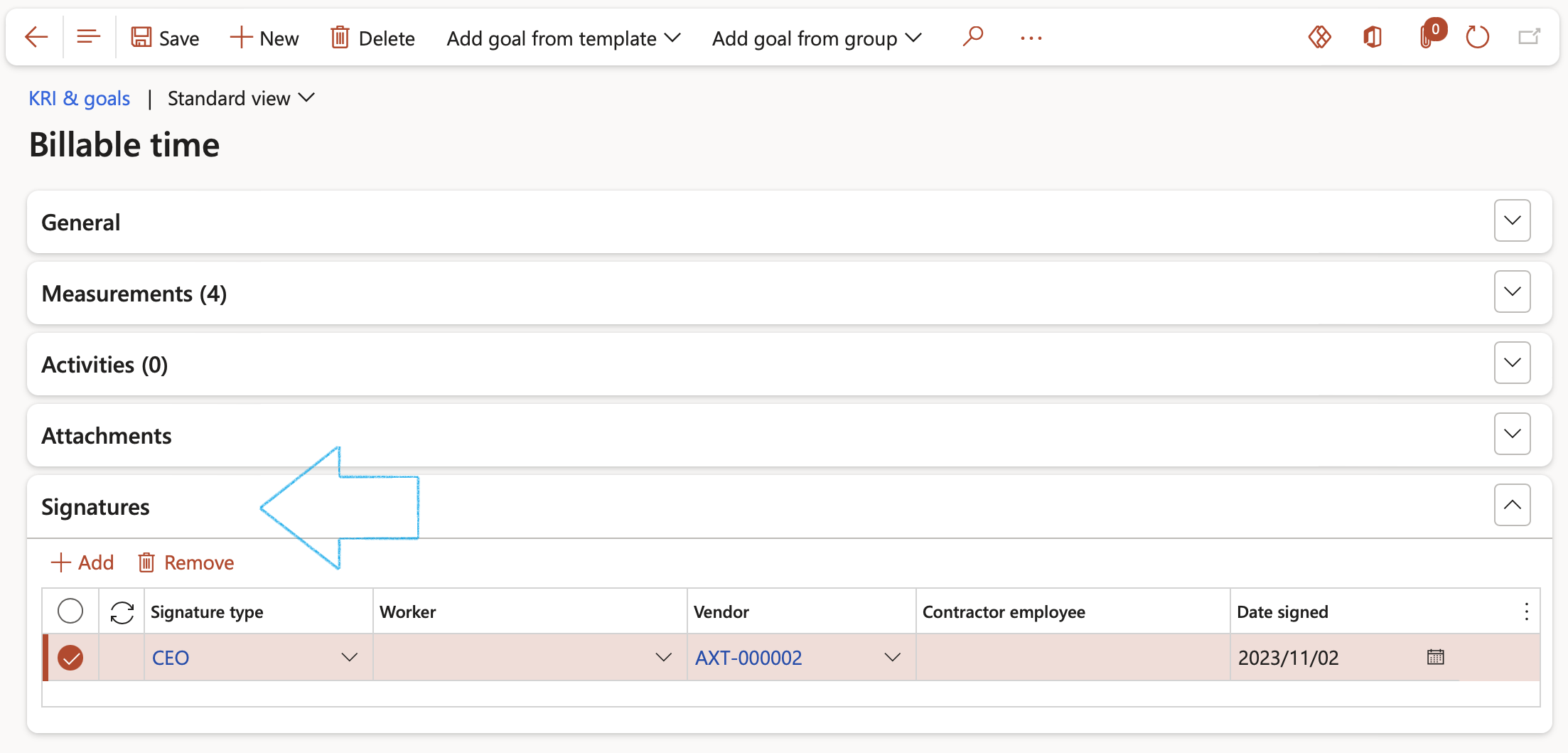
Only workers that have been linked to a Signature type can be selected under the Signatures Fast tab
¶ Step 14: Vendor performance
Vendor performance refers to how well a vendor meets the requirements of their contract, including factors such as:
- On-time delivery: Timeliness in delivering products or services.
- Quality of products or services: The standard of the goods or services provided.
- Compliance with specifications: Adherence to the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
- Vendor performance management: The practice of monitoring and analyzing vendor quality and reliability.
- Performance metrics: Measurements used to evaluate vendor efficiency and reliability, such as delivery times and product quality. Effective vendor performance management is crucial for maintaining strong supplier relationships and ensuring business success.
¶ Step 14.1: Create Goals
Go to: GRC > Performance > KRI & goals
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Under the General Fast tab, enter details as described above under Step 13.1
If a Vendor is specified, the Goal can only be selected for the selected Vendor. If the Vendor field is left blank, the Goal can be selected for any Vendor.
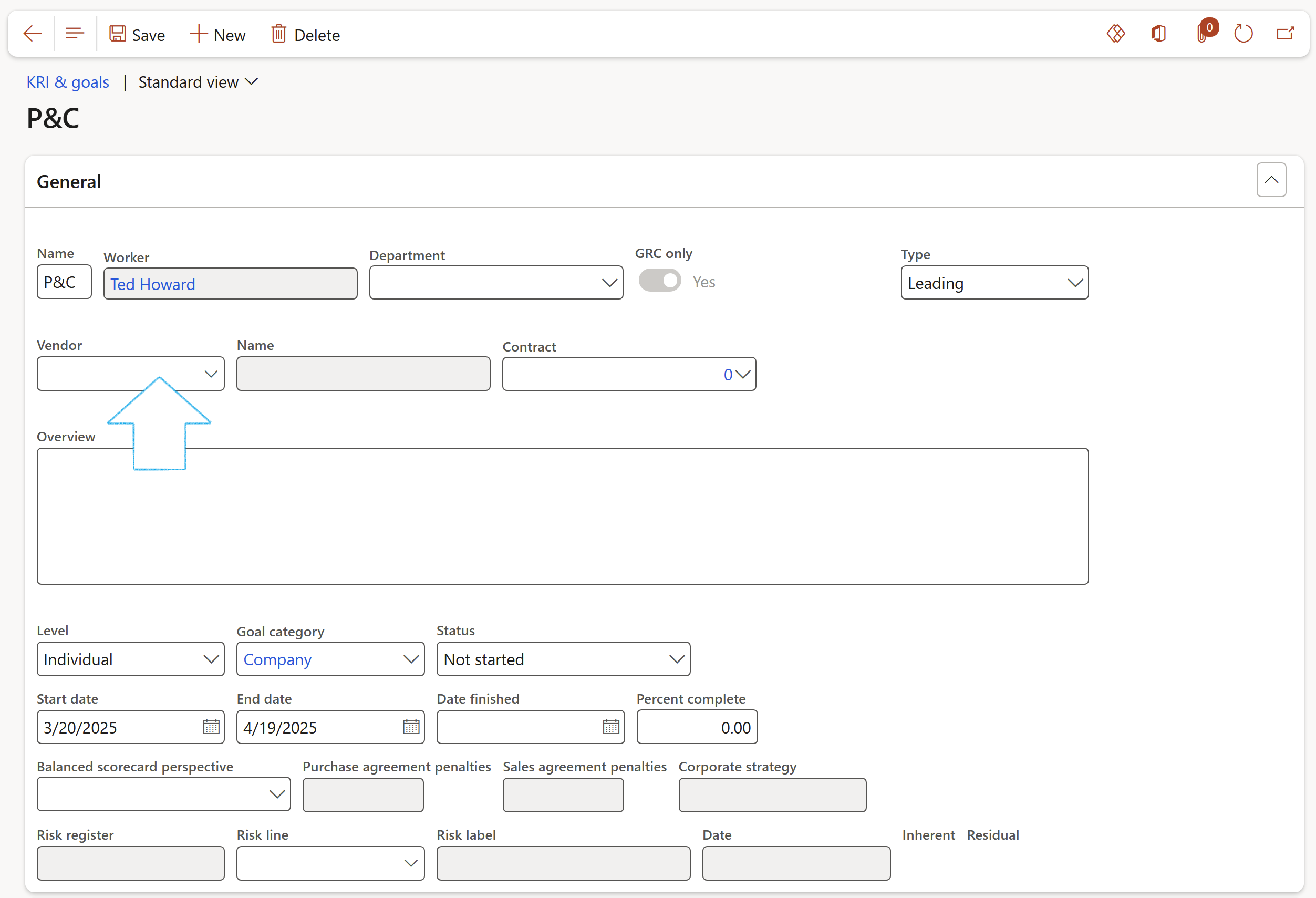
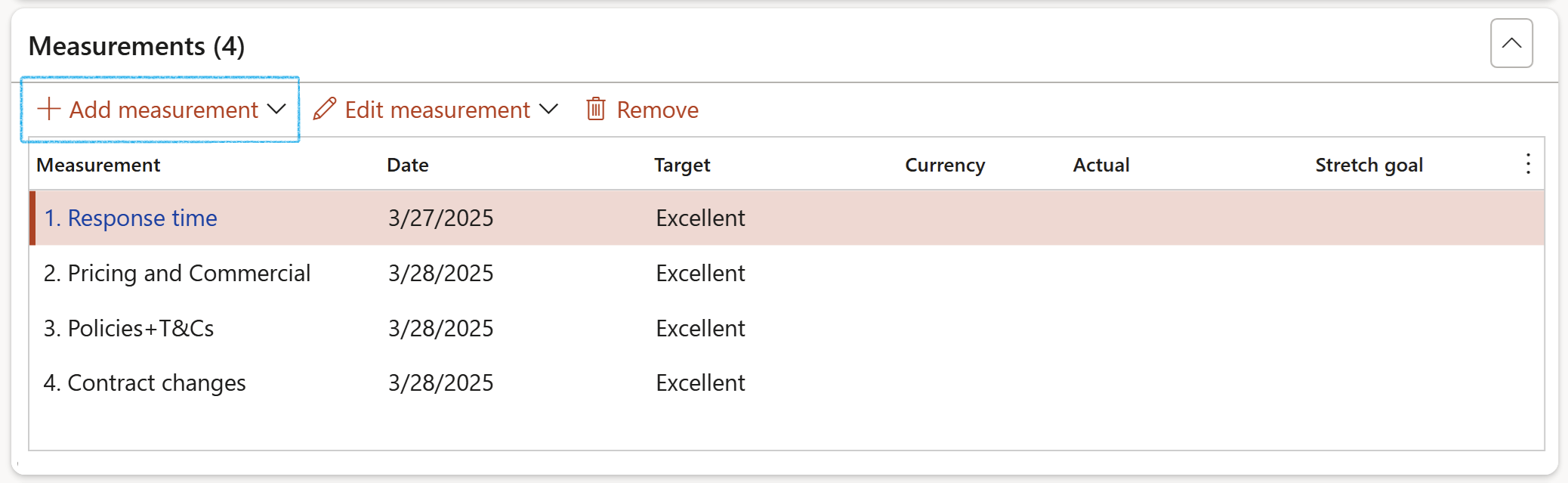
- Expand the Measurements Fast tab
- Add the Measurements as described above under Step 13.2
¶ Step 14.2: Adding Goals on the Vendor
On the Vendor groups setup form, select the relevant Goal group from the dropdown list
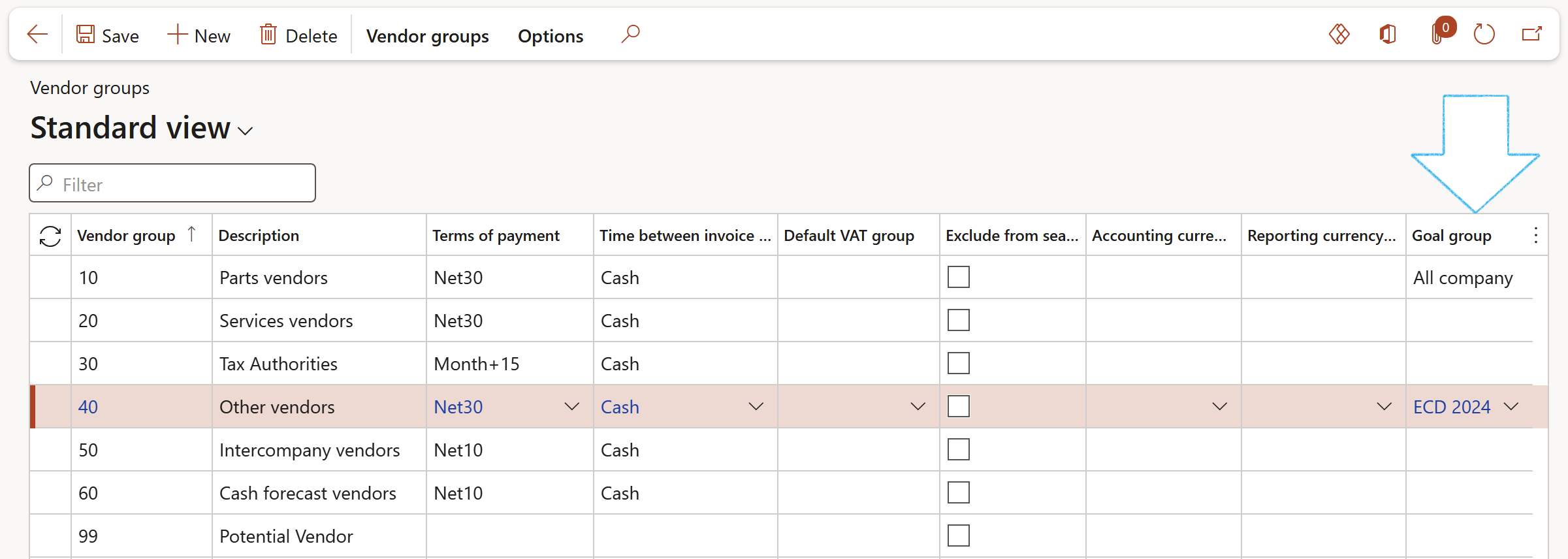
When a new Vendor is created and linked to the Vendor group, the Goal group field under the Vendor profle Fast tab will automatically be populated with the correct Goal group.
OR
Go to: Procurement and sourcing > Vendors > All vendors
- Select the relevant Vendor
- Expand the Vendor profile Fast tab
- Select the relevant Goal group from the dropdown list
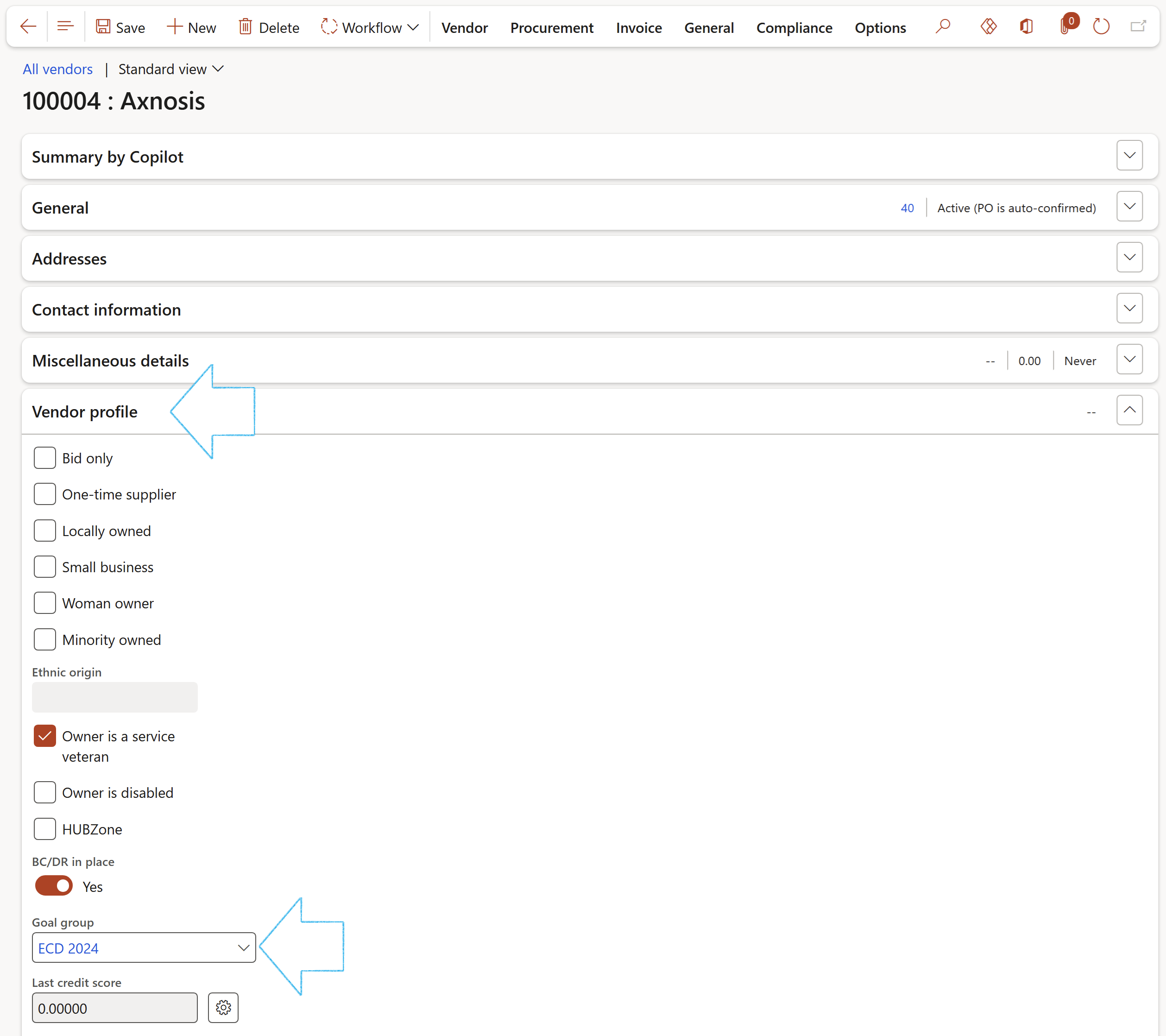
- In the Action pane, open the Compliance tab
- In the Performance button group, click on the Create goals button
- On the Create goals dialog, select the Planned assessor form the dropdown list
- Enter the Start date and End date
- Click on the Create button

A blue line at the top of the screen will notify the user of the number of goals that have been created for the vendor
- Refresh the screen to see the goals under the Performance Fast tab
- Tick the Print box for the lines that you want to print on the Vendor performance report
- The numbers in the Number column are populated from the selected Goal group
- The Actual column will be updated with the values entered on the Goal after scoring/measuring has been done
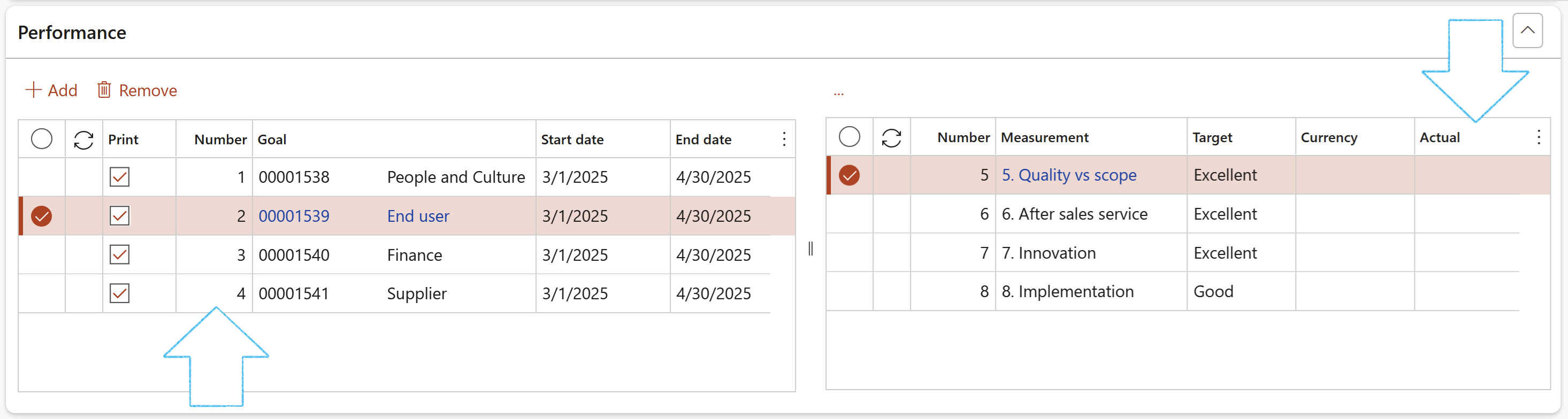
The numbers in the measurements grid, are populated from the Goal template measurements (lines)
¶ Step 14.3: Scoring/measuring Goals on the Vendor
The Planned assessor can follow the path below to see a list of his/her planned KRI & goals to score:
Go to: GRC > Performance > KRI & goals
OR
Go to: GRC > Performance > My planned KRI & goals to view the newly created goals for the Vendor
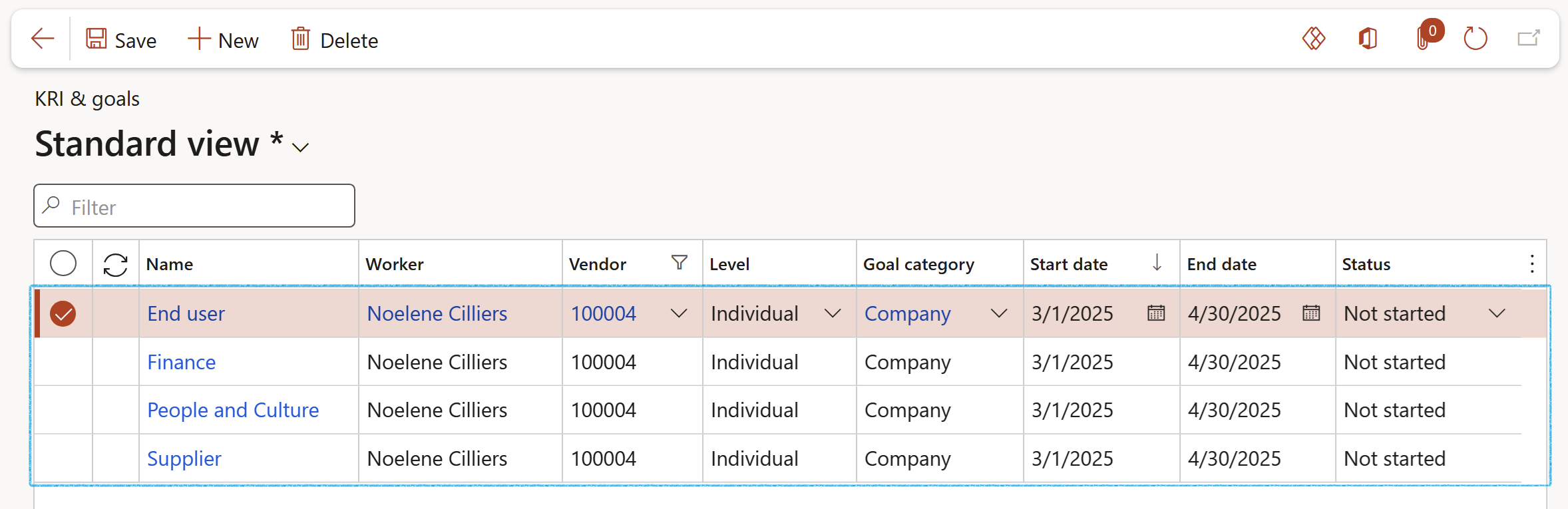
- Open the relevant Goal and expand the General Fast tab
- The Vendor number and Name will be populated with the Vendor details that the goal was created from
- The measurements linked to the goal will be listed under the Measurements Fast tab
- To rate the Measurements, click on the Edit measurement button and select the relevant Actual level from the dropdown list
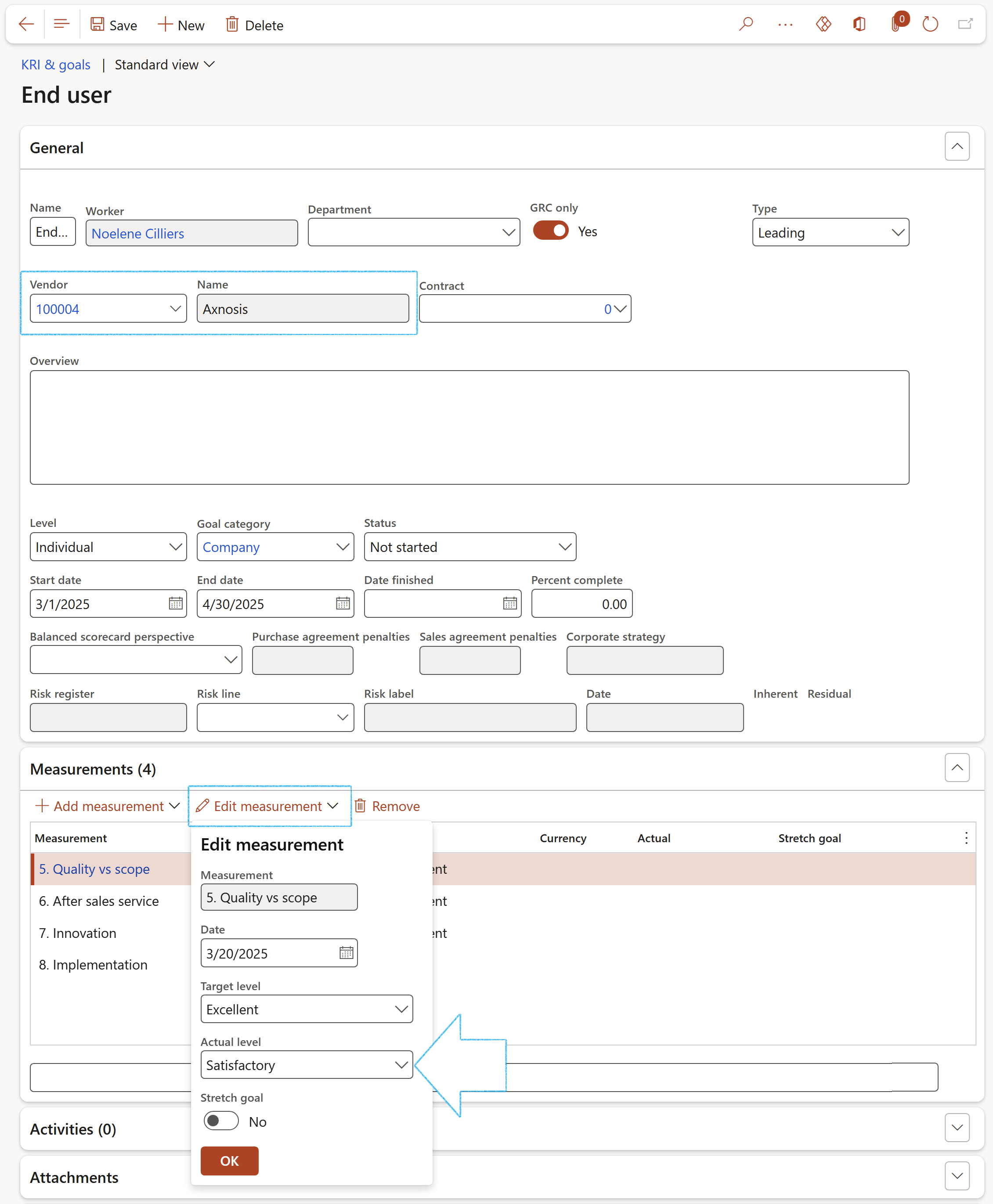
The name of the Worker (linked to the logged in user) doing the scoring will populate the Worker field
¶ Step 14.3.1: Creating a Non conformance on a measurement
If a low score is given to a measurement, a non conformance can be created by clicking on the Create non conformance button in the Button strip. A non conformance can be followed up and corrected.
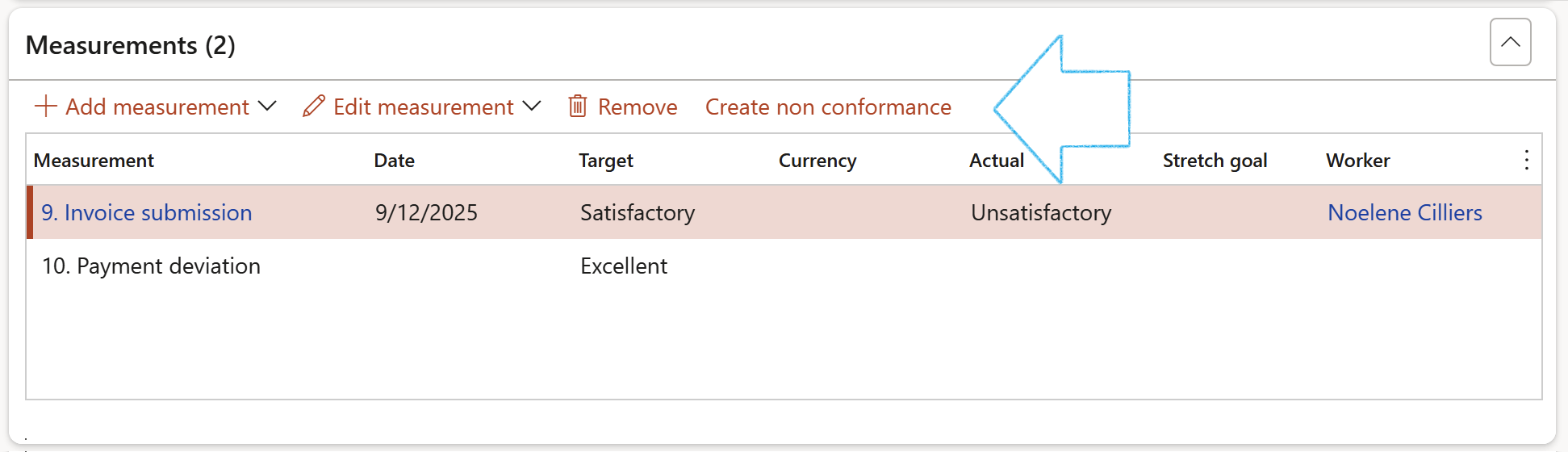
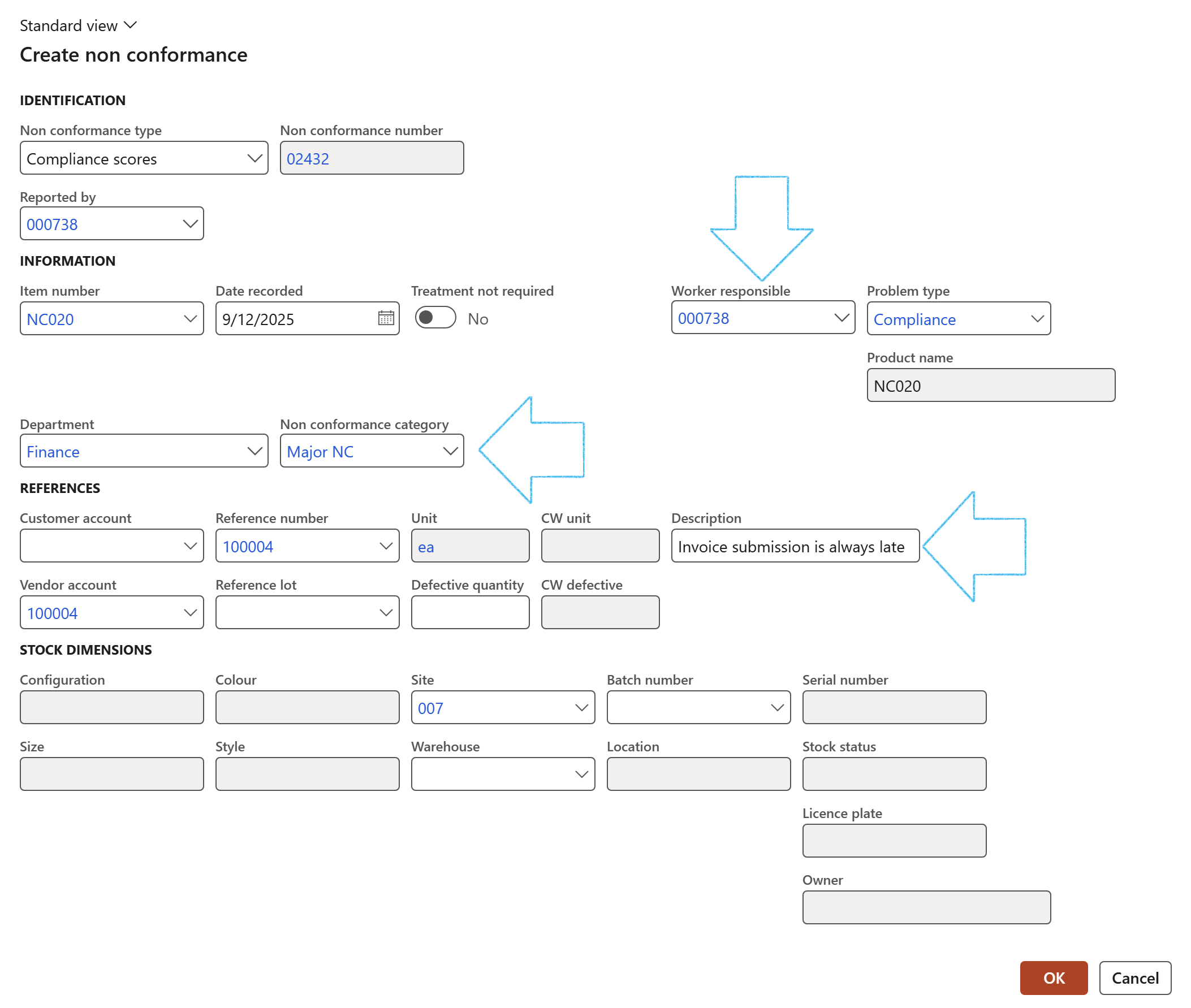
On the Create non conformance dialog:
- Select the relevant Worker responsible form the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Department form the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Non conformance category form the dropdown list
- Enter a Description for the non conformance
- Click on the OK button
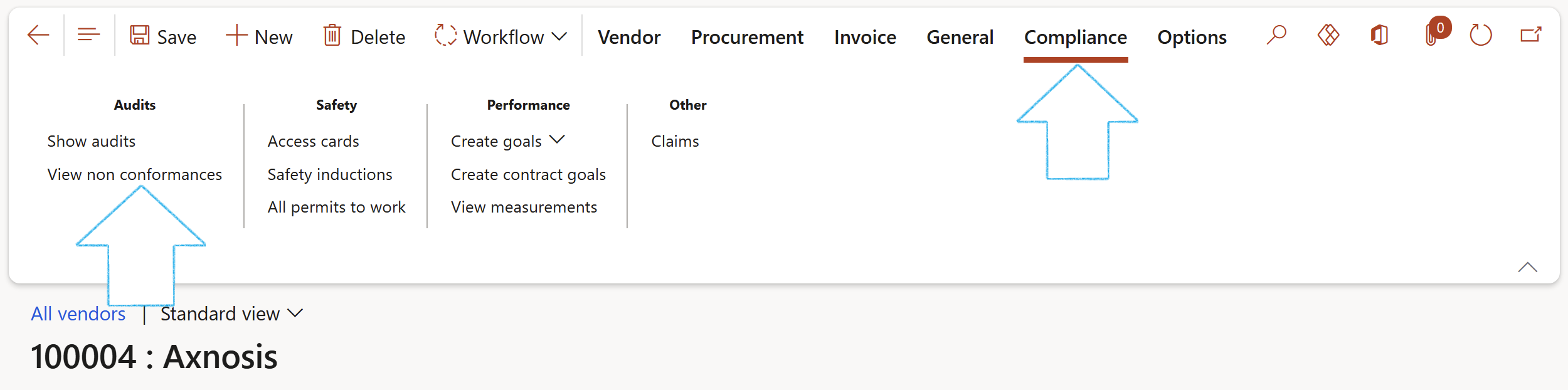
To view non conformances created on a measurement line:
Go to: GRC > Governance > Tender manmagement > All vendors
- Select the relevant vendor
- In the Action pane, open the Compliance tab and click on the View non conformances button in the Performance Audits group
Please refer to the GRC Non conformances Wiki page for more detail on approving and correcting a non conformance
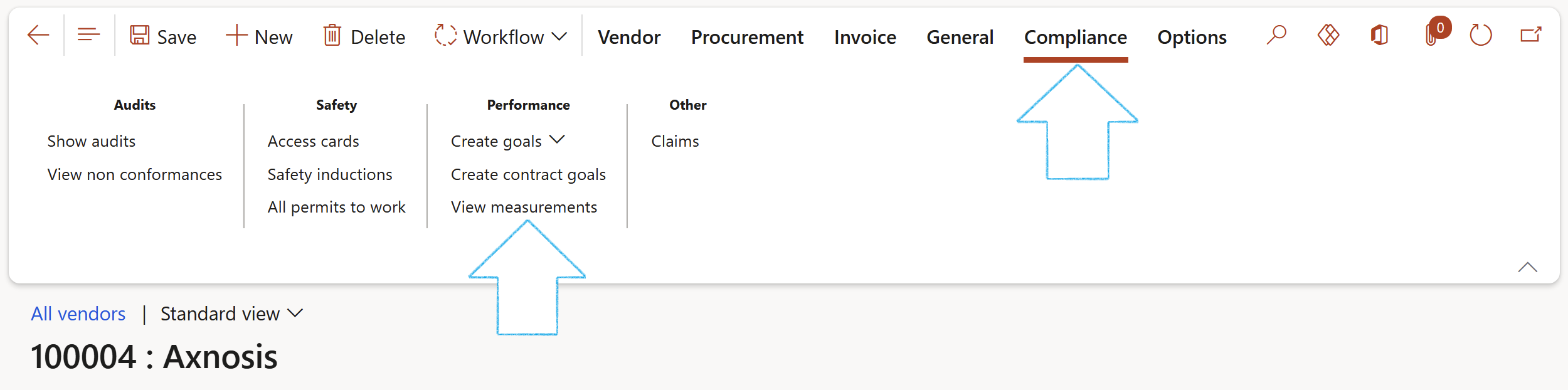
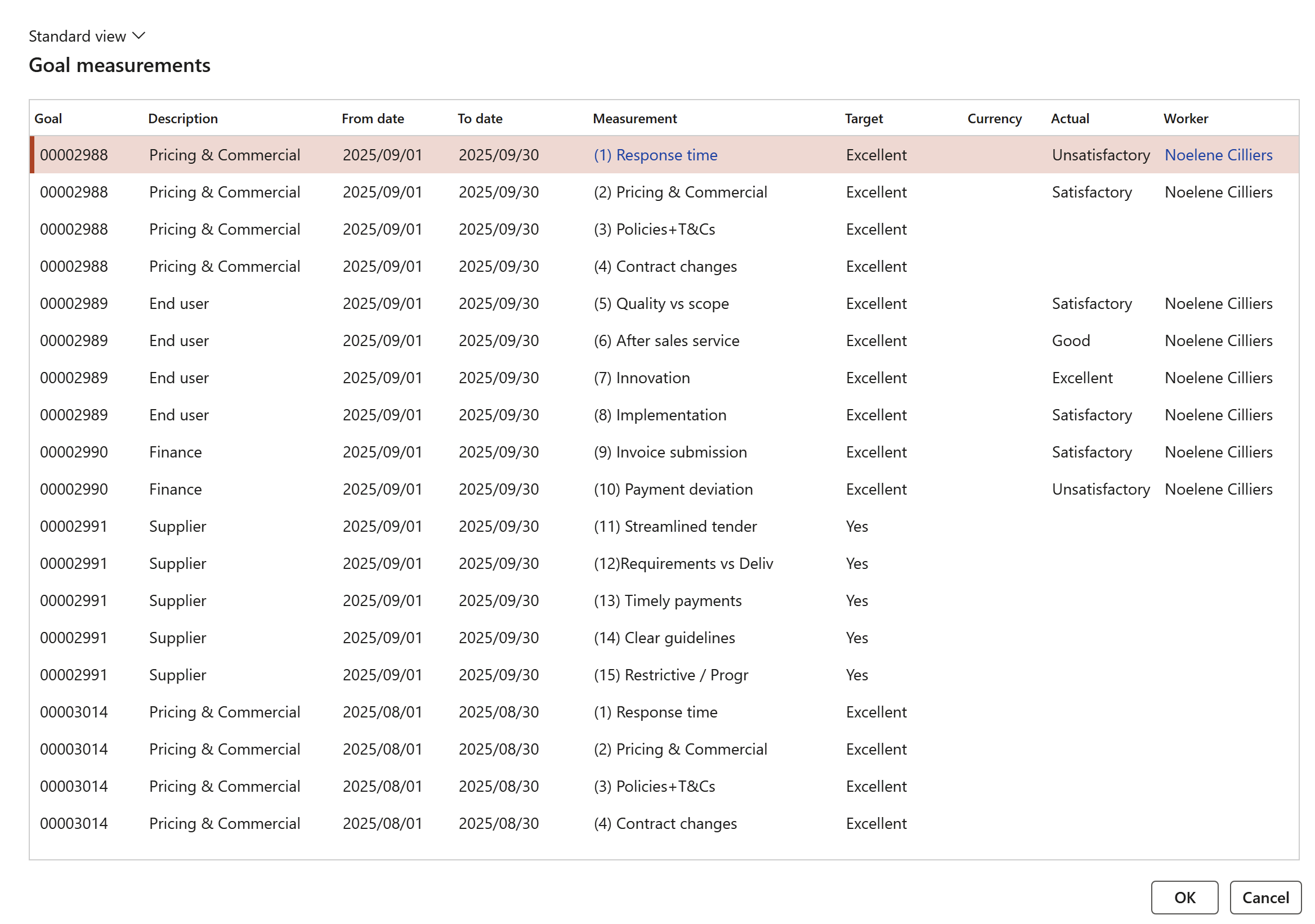
¶ Step 14.4: View the Goal measurements on the Vendor
Go to: GRC > Governance > Tender manmagement > All vendors
- Select the relevant vendor
- In the Action pane, open the Compliance tab and click on the View measurements button in the Performance Button group
¶ Step 15: Contracts
The management of a contract involves many activities to ensure fulfilment of that contract. Events can sometimes alter or disrupt the performance of a contract. For example, a contractor may default on contractual obligations, disputes may arise about contract conditions, or there may be a need to make amendments to the contract after it has been awarded.
Whenever the fulfilment of a contract is in question, contracting officers should take the necessary steps to serve and protect the interests of the organization. The Contracting department should keep complete and up to date files to provide a record of actions taken, such as contractor/vendor/supplier performance.
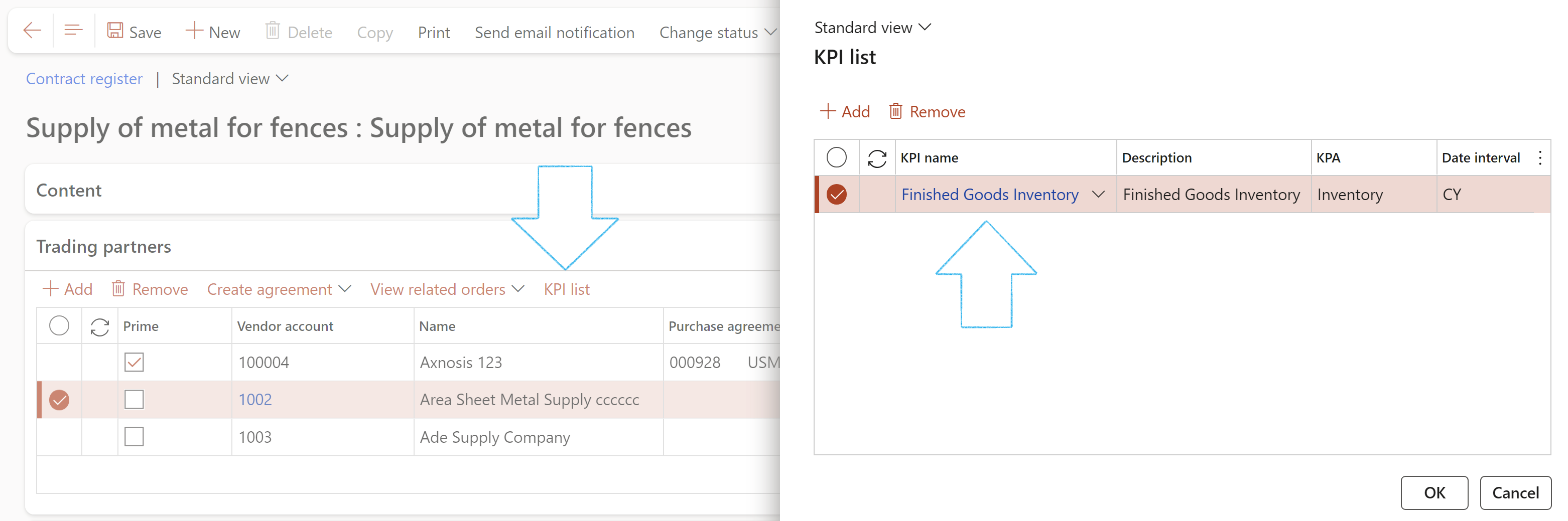
¶ Step 15.1: Link KPIs
Go to: GRC > Governance > Contracts > Contract register in legal entity
- Select the relevant record
- Expand the Trading partners Fast tab
- Select the vendor account that you want to add the KPIs to
- In the Button strip, click on the KPI button and click on KPI list
- On the KPI list dialog, click on the Add button
- Select the relevant KPI name from the dropdown list
- Click on the OK button
¶ Step 15.2: Create Balanced scorecard perspectives
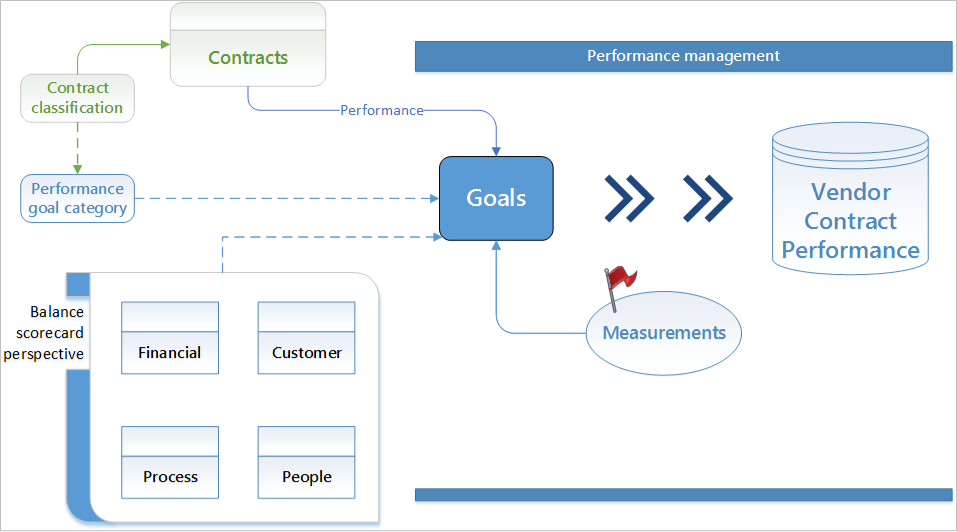
¶ Step 15.2.1: Create Balanced scorecard perspectives
The Balanced Scorecard concept is a management and measurement system which enables organizations to clarify their vision and strategy and translate them into action. The goal of the balanced scorecard is to tie business performance to organizational strategy by measuring results.
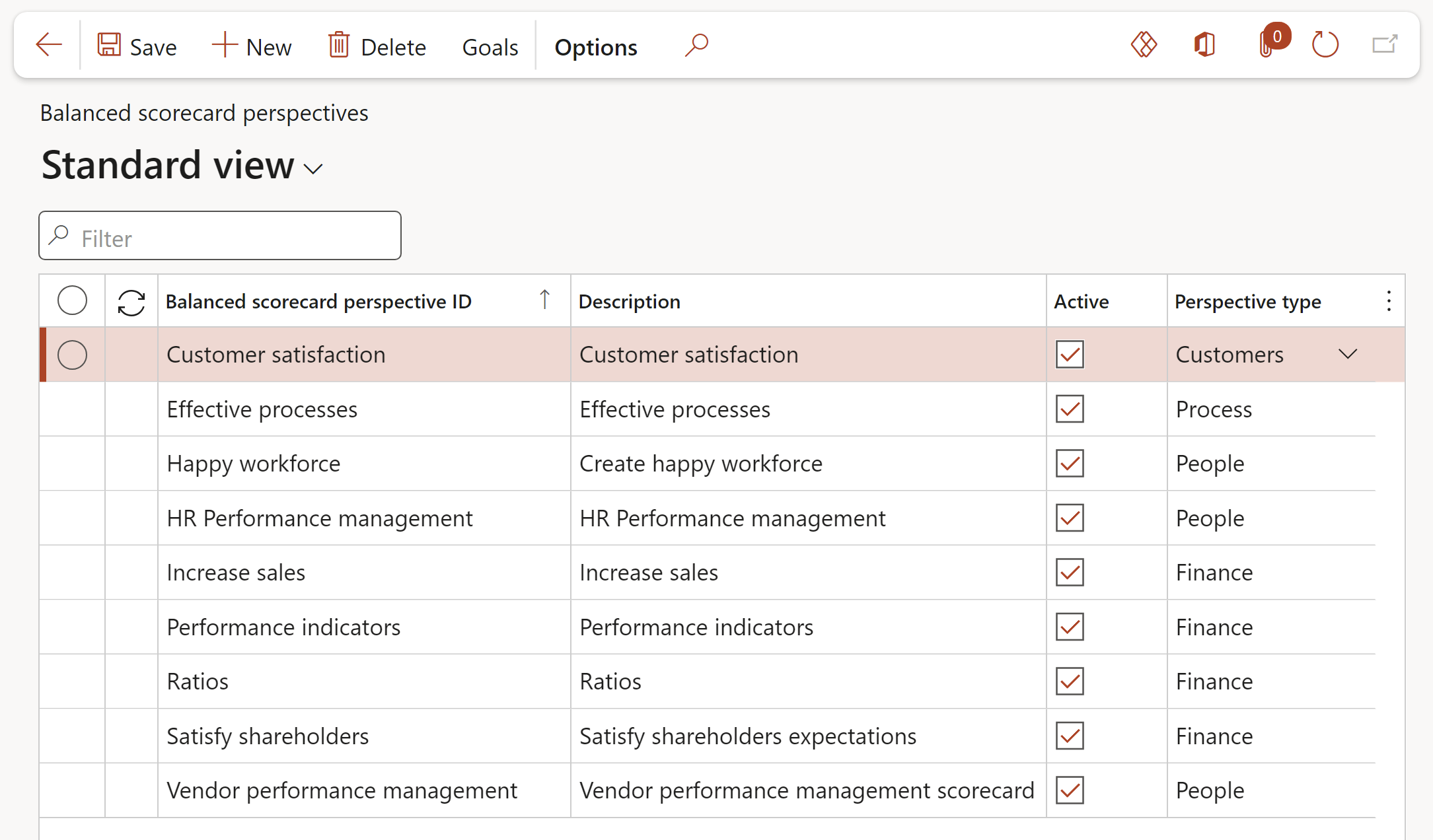
Go to: GRC > Performance > Balanced scorecard > Balanced scorecard perspectives
- On the Action pane, click New
- Enter a unique ID for the balanced scorecard perspective
- Enter a brief Description for the balanced scorecard perspective
- Indicate whether the balanced scorecard perspective is Active or not
- Select the relevant Perspective type from the dropdown list
¶ Step 15.2.2: Create Goal categories
Use goal categories to categorize goals. For example, if you set quarterly goals, the goal heading for a goal might be the quarter in which the trading partner (Suppliers and customers) is to achieve the goal.
Go to: GRC > Performance > Setup for performance > Goal category
- On the Action pane, click on the New button
- Enter a name for the new Goal category
- Enter a brief Description for the new Goal category
- In the Active field, select the option to allow employees and managers to assign goals to the heading
- Click Save
¶ Step 15.2.3: Create Goals
Before you can measure the performance of your trading partners (Suppliers and customers), you must first create goals. This is done by first setting a goal and then having specific (measurements) that will track performance against each goal.
Go to: GRC > Performance > KRI & Goals
- On the Action pane, click New
- In the Name field, enter an identification for the goal
- In the Worker field, select the worker that will be responsible for achieving the goal
- Move the GRC only slider to Yes. If the slider stays on No, the goal will not be on the GRC KRI & goals list page, but can be found under HR > Performance > Goals.
- Select the relevant Goal category from the dropdown list
- Select the Balance scorecard perspective from the drop down list
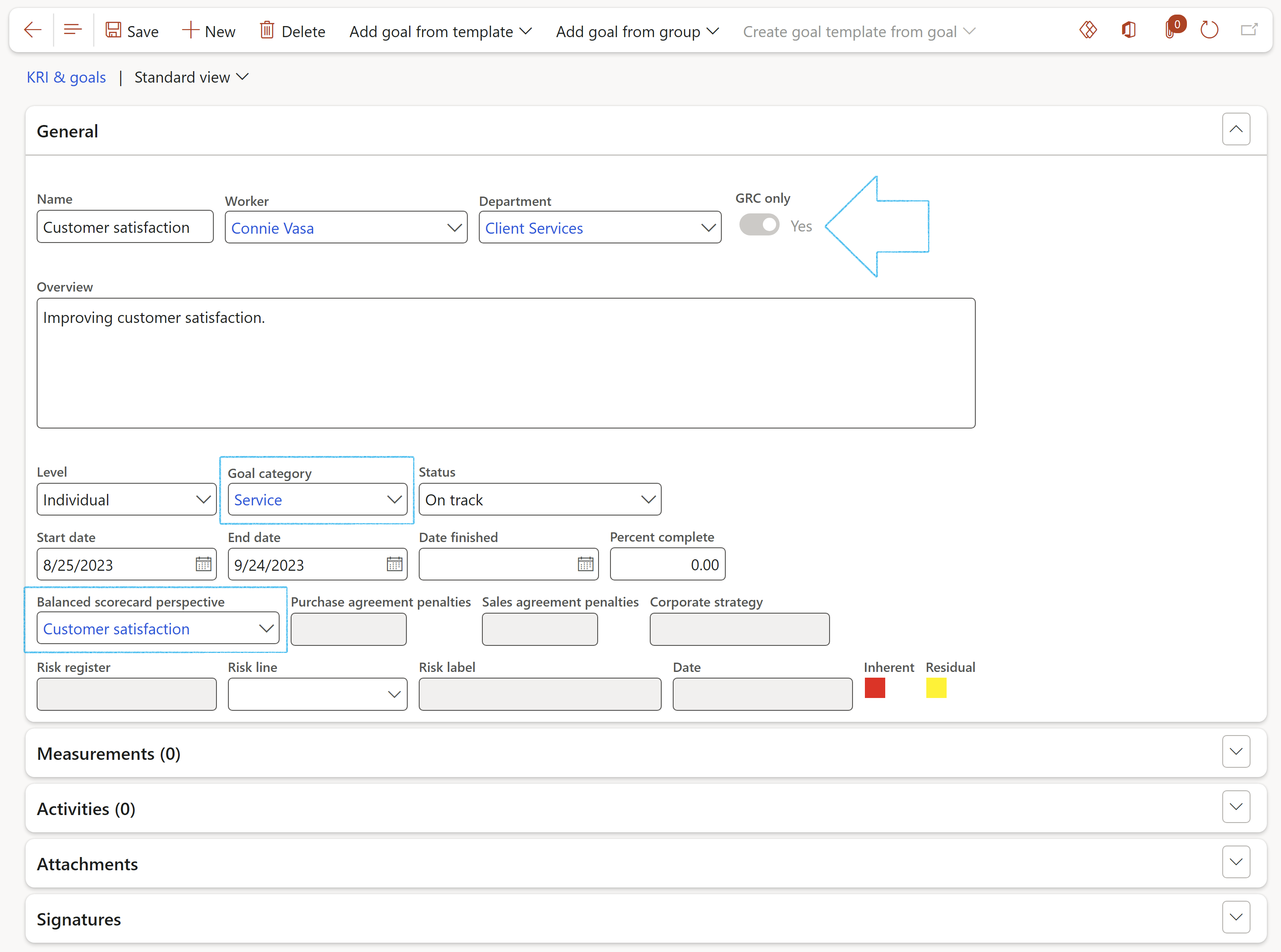
After linking Goals to the purchase or sales agreement (contracts), the reference will display in the General tab of the Goal.
- Expand the Measurements Fast tab
- In the Button strip, click on the Add measurement button
- On the Add measurement dialog, select the relevant Measurement from the dropdown list
- Complete the dialog with the relevant information
- Click OK
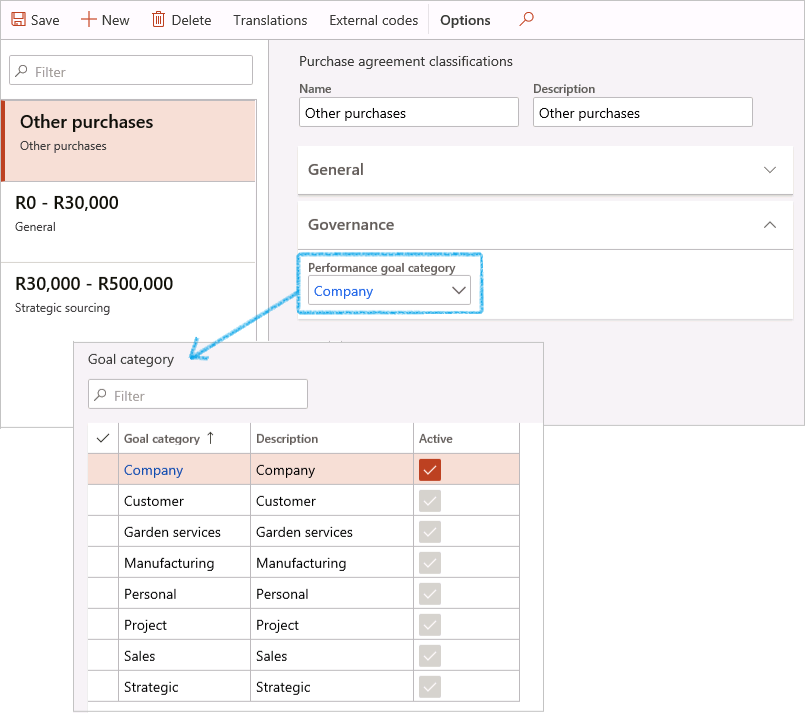
¶ Step 15.2.4: Create Goal category link to agreement classification
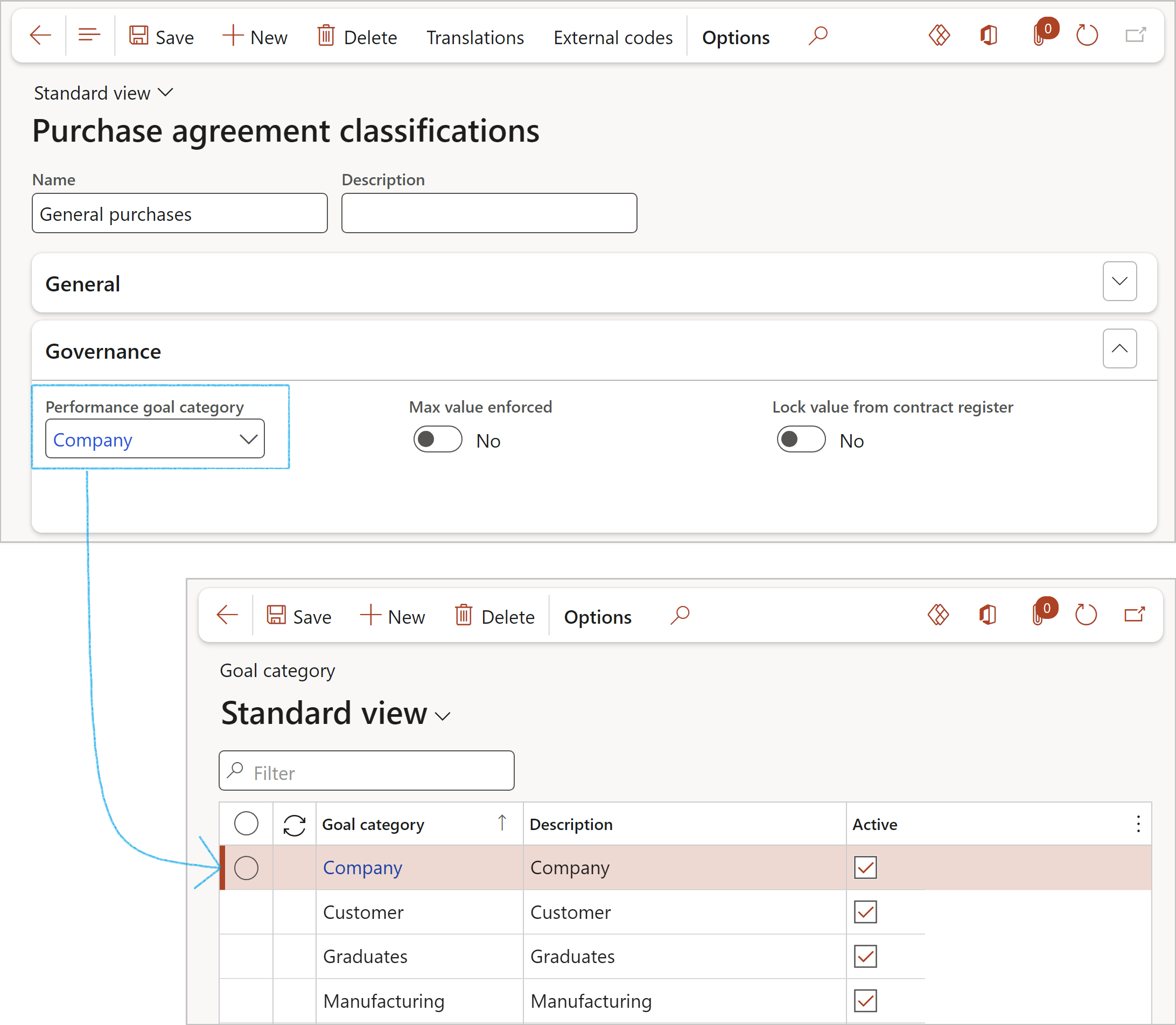
A specific goal category can also be linked to an agreement classification.
Go to: GRC > Governance > Setup for governance > Purchase agreement classifications
- Expand the Governance Fast tab
- Select the relevant Performance goal category from the dropdown list
- Click on the Save button in the Action pane
¶ Step 15.2.5: Performance management of Purchase agreements
Go to: GRC > Governance > Contracts > Purchase agreements
- Select the relevant purchase agreement from the list
- Open the Header view
- Expand the Performance Fast tab
- In the button strip, click on the Add button and select the relevant Goals to be linked to this contract
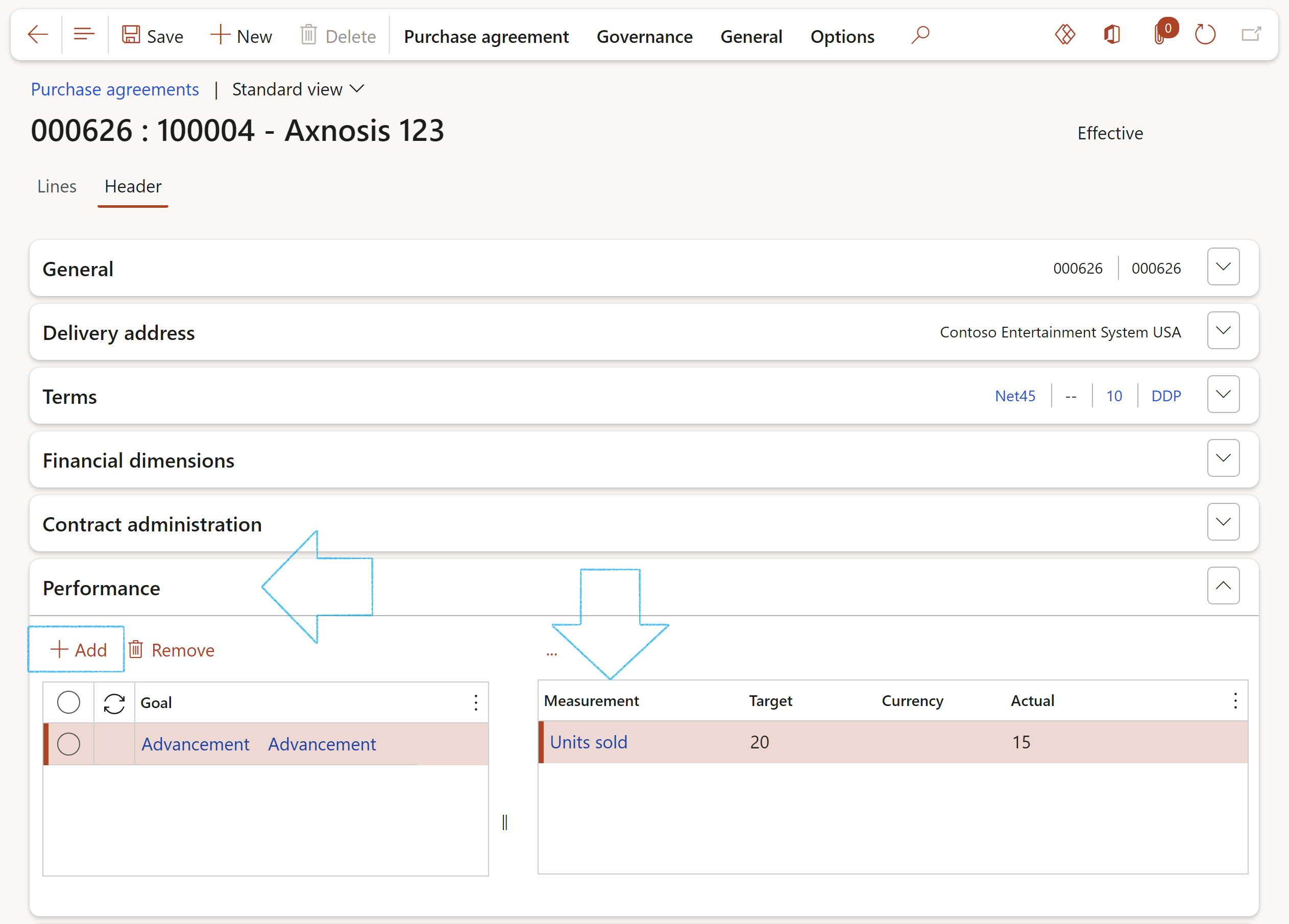
The goal “transactions” are displayed to the right of the selected goal
There are two filters on the Goal field:
- The Performance goal category on the Purchase agreement classification, and the Goal category on the KRI & goals, have to be the same
- The GRC only tick on the KRI & goals has to be Yes
HR performance management can be found in the Appraisals wiki page under HRM Daily use
¶ Reporting
¶ Step 16: Supplier performance report
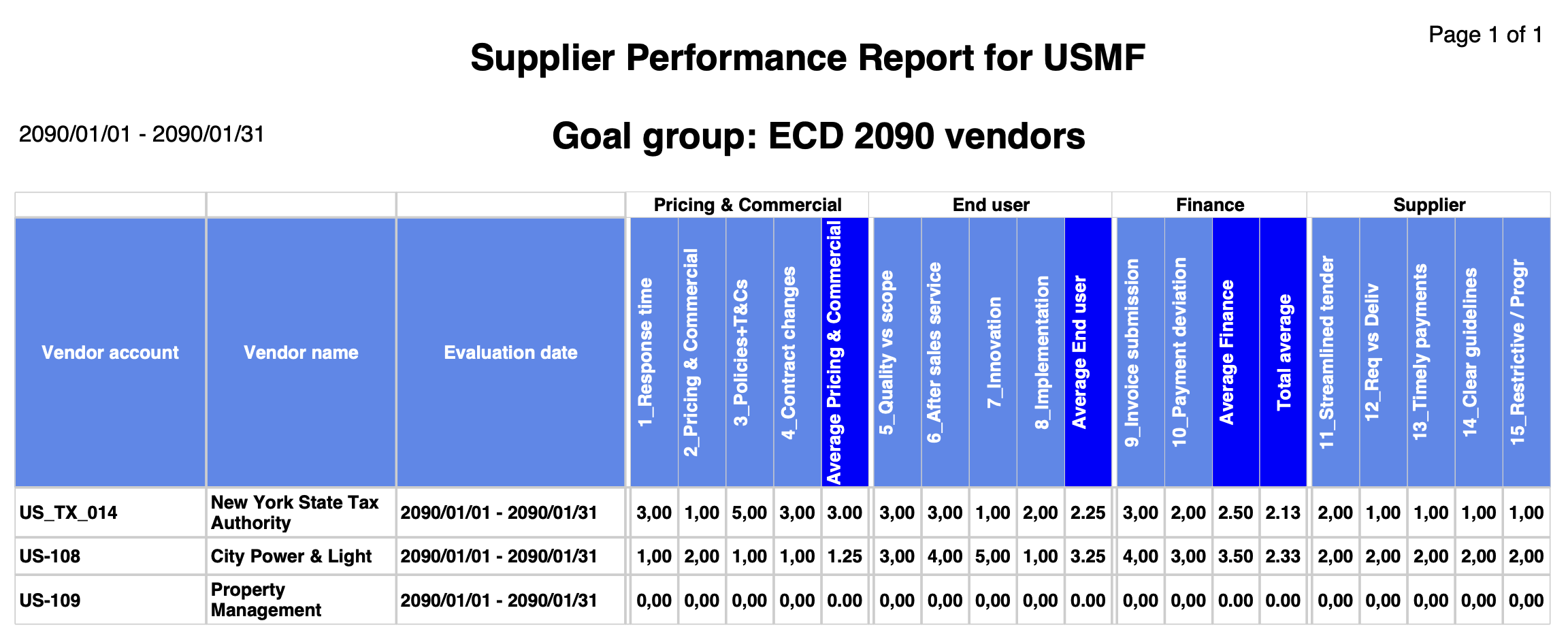
Go to: GRC > Reports and Inquiries > Supplier performance report
- Enter the following on the Supplier performance report dialog:
- From date for printing the report
- To date for printing the report
- Select the relevant Goal group from the dropdown list
- Select the relevant Vendor account from the dropdown list
- Click on the OK button
¶ Step 17: Open scorecard
Go to: GRC > Workspaces > Performance scorecard
¶ Step 17.1: Balanced scorecard grid
- Open the Balanced scorecard grid Index tab
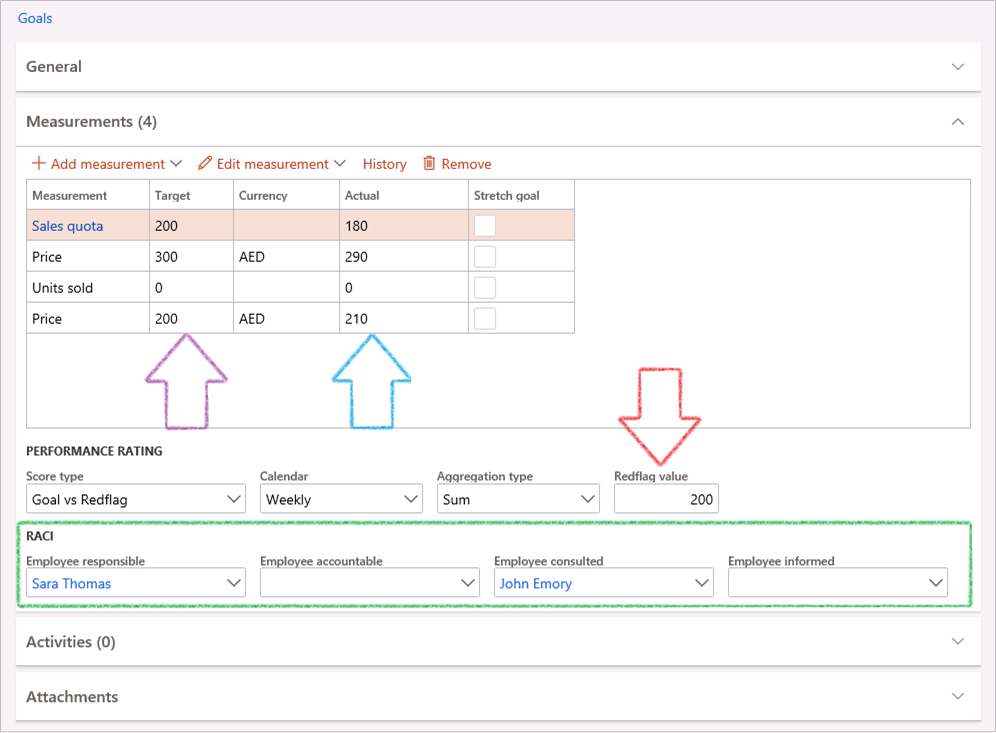
- A grid will show with all Balanced scorecard perspectives, goals, linked measurements and the values (Red flag, Actual and Target).
- The source of these values is the Measurement lines from the Goals under Period section.
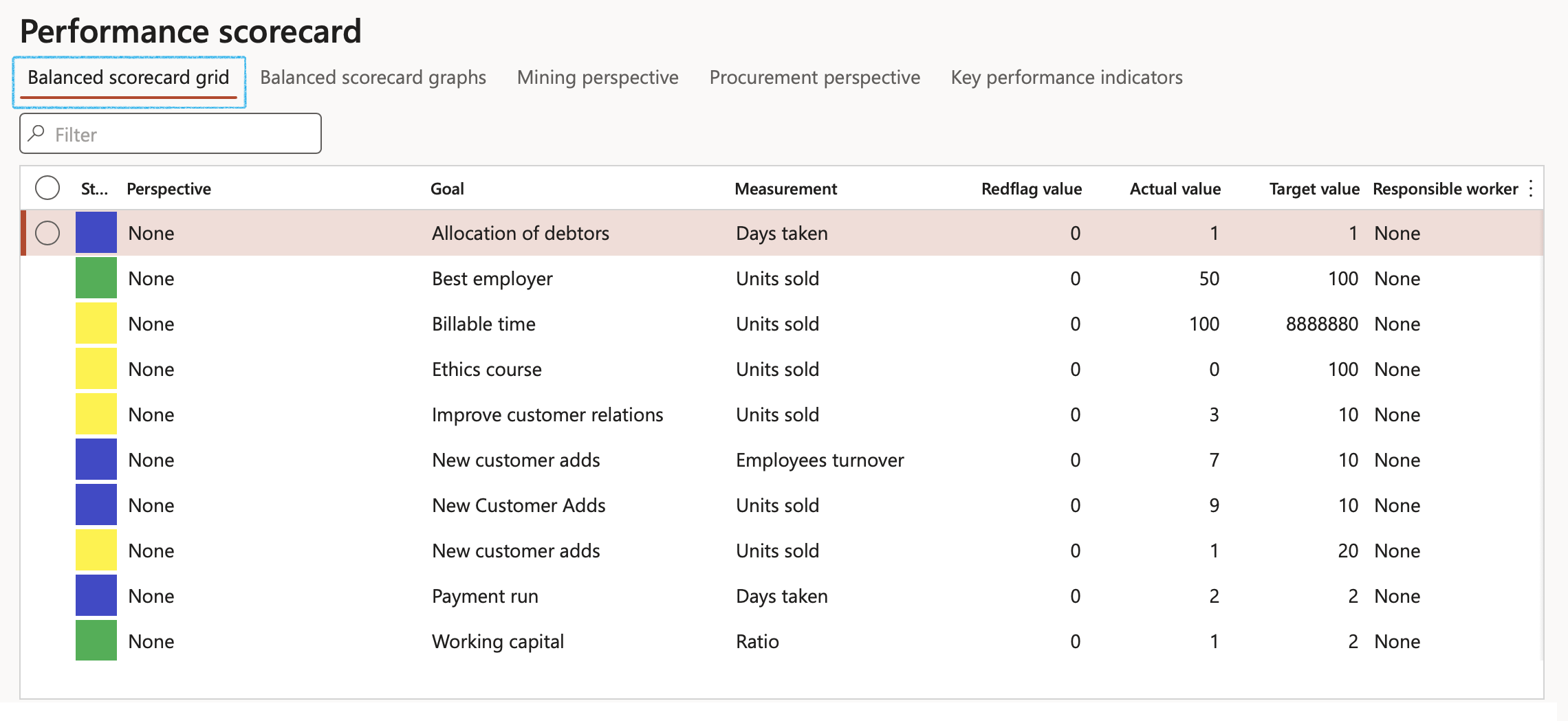
Threshold logic exists to look at the measurement scores and will compare it to the red flag in the following manner to derive the Status indicator (left column):
- If the Actual value (score) is LESS THAN the Red flag value; the status will be indicated as RED
- Then for the 1st range of possible values (1st third above the Red flag value and below the Target value) a status value of ORANGE will render.
- The 2nd range (2nd third Red flag value and below the Target value) will colour the status GREEN
- The last range (3rd and final third red flag value and below the Target value) and above will render a result status of BLUE
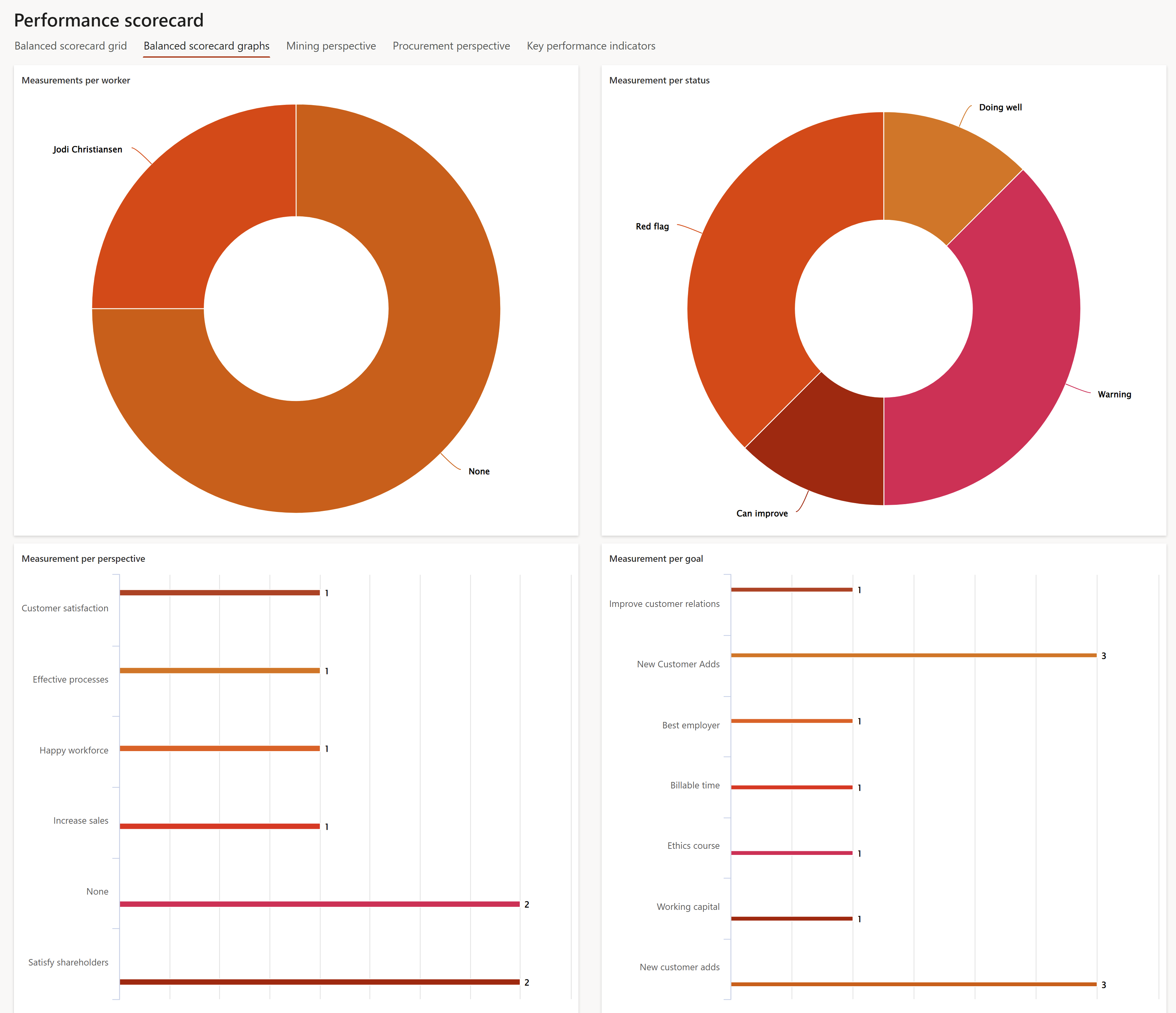
¶ Step 17.2: Balanced scorecard graphs
- Open the Balanced scorecard graphs Index tab
- The following can be viewed:
- Measurements per worker
- Measurements per status
- Measurement per perspective
- Measurement per goal
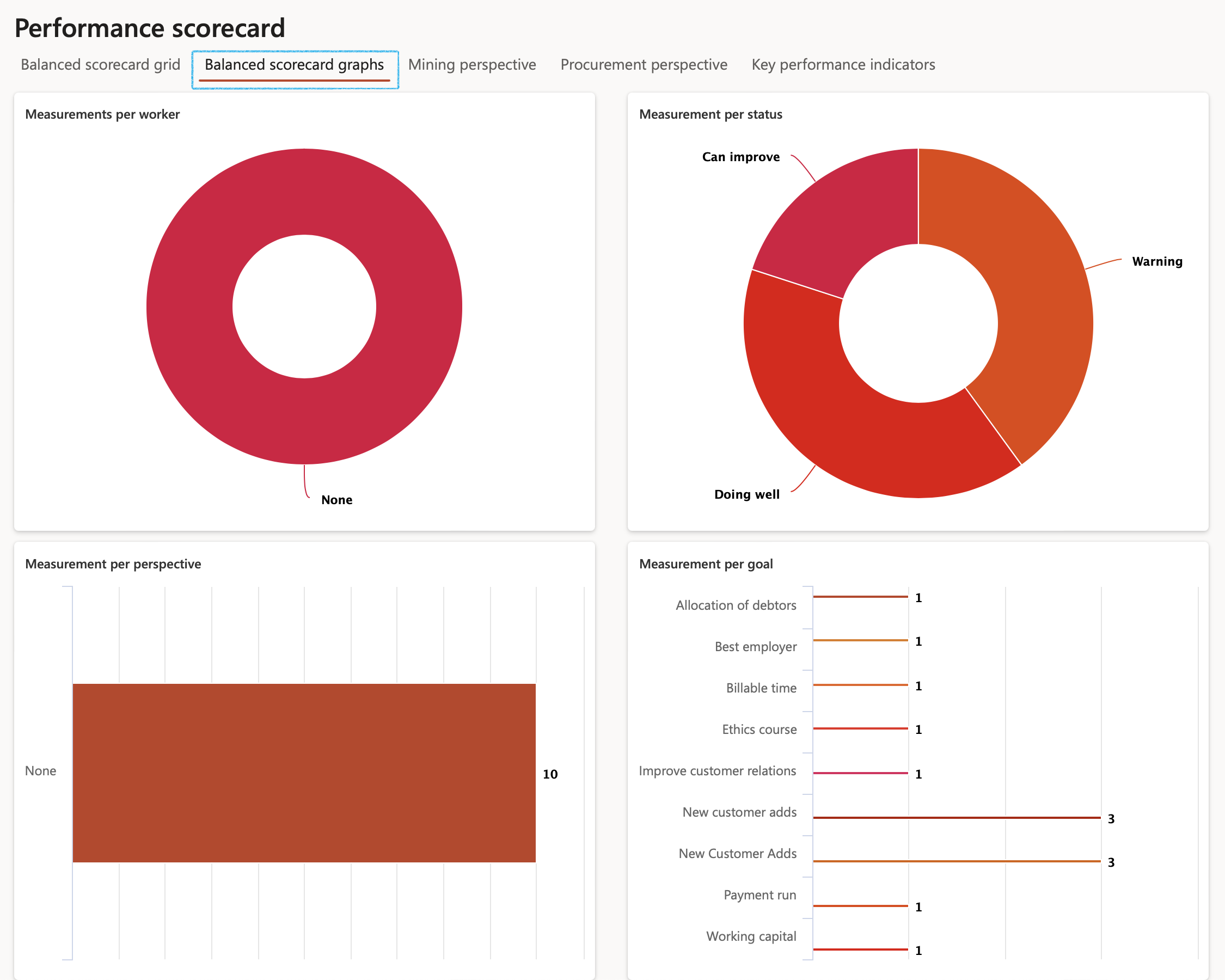
¶ Step 17.3: Key performance indicators list
- Open the Key performance indicators list Index tab
Only KPI list elements that have tick Publish box ticked, will be visible under the Key performance indicators list Index tab
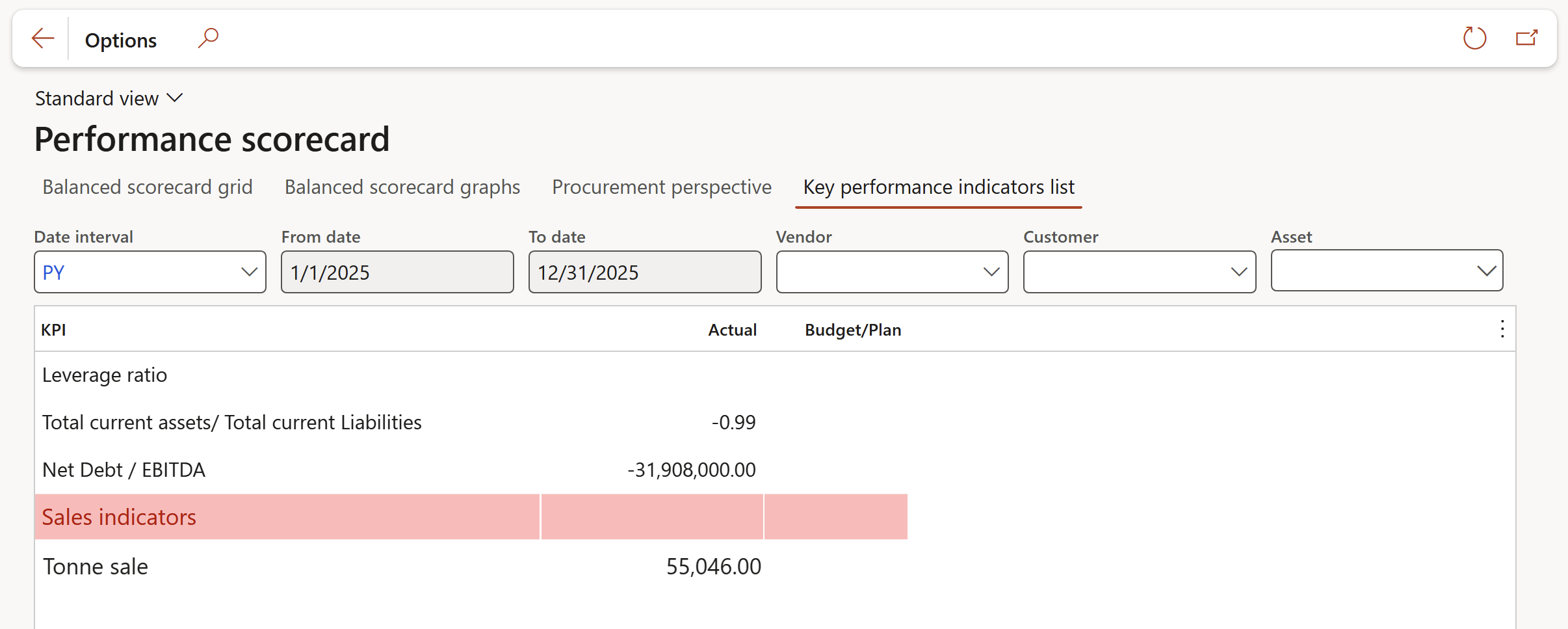
The following filters are for future use: Vendor, Customer and Asset